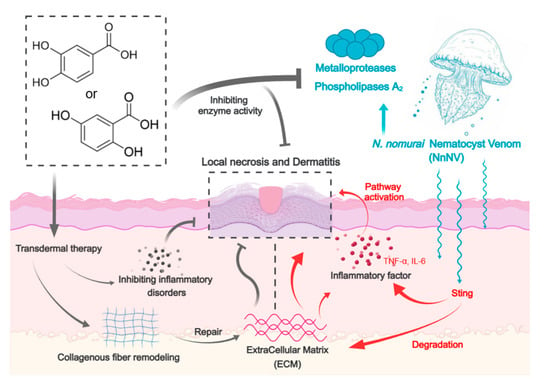
Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Suppression of NnNV Toxicity and Inflammatory Potential on HaCaT Cells by PCA and DHB
2.2. PCA and DHB Attenuate the Degree of Skin Necrosis Induced by NnNV In Vivo
2.3. PCA and DHB Facilitate Healing of NnNV-Induced Wounds
2.4. In Vivo Inflammatory Modulation by PCA and DHB in Response to NnNV-Induced Impact
2.5. Inhibition Analysis of Enzyme Activity in Venom by PCA and DHB
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. N. nomurai Nematocyst Venom (NnNV) Preparation
4.3. Enzyme Activity Determination
4.4. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
4.5. Quantification of Inflammatory FACTORS levels by ELISA
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Animal Maintenance
4.8. Skin Necrosis from Jellyfish Sting Model and Preclinical Efficacy via Post-Treatment
4.9. Histological Analysis of Necrotic Area Skin
4.10. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, A.J.; Pauly, D.; Gibbons, M.J. Degraded ecosystems: Keep jellyfish numbers in check. Nature 2012, 483, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, R.H.; Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Robinson, K.L.; Lucas, C.H.; Sutherland, K.R.; Mianzan, H.W.; Bogeberg, M.; Purcell, J.E.; Decker, M.B.; et al. Recurrent jellyfish blooms are a consequence of global oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.; Lo, W.T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 350, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Lucas, C.H.; Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.; Robinson, K.; Brotz, L.; Decker, M.B.; Sutherland, K.R.; Malej, A.; et al. Is global ocean sprawl a cause of jellyfish blooms? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badre, S. Bioactive toxins from stinging jellyfish. Toxicon 2014, 91, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.L.; Yue, Y.; Yin, X.J.; Li, R.F.; Yu, H.H.; Li, P.C. Identifying and revealing the geographical variation in Nemopilema nomurai venom metalloprotease and phospholipase A(2) activities. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remigante, A.; Costa, R.; Morabito, R.; La Spada, G.; Marino, A.; Dossena, S. Impact of Scyphozoan Venoms on Human Health and Current First Aid Options for Stings. Toxins 2018, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K. Jellyfish blooms in China: Dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, P.J.; Williamson, J.A. Worldwide deaths and severe envenomation from jellyfish stings. Med. J. Australia 1996, 165, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Uye, S.; Burnett, J.; Mianzan, H. Stings of edible jellyfish (Rhopilema hispidum, Rhopilema esculentum and Nemopilema nomurai) in Japanese waters. Toxicon 2006, 48, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Uye, S.; Ohtsu, K.; Izumi, H. Unusual population explosion of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) in East Asian waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 307, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Wang, T.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Unique Diversity of Sting-Related Toxins Based on Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata and Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.H.; Li, R.F.; Xing, R.G.; Liu, S.; Li, K.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Li, P.C. Biochemical and kinetic evaluation of the enzymatic toxins from two stinging scyphozoans Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii. Toxicon 2017, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.H.; Li, R.F.; Li, P.C. Topical Exposure to Nemopilema nomurai Venom Triggers Oedematogenic Effects: Enzymatic Contribution and Identification of Venom Metalloproteinase. Toxins 2021, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.Y.; Yu, H.H.; Li, R.F.; Yue, Y.; Yu, C.L.; Geng, H.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.E.; Li, P.C. Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai causes myotoxicity through the metalloprotease component of venom. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.Y.; Yu, H.H.; Li, R.F.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.E.; Li, P.C. Inhibitory Effect of Metalloproteinase Inhibitors on Skin Cell Inflammation Induced by Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Nematocyst Venom. Toxins 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.H.; Suo, Q.S.; Li, R.F.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.E.; Zhang, Q.B.; Li, P.C. Discovery of a novel jellyfish venom metalloproteinase inhibitor from secondary metabolites isolated from jellyfish-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SmT07. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 365, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zou, S.J.; Song, J.X.S.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.C.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Protective Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) against the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Envenoming. Toxins 2023, 15, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.H.; Lee, H.; Choudhary, I.; Kang, C.; Chae, J.; Kim, E. Protective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on toxic metalloproteinases-mediated skin damage induced by Scyphozoan jellyfish envenomation. Sci. Rep.-Uk 2020, 10, 18644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, A.; Adams, S.; Mignatti, P. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Turning Past Failures Into Future Successes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.; Golebiewska, E.; Swiderski, G.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Lewandowska, H.; Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Astel, A.; Swislocka, R.; Samsonowicz, M.; et al. Plant-Derived and Dietary Hydroxybenzoic Acids-A Comprehensive Study of Structural, Anti-/Pro-Oxidant, Lipophilic, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadem, S.; Marles, R.J. Monocyclic Phenolic Acids; Hydroxy- and Polyhydroxybenzoic Acids: Occurrence and Recent Bioactivity Studies. Molecules 2010, 15, 7985–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.C.; Lin, C.C.; Wu, H.C.; Tsao, S.M.; Hsu, C.K. Apoptotic Effects of Protocatechuic Acid in Human Breast, Lung, Liver, Cervix, and Prostate Cancer Cells: Potential Mechanisms of Action. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6468–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongwichai, T.; Teeyakasem, P.; Pruksakorn, D.; Kongtawelert, P.; Pothacharoen, P. Anthocyanins and metabolites from purple rice inhibit IL-1 beta-induced matrix metalloproteinases expression in human articular chondrocytes through the NF-kappa B and ERK/MAPK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Mauriz, J.L.; de Urbina, J.J.O.; Almar, M.; Tunon, M.J.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2017, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, R. Protocatechuic acid inhibits TGF-beta 1-induced proliferation and migration of human airway smooth muscle cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Kraus, V.; Pahl, A.; Brune, K. Salicylate metabolites inhibit cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E-2 synthesis in murine macrophages. Biochem. Bioph Res. Co. 2000, 274, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Gao, J. The use of botanical extracts as topical skin-lightening agents for the improvement of skin pigmentation disorders. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2008, 13, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschetta, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; Morabito, R.; Marino, A.; Ahmad, A.; Spano, N.; La Spada, G.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Pelagia noctiluca (Scyphozoa) Crude Venom Injection Elicits Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2182–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; McGee, R.G.; Isbister, G.; Webster, A.C. Interventions for the symptoms and signs resulting from jellyfish stings. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2015, CD009688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, Y.; Bousabbeh, M.; Ben Mabrouk, H.; Morjen, M.; Marrakchi, N.; Bacha, H. Impairment of the cell-to-matrix adhesion and cytotoxicity induced by the Mediterranean jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca venom and its fractions in cultured glioblastoma cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. The Extracellular Matrix: Not Just Pretty Fibrils. Science 2009, 326, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.L.M.; Hwang, D.H.; Hong, I.H.; Chae, J.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Danio rerio as an alternative vertebrate model for jellyfish venom study: The toxinological aspects of Nemopilema nomurai venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 335, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.F.; Yu, H.H.; Li, T.; Li, P.C. Comprehensive Proteome Reveals the Key Lethal Toxins in the Venom of Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.L.; Li, R.F.; Yin, X.J.; Yu, H.H.; Li, P.C. Synergistic Effect of Proteinase Activity by Purification and Identification of Toxic Protease From Nemopilema nomurai. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 791847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Han, D.Y.; Park, K.I.; Pyo, M.J.; Heo, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, E. Characterization and neutralization of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) jellyfish venom using polyclonal antibody. Toxicon 2014, 86, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of Toxins from Cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.A.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Raising Awareness on the Clinical and Forensic Aspects of Jellyfish Stings: A Worldwide Increasing Threat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pubulic Health 2022, 19, 8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.L.; Yu, H.H.; Li, P.C. Highlights of animal venom research on the geographical variations of toxin components, toxicities and envenomation therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Yu, H.H.; Li, A.Y.; Yu, C.L.; Li, P.C. Refinement and Neutralization Evaluation of the F(ab’)(2) Type of Antivenom against the Deadly Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Toxins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asirvatham, R.D.; Hwang, D.; Prakash, R.L.M.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Pharmacoinformatic Investigation of Silymarin as a Potential Inhibitor against Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Metalloproteinase Toxin-like Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, C.D.; Souza, H.G.T.; Rocha, L.W.; da Silva, G.F.; dos Anjos, M.F.; Pastor, V.D.; Bresolin, T.M.B.; Couto, A.G.; Santin, J.R.; Quintao, N.L.M. Ipomoea pes-caprae (L.) R. Br (Convolvulaceae) relieved nociception and inflammation in mice—A topical herbal medicine against effects due to cnidarian venom-skin contact. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 200, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Deng, X.Y.; Peng, J.M.; Li, C.M. Both non-covalent and covalent interactions were involved in the mechanism of detoxifying effects of persimmon tannin on Chinese cobra PLA(2). Fitoterapia 2017, 120, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; He, Y.N.; Luo, C.H.; Feng, B.; Ran, F.; Xu, H.; Ci, Z.M.; Xu, R.C.; Han, L.; Zhang, D.K. New progress in the pharmacology of protocatechuic acid: A compound ingested in daily foods and herbs frequently and heavily. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, F.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. A review on gentisic acid as a plant derived phenolic acid and metabolite of aspirin: Comprehensive pharmacology, toxicology, and some pharmaceutical aspects. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoop, V.M.; Mirancea, N.; Fusenig, N.E. Epidermal organization and differentiation of HaCaT keratinocytes in organotypic coculture with human dermal fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Jin, Y.B.; Kwak, J.; Jung, H.; Yoon, W.D.; Yoon, T.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, E. Protective Effect of Tetracycline against Dermal Toxicity Induced by Jellyfish Venom. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, I.; Hwang, D.H.; Lee, H.; Yoon, W.D.; Chae, J.; Han, C.H.; Yum, S.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Proteomic Analysis of Novel Components of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom: Deciphering the Mode of Action. Toxins 2019, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.S.; Elston, D.M. Aquatic Antagonists: Jellyfish Stings. Cutis 2022, 109, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.T.; Manion, J.; Littleboy, J.B.; Oyston, L.; Khuong, T.M.; Wang, Q.P.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hesselson, D.; Seymour, J.E.; Neely, G.G. Molecular dissection of box jellyfish venom cytotoxicity highlights an effective venom antidote. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.R.; Niu, Y.X.; Chen, X.L.; Luo, M.X.; Huang, S.X.; Cao, T.Q.; Shi, G.; Wei, A.S.; Huang, J.J. Gelatin Microspheres Loaded with Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Acute Full-Thickness Skin Wound Healing and Regeneration in Mice. Adv. Wound Care 2023, 12, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Di Paola, R.; Crisafulli, C.; Mazzon, E.; Morabito, R.; Paterniti, I.; Galuppo, M.; Genovese, T.; La Spada, G.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective effect of melatonin against the inflammatory response elicited by crude venom from isolated nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.S.; Xia, X.H.; Lai, Z.F.; Zhong, T.Z.; Li, G.; Fan, L.L.; Shu, W. Apoptosis-like cell death induced by nematocyst venom from Chrysaora helvola Brandt jellyfish and an in vitro evaluation of commonly used antidotes. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2016, 180, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albulescu, L.O.; Xie, C.F.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides broad preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6094, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laleh, M.; Tahernejad, M.; Bonakdar, S.; Asefnejad, A.; Golkar, M.; Kazemi-Lomedasht, F.; Habibi-Anbouhi, M. Positive effect of acellular amniotic membrane dressing with immobilized growth factors in skin wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2023, 111, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, F.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Wu, J.K.; Ma, G.X.; Zhang, B.W.; Gao, J.; Ding, Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Cheng, S.L.; et al. Comparison of the Effects of Open Surgery and Minimally Invasive Surgery on the Achilles Tendon Rupture Healing Based on Angiogenesis. Comput. Intel. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1447129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Gao, D.; Song, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tao, M.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhou, A.; et al. A natural biological adhesive from snail mucus for wound repair. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B.C.; Kokila, G.; Gopinathan, P.A.; Praveen, K.S. Picrosirius Red and Polarization Microscopy—A Tool for Gender Differentiation. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC107–ZC109. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like Receptors and Their Crosstalk with Other Innate Receptors in Infection and Immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Pyo, M.J.; Bae, S.K.; Heo, Y.; Choudhary, I.; Hwang, D.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.H.; Chae, J.; Han, C.H.; et al. Nemopilema nomurai jellyfish venom exerts an anti-metastatic effect by inhibiting Smad- and NF-kappaB-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HepG2 cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, L.; Shannon, J.D.; Valente, R.H.; Rucavado, A.; Alape-Giron, A.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Fox, J.W.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Arni, R.K. Amino acid sequence and crystal structure of BaP1, a metalloproteinase from Bothrops asper snake venom that exerts multiple tissue-damaging activities. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.J.; Gu, L.C.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, Y.C.; Lin, Z.J. Structures of cadmium-binding acidic phospholipase A(2) from the venom of Agkistrodon halys Pallas at 1.9A resolution. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.H.; Xiao, H.X.; Xiong, S.W.; Huang, C.H. Exploration of the Inhibitory Potential of Varespladib for Snakebite Envenomation. Molecules 2018, 23, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lausen, B.; Ahang, A.; Cummins, S.; Wang, T.F. Investigation of Best Practices for Venom Toxin Purification in Jellyfish towards Functional Characterisation. Toxins 2023, 15, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adasme, M.F.; Linnemann, K.L.; Bolz, S.N.; Kaiser, F.; Salentin, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. PLIP 2021: Expanding the scope of the protein-ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W530–W534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Venom (PDB ID) | Compound Name | Autodock Score (kcal/mol) | Ligand–Receptor Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snake Venom Metalloproteinase, BaP1 (1ND1) | Protocatechuic Acid | −5.6 | Hydrophobic Interactions (ILE108, THR139, LEU170), Hydrogen Bond (SER168), π-π Stacking (HIS142), Salt Bridge (HIS142) |
| Gentisic Acid | −5.3 | Hydrophobic Interactions (ILE108, THR139, LEU170), Hydrogen Bond (SER168, GLY109, ILE108), π-π Stacking (HIS142), Salt Bridge (HIS142) | |
| Snake Venom Cadmium-binding Acidic Phospholipase A2 (1M8S) | Protocatechuic Acid | −5.5 | Hydrophobic Interactions (PHE5, PHE106), Hydrogen Bond (GLY30, HIS48, ASP49) |
| Gentisic Acid | −5.4 | Hydrophobic Interactions (PHE5), Hydrogen Bond (GLY30, ASP49), Salt Bridge (HIS48) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, H.; Li, R.; Teng, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, K.; Li, A.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Yu, H.; et al. Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050205
Geng H, Li R, Teng L, Yu C, Wang W, Gao K, Li A, Liu S, Xing R, Yu H, et al. Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(5):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050205
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Hao, Rongfeng Li, Lichao Teng, Chunlin Yu, Wenjie Wang, Kun Gao, Aoyu Li, Song Liu, Ronge Xing, Huahua Yu, and et al. 2024. "Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms" Marine Drugs 22, no. 5: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050205
APA StyleGeng, H., Li, R., Teng, L., Yu, C., Wang, W., Gao, K., Li, A., Liu, S., Xing, R., Yu, H., & Li, P. (2024). Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms. Marine Drugs, 22(5), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050205