Identification of Anti-TNFα VNAR Single Domain Antibodies from Whitespotted Bambooshark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of mTNFα Specific VNAR from Whitespotted Bambooshark
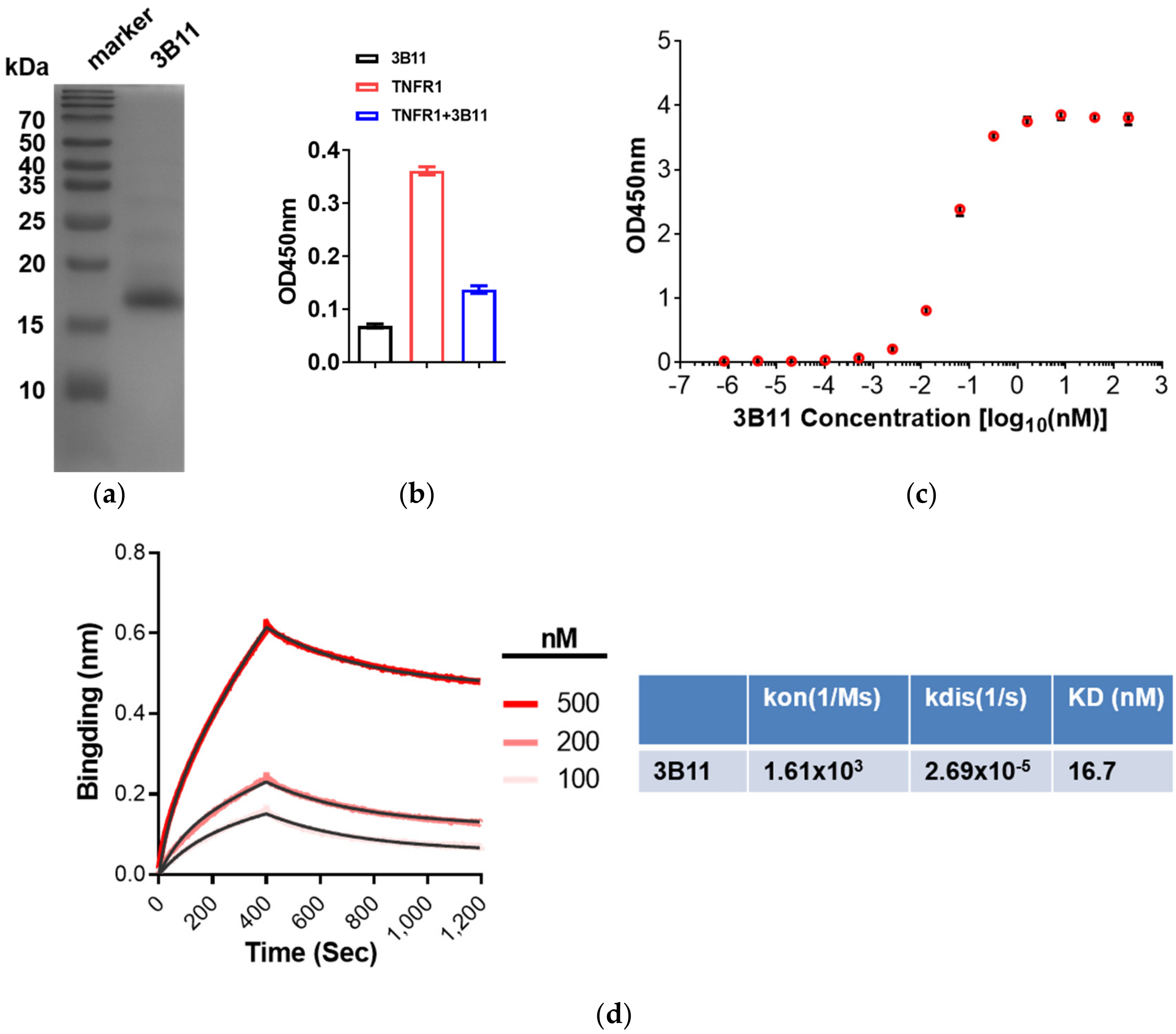
2.2. Expression of VNAR Single Domain Antibodies and 3B11 Antagonize the TNFR-TNFα Interaction
2.3. Affinity Assay of Anti-mTNFα 3B11 VNAR
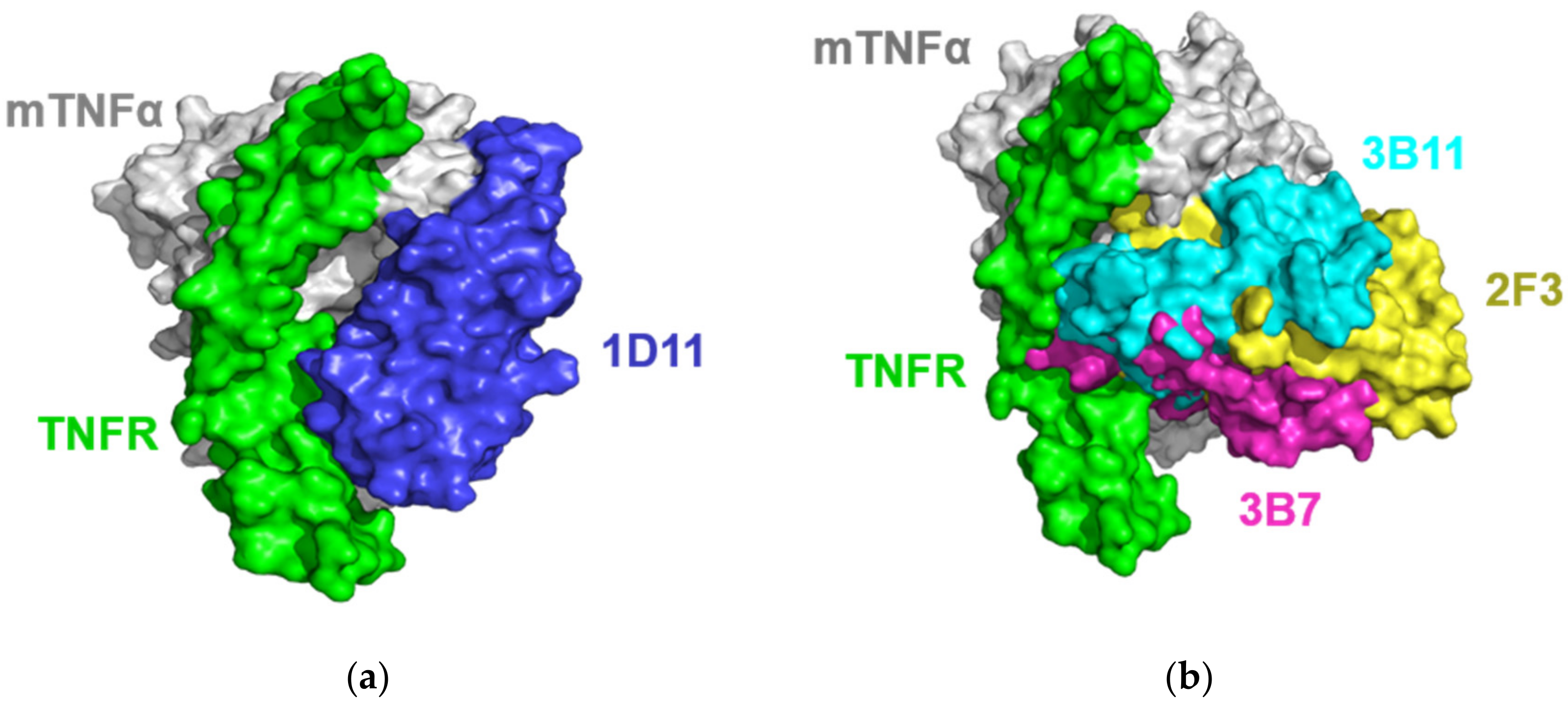
2.4. Models of VNARs-mTNFα Complexes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. mTNFα Protein Expressing
4.3. Immunization of Whitespotted Bamboo Sharks
4.4. VNAR Library Construction
4.5. Selection of TNFα-Specific VNAR by Phage ELISA
4.6. Soluble VNAR Production and Purification
4.7. ELISA for VNAR Affinity Detection
4.8. BLI-Based Affinity Assay
4.9. Computational Modeling
4.10. Statical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiner, L.M.; Murray, J.C.; Shuptrine, C.W. Antibody-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell 2012, 148, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leow, C.H.; Fischer, K.; Leow, C.Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chuah, C.; McCarthy, J. Single Domain Antibodies as New Biomarker Detectors. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belanger, K.; Iqbal, U.; Tanha, J.; MacKenzie, R.; Moreno, M.; Stanimirovic, D. Single-Domain Antibodies as Therapeutic and Imaging Agents for the Treatment of CNS Diseases. Antibodies 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.Q.; Wang, H.; Cai, B.; Wang, L.L.; Yue, S.T. Small antibody mimetics comprising two complementarity-determining regions and a framework region for tumor targeting. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chames, P.; Van Regenmortel, M.; Weiss, E.; Baty, D. Therapeutic antibodies: Successes, limitations and hopes for the future. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, T.T.; Kropshofer, H.; Singer, T.; Mitchell, J.A.; George, A.J. The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordenti, J.; Cuthbertson, R.A.; Ferrara, N.; Thomsen, K.; Berleau, L.; Licko, V.; Allen, P.C.; Valverde, C.R.; Meng, Y.G.; Fei, D.T.; et al. Comparisons of the intraocular tissue distribution, pharmacokinetics, and safety of 125I-labeled full-length and Fab antibodies in rhesus monkeys following intravitreal administration. Toxicol. Pathol. 1999, 27, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Avila, D.; Hughes, M.; Hughes, A.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A new antigen receptor gene family that undergoes rearrangement and extensive somatic diversification in sharks. Nature 1995, 374, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hamers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hamers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Hughes, A.L.; Guo, J.; Avila, D.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A novel “chimeric” antibody class in cartilaginous fish: IgM may not be the primordial immunoglobulin. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qin, L.; Cai, X.; Juma, S.N.; Xu, R.; Wei, L.; Wu, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, L.; et al. Sequence structure character of IgNAR Sec in whitespotted bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielonka, S.; Empting, M.; Grzeschik, J.; Konning, D.; Barelle, C.J.; Kolmar, H. Structural insights and biomedical potential of IgNAR scaffolds from sharks. MAbs 2015, 7, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, M.; Bian, H.; Wu, X.; Fu, T.; Fu, Y.; Hong, J.; Fleming, B.D.; Flajnik, M.F.; Ho, M. Construction and next-generation sequencing analysis of a large phage-displayed VNAR single-domain antibody library from six naive nurse sharks. Antib. Ther. 2019, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dooley, H.; Stanfield, R.L.; Brady, R.A.; Flajnik, M.F. First molecular and biochemical analysis of in vivo affinity maturation in an ectothermic vertebrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielonka, S.; Weber, N.; Becker, S.; Doerner, A.; Christmann, A.; Christmann, C.; Uth, C.; Fritz, J.; Schafer, E.; Steinmann, B.; et al. Shark Attack: High affinity binding proteins derived from shark vNAR domains by stepwise in vitro affinity maturation. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 191, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.; Stanfield, R.L.; Greenberg, A.S.; Flajnik, M.F. Structural analysis, selection, and ontogeny of the shark new antigen receptor (IgNAR): Identification of a new locus preferentially expressed in early development. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleva, M.; Johnson, K.; Steven, J.; Barelle, C.J.; Porter, A. Therapeutic Potential of Shark Anti-ICOSL VNAR Domains is Exemplified in a Murine Model of Autoimmune Non-Infectious Uveitis. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fennell, B.J.; Darmanin-Sheehan, A.; Hufton, S.E.; Calabro, V.; Wu, L.; Muller, M.R.; Cao, W.; Gill, D.; Cunningham, O.; Finlay, W.J. Dissection of the IgNAR V domain: Molecular scanning and orthologue database mining define novel IgNAR hallmarks and affinity maturation mechanisms. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streltsov, V.A.; Carmichael, J.A.; Nuttall, S.D. Structure of a shark IgNAR antibody variable domain and modeling of an early-developmental isotype. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, K.H.; Greenberg, A.S.; Greene, L.; Strelets, L.; Avila, D.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. Structural analysis of the nurse shark (new) antigen receptor (NAR): Molecular convergence of NAR and unusual mammalian immunoglobulins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11804–11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streltsov, V.A.; Varghese, J.N.; Carmichael, J.A.; Irving, R.A.; Hudson, P.J.; Nuttall, S.D. Structural evidence for evolution of shark Ig new antigen receptor variable domain antibodies from a cell-surface receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12444–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanfield, R.L.; Dooley, H.; Verdino, P.; Flajnik, M.F.; Wilson, I.A. Maturation of shark single-domain (IgNAR) antibodies: Evidence for induced-fit binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.R.; Saunders, K.; Grace, C.; Jin, M.; Piche-Nicholas, N.; Steven, J.; O’Dwyer, R.; Wu, L.; Khetemenee, L.; Vugmeyster, Y.; et al. Improving the pharmacokinetic properties of biologics by fusion to an anti-HSA shark VNAR domain. MAbs 2012, 4, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuttall, S.D.; Walsh, R.B. Display scaffolds: Protein engineering for novel therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barelle, C.; Gill, D.S.; Charlton, K. Shark novel antigen receptors—The next generation of biologic therapeutics? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 655, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, J.; Alzogaray, V.; Reyelt, J.; Unger, M.; Juarez, K.; Urrutia, M.; Cauerhff, A.; Danquah, W.; Rissiek, B.; Scheuplein, F.; et al. Single domain antibodies: Promising experimental and therapeutic tools in infection and immunity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 198, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, M. Inaugural Editorial: Searching for Magic Bullets. Antib. Ther. 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F.; Porter, A.J. Selection and characterization of naturally occurring single-domain (IgNAR) antibody fragments from immunized sharks by phage display. Mol Immunol. 2003, 40, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Y.; Secombes, C.J.; Porter, A.J. Rapid isolation of IgNAR variable single-domain antibody fragments from a shark synthetic library. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Dolezal, O.; Parisi, K.; Angerosa, J.; Dogovski, C.; Barraclough, M.; Sanalla, A.; Casey, J.; González, I.; Perugini, M.; et al. Shark Variable New Antigen Receptor (VNAR) Single Domain Antibody Fragments: Stability and Diagnostic Applications. Antibodies 2013, 2, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Brown, J.C.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Thermal stability and refolding capability of shark derived single domain antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 59, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Dong, C. Therapeutic antibodies that target inflammatory cytokines in autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunol. 2016, 28, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporali, R.; Crepaldi, G.; Codullo, V.; Benaglio, F.; Monti, S.; Todoerti, M.; Montecucco, C. 20 years of experience with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: What have we learned? Rheumatology 2018, 57, vii5–vii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minozzi, S.; Bonovas, S.; Lytras, T.; Pecoraro, V.; Gonzalez-Lorenzo, M.; Bastiampillai, A.J.; Gabrielli, E.M.; Lonati, A.C.; Moja, L.; Cinquini, M.; et al. Risk of infections using anti-TNF agents in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callhoff, J.; Weiss, A.; Zink, A.; Listing, J. Impact of biologic therapy on functional status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—A meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, B.L.; Sachar, D.B. Update on anti-tumor necrosis factor agents and other new drugs for inflammatory bowel disease. BMJ 2017, 357, j2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalayasingam, N.; Isaacs, J.D. Anti-TNF therapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalova, I.; Monaco, C.; Nanchahal, J.; Feldmann, M. Anti-TNF Therapy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Qiu, W.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Lian, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; et al. SYNBIP: Synthetic binding proteins for research, diagnosis and therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D560–D570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojalil, R.; Mata-Gonzalez, M.T.; Sanchez-Munoz, F.; Yee, Y.; Argueta, I.; Bolanos, L.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Camacho-Villegas, T.A.; Sanchez-Castrejon, E.; Garcia-Ubbelohde, W.J.; et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor VNAR single domains reduce lethality and regulate underlying inflammatory response in a murine model of endotoxic shock. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pepple, K.L.; Wilson, L.; Van Gelder, R.N.; Kovaleva, M.; Ubah, O.C.; Steven, J.; Barelle, C.J.; Porter, A. Uveitis Therapy With Shark Variable Novel Antigen Receptor Domains Targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha or Inducible T-Cell Costimulatory Ligand. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubah, O.C.; Steven, J.; Kovaleva, M.; Ferguson, L.; Barelle, C.; Porter, A.J.R.; Barelle, C.J. Novel, Anti-hTNF-alpha Variable New Antigen Receptor Formats with Enhanced Neutralizing Potency and Multifunctionality, Generated for Therapeutic Development. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Hou, T. HawkDock: A web server to predict and analyze the protein-protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W322–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, R.F.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; O’Meara, M.J.; DiMaio, F.P.; Park, H.; Shapovalov, M.V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Mulligan, V.K.; Kappel, K.; et al. The Rosetta All-Atom Energy Function for Macromolecular Modeling and Design. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3031–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirnaert, E.; Desmyter, A.; Spinelli, S.; Lauwereys, M.; Aarden, L.; Dreier, T.; Loris, R.; Silence, K.; Pollet, C.; Cambillau, C.; et al. Bivalent Llama Single-Domain Antibody Fragments against Tumor Necrosis Factor Have Picomolar Potencies due to Intramolecular Interactions. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dooley, H.; Flajnik, M.F. Shark immunity bites back: Affinity maturation and memory response in the nurse shark, Ginglymostoma cirratum. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Dooley, H. The generation and selection of single-domain, v region libraries from nurse sharks. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 562, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, K.; Smith, L.E.; Williams, R.; Cao, W.; Lee, M.; Jensen, A.; Dooley, H. Humoral immune response of the small-spotted catshark, Scyliorhinus canicula. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leow, C.H.; Fischer, K.; Leow, C.Y.; Braet, K.; Cheng, Q.; McCarthy, J. Isolation and characterization of malaria PfHRP2 specific VNAR antibody fragments from immunized shark phage display library. Malar J. 2018, 17, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Steinegger, M.; Soding, J. MMseqs2 desktop and local web server app for fast, interactive sequence searches. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2856–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baeyens, K.J.; De Bondt, H.L.; Raeymaekers, A.; Fiers, W.; De Ranter, C.J. The structure of mouse tumour-necrosis factor at 1.4 A resolution: Towards modulation of its selectivity and trimerization. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.; Qian, Y.; Xue, W. Cross-reactivity of two human IL-6 family cytokines OSM and LIF explored by protein-protein docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen Subj. 2021, 1865, 129907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Qian, Y.; Xue, W. Molecular Simulation of Oncostatin M and Receptor (OSM-OSMR) Interaction as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhu, F.; Xue, W. Computational design and modeling of nanobodies toward SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, S.; Berrondo, M.; Weitzner, B.D.; Muthu, P.; Bergman, H.; Gray, J.J. Benchmarking and analysis of protein docking performance in Rosetta v3.2. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Week Number | Procedure | Details | Immunization Route |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Immunization 1 | 200 μg mTNFα in CFA | Subcutaneous |
| 4 | Immunization 2 | 200 μg mTNFα in IFA | Subcutaneous |
| 8 | Immunization 3 | 100 μg mTNFα soluble | Intravenous |
| 12 | Immunization 4 | 100 μg mTNFα soluble | Intravenous |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| VNAR-1- Forward | TCGCTACCGT ggcccaggcggcc CAACGGGTTGAACAAACACC |
| VNAR-2- Forward | TCGCTACCGT ggcccaggcggcc GCATGGGTTGAGCAAACACCG |
| VNAR-1- Reverse | TGATGGTGCT ggccggcctggcc TTTCACAGTCAGAATGGTGC |
| VNAR-2- Reverse | TGATGGTGCT ggccggcctggcc TTTCACTGTTAGAAAAGTGCC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Kang, S.; Xue, W.; Li, Z. Identification of Anti-TNFα VNAR Single Domain Antibodies from Whitespotted Bambooshark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050307
Zhao L, Chen M, Wang X, Kang S, Xue W, Li Z. Identification of Anti-TNFα VNAR Single Domain Antibodies from Whitespotted Bambooshark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum). Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Linfei, Mingliang Chen, Xiaona Wang, Shoukai Kang, Weiwei Xue, and Zengpeng Li. 2022. "Identification of Anti-TNFα VNAR Single Domain Antibodies from Whitespotted Bambooshark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum)" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050307
APA StyleZhao, L., Chen, M., Wang, X., Kang, S., Xue, W., & Li, Z. (2022). Identification of Anti-TNFα VNAR Single Domain Antibodies from Whitespotted Bambooshark (Chiloscyllium plagiosum). Marine Drugs, 20(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050307






