Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Swim Bladder Biochemical Composition
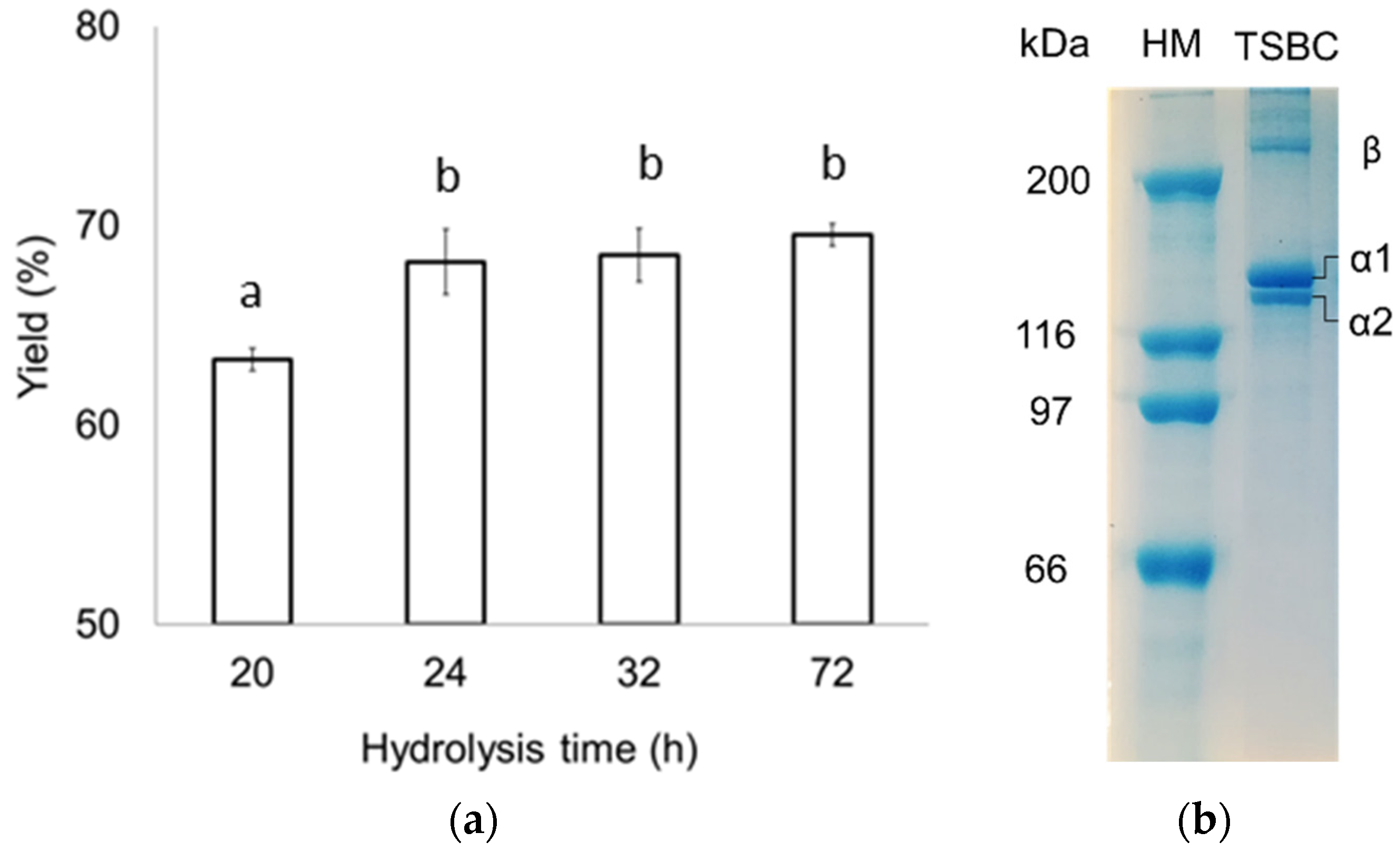
2.2. Collagen Yield
2.3. Collagen Characterization
2.3.1. Amino Acid Composition
2.3.2. Protein Patterns
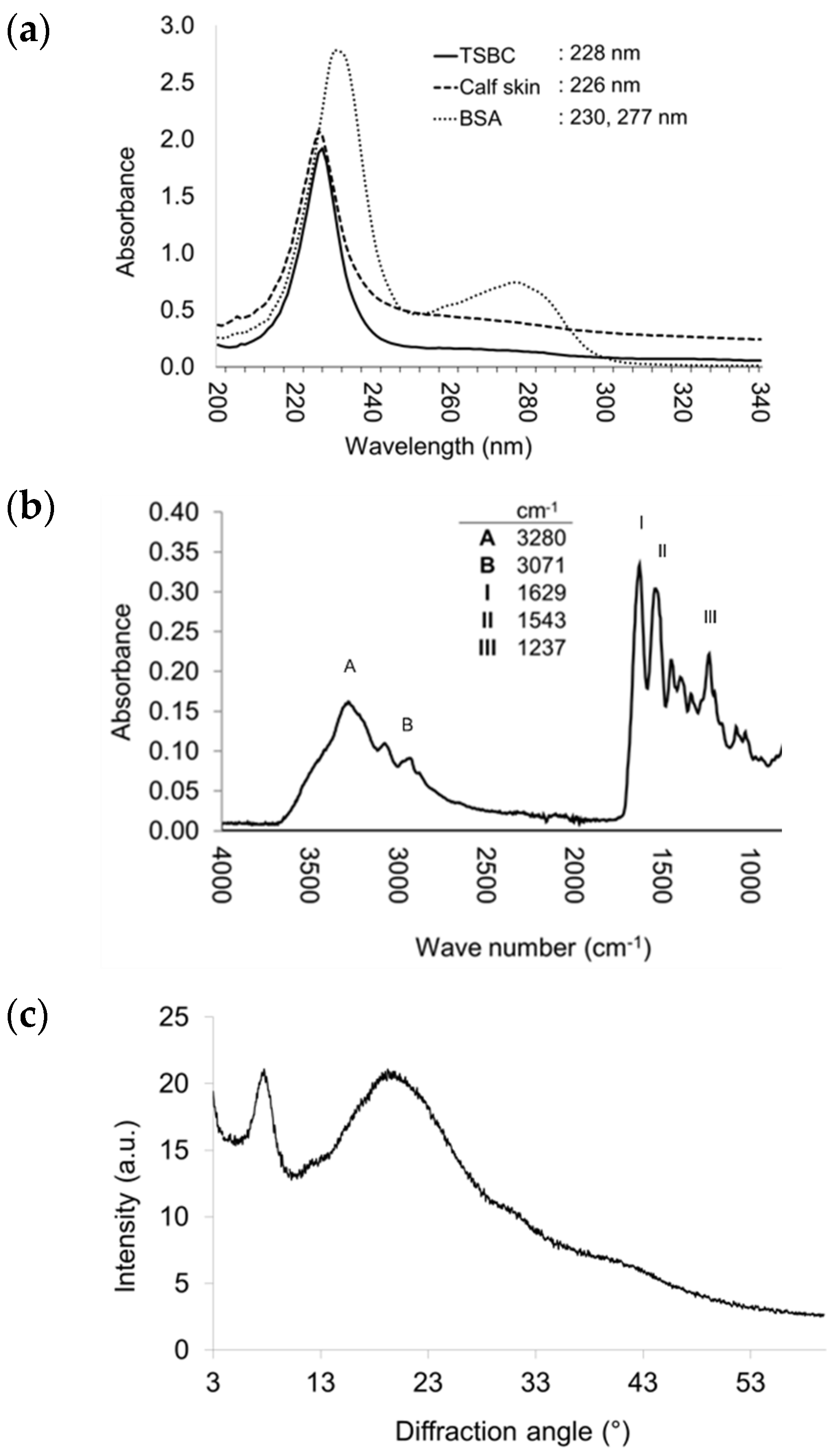
2.3.3. UV-Vis and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.3.4. Structural Integrity
2.3.5. Thermal Unfolding
2.3.6. Protein Solubility and Zeta Potential
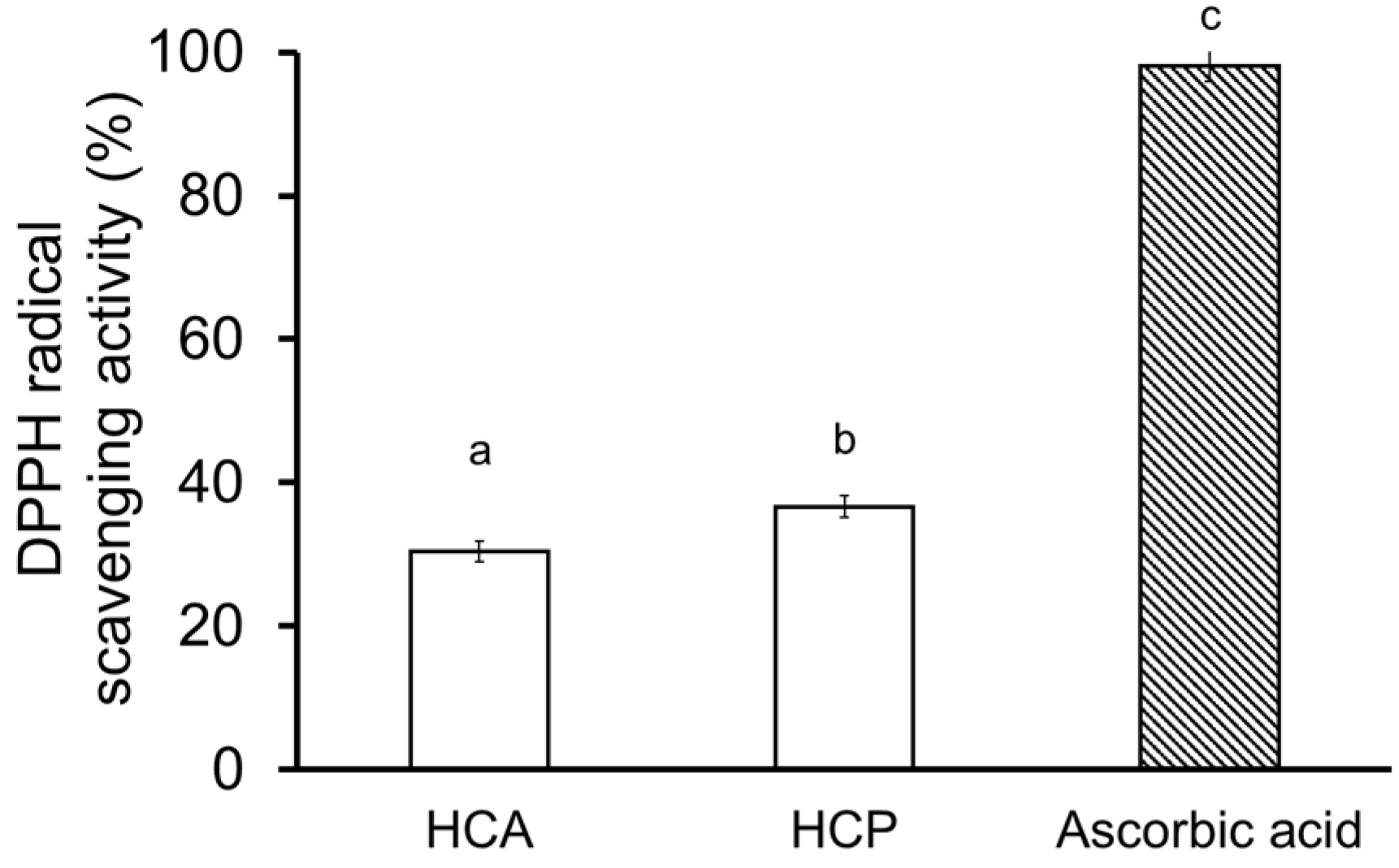
2.4. Collagen Hydrolysate
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Swim Bladder Collection and Preparation
3.3. Proximate Analysis
3.4. Amino Acid Analysis
3.5. Swim Bladder Collagen Isolation and Purification
3.5.1. Pre-Treatment
3.5.2. Collagen Extraction and Purification
3.6. Collagen Characterization
3.6.1. Amino Acid Composition
3.6.2. Electrophoretic Pattern
3.6.3. Ultraviolet Measurements
3.6.4. FTIR Analysis of Functional Groups
3.6.5. X-ray Diffraction and Circular Dichroism
3.6.6. Protein Solubility
3.6.7. Zeta Potential
3.7. Collagen Hydrolysate
3.7.1. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
3.7.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NOM-169-SEMARNAT-2018; Que Establece Las Especificaciones de Marcaje Para Los Ejemplares, Partes y Derivados de Totoaba (Totoaba macdonaldi) Provenientes de Unidades de Manejo Para la Conservación de Vida Silvestre. Norma Oficial Mexicana. 2018. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5539493&fecha=28/09/2018#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Cisneros-Mata, M.Á.; True, C.; Enriquez-Paredes, L.M.; Sadovy, Y.; Liu, M. Totoaba macdonaldi (Totoaba). In IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Gland, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Juarez, L.M.; Konietzko, P.A.; Schwarz, M.H. Totoaba aquaculture and conservation: Hope for an endangered fish from Mexico’s Sea of Cortez. World Aquac. 2016, 47, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S. Fish air-bladders of commercial value in China. Hong Kong Nat. A Q. Illus. J. Princ. Hong Kong South China 1939, 9, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; To, A.W.L.; Wong, N.W.; Kwan, H.Y.; Bud, W.S. Emerging from the murk: Threats, challenges and opportunities for the global swim bladder trade. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 809–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA Collateral Damage: How Illegal Trade in Totoaba Swim Bladders Is Driving the Vaquita to Extinction. Environmental Investigation Agency. Available online: https://eia-international.org/wp-content/uploads/EIA-Collateral-Damage-FINAL-mr.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Gelse, K.; Pöschl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.S.; Krishna Kumar, K.; Bhat, A.R.; Dinesh Kumar, B.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Collagen: Animal sources and biomedical application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.K.; Suresh, P.V. Physico-chemical characteristics and fibril-forming capacity of carp swim bladder collagens and exploration of their potential bioactive peptides by in silico approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dai, Z. Physicochemical, Structural and Antioxidant Properties of Collagens from the Swim Bladder of Four Fish Species. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lv, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Lin, F.; Wen, X. Structural, physicochemical properties and function of swim bladder collagen in promoting fibroblasts viability and collagen synthesis. LWT 2023, 173, 114294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-H.; Chi, C.-F.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, B. Preparation, Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Acid- and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from the Swim Bladders of Miiuy Croaker (Miichthys miiuy). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Toriumi, S.; Ura, K.; Takagi, Y. Feasibility of collagens obtained from bester sturgeon Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus for industrial use. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav Kumar, P.; Nidheesh, T.; Govindaraju, K.; Jyoti; Suresh, P.V. Enzymatic extraction and characterisation of a thermostable collagen from swim bladder of rohu (Labeo rohita). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of ten antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.J.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.Z.; Lü, J.N.; Shi, Y.H.; Li, H.Y. Hydrolysates of swim bladder collagen from miiuy croaker, Miichthys miiuy, enhances learning and memory in mice. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2010, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Huang, F.F.; Ding, G.F.; Wang, B. Anti-fatigue effect by peptide fraction from protein hydrolysate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) swim bladder through inhibiting the oxidative reactions including DNA damage. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Suo, S.K.; Zheng, S.L.; Wang, B. Isolation, identification, molecular docking analysis, and cytoprotection of seven novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from miiuy croaker byproducts-swim bladders. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Cytoprotective effect of antioxidant pentapeptides from the protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) against h2o2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell (huvec) injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, D.; Sims, T.; Miles, C.; Bailey, A.; de Mari, M.; Koopmans, M. Isinglass/collagen: Denaturation and functionality. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 79, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Amino acids: Metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Adachi, S.; Ura, K.; Takagi, Y. Properties of collagen extracted from Amur sturgeon Acipenser schrenckii and assessment of collagen fibrils in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Cortes-Santiago, Y.; López, L.M. Comparison of collagen characteristic from the skin and swim bladder of Gulf corvina (Cynoscion othonopterus). Tissue Cell 2021, 72, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bama, P.; Vijayalakshimi, M.; Jayasimman, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Deccaraman, M.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Extraction of collagen from cat fish (Tachysurus maculatus) by pepsin digestion and preparation and characterization of collagen chitosan sheet. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ookawa, M.; Tan, Y.; Ura, K.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Biochemical characterisation and assessment of fibril-forming ability of collagens extracted from Bester sturgeon Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, F.; Jin, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Cai, X.; et al. Physicochemical, antioxidant properties of giant croaker (Nibea japonica) swim bladders collagen and wound healing evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative study on molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Shigenobu, Y.; Ambe, D.; Morita, T.; Morioka, K.; Adachi, K. Correlation of proline, hydroxyproline and serine content, denaturation temperature and circular dichroism analysis of type I collagen with the physiological temperature of marine teleosts. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 126775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the scales, skins and swim-bladders of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Biosci. 2015, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cai, L.; Cao, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, J. Comparative study on acid-soluble and pepsin-soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud-Guille, M.-M.; Besseau, L.; Chopin, C.; Durand, P.; Herbage, D. Structural aspects of fish skin collagen which forms ordered arrays via liquid crystalline states. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Guanghua, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.R.; Li, C. Comparison of characteristics and fibril-forming ability of skin collagen from barramundi (Lates calcarifer) and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.O.; Alves, A.L.; Carvalho, D.N.; Martins, E.; Oliveira, C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Acid and enzymatic extraction of collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus Morhua) swim bladders envisaging health-related applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 31, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Effect of concentration and temperature on the rheological behavior of collagen solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, F.; Negrete-Aranda, R.; Harris, R.N.; Contreras, J.; Sclater, J.G.; González-Fernández, A. Systematic heat flow measurements across the Wagner Basin, northern Gulf of California. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 479, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rýglová, Š.; Braun, M.; Suchý, T. Collagen and Its Modifications-Crucial Aspects with Concern to Its Processing and Analysis. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemist. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; ISBN 0935584544. [Google Scholar]
- Cequier-Sánchez, E.; Rodríguez, C.; Ravelo, Á.G.; Zárate, R. Dichloromethane as a solvent for lipid extraction and assessment of lipid classes and fatty acids from samples of different natures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4297–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Oh, Y.C.; Cho, W.K.; Ma, J.Y. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity Determination of One Hundred Kinds of Pure Chemical Compounds Using Offline and Online Screening HPLC Assay. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 165457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Amino Acids | Swim Bladder | TSBC | PSC Miiuy Croaker 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asx | 5.13 ± 0.05 | 52 ± 1.48 | 39 |
| Glx | 9.61 ± 0.14 | 101 ± 1.95 | 85 |
| Hyp | 5.43 ± 0.05 | 83 ± 1.43 | 88 |
| Ser | 2.02 ± 0.08 | 23 ± 0.69 | 28 |
| Gly | 29.19 ± 0.31 | 309 ± 3.15 | 334 |
| His | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 5 ± 0.34 | 8 |
| Arg | 11.58 ± 0.37 | 59 ± 4.47 | 55 |
| Thr | 1.76 ± 0.06 | 13 ± 2.62 | 22 |
| Ala | 12.26 ± 0.13 | 132 ± 1.27 | 95 |
| Pro | 12.10 ± 0.13 | 122 ± 1.33 | 112 |
| Tyr | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 2 ± 0.19 | 2 |
| Val | 1.58 ± 0.04 | 16 ± 0.30 | 33 |
| Met | 1.36 ± 0.03 | 7 ± 0.47 | 5 |
| Cys | 0.03 ± 0.01 | Not detected | 0.4 |
| Ile | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 5 ± 0.22 | 13 |
| Leu | 1.94 ± 0.05 | 20 ± 0.08 | 27 |
| Hyl | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 5 ± 0.22 | 6 |
| Phe | 1.61 ± 0.03 | 19 ± 0.54 | 23 |
| Lys | 2.52 ± 0.04 | 31 ± 1.63 | 24 |
| Imino acid 2 | 205 | 199.5 | |
| Degree of Hydroxylation (%) | |||
| Pro | 40.65 | ||
| Lys | 14.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; True, C.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Fernández-Velasco, D.A.; López, L.M. Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030173
Cruz-López H, Rodríguez-Morales S, Enríquez-Paredes LM, Villarreal-Gómez LJ, True C, Olivera-Castillo L, Fernández-Velasco DA, López LM. Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030173
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-López, Honorio, Sergio Rodríguez-Morales, Luis M. Enríquez-Paredes, Luis Jesús Villarreal-Gómez, Conal True, Leticia Olivera-Castillo, D. Alejandro Fernández-Velasco, and Lus M. López. 2023. "Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen" Marine Drugs 21, no. 3: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030173
APA StyleCruz-López, H., Rodríguez-Morales, S., Enríquez-Paredes, L. M., Villarreal-Gómez, L. J., True, C., Olivera-Castillo, L., Fernández-Velasco, D. A., & López, L. M. (2023). Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen. Marine Drugs, 21(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030173








