Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of Nematocyst Discharge
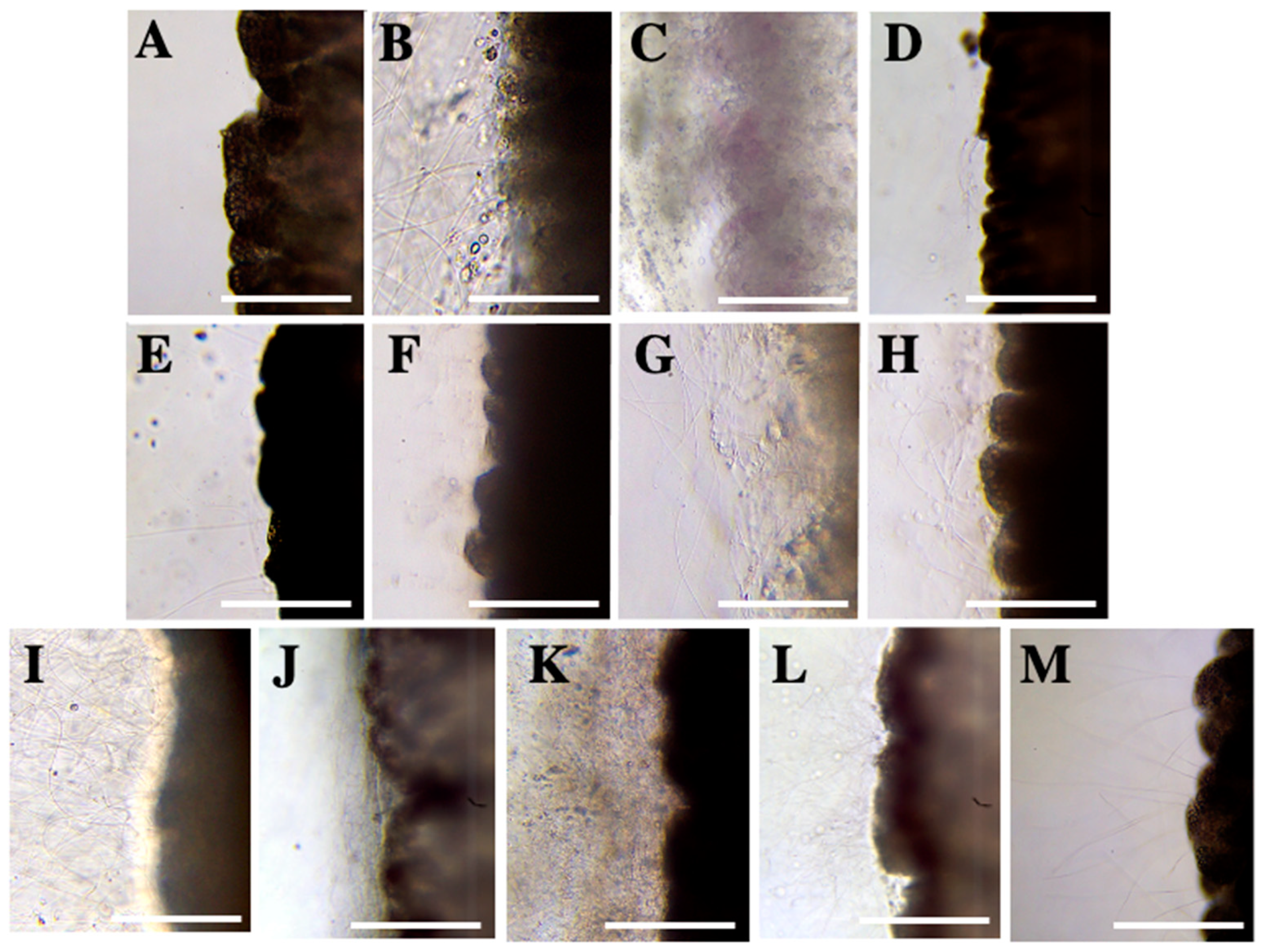
Test 1—Solution Screening
2.2. Evaluation of Inhibitory Effect
2.2.1. Test 2—Nematocyst Discharge
2.2.2. Test 3—Venom Load
3. Discussion
| Scyphozoan | Methodology/Metric | Compounds | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pelagia noctiluca | Tentacle Solution Assay/ Nematocyst discharge | Ammonia (10%), barium chloride (10%), bleach, scented ammonia, lemon juice | High discharge | Present study |
| Sodium bicarbonate solutions (10%), sodium chloride (10%), papain (10%), acetic acid (5%), vinegar | Mild discharge | |||
| Seawater, bromelain (10%), choline chloride (10%), copper gluconate (10%), gadolinium (III) chloride hexahydrate (10%), iodine (10%), lanthanum (III) chloride hexahydrate (10%), magnesium chloride (10%), magnesium sulfate (10%), distilled water, fresh water, physiological saline, urine, butylene glycol (50%) | Neutral (not inhibitory) | |||
| Butylene glycol | Reducer (only some isolated nematocysts discharged) | |||
| Hydroxyacetophenone (1.5%) in distilled water + butylene glycol (1:1), lidocaine (10%) and 3% Symsitive® in butylene glycol | Discharge inhibited | |||
| Tentacle Skin Blood Agarose Assay/Venom activity (hemolytic effect) | Butylene glycol, lidocaine (10%), butylene glycol, hydroxyacetophenone (1.5%) in distilled water + butylene glycol (1:1) and 3% Symsitive® in butylene glycol | Decreased hemolysis | ||
| Chemical-mechanical stimulation/Nematocyst discharge | Sodium bicarbonate (10%) | Discharge | [40] | |
| Lidocaine (1%), ammonia (20%), ethanol (70%), acetic acid (5%) | Discharge inhibited | |||
| Tentacle Solution Assay/ Nematocyst discharge | Vinegar | Mild discharge | [28] | |
| Sea water | Neutral (not inhibitory) | |||
| Tentacle Skin Blood Agarose Assay/Venom activity (hemolytic effect) | Seawater, vinegar | No decrease in hemolysis | ||
| Cytotoxicity assays/Venom activity (cytolytic effect) | Ananas comosus, Carica papaya | Improved cell survival | [34] | |
| Tentacle solution assay/Nematocyst discharge | Anions (I−, Cl−, F−), choline chloride, potassium chloride, sodium chloride, lithium chloride, cesium chloride, potassium iodine, sodium iodine, potassium sulfate, sodium sulfate, ammonium sulfate | Discharge | [45,50] | |
| Calcium chloride, barium chloride, magnesium chloride | Discharge inhibited | |||
| Case reports/Pain, redness and edema | Jellywash® | Prevention or improvement of pain, redness and edema | [23] | |
| Cyanea capillata | Tentacle solution assay/Nematocyst discharge) | Vinegar | Partial discharge | [43] |
| Urine, isopropanol | Moderate discharge | |||
| Seawater | No discharge | |||
| Tentacle Skin Blood Agarose Assay/Venom activity (hemolytic effect) | Seawater, urine | Increased hemolysis | ||
| Vinegar, Sting No More® spray | Decreased hemolysis | |||
| Randomized controlled trials/Pain and skin manifestations (color and structural changes and vesicles) | Safe Sea® (sunscreen with prophylaxis) | Reduction in the number of subjects with pain, discomfort and skin manifestations | [32] | |
| Tentacle solution assay/Nematocyst discharge | Acetic acid (5%) | Discharge | [38] | |
| Methylated spirits | No discharge | |||
| Nemopilema nomurai | Tentacle Solution Assay/ Nematocyst discharge | Acetic acid (4%), isopropanol | High discharge | [36] |
| Distilled water, ethanol (70%), ethanol (20%) | Low discharge | |||
| Seawater, lidocaine (10%) | No discharge | |||
| Nonrandomized controlled trials/Pain, redness and erythema | Seawater, lidocaine (10%) | Relief of pain and redness | ||
| Acetic acid (4%), ethanol (70%), ethanol (20%), isopropanol | Increased pain and redness, erythema | |||
| Cytotoxicity assays/Venom activity (cytolytic effect) | Tetracycline | Inhibition of the cytotoxic effect | [60] | |
| Dermal toxicity test | Tetracycline and lanoline + tetracycline | Decreased the level of hemorrhage | ||
| Chrysaora quinquecirrha | Tentacle Solution Assay/Nematocyst discharge | Ethanol (70%), ammonia (20%), bromelain (10%) | High discharge | [37] |
| Lidocaine (4%) | Discharge inhibited | |||
| Acetic acid (5%) | Mild discharge | |||
| Seawater, urea (10%) | No discharge | |||
| Nonrandomized controlled trials/Pain, redness and erythema | Seawater, deionizer water, bromelain (10%) | No change in pain intensity | ||
| Lidocaine (5%) | Noticeable alleviation of pain | |||
| Lidocaine (10%) | Further reduction in pain | |||
| Lidocaine (15%) | Maximum reduction in pain | |||
| Ammonia (20%), acetic acid (5%), ethanol (70%) | Exacerbation of pain | |||
| Tentacle Solution Assay/Nematocyst discharge | Sodium hypochlorite, acetone, vinegar (acetic acid 5%), ammonia, magnesium chloride | High discharge | [39] | |
| Papain, baking soda slurry, Stingose® (20% aluminum sulfate in detergent) | Discharge inhibited | |||
| Chrysaora fuscescens | Randomized controlled trials/Pain, discomfort, erythema and edema | Safe Sea® (sunscreen with prophylaxis) | Prevention and reduction in pain and erythema | [33] |
| Chrysaora chinensis | Tentacle Solution Assay/ Nematocyst discharge | Seawater, sodium bicarbonate, papain, lidocaine | No discharge | [46] |
| Acetic acid, isopropylalcohol | High discharge | |||
| Randomized controlled trials/Pain, erythema | Papain | Decreased pain and erythema | ||
| Sodium bicarbonate | Decreased erythema |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Jellyfish Cultures
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Screening of Solutions
Test 1: Nematocyst Discharge—Tentacle Solution Assay (TSA)
- 0: no discharge was observed;
- +: low discharge of nematocysts;
- ++: medium discharge of nematocysts;
- +++: high discharge of nematocysts.
- Activator effect solution: nematocysts were activated after incubation with the solution;
- Neutral effect solution: nematocysts were not activated after incubation with the solution.
4.4. Evaluation of Inhibitor Effect
4.4.1. Test 2: Nematocyst Discharge—Tentacle Solution Assay (TSA)
- 0: no discharge was observed;
- +: low discharge of nematocysts;
- ++: medium discharge of nematocysts;
- +++: high discharge of nematocysts.
- Neutral effect: nematocysts were not activated after the first incubation with the solution but did produce discharge with the consecutive chemical stimulation of 5% acetic acid solution;
- Reducer effect: nematocysts were not activated after the first incubation with the solution but isolated nematocyst discharge was observed with the subsequent chemical stimulation of 5% acetic acid solution in some areas;
- Inhibitor effect: nematocysts were not activated after the first incubation with the solution, nor after the consecutive chemical stimulation of 5% acetic acid solution.
4.4.2. Test 3: Venom Load—Tentacle Skin Blood Agarose Assay (TSBAA)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daly, M.; Brugler, M.R.; Cartwright, P.; Collins, A.G.; Dawson, M.N.; Fautin, D.G.; France, S.C.; Mcfadden, C.S.; Opresko, D.M.; Rodriguez, E.; et al. The phylum Cnidaria: A review of phylogenetic patterns and diversity 300 years after Linnaeus. In Linnaeus Tercentenary: Progress in Invertebrate Taxonomy; Zhang, Z.-Q.S., Shear, W.A., Eds.; Magnolia Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2007; pp. 127–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.; Alewood, P.; Fry, B. Ancient venom systems: A review on cnidaria toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariscal, R. Nematocysts. In Coelenterate Biology: Reviews and New Perspectives; Muscatine, L., Lenhoff, H.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 129–166. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, G.M.; Wood, R.L. Colloquium on Terminology. In The Biology of Nematocysts; Hessinger, D.A., Lenhoff, H.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Holstein, T.W. Cnidocyst structure and the biomechanics of discharge. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, C.; Hydman, J. Nematocyst analysis of Cyanea capillata and Cyanea lamarckii (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria). Sci. Mar. 1996, 61, 313–344. [Google Scholar]
- Fautin, D.A. Structural diversity, systematics, and evolution of cnidae. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, R. Contribution à l’étude Des Cnidaires et de Leurs Nématocystes I, II. In Travaux de la Station Zoologique de Wimereux, 10 and 11; Laboratoire D’évolution Des Êtres Organisés: Paris, France, 1934; pp. 1–701. [Google Scholar]
- Remigante, A.; Costa, R.; Morabito, R.; La Spada, G.; Marino, A.; Dossena, S. Impact of scyphozoan venoms on human health and current first aid options for stings. Toxins 2018, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Donno, A.; Idolo, A.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Leomanni, A.; Serio, F.; Guido, M.; Canitano, M.; Zampardi, S.; Boero, F.; et al. Impact of stinging jellyfish proliferations along South Italian coasts: Human health hazards, treatment and social costs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R. A randomized, controlled field trial for the prevention of jellyfish stings with a topical sting inhibitor. J. Travel Med. 2006, 13, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.J.; Jacups, S.P. Prospective study of Chironex fleckeri and other box jellyfish stings in the “top end” of Australia’s Northern territory. M. J. Aust. 2005, 183, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.A.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Raising awareness on the clinical and forensic aspects of jellyfish stings: A worldwide increasing threat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, L.; Seys, J.; Mees, J. To Pee, or Not to Pee: A Review on envenomation and treatment in European jellyfish species. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio, M.; Canepa, A.; Lòpez, L.; Gauci, A.A.; Gueroun, S.K.M.; Zampardi, S.; Boero, F.; Yahia, O.K.-D.; Yahia, M.N.D.; Fuentes, V.; et al. Unfolding jellyfish bloom dynamics along the Mediterranean basin by transnational citizen science initiatives. Diversity 2021, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio, M.; Ballesteros, A.; López-Castillo, L.; Fuentes, V.; Gili, J.M. Guía de Identificación de Medusas y Otros Organismos Gelatinosos. Available online: https://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/245294 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Friedel, N.; Scolnik, D.; Adir, D.; Glatstein, M. Severe anaphylactic reaction to Mediterranean jellyfish (Ropilhema nomadica) envenomation: Case Report. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Donno, A.; Idolo, A.; Bagordo, F. Epidemiology of jellyfish stings reported to summer health centres in the Salento peninsula (Italy). Contact Derm. 2009, 60, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Pane, L. Mediterranean jellyfish venoms: A review on scyphomedusae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1122–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusell, F.S., II. Pelagic Svyphozoa with a Supplement to the First Volume on Hydromedusae. In The Medusae of the British Isles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970; p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Elisabetta, G.; Luigi, P. The mauve stinger Pelagia noctiluca (Forsskål, 1775). Distribution, ecology, toxicity and epidemiology of stings. A review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, A.; Fuentes, V.; Sabatés, A.; Piraino, S.; Boero, F.; Gili, J.-M. Pelagia noctiluca in the Mediterranean Sea. In Jellyfish Blooms; Pitt, K., Lucas, C., Eds.; Sprinter: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 237–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.; Mathieu, L.; Blomet, J. Pelagia noctiluca jellyfish: Can lesions and symptoms be prevented or ameliorated? J. Mar. Biol. Aquac. 2018, 4, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghili, B.; Analla, M.; Aksissou, M. Epidemiology of the cnidarian Pelagia noctiluca stings on moroccan Mediterranean beaches. Trop. Doct. 2020, 50, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, A.; Östman, C.; Santín, A.; Marambio, M.; Narda, M.; Gili, J.-M. Cnidome and morphological features of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) throughout the different life cycle stages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, L.J.; Knöpfel, N.; Martín-Santiago, A.; Escudero-Góngora, M.M.; Saus, C.; Izquierdo-Herce, N.; Bauzà-Alonso, A. Dermoscopic findings of jellyfish stings caused by Pelagia noctiluca. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr 2016, 107, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.A.; Schwartz, M.S. Guillain-Barré syndrome following jellyfish stings (Pelagia noctiluca). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, A.; Marambio, M.; Fuentes, V.; Narda, M.; Santín, A.; Gili, J.M. Differing effects of vinegar on Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Carybdea marsupialis (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) stings—Implications for first aid protocols. Toxins 2021, 13, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, A.; Salazar, J.; Marambio, M.; Tena, J.; García-March, J.R.; López, D.; Tellez, C.; Trullas, C.; Jourdan, E.; Granger, C.; et al. Trial assay for safe first-aid protocol for the stinging sea anemone Anemonia viridis (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) and a severe toxic reaction. Toxins 2022, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagihara, A.; Wilcox, C.; King, R.; Hurwitz, K.; Castelfranco, A. Experimental assays to assess the efficacy of vinegar and other topical first-Aid approaches on cubozoan (Alatina alata) tentacle firing and venom toxicity. Toxins 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killi, N.; Mariottini, G.L. Cnidarian jellyfish: Ecological aspects, nematocyst isolation, and treatment methods of sting. In Marine Organisms as Model Systems in Biology and Medicine; Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation; Kloc, M., Kubiak, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 477–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønseth, K.A.; Andersen, T.S.; Pripp, A.H.; Karlsen, E.H. Prophylactic Treatment of jellyfish stings—A randomised trial. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen 2012, 132, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Arambula, K.Z.; Stauffer, A.R.; Levy, V.; Davis, V.W.; Liu, M.; Rehmus, W.E.; Lotan, A.; Auerbach, P.S. Efficacy of a jellyfish sting inhibitor in preventing jellyfish stings in normal volunteers. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2004, 15, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, R.; Cornara, L.; la Spada, G.; Marino, A.; Mariottini, G.L.; Remigante, A.; Burlando, B. Inhibitory effect of plant extracts on the cytotoxicity of eurytele nematocysts from Pelagia noctiluca. J. Biol. Res. 2020, 93, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, M.J.; Becken, S.; Bordehore, C.; Fuentes, V.L.; Pitt, K.A.; Yangihara, A.A. Empowering stakeholders to manage stinging jellyfish: A perspective. Coast. Manag. 2018, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, M.J.; Lee, H.; Bae, S.K.; Heo, Y.; Choudhary, I.; Yoon, W.D.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. modulation of jellyfish nematocyst discharges and management of human skin stings in Nemopilema nomurai and Carybdea mora. Toxicon 2016, 109, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsa, L.M.; Verity, P.G.; Lee, R.F. Evaluation of the effects of various chemicals on discharge of and pain caused by jellyfish nematocysts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, P.; Fitzpatrick, P. Experiments with the nematocysts of Cyanea capillata. Med. J. Aust. 1986, 145, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.W.; Rubinstein, H.; Calton, G.J. First aid for jellyfish envenomation. South. Med. J. 1983, 76, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, R.; Marino, A.; Dossena, S.; La Spada, G. Nematocyst discharge in Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) oral arms can be affected by lidocaine, ethanol, ammonia and acetic acid. Toxicon 2014, 83, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Distintas Picaduras y Cómo Aliviarlas—Afterbite. Available online: https://www.afterbite.es/consejo/consejo-2/ (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Wilcox, C.; Headlam, J.; Doyle, T.; Yanagihara, A. Assessing the efficacy of first-aid measures in Physalia sp. envenomation, using solution- and blood agarose-based models. Toxins 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.; Headlam, J.; Wilcox, C.; MacLoughlin, E.; Yanagihara, A. Evaluation of Cyanea capillata sting management protocols using ex vivo and in vitro envenomation models. Toxins 2017, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Costello, J.H. Functional characteristics of nematocysts found on the scyphomedusa Cyanea capillata. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 351, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleo, A.; la Spada, G.; Felzea, G.; Denaro, M.G. Discharging effect of anions and inhibitory effect of divalent cations on isolated nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca. Mol. Physiol. 1984, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- De Clerck, M.P.; Bailey, Y.; Craig, D.; Lin, M.; Auerbach, L.J.; Linney, O.; Morrison, D.E.; Patry, W.; Auerbach, P.S. Efficacy of topical treatments for Chrysaora chinensis species: A human model in comparison with an in vitro model. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Frau, A. Impacts of jellyfish presence on tourists’ holiday destination choices and their willingness to pay for mitigation measures. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govern Illes Balears. Available online: https://www.caib.es/sites/112/es/con_las_medusas_seguros-11487/ (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Marambio, M.; López-Castillo, L.; Fuentes, V.; Gili, J.-M. Guía de Identificación y Tratamiento de Picaduras de Medusas y Otros Organismos Gelatinosos de la Costa Mediterránea Española. Available online: https://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/170777 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Salleo, A.; la Spada, G.; Felzea, G.; Denaro, M. Discharging effectiveness of lyotropic anions on nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca. Mol. Physiol. 1984, 6, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Salleo, A.; La Spada, G.; Barbera, R. Gadolinium is a powerful blocker of the nematocytes of Pelagia noctiluca. J. Exp. Biol. 1994, 187, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogué, S.; Gili, J.M. Toxicidad Por Picadura de Medusas. Jano 2006, 1816, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lakkis, N.A.; Maalouf, G.J.; Mahmassani, D.M. Jellyfish stings: A practical approach. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2015, 26, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Crupi, R.; Musci, G.; la Spada, G. morphological integrity and toxicological properties of Pelagia noctiluca (Scyphozoa) nematocysts. Chemand. Ecol. 2006, 22, S127–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmetic Ingredient. Available online: https://www.thgeyer-ingredients.com/fileadmin/user_upload/Ingredients/de/Formulare/Symrise_CI_sales_program_2020_102020.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Sting No More. Available online: http://stingnomore.com/ (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Mickle, A.D.; Shepherd, A.J.; Mohapatra, D.P. Nociceptive TRP channels: Sensory detectors and transducers in multiple pain pathologies. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzberger, M.; Worthmann, A.-C.; Holtzmann, U.; Buck, B.; Jung, K.A.; Schoelermann, A.M.; Rippke, F.; Stäb, F.; Wenck, H.; Neufang, G.; et al. Effective treatment for sensitive skin: 4-t-butylcyclohexanol and licochalcone A. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srour, J.; Bengel, J.; Linden, T.; Jovanovic, Z.; Roggenkamp, D.; Reinholz, M.; Rothenberger, C.; Neufang, G.; Wollenberg, A. efficacy of a skin care cream with TRPV1 Inhibitor 4-t-Butylcyclohexanol in the topical therapy of perioral dermatitis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Jin, Y.B.; Kwak, J.; Jung, H.; Yoon, W.D.; Yoon, T.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, E. Protective effect of tetracycline against dermal toxicity induced by jellyfish venom. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, A.; Páez, D.; Santín, A.; García, A.; Martín, Y.; Alonso, E.; Jourdan, E.; Gili, J.-M. Successful culture of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) over time: A continuous supply of the holoplanktonic jellyfish for research and industrial applications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2017. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).



| Compounds | Test 1: Incubation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n | Discharge 1 | Effect 2 | |
| Seawater (control) | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Ammonia in distilled water | 8 | +++ | Activator |
| 10% Barium chloride in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Activator |
| Bleach | 3 | +++ | Activator |
| Lemon juice | 3 | +++ | Activator |
| Scented ammonia | 3 | +++ | Activator |
| 10% Sodium bicarbonate in seawater | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| 10% Sodium bicarbonate in distilled water | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| 10% Sodium chloride in distilled water | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| 10% Papain in distilled water | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| 5% Acetic acid in distilled water | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| Carbonated cola | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| Vinegar | 3 | ++ | Activator |
| 10% Bromelain in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Choline chloride in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Copper gluconate in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Gadolinium (III) chloride hexahydrate in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Iodine in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Iodine in seawater | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Lanthanum (III) chloride hexahydrate in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Magnesium chloride hexahydrate in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Magnesium sulfate in distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| Distilled water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| Fresh water | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| Physiological saline | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| Urine | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| 10% Lidocaine in ethanol | 3 | 0 | Neutral |
| Butylene glycol | 6 | 0 | Neutral |
| Butylene glycol + distilled water (1:1) | 7 | 0 | Neutral |
| 1.5% Hydroxyacetophenone in distilled water + butylene glycol (1:1) | 6 | 0 | Neutral |
| 3% Symsitive® in butylene glycol | 8 | 0 | Neutral |
| Compounds | Test 2: Discharge | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n | Discharge 1 | Effect 2 | |
| Seawater (control) | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Bromelain in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Choline chloride in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Copper gluconate in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Gadolinium (III) chloride hexahydrate in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Iodine in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Iodine in seawater | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Lanthanum (III) chloride hexahydrate in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Magnesium chloride in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| 10% Magnesium sulfate in distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| Distilled water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| Fresh water | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| Physiological saline | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| Urine | 3 | +++ | Neutral |
| Butylene glycol + distilled water (1:1) | 6 | +++ | Neutral |
| Butylene glycol | 6 | + | Reducer |
| 1.5% Hydroxyacetophenone in distilled water + butylene glycol (1:1) | 6 | 0 | Inhibitor |
| 3% Symsitive® in butylene glycol | 8 | 0 | Inhibitor |
| 10% Lidocaine in ethanol | 3 | 0 | Inhibitor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballesteros, A.; Trullas, C.; Jourdan, E.; Gili, J.-M. Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090571
Ballesteros A, Trullas C, Jourdan E, Gili J-M. Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(9):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090571
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallesteros, Ainara, Carles Trullas, Eric Jourdan, and Josep-Maria Gili. 2022. "Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings" Marine Drugs 20, no. 9: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090571
APA StyleBallesteros, A., Trullas, C., Jourdan, E., & Gili, J.-M. (2022). Inhibition of Nematocyst Discharge from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Prevention Measures against Jellyfish Stings. Marine Drugs, 20(9), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090571






