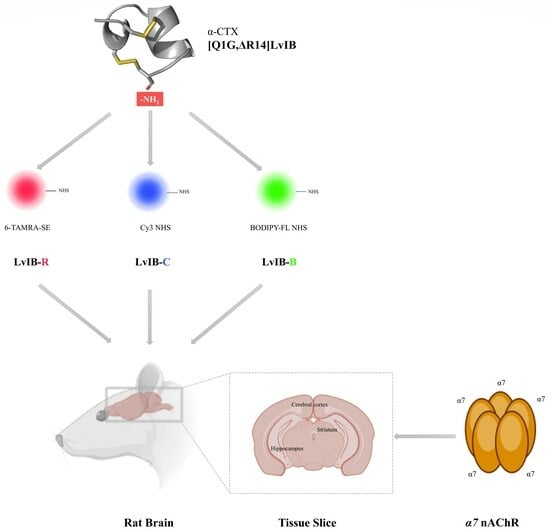
Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Identifies the Distribution of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in the Rat Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Oxidative Folding of α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB
2.2. Synthesis of Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB
2.3. Electrophysiological Activity of [Q1G, ΔR14] LvIB and Its Fluorescent Analogs
2.4. Stability Analysis of [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Fluorescent Analogs in Artificial Cerebrospinal Fluid
2.5. Fluorescence Imaging of Rat Brain Slices
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Oxidative Folding and Purification of α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14] LvΙB
4.3. Synthesis and Identification of Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14] LvΙB
4.4. Electrophysiology
4.5. Stability Analysis
4.6. Fluorescence Imaging
4.7. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlin, A. Ion channel structure: Emerging structure of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.C.; Raggenbass, M.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From structure to brain function. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 147, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Xiao, T.; Sun, Q.; Wang, K. The current agonists and positive allosteric modulators of α7 nAChR for CNS indications in clinical trials. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017, 7, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlin, A.; Akabas, M.H. Toward a structural basis for the function of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and their cousins. Neuron 1995, 15, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giastas, P.; Zouridakis, M.; Tzartos, S.J. Understanding structure–function relationships of the human neuronal acetylcholine receptor: Insights from the first crystal structures of neuronal subunits. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmer, A.T.; Esterlis, I.; Gallezot, J.D.; Bois, F.; Zheng, M.Q.; Nabulsi, N.; Lin, S.F.; Papke, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Sabri, O.; et al. Imaging of cerebral α4β2 * nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with (−)-[ 18 F]Flubatine PET: Implementation of bolus plus constant infusion and sensitivity to acetylcholine in human brain. NeuroImage 2016, 141, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslikiewicz-Bouet, M.; Naldi, M.; Bartolini, M.; Pérez, B.; Servent, D.; Jean, L.; Aráoz, R.; Renard, P.-Y. Functional characterization of multifunctional ligands targeting acetylcholinesterase and alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayuk, D.; Yakel, J.L. Dendritic Ca2+ signalling due to activation of α7-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Yakel, J.L. The effect of α7 nicotinic receptor activation on glutamatergic transmission in the hippocampus. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quik, M.; Huang, L.Z.; Parameswaran, N.; Bordia, T.; Campos, C.; Perez, X.A. Multiple roles for nicotine in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, A.; Takada-Takatori, Y.; Kume, T.; Izumi, Y. Mechanisms of Neuroprotective Effects of Nicotine and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Role of α4 and α7 Receptors in Neuroprotection. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 40, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hung, S.-Y. Physiologic Functions and Therapeutic Applications of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in Brain Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiser, S.C.; Bowlby, M.R.; Comery, T.A.; Dunlop, J. A cog in cognition: How the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is geared towards improving cognitive deficits. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 122, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallés, A.S.; Barrantes, F.J. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Dysfunction in Addiction and in Some Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, R.; Coon, H.; Myles-Worsley, M.; Orr-Urtreger, A.; Olincy, A.; Davis, A.; Polymeropoulos, M.; Holik, J.; Hopkins, J.; Hoff, M. Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome15locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Y. α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhowail, A. Molecular insights into the benefits of nicotine on memory and cognition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkman, H.O.; Feuerbach, D. Modulatory effects of α7 nAChR on the immune system and its relevance for CNS disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2511–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ochani, M.; Amella, C.A.; Tanovic, M.; Susarla, S.; Li, J.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Ulloa, L. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 2003, 421, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tusche, M.W.; Pavlov, V.A.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.; et al. Acetylcholine-Synthesizing T Cells Relay Neural Signals in a Vagus Nerve Circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.R.; Jones, B.; Squires, C.L.M.; Imhoff, F.M.; Harwood, D.T.; Rhodes, L.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.S.; Baird, S.K. Cyclic Imine Pinnatoxin G is Cytotoxic to Cancer Cell Lines via Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor-Driven Classical Apoptosis. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, H.R. Localization of agonist and competitive antagonist binding sites on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 36, 595–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiram, P.A.; Jones, J.J.; Sine, S.M. Pairwise interactions between neuronal alpha7 acetylcholine receptors and alpha-conotoxin ImI. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19517–19524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J.; Dolphin, A.C. Conus Venom Peptide Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, H.R.; Blanton, M.P. Alpha-conotoxins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 2725, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttenthaler, M.; BAkondi, K.; Alewood, P.F. Structure-activity studies on alpha-conotoxins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 4226–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, F.; Jiang, H. α-Conotoxin as Potential to α7-nAChR Recombinant Expressed in Escherichia coli. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, M.; McIntosh, J.M.; Olivera, B.M. α-Conotoxins ImI and ImII. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Nguyen, T.A.; Cartier, G.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Mcintosh, J.M. Single-residue alteration in alpha-conotoxin PnIA switches its nAChR subtype selectivity. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 14542–14548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Zhmak, M.N.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Spirova, E.N.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Zelepuga, E.A.; Efremov, R.G.; et al. High-Affinity α-Conotoxin PnIA Analogs Designed on the Basis of the Protein Surface Topography Method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Zhangsun, D.; Craik, D.J.; Luo, S. Engineered Conotoxin Differentially Blocks and Discriminates Rat and Human α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5620–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. Design, Synthesis, and Activity of an α-Conotoxin LtIA Fluorescent Analogue. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 3662–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttenthaler, M.; Nevin, S.T.; Inserra, M.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. On-Resin Strategy to Label α-Conotoxins: Cy5-RgIA, a Potent α9α10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Imaging Probe. Aust. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwanath, V.A.; McIntosh, J.M. Synthesis of Fluorescent Analogs of α-Conotoxin MII. Bioconjugate Chem. 2006, 17, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Xu, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. Synthesis, Activity, and Application of Fluorescent Analogs of [D1G, Δ14Q]LvIC Targeting α6β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.L.; Dani, J.A. Nicotinic receptors on hippocampal cultures can increase synaptic glutamate currents while decreasing the NMDA-receptor component. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 2756–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.N.T.; Abraham, N.; Lewis, R.J. Structure-Function of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitors Derived From Natural Toxins. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armishaw, C.; Jensen, A.A.; Balle, T.; Clark, R.J.; Harpsøe, K.; Skonberg, C.; Liljefors, T.; Strømgaard, K. Rational Design of α-Conotoxin Analogues Targeting α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9498–9512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, J.S.; Lorsch, J.R. Labeling a Protein with Fluorophores Using NHS Ester Derivitization. Lab. Methods Enzymol. Protein Part A 2014, 536, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Pan, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Kasheverov, I.E.; et al. High Selectivity of an α-Conotoxin LvIA Analogue for α3β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Is Mediated by β2 Functionally Important Residues. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13656–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. Two-Electrode Voltage Clamp. In Ion Channels; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar]







| Peptide | IC50 (nM) | Hill Slope |
|---|---|---|
| [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB | 165.9 (135.3–203.5) | 0.99 (0.8–1.19) |
| LvIB-R | 643.3 (494–837.7) | 0.89 (0.67–1.14) |
| LvIB-C | 298 (238.5–372.3) | 1.39 (1.05–1.72) |
| LvIB-B | 186.9 (150.1–232.8) | 1.04 (0.83–1.24) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, H.; Wang, N.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Identifies the Distribution of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in the Rat Brain. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050200
Shan H, Wang N, Gao X, Wang Z, Yu J, Zhangsun D, Zhu X, Luo S. Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Identifies the Distribution of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in the Rat Brain. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(5):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050200
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Hongyu, Nan Wang, Xinyu Gao, Zihan Wang, Jinpeng Yu, Dongting Zhangsun, Xiaopeng Zhu, and Sulan Luo. 2024. "Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Identifies the Distribution of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in the Rat Brain" Marine Drugs 22, no. 5: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050200
APA StyleShan, H., Wang, N., Gao, X., Wang, Z., Yu, J., Zhangsun, D., Zhu, X., & Luo, S. (2024). Fluorescent α-Conotoxin [Q1G, ΔR14]LvIB Identifies the Distribution of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in the Rat Brain. Marine Drugs, 22(5), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050200