Dicerandrol C Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of HepG2 and Hela Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
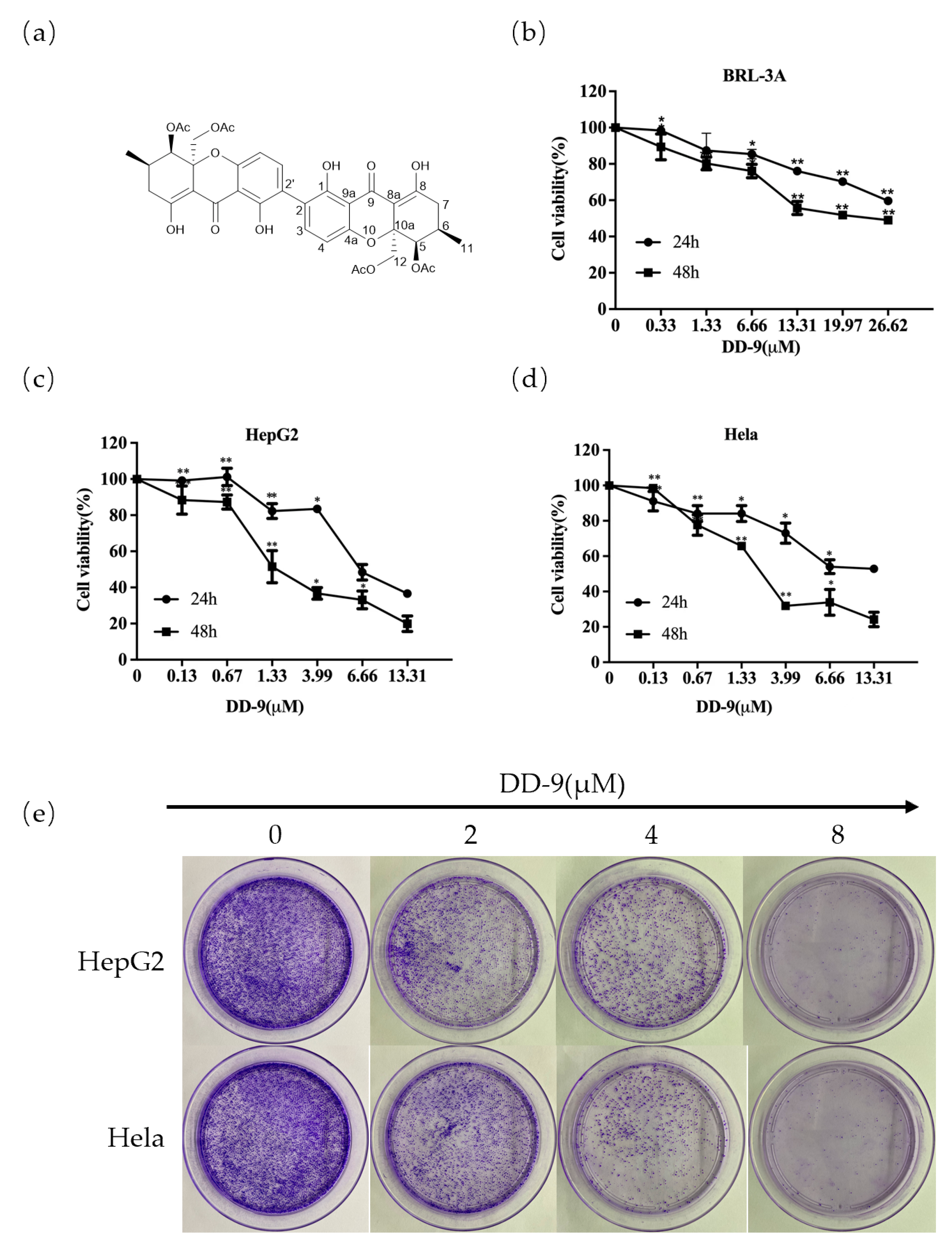
2.1. Identification of DD-9
2.2. DD-9 Inhibited the Viability and Proliferation of HepG2 and HeLa Cells In Vitro
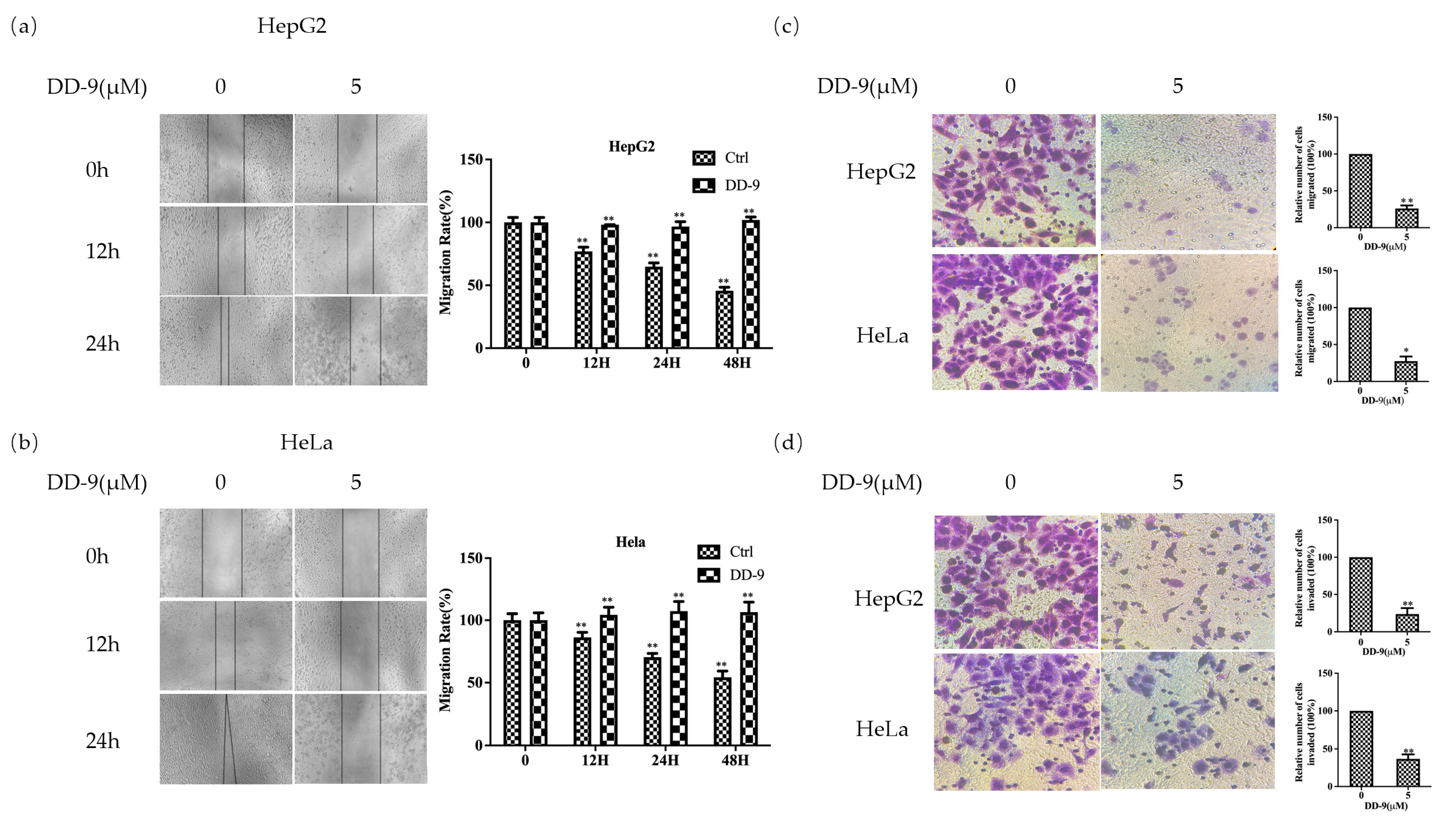
2.3. DD-9 Inhibited the Migration and Invasion of HepG2 and HeLa Cells
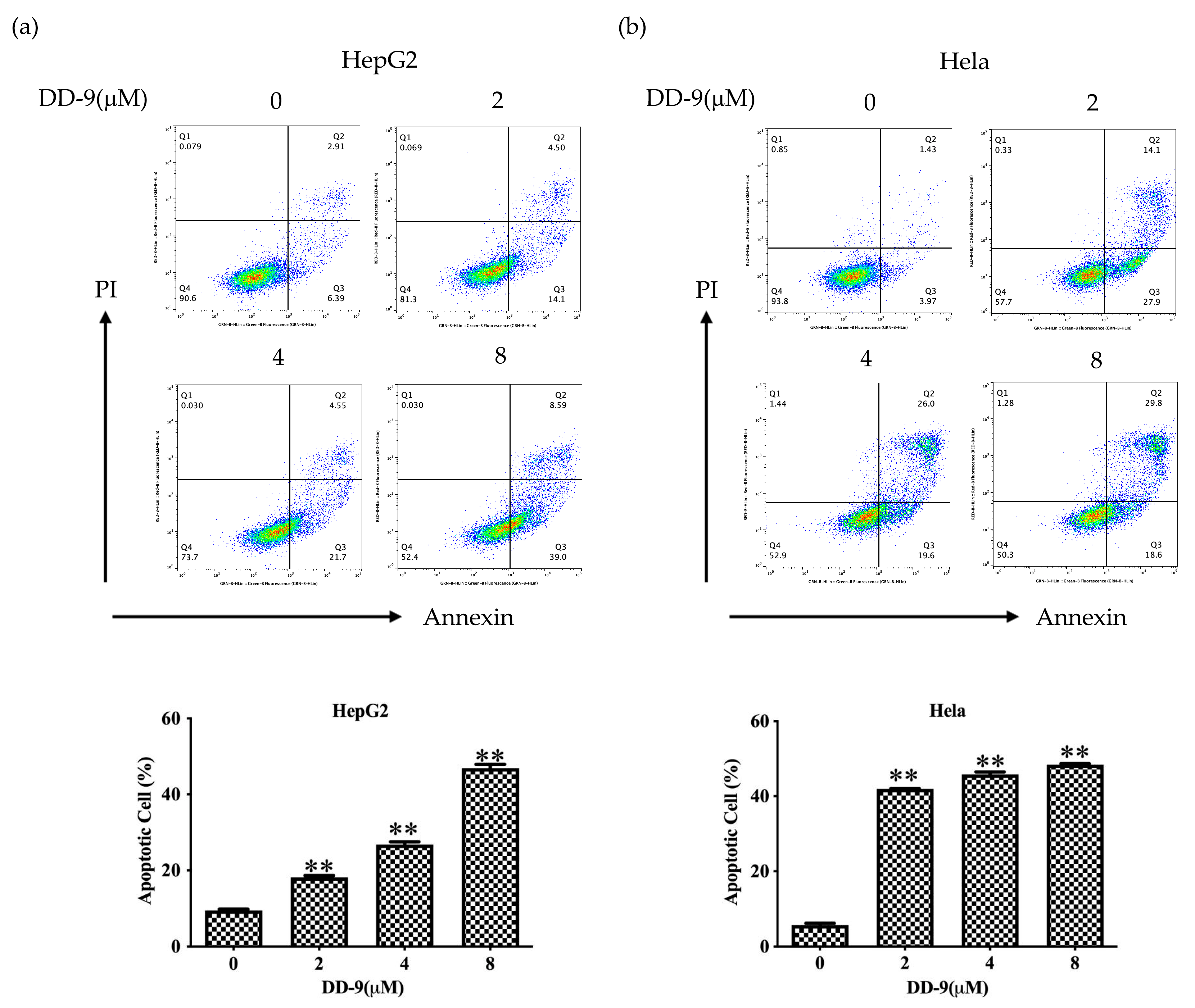
2.4. DD-9 Induced Apoptosis of HepG2 and HeLa Cancer Cells
2.5. DD-9 Stimulated G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest in HepG2 and HeLa Cells
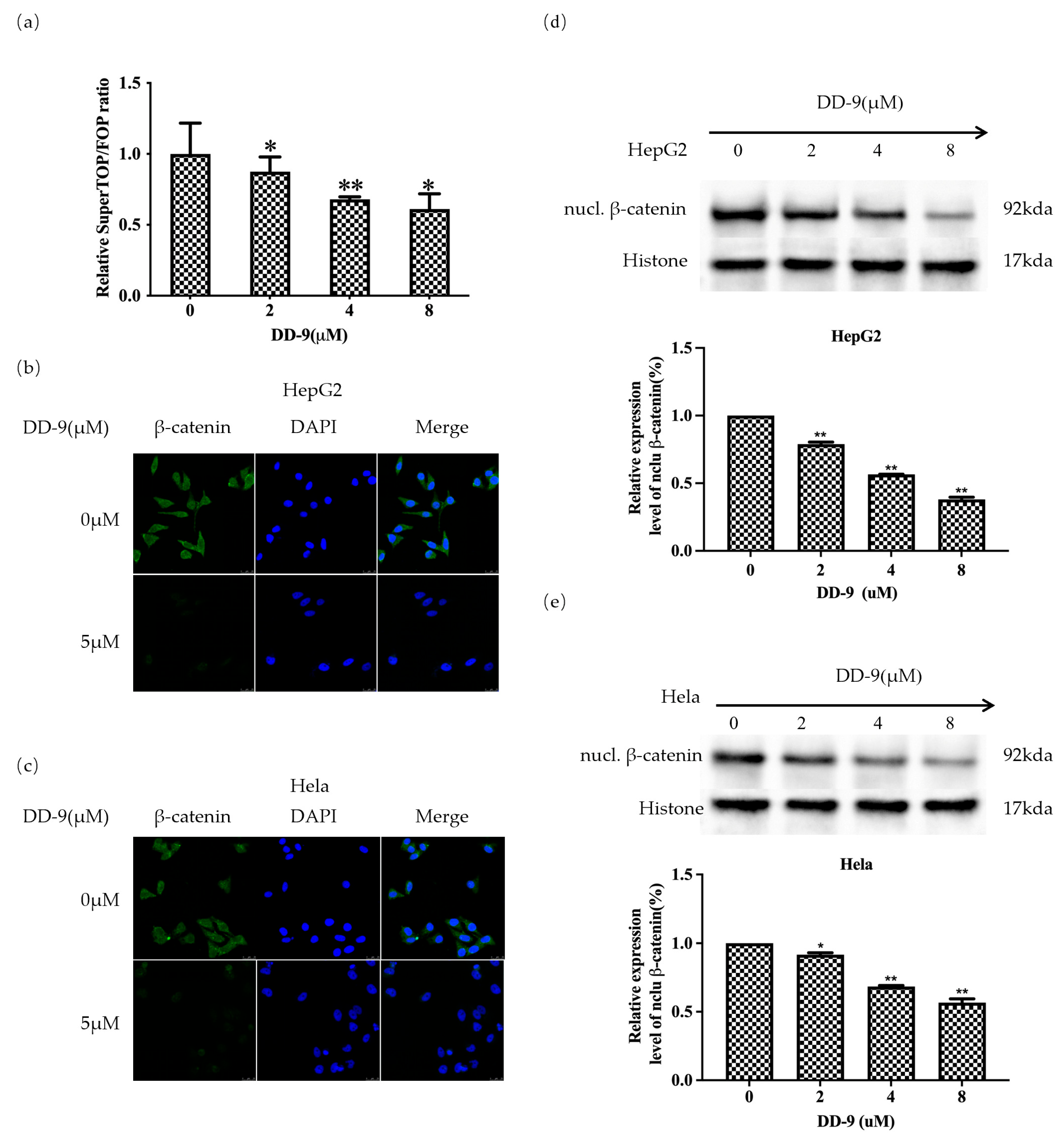
2.6. DD-9 Inhibited the Activation Level of β-Catenin
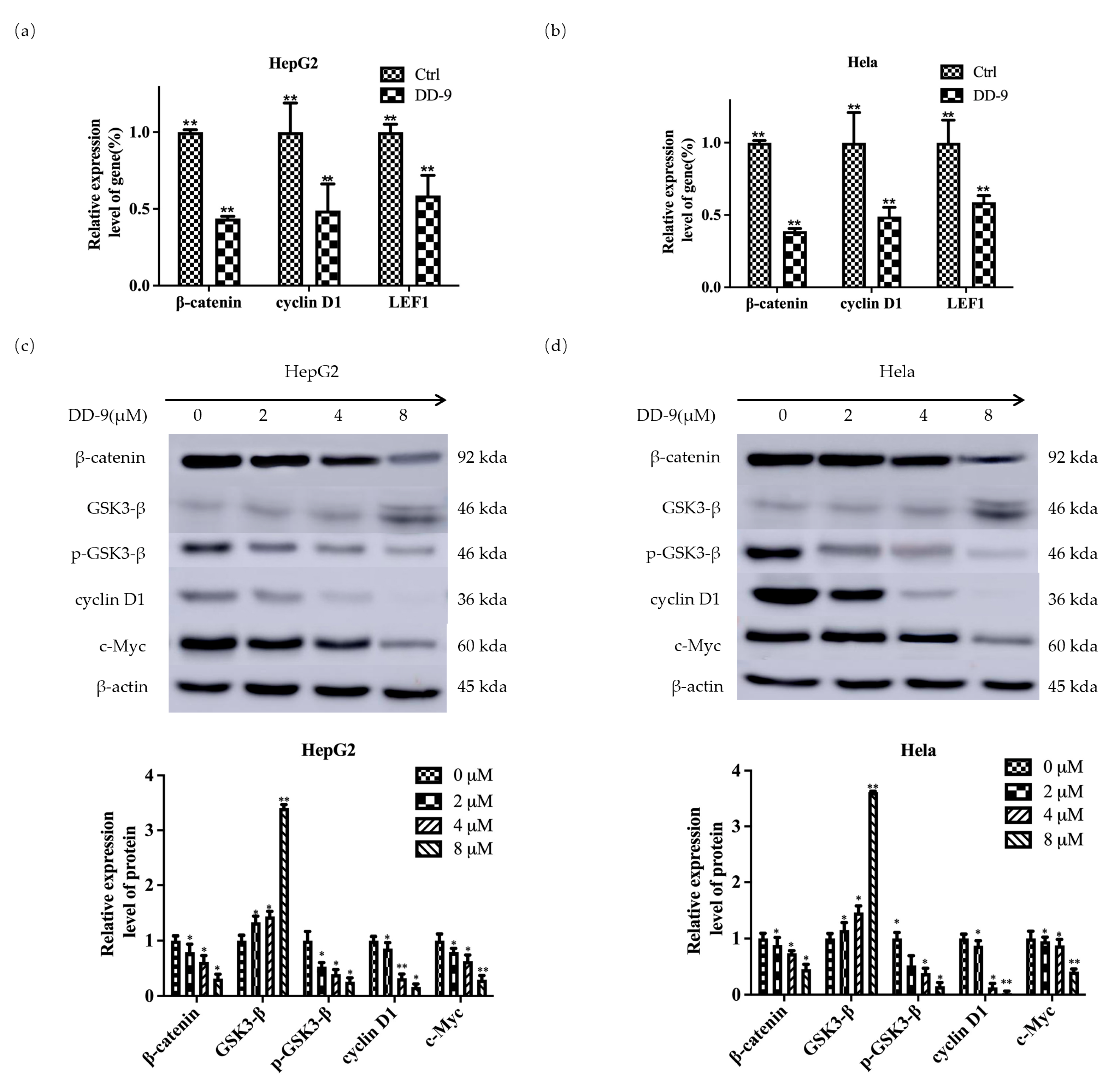
2.7. DD-9 Suppressed Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Cascade in HepG2 and HeLa Cells
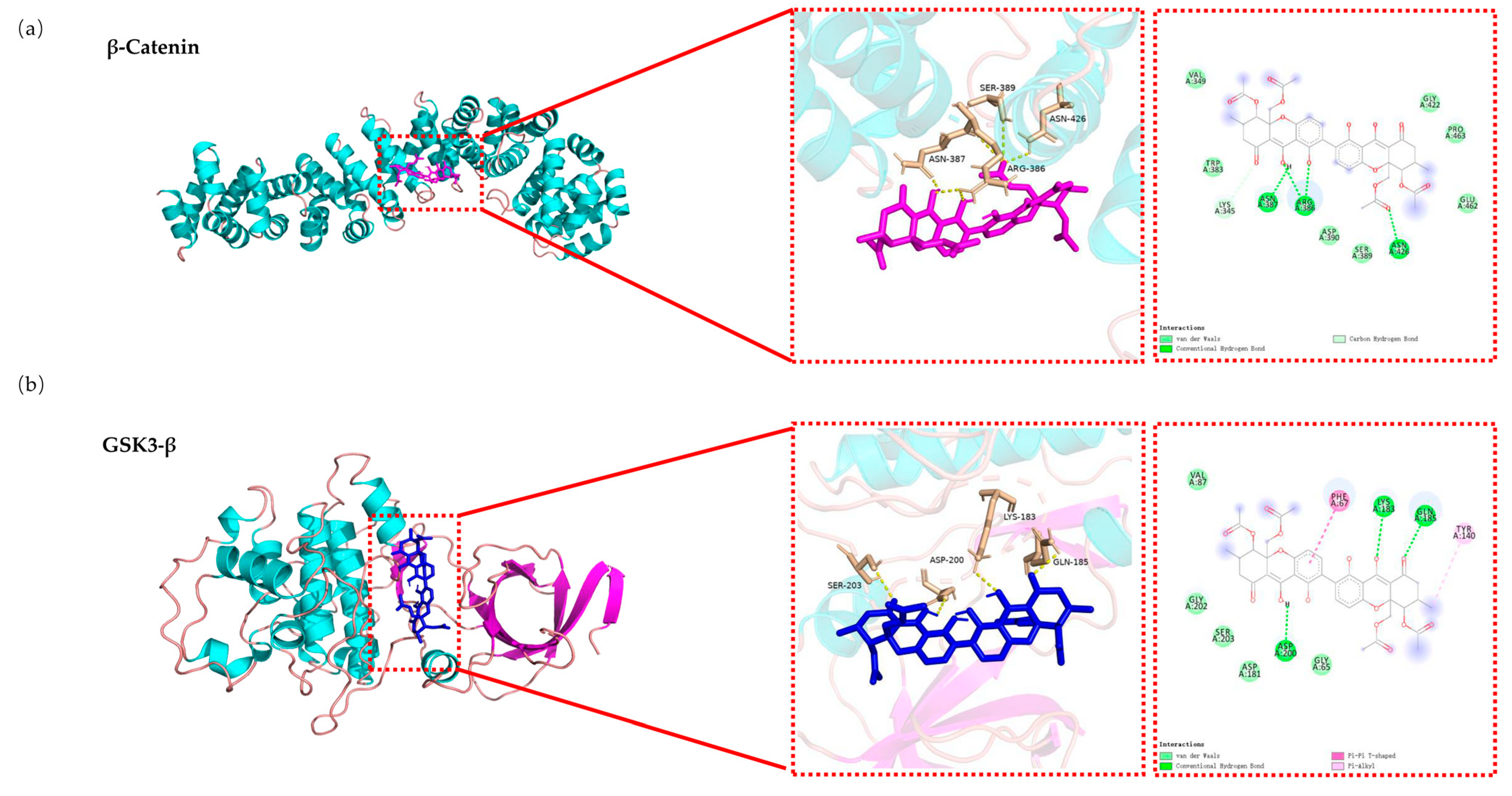
2.8. Molecular Docking Analysis of the Binding Interaction of DD-9 with β-catenin and GSK3-β
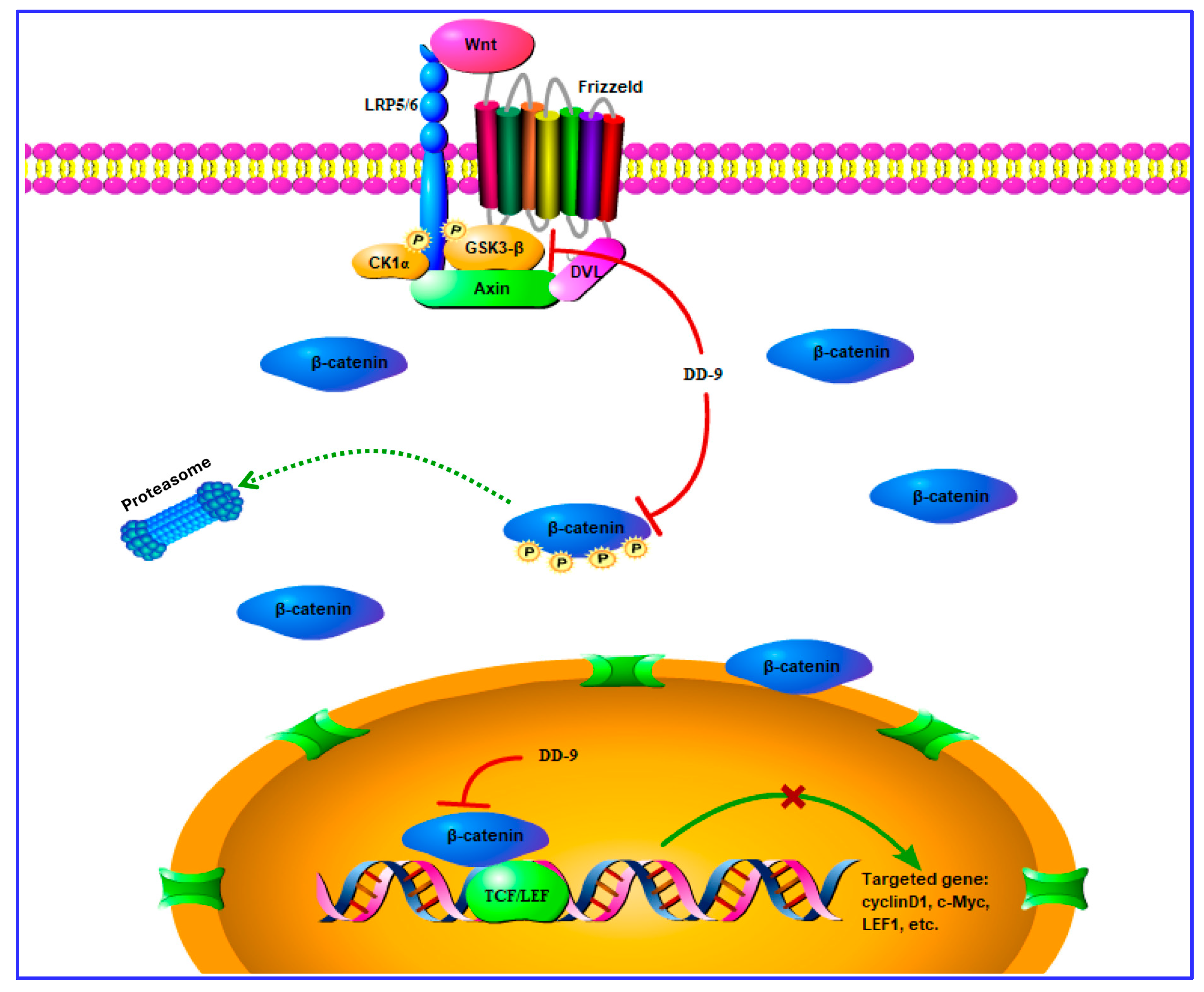
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedure
4.2. Fungal Material
4.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. MTT Assay
4.6. Cell Migration Assay
4.7. Transwell Assays
4.8. Colony Formation Assay
4.9. Apoptosis Assay
4.10. Cell Cycle Assay
4.11. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.12. qPCR Analysis
4.13. Immunocytochemical Staining
4.14. Western Blot Analysis
4.15. Molecular Docking Studies
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, L.; Jiang, C.; Qian, Q. Marine natural products: A potential source of anti-hepatocellular carcinoma drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7879–7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Pan, W.; Jin, L.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.; Ma, D.; Liao, S. Human papillomavirus vaccine against cervical cancer: Opportunity and challenge. Cancer Lett. 2020, 471, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, K.S.; Sill, M.W.; Long, H.J., III; Penson, R.T.; Huang, H.; Ramondetta, L.M.; Landrum, L.M.; Oaknin, A.; Reid, T.J.; Leitao, M.M.; et al. Improved survival with bevacizumab in advanced cervical cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Sci. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Ashihara, E.; Maekawa, T. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Shen, T.; Yi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W. Crosstalk between long non-coding RNAs and Wnt/β-catenin signalling in cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Amerizadeh, F.; ShahidSales, S.; Khazaei, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Maftouh, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; Avan, A. Therapeutic potential of targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in treatment of colorectal cancer: Rational and progress. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 1979–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodon, J.; Argilés, G.; Connolly, R.M.; Vaishampayan, U.; De Jonge, M.; Garralda, E.; Giannakis, M.; Smith, D.C.; Dobson, J.R.; McLaughlin, M.E.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Single-Agent WNT974, a First-in-Class Porcupine Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.J.; Xu, B.; Guo, Y.W. Unusual Secondary Metabolites from the Mangrove Ecosystems: Structures, Bioactivities, Chemical, and Bio-syntheses. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, S.; Gupta, M.; Prakash, V.; Reddy, M.S. Mangrove-Associated Fungi: A Novel Source of Potential Anticancer Compounds. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.W.; Sun, C.X.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, J. Four new chromones from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis asparagi DHS-48 isolated from the Chinese mangrove plant Rhizophora mangle. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Wu, J.W.; Wei, C.W.; Feng, T.; Zhou, D.D.; Wen, Z.C.; Xu, J. Immunosuppressive cytochalasins from the mangrove endophytic fungus Phomopsis asparagi DHS-48. Mar. Drugs. 2022, 20, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, F.; Wei, C.W.; Deng, X.L.; Chen, D.D.; Wen, Z.C.; Xu, J. Epigenetic Manipulation Induced Production of Immunosuppressive Chromones and Cytochalasins from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Phomopsis asparagi DHS-48. Mar. Drugs. 2022, 20, 616. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.W.; Chen, D.D.; Li, Q.; Feng, T.; Xu, J. Metabolomics-Guided Discovery of New Dimeric Xanthones from Co-Cultures of Mangrove Endophytic Fungi Phomopsis asparagi DHS-48 and Phomopsis sp. DHS-11. Mar. Drugs. 2024, 22, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Bioactive natural products derived from Mangrove-Associated Microbes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 841–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Mándi, A.; Li, X.M.; Hu, X.Y.; Göker, H.; Kurtán, T.; Zhu, H.J.; Zhang, W.M.; Li, C.Y.; et al. Three Diketopiperazine Alkaloids with Spirocyclic Skeletons and One Bisthiodiketopiperazine Derivative from the Mangrove-Derived Endophytic Fungus Penicillium brocae MA-231. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5304–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.L.; Wei, M.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Fu, X.M.; Guo, Z.Y.; Xu, R.F.; Zheng, C.J.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y. Antibacterial anthraquinone derivatives from a sea anemone-derived fungus Nigrospora sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Rotinsulu, H.; Namikoshi, M. Tetrahydrobostrycin and 1-deoxytetrahydrobostrycin, two new hexahydroanthrone derivatives, from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, K.; Okudaira, M.; Shindo, T.; Sato, A. Bostrycin, a tetrahydroanthraquinone compound possessing a potent anti-tumor activity. J. Antibiot. 1968, 21, 668–669. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Xia, X.; Liang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Shao, R.; Zhang, J.; Liang, G. Anthracenedione Derivative 1403P-3 Induces Apoptosis in KB and KBv200 Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Independent Mitochondrial Pathway and Death Receptor Pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Gu, M.; He, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; She, Z.; et al. SZ-685C, a Marine Anthraquinone, Is a Potent Inducer of Apoptosis with Anticancer Activity by Suppression of the Akt/FOXO Pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, D.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J. Sdy-1 executes anticancer activity in HepG2 and HeLa cancer cells by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Deng, Q.; Zheng, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Cytotoxic constituents from the mangrove endophytic Pestalotiopsis sp. induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cancer cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2968–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, M.M.; Clardy, J. Dicerandrols, new antibiotic and cytotoxic dimers produced by the fungus Phomopsis longicolla Isolated from an endangered mint. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Yuan, J.; Huang, X.; Wen, W.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; She, Z. New dimeric members of the phomoxanthone family: Phomolactonexanthones A, B and deacetylphomoxanthone C isolated from the fungus Phomopsis sp. Mar. Drugs. 2013, 11, 4961–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.N.; Ponnusamy, K.; Jeon, Y.T.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.H. Identification, fermentation, and bioactivity against Xanthomonas oryzae of antimicrobial metabolites isolated from Phomopsis longicolla S1B4. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erbert, C.; Lopes, A.A.; Yokoya, N.S.; Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Conti, R.; Pupo, M.T.; Lopes, J.L.C.; Debonsi, H.M. Antibacterial compound from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis longicolla isolated from the tropical red seaweed Bostrychia radicans. Bot. Mar. 2012, 55, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönsberg, D.; Debbab, A.; Mándi, A.; Vasylyeva, V.; Böhler, P.; Stork, B.; Engelke, L.; Hamacher, A.; Sawadogo, R.; Diederich, M.; et al. Pro-apoptotic and immunostimulatory tetrahydroxanthone dimers from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis longicolla. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 12409–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.K.; Rao, K.V.; Aalinkeel, R.; Mahajan, S.; Chawda, R.; Schwartz, S.A. Inhibition of prostate cancer cell colony formation by the flavonoid quercetin correlates with modulation of specific regulatory genes. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2004, 11, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Kang, D.; Ji, D.; Wang, X.; Zhan, W.; Fu, M.; Wang, J.B. How does cancer cell metabolism affect tumor migration and invasion? Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittekind, C.; Neid, M. Cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. S1), 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, K.; Berneman, Z.N.; Van Bockstaele, D.R. Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2003, 36, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, S.; Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle and cancer: The G1 restriction point and the G1/S transition. Curr. Genom. 2002, 3, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Paul, S.; Bisht, B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sivasubramaniam, S.; Paul, M.K. Advances in targeting the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, T.; Yeh, J.; Bowman, B.R.; Chu, Q.; Moellering, R.; Verdine, G. Inhibition of oncogenic Wnt signaling through direct targeting of β-catenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17942–17947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, V.; Turcios, L.; Marti, F.; Gedaly, R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, M. β-Catenin: Oncogenic role and therapeutic target in cervical cancer. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdek, K.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Toksoz, D. Distinct Activities of the β-catenin Family, β-catulin and β-catenin, on β-catenin-Mediated Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, G.; Jawanjal, P.; Salhan, S.; Nalliah, M.; Dhawan, I. Clinical Significance of Inactivated Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β in HPV-Associated Cervical Cancer: Relationship with Wnt/β-catenin Pathway Activation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 73, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Yanaga, F.; Sasaguri, T. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway as a target in drug discovery. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 104, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evan, G.I.; Brown, L.; Whyte, M.; Harrington, E. Apoptosis and the cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995, 7, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neogi, K.; Murumkar, P.; Sharma, P.; Yadav, P.; Tewari, M.; Karunagaran, D.; Nayak, P.; Yadav, M. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 4,7-disubstituted 8-methoxyquinazoline derivatives as potential cytotoxic agents targeting β-catenin/TCF4 signaling pathway. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 19, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Han, X.; Yan, M.; Xu, Y.; Duggineni, S.; Lin, N.; Luo, G.; Li, Y.M.; Han, X.; Huang, Z. Structure-Based Discovery of a Novel Inhibitor Targeting the β-Catenin/Tcf4 Interaction. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Fang, X.Q.; Lim, W.J.; Park, J.; Kang, T.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, J.H. Cinobufagin Suppresses Melanoma Cell Growth by Inhibiting LEF1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar-Finkelman, H.; Martínez, A. GSK-3 Inhibitors: Preclinical and Clinical Focus on CNS. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, D.; Luo, H.; Long, L.; Hu, Z.; Bao, J. Identification of two potential glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibitors for the treatment of osteosarcoma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilouz, R.; Kowalsman, N.; Eisenstein, M.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. Identification of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Substrate-interacting Residues Suggests a Common Mechanism for Substrate Recognition. J. Biochem. 2006, 281, 30621–30630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajani, R.; Fraser, E.; Roe, S.M.; Young, N.; Good, V.; Dale, T.C.; Pearl, L.H. Crystal structure of glycogen synthase kinase 3β: Structural basis for phosphate-primed substrate specificity and autoinhibition. Cell 2001, 105, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Feng, T.; Liu, P.; Xu, J. Dicerandrol C Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of HepG2 and Hela Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060278
Zhou D, Chen D, Wu J, Feng T, Liu P, Xu J. Dicerandrol C Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of HepG2 and Hela Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(6):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060278
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dongdong, Dandan Chen, Jingwan Wu, Ting Feng, Pinghuai Liu, and Jing Xu. 2024. "Dicerandrol C Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of HepG2 and Hela Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 22, no. 6: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060278
APA StyleZhou, D., Chen, D., Wu, J., Feng, T., Liu, P., & Xu, J. (2024). Dicerandrol C Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of HepG2 and Hela Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 22(6), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060278





