The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Virtual Screening Identifies Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Oysters
2.2. Synthesis and Validation of DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of LRGFGNPPT
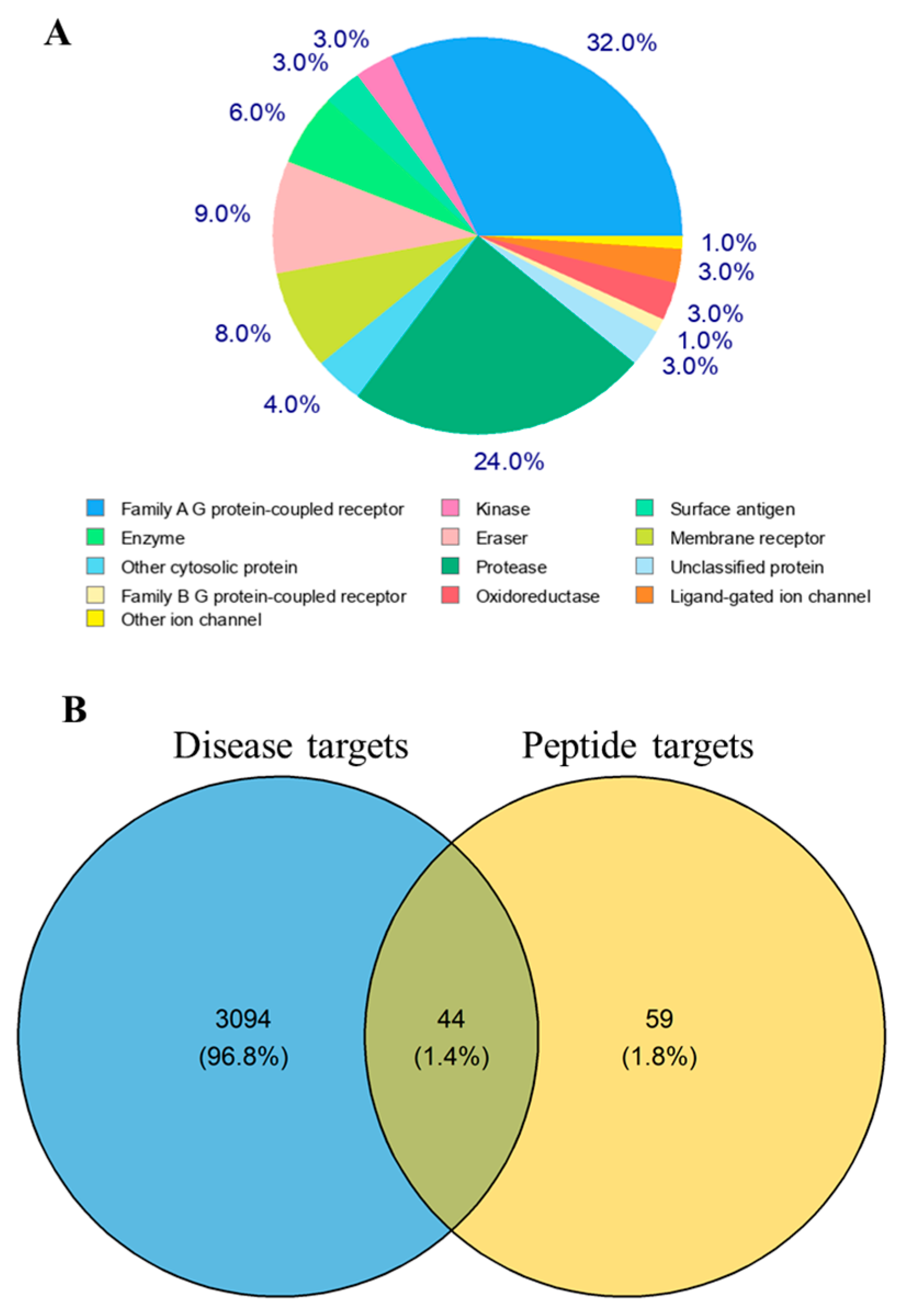
2.3. Identification of Intersection Targets between LRGFGNPPT and T2D
2.4. PPI Network Analysis Reveals Core Targets of LRGFGNPPT in T2D Treatment
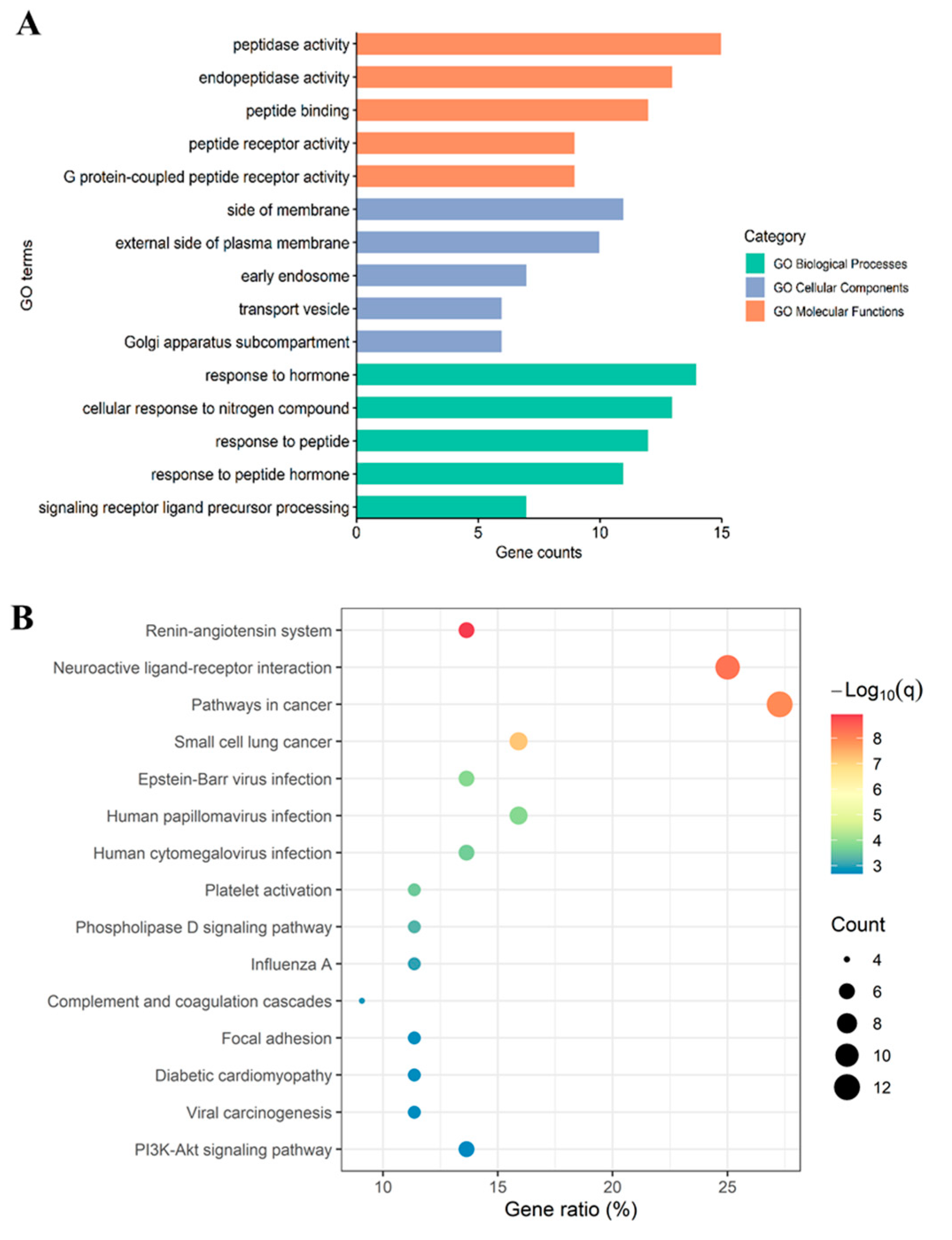
2.5. Enrichment Analysis of LRGFGNPPT Target Pathways for Anti-T2D
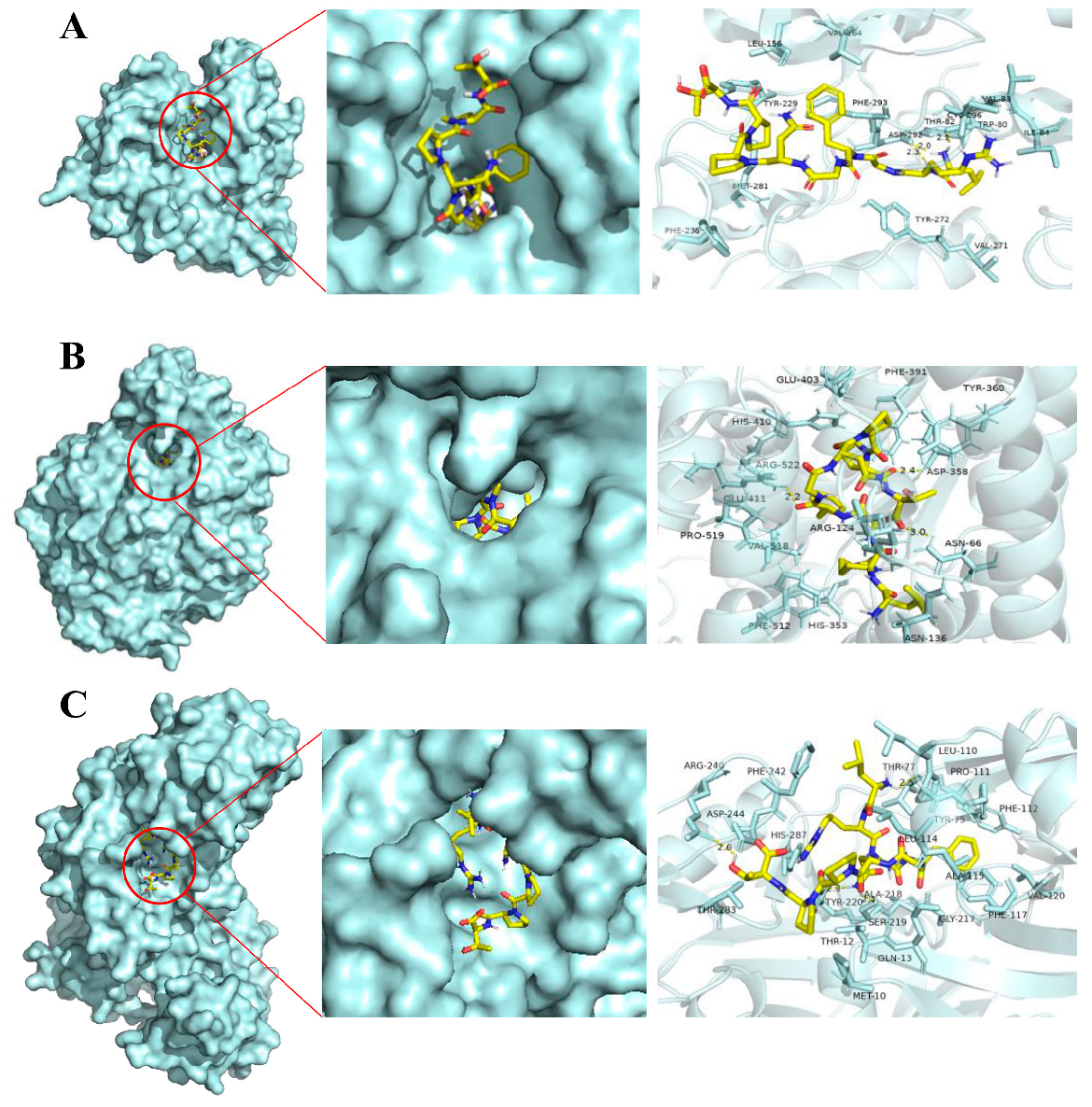
2.6. Molecular Docking Reveals a High Affinity between LRGFGNPPT and Its Core Anti-T2D Targets
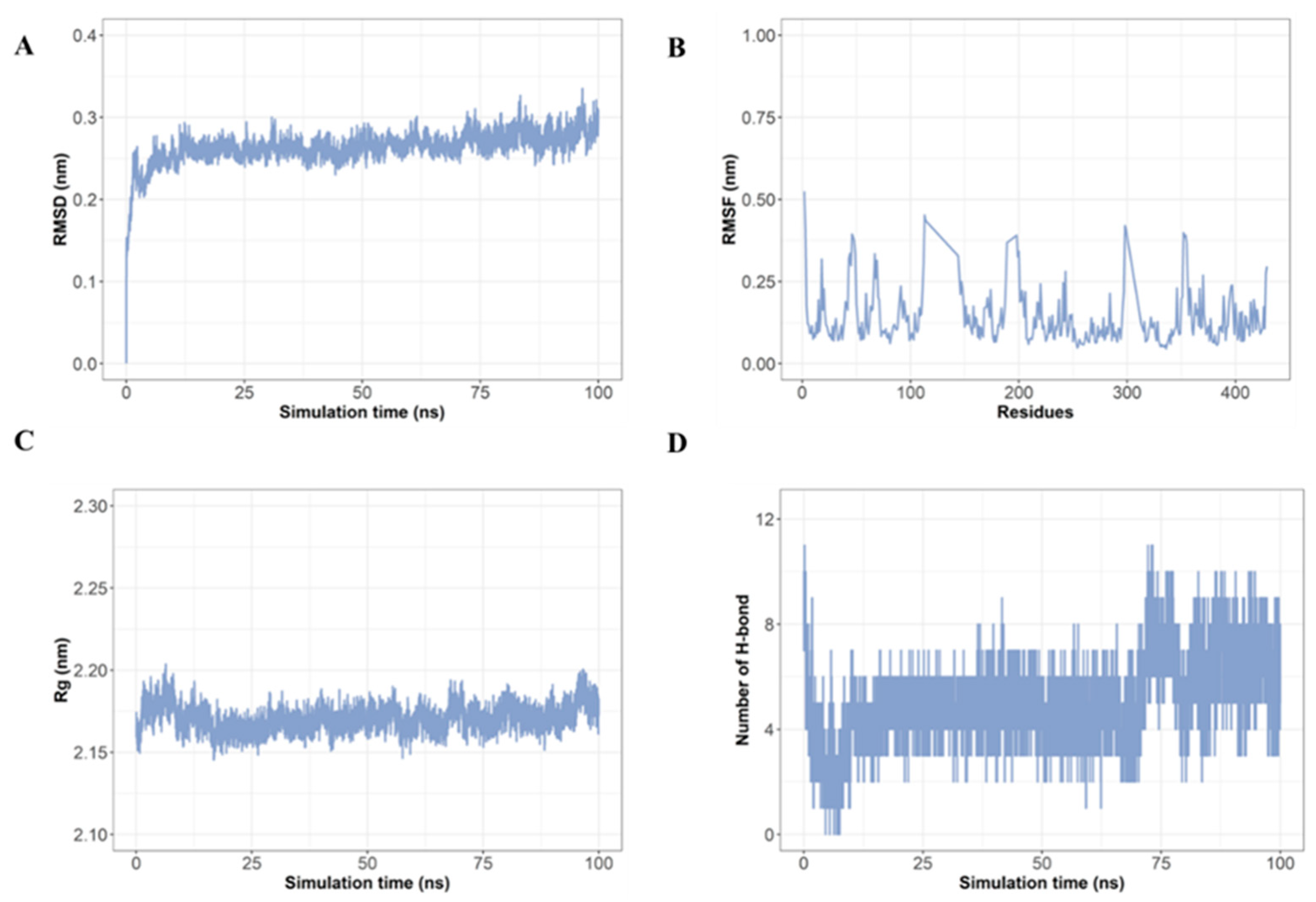
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Confirms Stable Interaction of LRGFGNPPT with AKT1
2.8. Analysis of ADMET Properties and Susceptibility to Degradation by Proteases of LRGFGNPPT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virtual Screening of Oyster DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides
4.2. Peptide Synthesis and Analysis of Its DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity In Vitro
4.3. Potential Targets Prediction of Oyster Peptide and T2D
4.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction and Core Targets Identification
4.5. Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.8. Prediction of ADMET Properties and Susceptibility to Degradation by Proteases
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.H.Y.; Micha, R.; Mozaffarian, D. Dietary fats and cardiometabolic disease: Mechanisms and effects on risk factors and outcomes. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Sailani, M.R.; Contrepois, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ahadi, S.; Leopold, S.R.; Zhang, M.J.; Rao, V.; Avina, M.; Mishra, T.; et al. Longitudinal multi-omics of host-microbe dynamics in prediabetes. Nature 2019, 569, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, W.; Qin, X.; Gao, J.; Zheng, H. The purification and identification of immunoregulatory peptides from oyster (Crassostrea hongkongensis) enzymatic hydrolysate. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32854–32863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. A comprehensive review of oyster peptides: Preparation, characterisation and bioactivities. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.Q.; Zhu, S.S.; He, M.J.; Luo, F.; Fu, C.Z.; Zou, T.B. Marine peptides as potential agents for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus-a prospect. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullius, A.; Fassina, P.; Giroldi, M.; Goettert, M.I.; Volken de Souza, C.F. A biotechnological approach for the production of branched chain amino acid containing bioactive peptides to improve human health: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartrand, D.; Da Silva, M.S.; Julien, P.; Rudkowska, I. Influence of amino acids in dairy products on glucose homeostasis: The clinical evidence. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.A.; Pintado, M.E. Bioactive peptides derived from marine sources: Biological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 348–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boezio, B.; Audouze, K.; Ducrot, P.; Taboureau, O. Network-based approaches in pharmacology. Mol. Inform. 2017, 36, 1700048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Wei, J.; Tang, K.; Feuers, R.; Hong, H. Drug repositioning through network pharmacology. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 3646–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, S.S.; Abbasi, S.W. Molecular docking studies for the identification of novel melatoninergic inhibitors for acetylserotonin-O-methyltransferase using different docking routines. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2013, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantsar, T.; Poso, A. Binding affinity via docking: Fact and fiction. Molecules 2018, 23, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, K.M.; Le, D.P.; Tran, N.V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, T.D.; Le, M.T. Computational assay of Zanamivir binding affinity with original and mutant influenza neuraminidase 9 using molecular docking. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 385, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Sercu, T.; Wadhawan, K.; Padhi, I.; Gehrmann, S.; Cipcigan, F.; Chenthamarakshan, V.; Strobelt, H.; Dos Santos, C.; Chen, P.Y.; et al. Accelerated antimicrobial discovery via deep generative models and molecular dynamics simulations. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohlke, H.; Hendlich, M.; Klebe, G. Knowledge-based scoring function to predict protein-ligand interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 295, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevener, K.E.; Zhao, W.; Ball, D.M.; Babaoglu, K.; Qi, J.; White, S.W.; Lee, R.E. Validation of molecular docking programs for virtual screening against dihydropteroate synthase. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, P.; Piovesana, S.; Samperi, R.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Laganà, A. Development of an analytical strategy for the identification of potential bioactive peptides generated by in vitro tryptic digestion of fish muscle proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Huang, A.; Xu, F.; Wang, X. Identification, characterization and in vitro activity of hypoglycemic peptides in whey hydrolysates from rubing cheese by-product. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S. “PP-type” self-assembling peptides with superior rheological properties. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 6056–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Wang, X.; Yi, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Diao, Y.; Lin, M.C.; et al. A conjugate of octamer-binding transcription factor 4 and toll-like receptor 7 agonist prevents the growth and metastasis of testis embryonic carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, Y.M.; El-Karim, S.S.A.; Nasr, T.; Elseginy, S.A.; Anwar, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Ali, H.F. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Spiro Cyclohexane-1,2- Quinazoline Derivatives as Potent Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitors. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, A.; Lakshmikanth, M.; Lokanath, N.K.; Poornima Priyadarshini, C.G. Generation, characterization and molecular binding mechanism of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitory peptides from sorghum bicolor seed protein. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Val.) Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, W. Identification of two novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from sheep whey protein and inhibition mechanism revealed by molecular docking. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards suite: From gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1.30.31–31.30.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Huddart, R.; Gong, L.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Whaley, R.; Klein, T.E. An evidence-based framework for evaluating pharmacogenomics knowledge for personalized medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.M.; Coughlan, M.T.; Cooper, M.E. Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K. Obesity and diabetic kidney disease: Role of oxidant stress and redox balance. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2016, 25, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajja, R.K.; Prasad, S.; Cucullo, L. Impact of altered glycaemia on blood-brain barrier endothelium: An in vitro study using the hCMEC/D3 cell line. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.X.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhu, Y.M. Diabetes and cancer: Associations, mechanisms, and implications for medical practice. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scappaticcio, L.; Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Insights into the relationships between diabetes, prediabetes, and cancer. Endocrine 2017, 56, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Guo, T.; Yang, M.; Qi, J.; Huang, C.; Hong, Y.; Gu, J.; Pang, X.; Liu, W.J.; Peng, R.; et al. Light chain modulates heavy chain conformation to change protection profile of monoclonal antibodies against influenza A viruses. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Pandey, P.; Prasad, B.; Robinson, T.; Purohit, R.; D’Cruz, L.G.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Mutreja, A.; Harkin, J.; Rai, T.S.; et al. Immuno-informatics analysis predicts B and T cell consensus epitopes for designing peptide vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 with 99.82% global population coverage. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Shi, S.; Yi, J.; Wang, N.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Peng, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; et al. ADMETlab 3.0: An updated comprehensive online ADMET prediction platform enhanced with broader coverage, improved performance, API functionality and decision support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W422–W431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.e.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaoka, Y.; Takagi, T.; Michiba, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Kishimura, H. Study on the mechanism of the blood-glucose-lowering effect of collagen peptides from sturgeon by-products. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Evaluation of the potential of dietary proteins as precursors of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV inhibitors by an in silico approach. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; You, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, L. Identification and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from oat proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elam, E.; Feng, J.; Lv, Y.-M.; Ni, Z.-J.; Sun, P.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Ma, Y.-L.; Wei, Z.-J. Recent advances on bioactive food derived anti-diabetic hydrolysates and peptides from natural resources. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaroakpo, J.U.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. In vitro modulation of glucagon-like peptide release by DPP-IV inhibitory polyphenol-polysaccharide conjugates of sprouted quinoa yoghurt. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestri, E.; Pavlicevic, M.; Montorsi, M.; Marmiroli, N. Meta-analysis for correlating structure of bioactive peptides in foods of animal origin with regard to effect and stability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, I.M.E.; Chen, X.M.; Kitts, D.D.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Investigation into the bioavailability of milk protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitory activity using Caco-2 cell monolayers. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Montoya, M.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C. Bioactive peptides from germinated soybean with anti-diabetic potential by inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-iv, α-amylase, and α-glucosidase enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretskaya, Y.; Glanz, V.; Gryaznova, M.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Popov, V. Mitochondrial antioxidant SkQ1 has a beneficial effect in experimental diabetes as based on the analysis of expression of microRNAs and mRNAs for the oxidative metabolism regulators. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Stepicheva, N.A.; Ghosh, S.; Shang, P.; Chowdhury, O.; Daley, R.A.; Yazdankhah, M.; Gupta, U.; Hose, S.L.; Valapala, M.; et al. Reducing Akt2 in retinal pigment epithelial cells causes a compensatory increase in Akt1 and attenuates diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Santhanam, R.K.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Chen, H. Anthocyanins from dietary black soybean potentiate glucose uptake in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells via up-regulating phosphorylated Akt and GLUT4. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Wan, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Yan, T.; Jia, Y. A network pharmacology approach and experimental validation to investigate the anticancer mechanism and potential active targets of ethanol extract of Wei-Tong-Xin against colorectal cancer through induction of apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Jung, F.F.; Ingelfinger, J.R. Renal renin-angiotensin system in diabetes: Functional, immunohistochemical, and molecular biological correlations. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, F477–F486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saumya, M.; Subin, E.K.; Suchithra, T.V. Network analysis of MPO and other relevant proteins involved in diabetic foot ulcer and other diabetic complications. Interdiscip. Sci. 2019, 11, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Uekita, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Takeishi, Y. Advanced glycation end product-mediated matrix metallo-proteinase-9 and apoptosis via renin-angiotensin system in type 2 diabetes. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuissa, H.; Jones, P.G.; Marso, S.P.; O’Keefe, J.H., Jr. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers for prevention of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niechciał, E.; Acerini, C.L.; Chiesa, S.T.; Stevens, T.; Dalton, R.N.; Daneman, D.; Deanfield, J.E.; Jones, T.W.; Mahmud, F.H.; Marshall, S.M.; et al. Medication adherence during adjunct therapy with statins and ACE inhibitors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.J.; Echouffo Tcheugui, J.B.; Effoe, V.S.; Hsueh, W.A.; Allison, M.A.; Golden, S.H. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, glucose metabolism and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: MESA. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osonoi, T.; Gouda, M.; Kubo, M.; Arakawa, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Abe, M. Effect of canagliflozin on urinary albumin excretion in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: A pilot study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Awadhi, F.H.; Luesch, H. Targeting eukaryotic proteases for natural products-based drug development. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 827–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchens, T.; Piston, D.W. EphA4 receptor forward signaling inhibits glucagon secretion from α-cells. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3839–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaeil, A.; Babiker, F.; Al-Sabah, S. Discrepancy between the actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor ligands in the protection of the heart against ischemia reperfusion injury. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.; Wan, S.; Jaiswal, N.; Vega, R.B.; Ayer, D.E.; Titchenell, P.M.; Han, X.; Won, K.J.; Kelly, D.P. MondoA drives muscle lipid accumulation and insulin resistance. JCI Insight 2019, 5, e129119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.; Yiannikouris, F.; Thatcher, S.; Cassis, L. ACE2 deficiency reduces β-cell mass and impairs β-cell proliferation in obese C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E621–E631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, O.; Al-Sunni, A.; Khavandi, K.; Khavandi, A.; Withers, S.; Greenstein, A.; Heagerty, A.M.; Malik, R.A. Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, Y.; Yu, D.; Jin, L.; Gong, X.; Zhang, B. Perilla oil regulates intestinal microbiota and alleviates insulin resistance through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in type-2 diabetic KKAy mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xie, Y.Z.; Peng, C.W.; Yao, K.N.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhan, S.F.; Zhuang, H.F.; Huang, H.T.; Liu, X.H.; Huang, X.F.; et al. Modeling Kaempferol as a potential pharmacological agent for COVID-19/PF co-occurrence based on bioinformatics and system pharmacological tools. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 865097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.Q.; Cao, W.H.; Gao, J.L.; Zheng, H.N.; Lin, H.S.; Zhang, C.H.; Qin, X.M. Structural characteristics of antioxidant and hypoglycemic peptides from oyster (Crassostrea hongkongensis) and their simulated digestion characteristics in vitro. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New docking methods, expanded force field, and Python bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, A.; Teemu, J.M.; Roland, S.; Szilárd, P.; Jeremy, C.S.; Berk, H.; Erik, L. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99sb. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Target | PDB Entry | Ligand | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | Linagliptin (positive control) | −8.7 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | SSGPIPTTPPPPPPVPK | −9 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | LRGFGNPPT | −8.9 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | YDDTYVPR | −8.4 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | GEDGAEGPTGPVGPL | −8 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | NGEVGPLGLPG | −8 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | YDNLPAECKLA | −8 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | GEPGPEGPAGPIGPR | −7.9 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | QDRDHIIIGWEP | −7.8 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | IDEDIEPPR | −7.7 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | VDVVLPK | −7.7 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | GPSGEPGPEGPAGPIGPR | −7.6 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | EAAKGGGETWILYRG | −7.6 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | GVGDDIAPR | −7.6 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | LPYDKPGAPGTPK | −7.5 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | GLIDEDIEPPR | −7.4 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | LVLECKASNPH | −7.4 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | QDIGGQIPGNKGQN | −7.2 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | QEAEVFSIMENL | −7.1 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | DMEGKPSPPGPS | −6.9 |
| DPP-IV | 3KWF | ITTLLTAI | −6.5 |
| Protein | PDB Entry | Ligand | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 3o96 | LRGFGNPPT | −9.3 |
| ACE | 1o8a | LRGFGNPPT | −8.9 |
| REN | 2v0z | LRGFGNPPT | −9.0 |
| Property | Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Pfizer rule | Acceptable | Excellent |
| Caco-2 permeability | −6.639 | Bad |
| Plasma protein binding (PPB) | 14.045 | Excellent |
| Plasma clearance | 2.205 | Excellent |
| The half-life (T1/2) | 1.18 | Medium |
| Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) | 0.038 | Excellent |
| AMES toxicity | 0.031 | Excellent |
| Rat oral acute toxicity | 0.025 | Excellent |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | 0.0 | Excellent |
| CYP1A2 substrate | 0.0 | Excellent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Su, X.; Cao, W.; Tan, M.; Zhu, G.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L. The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22080361
Chen Z, Su X, Cao W, Tan M, Zhu G, Gao J, Zhou L. The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(8):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22080361
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhongqin, Xiaojie Su, Wenhong Cao, Mingtang Tan, Guoping Zhu, Jialong Gao, and Longjian Zhou. 2024. "The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies" Marine Drugs 22, no. 8: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22080361
APA StyleChen, Z., Su, X., Cao, W., Tan, M., Zhu, G., Gao, J., & Zhou, L. (2024). The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies. Marine Drugs, 22(8), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22080361







