The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife
Abstract
1. Introduction to Harmful Algal Biotoxins
2. History of DA Toxicosis
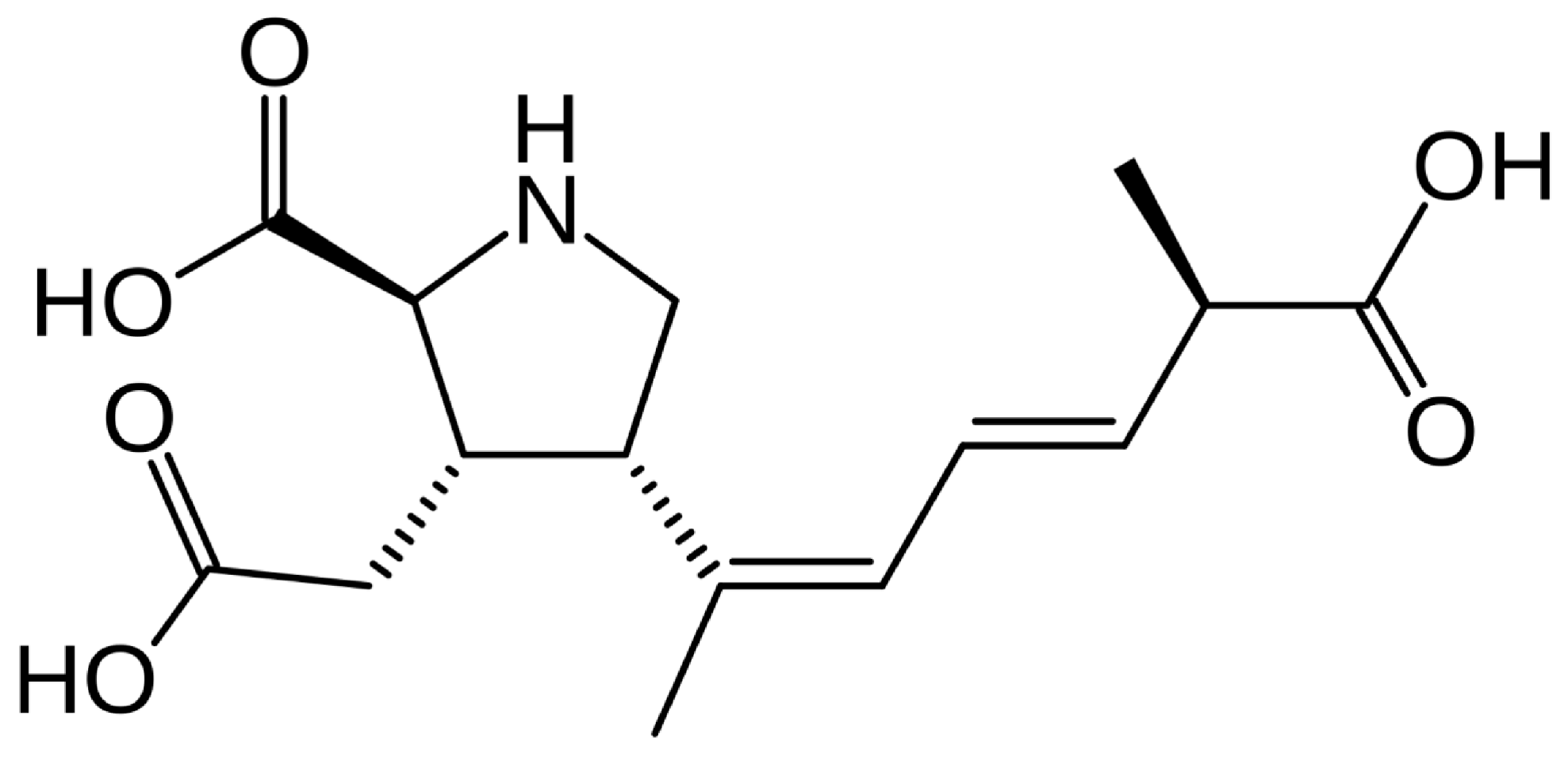
3. Domoic Acid Production
4. Toxicokinetic Properties of DA
5. Susceptibility
5.1. Species
5.2. Age
5.3. Sex
5.4. Underlying Health Status
5.5. Exposure Scenario
6. Clinical Signs and Symptoms
6.1. Gastrointestinal
6.2. Central Nervous System
6.3. Cardiovascular/Respiratory
6.4. Urogenital
6.5. Integumentary/Musculoskeletal
6.6. Other/Indirect
7. Diagnostic Tests
7.1. Diagnosis of DA Exposure
7.1.1. Pseudo-nitzschia spp. Detection
7.1.2. Domoic Acid Antigen Detection
7.1.3. Domoic Acid Antibody Detection
7.1.4. Vector Prey Detection
7.2. Diagnosis of DA Toxicosis
7.2.1. Blood Parameters
7.2.2. Hormone Testing
7.2.3. Kidney Injury Biomarkers
7.2.4. Cardiovascular Injury Biomarkers
7.2.5. Neurobehavioral Injury Markers
7.2.6. Reproductive Failure Confirmation
7.2.7. Gastrointestinal Lesion Identification
7.3. Gross and Microscopic Histopathology
7.3.1. Gastrointestinal Tract
7.3.2. Central Nervous System
7.3.3. Ocular
7.3.4. Cardiovascular/Respiratory
7.3.5. Urogenital
7.3.6. Integumentary/Musculoskeletal
7.3.7. Other
7.4. Molecular Diagnostics
8. Time Course of DA Toxicosis
9. Medical Treatment for DA Toxicosis
10. Prognosis
11. California Sea Lions as Models of DA Toxicosis
12. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bates, S.S.; Hubbard, K.A.; Lundholm, N.; Montresor, M.; Leaw, C.P. Pseudo-Nitzschia, Nitzschia, and Domoic Acid: New Research since 2011. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, S.E.; Van Dolah, F.M. Marine Biotoxins. In New Directions in Conservation Medicine: Applied Cases of Ecological Health; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 374. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Belin, C.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Bresnan, E.; Chinain, M.; Enevoldsen, H.; Iwataki, M.; Karlson, B.; McKenzie, C.H. Perceived Global Increase in Algal Blooms Is Attributable to Intensified Monitoring and Emerging Bloom Impacts. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Bates, S.S.; Lundholm, N.; Thessen, A.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Adams, N.G.; Trick, C.G. Pseudo-nitzschia Physiological Ecology, Phylogeny, Toxicity, Monitoring and Impacts on Ecosystem Health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, S.K.; Hallegraeff, G.; Kudela, R.M.; Clement, A.; Mardones, J.I.; Cochlan, W.P. Pelagic Harmful Algal Blooms and Climate Change: Lessons from Nature’s Experiments with Extremes. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fey, S.B.; Siepielski, A.M.; Nusslé, S.; Cervantes-Yoshida, K.; Hwan, J.L.; Huber, E.R.; Fey, M.J.; Catenazzi, A.; Carlson, S.M. Recent Shifts in the Occurrence, Cause, and Magnitude of Animal Mass Mortality Events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onens, P.; Wilkin, S.; Fauquier, D.; Spradlin, T.; Manley, S.; Greig, D.; Brill, K.; Garron, M.; Smith, A.; Fougeres, E. 2019 Report of Marine Mammal Strandings in the United States: National Overview. Natl. Mar. Fish. Serv. Off. Prot. Resour. 2023, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fire, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Byrd, M.; Whitehead, H.R.; Paternoster, J.; Morton, S.L. Co-Occurrence of Multiple Classes of Harmful Algal Toxins in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Stranding during an Unusual Mortality Event in Texas, USA. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T. Prevalence of Algal Toxins in Alaskan Marine Mammals Foraging in a Changing Arctic and Subarctic Environment. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, S.E.; Adkesson, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Jankowski, G.; Cárdenas-Alayza, S.; Broadwater, M. Peruvian Fur Seals (Arctocephalus australis ssp.) and South American Sea Lions (Otaria byronia) in Peru Are Exposed to the Harmful Algal Toxins Domoic Acid and Okadaic Acid. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2017, 33, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil, K.; Berman, M.; Frame, E.; Preti, A.; Fire, S.E.; Leighfield, T.; Carretta, J.; Carter, M.L.; Lefebvre, K. Marine Algal Toxins and Their Vectors in Southern California Cetaceans. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.L.; Schaefer, A.M.; McFarland, M.; Fire, S.; Perkins, C.R.; Ajemian, M.J. Detection of Numerous Phycotoxins in Young Bull Sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) Collected from an Estuary of National Significance. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobo, L.; Lacaze, J.-P.; Scott, A.; Petrie, J.; Turrell, E. Surveillance of Algal Toxins in Shellfish from Scottish Waters. Toxicon 2008, 51, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, J.L.; Jensen, S.-K.; McConnell, B.; Fraser, S.; Cummings, C.; Lacaze, J.-P.; Hermann, G.; Bresnan, E.; Dean, K.J.; Turner, A.D. Toxins from Harmful Algae in Fish from Scottish Coastal Waters. Harmful Algae 2021, 105, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragunow, M.; Trzoss, M.; Brimble, M.A.; Cameron, R.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; Mountfort, D. Investigations into the Cellular Actions of the Shellfish Toxin Gymnodimine and Analogues. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cai, J.; Gao, T.; Ma, A. Shellfish Consumption and Health: A Comprehensive Review of Human Studies and Recommendations for Enhanced Public Policy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4656–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.; Zabka, T.; Langlois, G.; Colegrove, K.; Silver, M.; Bargu, S.; Van Dolah, F.; Leighfield, T.; Conrad, P. Novel Symptomatology and Changing Epidemiology of Domoic Acid Toxicosis in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus): An Increasing Risk to Marine Mammal Health. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattan, L.M.; Boushey, C.J.; Liang, Y.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Castellon, L.J.; Roberts, K.A.; Toben, A.C.; Morris Jr, J. Repeated Dietary Exposure to Low Levels of Domoic Acid and Problems with Everyday Memory: Research to Public Health Outreach. Toxins 2018, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Robertson, A. Domoic Acid and Human Exposure Risks: A Review. Toxicon 2010, 56, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, T.; Daigo, K. Constituents of Chondria armata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1958, 6, 578b–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigo, K. Constituents of Chondria armata. II. Isolation of an Antihelminthic Constituent. Yakugaku Zasshi 1959, 79, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, Y.; Kojima, K.; Kumada, M.; Ogawa, H. The Anthelmintic Effect of Domoic Acid for Ascariasis. Jpn. J. Parasitol. 1960, 9, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, T. The Anthelmintic Effect of Domoic Acid against Ascaris lumbricoides. Kiseichugaku Zasshi 1961, 10, 614–616. [Google Scholar]
- Perl, T.M.; Bédard, L.; Kosatsky, T.; Hockin, J.C.; Todd, E.C.; Remis, R.S. An Outbreak of Toxic Encephalopathy Caused by Eating Mussels Contaminated with Domoic Acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, B.; Barlow, T.; Moizer, K.; Paul, S.; Boyle, C. Amnesic Shellfish Poison. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C. Domoic Acid and Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning-A Review. J. Food Prot. 1993, 56, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wekell, J.C.; Hurst, J.; Lefebvre, K.A. The Origin of the Regulatory Limits for PSP and ASP Toxins in Shellfish. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 927–930. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Fensin, E.; Gobler, C.J.; Hoeglund, A.E.; Hubbard, K.A.; Kulis, D.M.; Landsberg, J.H.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Provoost, P.; Richlen, M.L. Marine Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) in the United States: History, Current Status and Future Trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domoic Acid in Razor Clams|Washington State Department of Health. Available online: https://doh.wa.gov/community-and-environment/shellfish/recreational-shellfish/illnesses/biotoxins/domoic-acid-razor-clams (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Cendes, F.; Andermann, F.; Carpenter, S.; Zatorre, R.J.; Cashman, N.R. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Caused by Domoic Acid Intoxication: Evidence for Glutamate Receptor–Mediated Excitotoxicity in Humans. Ann. Neurol. Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 1995, 37, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, K.; Boushey, C.J.; Roberts, S.M.; Morris Jr, J.G.; Grattan, L.M. Communities Advancing the Studies of Tribal Nations across Their Lifespan: Design, Methods, and Baseline of the CoASTAL Cohort. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuchal, L.D.; Grattan, L.M.; Portier, K.M.; Kilmon, K.A.; Manahan, L.M.; Roberts, S.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Dose-Response Assessment for Impaired Memory from Chronic Exposure to Domoic Acid among Native American Consumers of Razor Clams. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 117, 104759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, L.; Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L.; Beale, A.M.; Work, T.M. An Outbreak of Domoic Acid Poisoning Attributed to the Pennate Diatom Pseudonitzschia australis. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, T.M.; Barr, B.; Beale, A.M.; Fritz, L.; Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L. Epidemiology of Domoic Acid Poisoning in Brown Pelicans (Pelecanus occidentalis) and Brandt’s Cormorants (Phalacrocorax penicillatus) in California. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1993, 24, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, A.S.; Palafox-Uribe, M.; Grajales-Montiel, J.; Cruz-Villacorta, A.; Ochoa, J. Sea Bird Mortality at Cabo San Lucas, Mexico: Evidence That Toxic Diatom Blooms Are Spreading. Toxicon 1997, 35, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.M.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An Unprecedented Coastwide Toxic Algal Bloom Linked to Anomalous Ocean Conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solino, L.; Ferrer-Obiol, J.; Navarro-Herrero, L.; Gonzalez-Solis, J.; Costa, P.R. Are Pelagic Seabirds Exposed to Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins? Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hemert, C.; Schoen, S.K.; Litaker, R.W.; Smith, M.M.; Arimitsu, M.L.; Piatt, J.F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Pearce, J.M. Algal Toxins in Alaskan Seabirds: Evaluating the Role of Saxitoxin and Domoic Acid in a Large-Scale Die-off of Common Murres. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibble, C.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Knowles, S.; Bodenstein, B.; Lefebvre, K.A. Domoic Acid and Saxitoxin in Seabirds in the United States between 2007 and 2018. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulland, E.M.; Haulena, M.; Fauquier, D.; Lander, M.; Zabka, T.; Duerr, R.; Langlois, G. Domoic Acid Toxicity in Californian Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus): Clinical Signs, Treatment and Survival. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Moriarty, M.E.; Duignan, P.J.; Zabka, T.S.; Dodd, E.; Batac, F.I.; Young, C.; Reed, A.; Harris, M.D.; Greenwald, K. Clinical Signs and Pathology Associated with Domoic Acid Toxicosis in Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 585501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuder, C.; Miller, M.A.; Jessup, D.A.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Harris, M.; Ames, J.A.; Carpenter, T.E.; Conrad, P.A.; Mazet, J. Patterns of Mortality in Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) from 1998–2001. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Riva, G.T.; Johnson, C.K.; Gulland, F.M.; Langlois, G.W.; Heyning, J.E.; Rowles, T.K.; Mazet, J.A. Association of an Unusual Marine Mammal Mortality Event with Pseudo-nitzschia spp. Blooms along the Southern California Coastline. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Bargu, S.; Kieckhefer, T.; Silver, M.W. From Sanddabs to Blue Whales: The Pervasiveness of Domoic Acid. Toxicon 2002, 40, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Leighfield, T.A.; Morton, S.L.; McFee, W.E.; McLellan, W.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.A.; Hohn, A.A.; Lovewell, G. Domoic Acid Exposure in Pygmy and Dwarf Sperm Whales (Kogia spp.) from Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic US Waters. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, L.F.; Rolland, R.M.; Roth, P.B.; Lundholm, N.; Wang, Z.; Doucette, G.J. Exposure of the North Atlantic Right Whale Eubalaena glacialis to the Marine Algal Biotoxin, Domoic Acid. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 398, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, G.J.; Mikulski, C.M.; King, K.L.; Roth, P.B.; Wang, Z.; Leandro, L.F.; DeGrasse, S.L.; White, K.D.; De Biase, D.; Gillett, R.M. Endangered North Atlantic Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis) Experience Repeated, Concurrent Exposure to Multiple Environmental Neurotoxins Produced by Marine Algae. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Sastre, A.V.; Hoffmeyer, M.; Rowntree, V.J.; Fire, S.E.; Santinelli, N.H.; Ovejero, S.D.; D’Agostino, V.; Marón, C.F.; Doucette, G.J. Southern Right Whale (Eubalaena australis) Calf Mortality at Península Valdés, Argentina: Are Harmful Algal Blooms to Blame? Mar. Mammal Sci. 2016, 32, 423–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson Nash, S.; Baddock, M.; Takahashi, E.; Dawson, A.; Cropp, R. Domoic Acid Poisoning as a Possible Cause of Seasonal Cetacean Mass Stranding Events in Tasmania, Australia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, V.C.; Degrati, M.; Sastre, V.; Santinelli, N.; Krock, B.; Krohn, T.; Dans, S.L.; Hoffmeyer, M.S. Domoic Acid in a Marine Pelagic Food Web: Exposure of Southern Right Whales (Eubalaena australis) to Domoic Acid on the Península Valdés Calving Ground, Argentina. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, G.K.; Silber, K.M. Co-Occurrence of Harmful Algal Blooms and Whale Deaths. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1454656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, J.R.; Perkins, C.R.; Ajemian, M.J.; Bresette, M.J.; Mott, C.R.; Page-Karjian, A. Harmful Algal and Cyanobacterial Toxins in Foraging Green Turtles (Chelonia mydas) in Florida’s Big Bend. Toxicon X 2020, 5, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.; Benson, S.; Miller, M.; Fire, S.; Stacy, B.; Kudela, R.; Fahy, C.; Seminoff, J. Domoic Acid in the Leatherback Turtle Food Web on Critical Foraging Grounds in Central California. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Conference of the International Association of Aquatic Animal Medicine, Sausalito, CA, USA, 21–26 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, H. Exposure to Algal Biotoxins: Exploring Health Effects in Green Sea Turtles (Chelonia mydas). Master’s Thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, S.S. Domoic-acid-producing Diatoms: Another Genus Added! J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Stehr, C.M.; Wekell, J.C.; Moeller, P.; Busman, M.; Woodruff, D. Domoic Acid Production near California Coastal Upwelling Zones, June 1998. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1818–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.J.; Gillman, M.; Amandi, M.F.; López-Rivera, A.; Puente, P.F.; Lehane, M.; Mitrovic, S.; Furey, A. Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs in Ireland. Toxicon 2005, 46, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Lirdwitayaprasit, T.; Kotaki, Y.; Lundholm, N.; Relox, J.; Furio, E.; Terada, R.; Yokoyama, T.; Kodama, M.; Fukuyo, Y. Isolation of ASP Toxin-Producing Nitzschia from Thailand. Mar. Res. Indones. 2008, 33, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujević, I.; Ninčević-Gladan, Ž.; Roje, R.; Skejić, S.; Arapov, J.; Marasović, I. Domoic Acid-a New Toxin in the Croatian Adriatic Shellfish Toxin Profile. Molecules 2010, 15, 6835–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.W.; Bargu, S.; Coale, S.L.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Garcia, A.C.; Roberts, K.J.; Sekula-Wood, E.; Bruland, K.W.; Coale, K.H. Toxic Diatoms and Domoic Acid in Natural and Iron Enriched Waters of the Oceanic Pacific. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20762–20767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinder, S.L.; Hays, G.C.; Brooks, C.J.; Davies, A.P.; Edwards, M.; Walne, A.W.; Gravenor, M.B. Toxic Marine Microalgae and Shellfish Poisoning in the British Isles: History, Review of Epidemiology, and Future Implications. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andjelkovic, M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Van Klaveren, J.; Van Oyen, H.; Van Loco, J. Exposure to Domoic Acid through Shellfish Consumption in Belgium. Environ. Int. 2012, 49, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Cembella, A.D.; Krock, B.; Macey, B.; Mansfield, L.; Probyn, T. Identification of the Marine Diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries (Bacillariophyceae) as a Source of the Toxin Domoic Acid in Algoa Bay, South Africa. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 36, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.F.; Hubbard, K.A.; Richlen, M.L.; Smith, J.; Bates, S.S.; Ehrman, J.; Léger, C.; Mafra, L.L., Jr.; Kulis, D.; Quilliam, M. Diversity and Toxicity of the Diatom Pseudo-nitzschia peragallo in the Gulf of Maine, Northwestern Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 103, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, C.; Álvarez, G.; Quijano-Scheggia, S.; Perez-Alania, M.; Arakaki, N.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Blanco, J.; Uribe, E. First Report of Domoic Acid Production from Pseudo-nitzschia multistriata in Paracas Bay (Peru). Toxins 2021, 13, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelchner, H.; Reeve-Arnold, K.E.; Schreiner, K.M.; Bargu, S.; Roques, K.G.; Errera, R.M. Domoic Acid and Pseudo-nitzschia spp. Connected to Coastal Upwelling along Coastal Inhambane Province, Mozambique: A New Area of Concern. Toxins 2021, 13, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiner, M.J.; Fire, S.; Schwacke, L.; Davidson, L.; Wang, Z.; Morton, S.; Roth, S.; Balmer, B.; Rowles, T.K.; Wells, R.S. Concurrent Exposure of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) to Multiple Algal Toxins in Sarasota Bay, Florida, USA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, N.; Turnbull, A.; Tan, J.; Kiermeier, A.; Nimmagadda, R.; McLeod, C. A National Survey of Marine Biotoxins in Wild-Caught Abalone in Australia. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Scholin, C.; Garthwaite, I. Pseudo-nitzschia in New Zealand and the Role of DNA Probes and Immunoassays in Refining Marine Biotoxin Monitoring Programmes. Nat. Toxins 1998, 6, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKibben, S.M.; Peterson, W.; Wood, A.M.; Trainer, V.L.; Hunter, M.; White, A.E. Climatic Regulation of the Neurotoxin Domoic Acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Qu, P.; Fu, F.; Tennenbaum, N.; Tatters, A.O.; Hutchins, D.A. Understanding the Blob Bloom: Warming Increases Toxicity and Abundance of the Harmful Bloom Diatom Pseudo-nitzschia in California Coastal Waters. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlrab, S.; John, U.; Klemm, K.; Eberlein, T.; Grivogiannis, A.M.F.; Krock, B.; Frickenhaus, S.; Bach, L.T.; Rost, B.; Riebesell, U. Ocean Acidification Increases Domoic Acid Contents during a Spring to Summer Succession of Coastal Phytoplankton. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargu, S.; Goldstein, T.; Roberts, K.; Li, C.; Gulland, F. Pseudo-nitzschia Blooms, Domoic Acid, and Related California Sea Lion Strandings in Monterey Bay, California. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2012, 28, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefer, J.D.; Robertson, A.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Smith, W.L.; Dorsey, C.P. Characterization of a Toxic Pseudo-nitzschia spp. Bloom in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Associated with Domoic Acid Accumulation in Fish. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Dortch, Q.; Doucette, G.J. An Assessment of Pseudo-nitzschia Population Dynamics and Domoic Acid Production in Coastal Louisiana. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.; Silver, M.; Coale, S.; Tjeerdema, R. Domoic Acid in Planktivorous Fish in Relation to Toxic Pseudo-nitzschia Cell Densities. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 625–631. [Google Scholar]
- Sekula-Wood, E.; Schnetzer, A.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Anderson, C.; Berelson, W.M.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Burns, J.M.; Caron, D.A.; Cetinic, I.; Ferry, J.L. Rapid Downward Transport of the Neurotoxin Domoic Acid in Coastal Waters. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnetzer, A.; Lampe, R.H.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Marchetti, A.; Osburn, C.L.; Tatters, A.O. Marine Snow Formation by the Toxin-Producing Diatom, Pseudo-nitzschia australis. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, M. Chemical Methods for Domoic Acid, the Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning (ASP) Toxin. Man. Harmful Mar. Microalgae Monogr. Oceanogr. Methodol. 2003, 11, 247–266. [Google Scholar]
- McCarron, P.; Hess, P. Tissue Distribution and Effects of Heat Treatments on the Content of Domoic Acid in Blue Mussels, Mytilus edulis. Toxicon 2006, 47, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Pulido, O.M. Glutamate Receptors in Peripheral Tissues: Current Knowledge, Future Research, and Implications for Toxicology. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001, 29, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y. Microalgal Metabolites. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, J.T. Kainic Acid: Insights into Excitatory Mechanisms Causing Selective Neuronal Degeneration. In Ciba Foundation Symposium 126—Selective Neuronal Death; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 186–203. [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe, T.; Evans, R.; Headley, P.; Martin, M.; Watkins, J. Domoic and Quisqualic Acids as Potent Amino Acid Excitants of Frog and Rat Spinal Neurones. Nature 1975, 255, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcache, L.M.; Rodriguez, J.; Rein, K.S. The Structural Basis for Kainoid Selectivity at AMPA Receptors Revealed by Low-Mode Docking Calculations. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Giordano, G.; Faustman, E.M. Domoic Acid as a Developmental Neurotoxin. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Frame, E.R.; Kendrick, P.S. Domoic Acid and Fish Behavior: A Review. Harmful Algae 2012, 13, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Noren, D.P.; Schultz, I.R.; Bogard, S.M.; Wilson, J.; Eberhart, B.-T.L. Uptake, Tissue Distribution and Excretion of Domoic Acid after Oral Exposure in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Berman, M.; Langlois, G.W.; Morton, S.L.; Sekula-Wood, E.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R. Trophic Transfer of the Harmful Algal Toxin Domoic Acid as a Cause of Death in a Minke Whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) Stranding in Southern California. Aquat. Mamm. 2010, 36, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, F.; Truelove, J.; Nera, E.; Tryphonas, L.; Campbell, J.; Lok, E. Domoic Acid Poisoning and Mussel-Associated Intoxication: Preliminary Investigations into the Response of Mice and Rats to Toxic Mussel Extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1989, 27, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, F.; Truelove, J.; Tryphonas, L.; Nera, E. The Toxicology of Domoic Acid Administered Systemically to Rodents and Primates. Can. Dis. Wkly. Rep.=Rapp. Hebd. Des Mal. Au Can. 1990, 16, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Crouthamel, B.; Topletz, A.R.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Isoherranen, N. Toxicokinetics and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of the Shellfish Toxin Domoic Acid in Nonhuman Primates. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, E.C.; Gulland, F.M.; Greig, D.J.; Hunter, M.; Jaakola, J.; Leger, J.S.; Leighfield, T.A.; Van Dolah, F.M. Domoic Acid Causes Reproductive Failure in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucher, J.M.; Ramsdell, J.S. Maternal–Fetal Transfer of Domoic Acid in Rats at Two Gestational Time Points. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, L.; Gulland, F.; Frame, E.; Lefebvre, K. Domoic Acid in Milk of Free Living California Marine Mammals Indicates Lactational Exposure Occurs. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2014, 30, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Hendrix, A.; Halaska, B.; Duignan, P.; Shum, S.; Isoherranen, N.; Marcinek, D.J.; Gulland, F.M. Domoic Acid in California Sea Lion Fetal Fluids Indicates Continuous Exposure to a Neuroteratogen Poses Risks to Mammals. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsdell, J.S. The Molecular and Integrative Basis to Domoic Acid Toxicity. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and Biochemistry; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, I.R.; Skillman, A.; Sloan-Evans, S.; Woodruff, D. Domoic Acid Toxicokinetics in Dungeness Crabs: New Insights into Mechanisms That Regulate Bioaccumulation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasker, R.A. Domoic Acid. In Advances in Neurotoxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 6, pp. 49–88. ISBN 2468-7480. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.; Goldstein, T.; Situ, D.; Zabka, T.S.; Gulland, F.M.; Mueller, R.W. Cloning and Characterization of Glutamate Receptors in Californian Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvagni, P.; Lowenstine, L.; Spraker, T.; Lipscomb, T.; Gulland, F. Pathology of Domoic Acid Toxicity in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryphonas, L.; Truelove, J.; Nera, E.; Iverson, F. Acute Neurotoxicity of Domoic Acid in the Rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 1990, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavin, G.; Pinsky, C.; Bose, R. Gastrointestinal Effects of Contaminated Mussels and Putative Antidotes Thereof. Can. Dis. Wkly. Rep.=Rapp. Hebd. Des Mal. Au Can. 1990, 16, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zabka, T.; Goldstein, T.; Cross, C.; Mueller, R.; Kreuder-Johnson, C.; Gill, S.; Gulland, F. Characterization of a Degenerative Cardiomyopathy Associated with Domoic Acid Toxicity in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranyac-Tramoundanas, A.; Harrison, J.C.; Sawant, P.M.; Kerr, D.S.; Sammut, I.A. Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Following Seizure Induction by Domoic Acid. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, O.M. Domoic Acid Toxicologic Pathology: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 180–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.; Hendrix, A.; Shum, S.; Grant, K.S.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Burbacher, T.M. Public Health Risks Associated with Chronic, Low-Level Domoic Acid Exposure: A Review of the Evidence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsdell, J.S.; Gulland, F.M. Domoic Acid Epileptic Disease. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1185–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, I.; Johnson, W.; Sapienza, P.; Kim, C. Effects of the Seafood Toxin Domoic Acid on Glutamate Uptake by Rat Astrocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Hou, Y.; Ghane, T.; Pulido, O.M. Regional Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Primary Astrocyte Cells Cultured from the Brain Stem and Hippocampus. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.; Leibrecht, H.; Ryan, J.; Van Dolah, F.; De Guise, S. Immunomodulatory Effects of Domoic Acid Differ between in Vivo and in Vitro Exposure in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 636–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.; Joshi, D.; Draghi, A.; Gulland, F.M.; Jessup, D.; De Guise, S. Immunomodulatory Effects upon in Vitro Exposure of California Sea Lion and Southern Sea Otter Peripheral Blood Leukocytes to Domoic Acid. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkley, K.S.; Madl, J.E.; Duncan, C.; Gulland, F.M.; Tjalkens, R.B. Domoic Acid-Induced Seizures in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) Are Associated with Neuroinflammatory Brain Injury. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 156, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiolski, E.; Ito, S.; Beggs, J.; Lefebvre, K.; Litke, A.; Smith, D. Domoic Acid Disrupts the Activity and Connectivity of Neuronal Networks in Organotypic Brain Slice Cultures. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.C.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Ferreiro, S.F.; Castro, A.R.; Botana, L.M. Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats. Toxins 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, C.E.; Hiolski, E.M.; Marcinek, D.J.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Smith, D.R.; Zuo, Y. Repeated Low Level Domoic Acid Exposure Increases CA1 VGluT1 Levels, but Not Bouton Density, VGluT2 or VGAT Levels in the Hippocampus of Adult Mice. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madl, J.; Duncan, C.; Stanhill, J.; Tai, P.-Y.; Spraker, T.; Gulland, F. Oxidative Stress and Redistribution of Glutamine Synthetase in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2014, 150, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, C.; Hierlihy, S. Renal Clearance of Domoic Acid in the Rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, J.A.; Janech, M.G.; Dillon, J.C.; Bissler, J.J.; Siroky, B.J.; Bell, P.D. Characterization of Renal Toxicity in Mice Administered the Marine Biotoxin Domoic Acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maucher Fuquay, J.; Muha, N.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Elimination Kinetics of Domoic Acid from the Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid of the Pregnant Rat. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2805–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventoso, P.; Pazos, A.J.; Blanco, J.; Pérez-Parallé, M.L.; Triviño, J.C.; Sánchez, J.L. Transcriptional Response in the Digestive Gland of the King Scallop (Pecten maximus) after the Injection of Domoic Acid. Toxins 2021, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulland, F.M. Domoic Acid Toxicity in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) Stranded along the Central California Coast, May-October 1998: Report to the National Marine Fisheries Service Working Group on Unusual Marine Mammal Mortality Events; US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 1–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Yakes, B.J.; Frame, E.; Kendrick, P.; Shum, S.; Isoherranen, N.; Ferriss, B.E.; Robertson, A.; Hendrix, A.; Marcinek, D.J. Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor. Toxins 2019, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmaack, C.; Lahvis, G.P.; Keith, E.O.; Self-Sullivan, C. Diagnosing Domoic Acid Toxicosis in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) Using Behavioral Criteria: A Novel Approach. Zoo Biol. 2015, 34, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbacher, T.M.; Grant, K.S.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Crouthamel, B.; Stanley, C.; McKain, N.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N. Effects of Oral Domoic Acid Exposure on Maternal Reproduction and Infant Birth Characteristics in a Preclinical Nonhuman Primate Model. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 72, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargu, S.; Lefebvre, K.; Silver, M.W. Effect of Dissolved Domoic Acid on the Grazing Rate of Krill Euphausia pacifica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 312, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.S.; Razak, A.; Crawford, N. Age-Related Changes in Tolerance to the Marine Algal Excitotoxin Domoic Acid. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Frame, E.R.; Gulland, F.; Hansen, J.D.; Kendrick, P.S.; Beyer, R.P.; Bammler, T.K.; Farin, F.M.; Hiolski, E.M.; Smith, D.R. A Novel Antibody-Based Biomarker for Chronic Algal Toxin Exposure and Sub-Acute Neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.L.; Williams, C.; Li, J.-L.; MacDonald, J.W.; Bammler, T.K.; Richards, T.; English, C.N.; Baldessari, A.; Shum, S.; Jing, J. Prolonged, Low-Level Exposure to the Marine Toxin, Domoic Acid, and Measures of Neurotoxicity in Nonhuman Primates. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 097003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzillo, F.F.; Pomeroy, C.; Kuo, J.; Ramondi, P.T.; Prado, R.; Silver, M.W. Angler Exposure to Domoic Acid via Consumption of Contaminated Fishes. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Pauly, D.; Weatherdon, L.V.; Ota, Y. A Global Estimate of Seafood Consumption by Coastal Indigenous Peoples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.F.; Reichmuth, C.; Rouse, A.; Dennison, S.; Van Bonn, B.; Gulland, F. Natural Exposure to Domoic Acid Causes Behavioral Perseveration in Wild Sea Lions: Neural Underpinnings and Diagnostic Application. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 57, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.; Richards, T.; Crouthamel, B.; McKain, N.; Stanley, C.; Grant, K.S.; Shum, S.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N.; Burbacher, T.M. Chronic, Low-Level Oral Exposure to Marine Toxin, Domoic Acid, Alters Whole Brain Morphometry in Nonhuman Primates. Neurotoxicology 2019, 72, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, A.C.; VanDola, F.M.; Gulland, F.M.; Rowles, T.K.; Schwacke, L.H. Production and Toxicity of the Marine Biotoxin Domoic Acid and Its Effects on Wildlife: A Review. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2008, 14, 544–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvagni, P.A. Comparative Pathology and Diagnosis of Domoic Acid Toxicity. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Davis, CA, USA, 2003; 139p. ISBN 0-496-55169-8. [Google Scholar]
- Akmajian, A.M.; Scordino, J.J.; Acevedo-Gutiérrez, A. Year-Round Algal Toxin Exposure in Free-Ranging Sea Lions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 583, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.L.; St. Leger, J.; Inglis, B.A.; Michal, I.; Stedman, N.; Nollens, H.H.; Dennison-Gibby, S.; Herrick, K.; Clarke, E.O.; Mena, A. Twenty Years of Managed Epilepsy for a Stranded Male Guadalupe Fur Seal (Arctocephalus townsendi) Secondary to Suspect Domoic Acid Toxicosis. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agnese, E.; Lambourn, D.; Rice, J.; Duffield, D.; Huggins, J.; Spraker, T.; Raverty, S.; Kuzmina, T.; Grigg, M.E.; Wilkinson, K. Reemergence of Guadalupe Fur Seals in the US Pacific Northwest: The Epidemiology of Stranding Events during 2005–2016. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2020, 36, 828–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Robertson, A.; Frame, E.R.; Colegrove, K.M.; Nance, S.; Baugh, K.A.; Wiedenhoft, H.; Gulland, F.M. Clinical Signs and Histopathology Associated with Domoic Acid Poisoning in Northern Fur Seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and Comparison of Toxin Detection Methods. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHuron, E.A.; Greig, D.J.; Colegrove, K.M.; Fleetwood, M.; Spraker, T.R.; Gulland, F.M.; Harvey, J.T.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Frame, E.R. Domoic Acid Exposure and Associated Clinical Signs and Histopathology in Pacific Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina richardii). Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.-K.; Lacaze, J.-P.; Hermann, G.; Kershaw, J.; Brownlow, A.; Turner, A.; Hall, A. Detection and Effects of Harmful Algal Toxins in Scottish Harbour Seals and Potential Links to Population Decline. Toxicon 2015, 97, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.J.; Frame, E. Evidence of Domoic Acid Exposure in Harbour Seals from Scotland: A Potential Factor in the Decline in Abundance? Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, A.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Bryan, A.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Sheffield, G.; Wisswaesser, G.; Willis, M.L.; Bowers, E.K.; Kendrick, P. Ice Seals as Sentinels for Algal Toxin Presence in the Pacific Arctic and Subarctic Marine Ecosystems. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2021, 37, 1292–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, E.K.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Lefebvre, K.A. Stability of Domoic Acid in 50% Methanol Extracts and Raw Fecal Material from Bowhead Whales (Balaena mysticetus). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Twiner, M.J.; De Guise, S.; Balmer, B.C.; Wells, R.S.; Townsend, F.I.; Rotstein, D.C.; Varela, R.A.; Hansen, L.J.; Zolman, E.S. Eosinophilia and Biotoxin Exposure in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from a Coastal Area Impacted by Repeated Mortality Events. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twiner, M.J.; Flewelling, L.J.; Fire, S.E.; Bowen-Stevens, S.R.; Gaydos, J.K.; Johnson, C.K.; Landsberg, J.H.; Leighfield, T.A.; Mase-Guthrie, B.; Schwacke, L. Comparative Analysis of Three Brevetoxin-Associated Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Mortality Events in the Florida Panhandle Region (USA). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn-Watson, S.; Colegrove, K.M.; Litz, J.; Kinsel, M.; Terio, K.; Saliki, J.; Fire, S.; Carmichael, R.; Chevis, C.; Hatchett, W. Adrenal Gland and Lung Lesions in Gulf of Mexico Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Found Dead Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek-Huntington, K.A.; Dushane, J.L.; Goertz, C.E.; Romero, C.H.; Raverty, S.A. Morbidity and Mortality in Stranded Cook Inlet Beluga Whales (Delphinapterus leucas). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 114, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwald, K.M.; Gibble, C.M.; Miller, M.A.; Donnelly-Greenan, E.; Kudela, R.M. Investigation of a Mass Stranding Event Reveals a Novel Pattern of Cascading Comorbidities in Northern Fulmars (Fulmarus glacialis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2024, 60, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Silver, M.W.; Ohman, M.D.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Garrison, D.L. Mystery behind Hitchcock’s Birds. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, M.Z.; Beissinger, S.R.; Burkett, E.; Newman, S.H. Local Survival of Marbled Murrelets in Central California: Roles of Oceanographic Processes, Sex, and Radiotagging. J. Wildl. Manag. 2006, 70, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Dovel, S.L.; Silver, M.W. Tissue Distribution and Neurotoxic Effects of Domoic Acid in a Prominent Vector Species, the Northern Anchovy Engraulis mordax. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reizopoulou, S.; Strogyloudi, E.; Giannakourou, A.; Granéli, E.; Pagou, K. Toxin Accumulation in Benthic Populations under Blooms of Dinophysis acuminata and Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries. Mar. Drugs 2012, 121, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, K.B.; Lacaze, J.-P.; Machairopoulou, M.; Bresnan, E. Investigations into the Relationship between Domoic Acid and Copepods in Scottish Waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Solís, K.; García-Mendoza, E.; Sánchez-Serrano, S.; López, L.M. Domoic Acid Affects Brain Morphology and Causes Behavioral Alterations in Two Fish Species. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panlilio, J.M.; Hammar, K.M.; Aluru, N.; Hahn, M.E. Developmental Exposure to Domoic Acid Targets Reticulospinal Neurons and Leads to Aberrant Myelination in the Spinal Cord. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, P.; Reeves, C.; Casper, D.; Davis, C. Absence of Neurotoxic Effects in Leopard Sharks, Triakis semifasciata, Following Domoic Acid Exposure. Toxicon 2006, 47, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Zhu, R.; Gao, Y. Influences of Domoic Acid Exposure on Cardiac Development and the Expression of Cardiovascular Relative Genes in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.O.; Whyte, J.N.; Ginther, N.G.; Townsend, L.D.; Iwama, G.K. Haemocyte Changes in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea Gigas, Caused by Exposure to Domoic Acid in the Diatom Pseudonitzschia pungens F. multiseries. Toxicon 1995, 33, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.; Whyte, J.; Townsend, L.; Ginther, N.; Iwama, G. Effects of Domoic Acid on Haemolymph pH, PCO2 and PO2 in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas and the California Mussel, Mytilus californianus. Aquat. Toxicol. 1995, 31, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.; Andersen, R.; Harrison, P. Feeding Deterrent and Toxicity Effects of Apo-Fucoxanthinoids and Phycotoxins on a Marine Copepod (Tigriopus californicus). Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizer, H.; Fischer, B.; Harabawy, A.; Hennion, M.-C.; Hansen, P.-D. Toxicity of Domoic Acid in the Marine Mussel Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 55, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargu, S.; Marinovic, B.; Mansergh, S.; Silver, M.W. Feeding Responses of Krill to the Toxin-Producing Diatom Pseudo-nitzschia. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 284, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kelly, M.S.; Campbell, D.A.; Dong, S.L.; Zhu, J.X.; Wang, S.F. Exposure to Domoic Acid Affects Larval Development of King Scallop Pecten maximus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kelly, M.S.; Campbell, D.A.; Fang, J.; Zhu, J. Accumulation of Domoic Acid and Its Effect on Juvenile King Scallop Pecten maximus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquaculture 2008, 284, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammilehto, A.; Nielsen, T.G.; Krock, B.; Møller, E.F.; Lundholm, N. Calanus spp.—Vectors for the Biotoxin, Domoic Acid, in the Arctic Marine Ecosystem? Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harðardóttir, S.; Pančić, M.; Tammilehto, A.; Krock, B.; Møller, E.F.; Nielsen, T.G.; Lundholm, N. Dangerous Relations in the Arctic Marine Food Web: Interactions between Toxin Producing Pseudo-nitzschia Diatoms and Calanus Copepodites. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3809–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harðardóttir, S.; Krock, B.; Wohlrab, S.; John, U.; Nielsen, T.G.; Lundholm, N. Can Domoic Acid Affect Escape Response in Copepods? Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos, A.J.; Ventoso, P.; Martínez-Escauriaza, R.; Pérez-Parallé, M.L.; Blanco, J.; Triviño, J.C.; Sánchez, J.L. Transcriptional Response after Exposure to Domoic Acid-Producing Pseudo-nitzschia in the Digestive Gland of the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2017, 140, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X. Effects of Marine Toxin Domoic Acid on Innate Immune Responses in Bay Scallop Argopecten irradians. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.A.; Choi, C.Y.; Park, H.-S. Exposure to Domoic Acid Causes Oxidative Stress in Bay Scallops Argopecten irradians. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventoso, P.; Pazos, A.J.; Pérez-Parallé, M.L.; Blanco, J.; Triviño, J.C.; Sánchez, J.L. RNA-Seq Transcriptome Profiling of the Queen Scallop (Aequipecten opercularis) Digestive Gland after Exposure to Domoic Acid-Producing Pseudo-nitzschia. Toxins 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Faustman, E.M.; Grattan, L. Domoic Acid: Neurobehavioral Consequences of Exposure to a Prevalent Marine Biotoxin. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakshinamurti, K.; Sharma, S.; Sundaram, M.; Watanabe, T. Hippocampal Changes in Developing Postnatal Mice Following Intrauterine Exposure to Domoic Acid. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsdell, J.S.; Zabka, T.S. In Utero Domoic Acid Toxicity: A Fetal Basis to Adult Disease in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus). Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 262–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, K.S.; Crouthamel, B.; Kenney, C.; McKain, N.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N.; Burbacher, T.M. Preclinical Modeling of Exposure to a Global Marine Bio-Contaminant: Effects of in Utero Domoic Acid Exposure on Neonatal Behavior and Infant Memory. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcoitia, I.; Sierra, A.; Veiga, S.; Honda, S.; Harada, N.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Brain Aromatase Is Neuroprotective. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 47, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, R.L.; Lewy, A.J.; Erb, D.L.; Vollmer, W.M.; Singer, C.M. Human Melatonin Production Decreases with Age. J. Pineal Res. 1986, 3, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, A.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Bowers, E.K.; Stuppard, R.; Burbacher, T.; Marcinek, D.J. Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model. Toxins 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedeken, J.A.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Ramsdell, A.F. Developmental Toxicity of Domoic Acid in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Kendrick, P.S.; Ladiges, W.; Hiolski, E.M.; Ferriss, B.E.; Smith, D.R.; Marcinek, D.J. Chronic Low-Level Exposure to the Common Seafood Toxin Domoic Acid Causes Cognitive Deficits in Mice. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, T.; Zabka, T.S.; DeLong, R.L.; Wheeler, E.A.; Ylitalo, G.; Bargu, S.; Silver, M.; Leighfield, T.; Dolah, F.V.; Langlois, G. The Role of Domoic Acid in Abortion and Premature Parturition of California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) on San Miguel Island, California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallet, A.; Binienda, Z.; Caputo, F.; Hall, S.; Paule, M.; Rountree, R.; Schmued, L.; Sobotka, T.; Slikker Jr, W. Domoic Acid-Treated Cynomolgus Monkeys (M. fascicularis): Effects of Dose on Hippocampal Neuronal and Terminal Degeneration. Brain Res. 1993, 627, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truelove, J.; Mueller, R.; Pulido, O.; Iverson, F. Subchronic Toxicity Study of Domoic Acid in the Rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1996, 34, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montie, E.W.; Wheeler, E.; Pussini, N.; Battey, T.W.; Van Bonn, W.; Gulland, F. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals That Brain Atrophy Is More Severe in Older California Sea Lions with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, M.E.; Tinker, M.T.; Miller, M.A.; Tomoleoni, J.A.; Staedler, M.M.; Fujii, J.A.; Batac, F.I.; Dodd, E.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Zubkousky-White, V. Exposure to Domoic Acid Is an Ecological Driver of Cardiac Disease in Southern Sea Otters. Harmful Algae 2021, 101, 101973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Hernandez-Camacho, C.J.; Álvarez-Santamaría, L.; Paniagua-Mendoza, A.; Robles-Hernandez, R.; Rebolledo-Villa, F.; Rosales-Nanduca, H.; Ramos-Rodriguez, A.; Acevedo-Whitehouse, K. Largest Mortality Event to Date of California Sea Lions in Mexico Might Be Linked to a Harmful Algal Bloom. Aquat. Mamm. 2022, 48, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, D.J.; Gulland, F.M.; Kreuder, C. A Decade of Live California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) Strandings along the Central California Coast: Causes and Trends, 1991–2000. Aquat. Mamm. 2005, 31, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, A.L.; Ryan, C.L.; Doucette, T.A. Neonatal Domoic Acid Treatment Produces Alterations to Prepulse Inhibition and Latent Inhibition in Adult Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuloaga, D.; Lahvis, G.; Mills, B.; Pearce, H.; Turner, J.; Raber, J. Fetal Domoic Acid Exposure Affects Lateral Amygdala Neurons, Diminishes Social Investigation and Alters Sensory-Motor Gating. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.G. Gender Differences in the Renal Toxicity of the Neurotoxin Domoic Acid Griffin Thompson, Hernan Grenett, Lan He, Noor Alsirafi, Amanda Hanninen, and P. Darwin Bell University of Alabama Birmingham, and Birmingham VA, Birmingham, AL. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1030.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.W.; Rushton, S.P.; Rens, N.; Morris, C.M.; Blain, P.G.; Judge, S.J. Sex Differences in Effects of Low Level Domoic Acid Exposure. Neurotoxicology 2013, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucette, T.A.; Ryan, C.L.; Tasker, R. Gender-Based Changes in Cognition and Emotionality in a New Rat Model of Epilepsy. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.L.; Robbins, M.A.; Smith, M.T.; Gallant, I.C.; Adams-Marriott, A.L.; Doucette, T.A. Altered Social Interaction in Adult Rats Following Neonatal Treatment with Domoic Acid. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 102, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, D.A.; Perry, M.A.; McGuire, E.P.; Pérez-Gómez, A.; Tasker, R.A. Low-Dose Neonatal Domoic Acid Causes Persistent Changes in Behavioural and Molecular Indicators of Stress Response in Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 230, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, B.D.; Pearce, H.L.; Khan, O.; Jarrett, B.R.; Fair, D.A.; Lahvis, G.P. Prenatal Domoic Acid Exposure Disrupts Mouse Pro-Social Behavior and Functional Connectivity MRI. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 308, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, J.S.; Zatorre, R.J.; Carpenter, S.; Gendron, D.; Evans, A.C.; Gjedde, A.; Cashman, N.R. Neurologic Sequelae of Domoic Acid Intoxication Due to the Ingestion of Contaminated Mussels. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, G.; Bates, S.; Spallino, J. Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning: Emergency Medical Management. J. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuder, C.; Miller, M.A.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Conrad, P.A.; Carpenter, T.E.; Jessup, D.A.; Mazet, J.A. Evaluation of Cardiac Lesions and Risk Factors Associated with Myocarditis and Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrove, K.; Gulland, F.; Harr, K.; Naydan, D.; Lowenstine, L. Pathological Features of Amyloidosis in Stranded California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.L.; Gulland, F.M.; Johnson, S.P.; Simeone, C.A.; Whoriskey, S.T. Seal and Sea Lion Medicine. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 909–934. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, S.; Lynch, D.; Thomas, N. Leptospirosis in Northern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris kenyoni) from Washington, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshavsky, J.; Smith, A.; Wang, A.; Hom, E.; Izano, M.; Huang, H.; Padula, A.; Woodruff, T.J. Heightened Susceptibility: A Review of How Pregnancy and Chemical Exposures Influence Maternal Health. Reprod. Toxicol. 2020, 92, 14–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadwater, M.H.; Van Dolah, F.M.; Fire, S.E. Vulnerabilities of Marine Mammals to Harmful Algal Blooms. In Harmful Algal Blooms: A Compendium Desk Reference; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Bargu, S.; Silver, M.; Goldstein, T.; Roberts, K.; Gulland, F. Complexity of Domoic Acid-Related Sea Lion Strandings in Monterey Bay, California: Foraging Patterns, Climate Events, and Toxic Blooms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 418, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, L.M.; Holobaugh, S.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Harmful Algal Blooms and Public Health. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, L.M.; Kaddis, L.; Tracy, J.K.; Morris, J.G. Long Term Memory Outcome of Repetitive, Low-Level Dietary Exposure to Domoic Acid in Native Americans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.; Bastlund, J.; Watson, W.; Ryan, C.; Reynolds, D.; Tasker, R. Neonatal Exposure to Low-Dose Domoic Acid Lowers Seizure Threshold in Adult Rats. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, A.M.; Field, C.L.; Norris, T.A.; Borremans, B.; Duignan, P.J.; Johnson, S.P.; Whoriskey, S.T.; Thompson-Barbosa, L.; Gulland, F.M. The Symptomatology and Diagnosis of Domoic Acid Toxicosis in Stranded California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus): A Review and Evaluation of 20 Years of Cases to Guide Prognosis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1245864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santora, J.A.; Mantua, N.J.; Schroeder, I.D.; Field, J.C.; Hazen, E.L.; Bograd, S.J.; Sydeman, W.J.; Wells, B.K.; Calambokidis, J.; Saez, L. Habitat Compression and Ecosystem Shifts as Potential Links between Marine Heatwave and Record Whale Entanglements. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauquier, D.; Landsberg, J. Harmful Algae and Biotoxins. In CRC handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, K.A.; Villac, M.C.; Chadwick, C.; DeSmidt, A.A.; Flewelling, L.; Granholm, A.; Joseph, M.; Wood, T.; Fachon, E.; Brosnahan, M.L. Spatiotemporal Transitions in Pseudo-nitzschia Species Assemblages and Domoic Acid along the Alaska Coast. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shum, S.; Kirkwood, J.S.; Jing, J.; Petroff, R.; Crouthamel, B.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Nelson, W.L.; Isoherranen, N. Validated HPLC-MS/MS Method to Quantify Low Levels of Domoic Acid in Plasma and Urine after Subacute Exposure. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12079–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Soliño, L.; Bravo, I.; Rodríguez, F.; Casero, M.V. Paralytic and Amnesic Shellfish Toxins Impacts on Seabirds, Analyses and Management. Toxins 2021, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frame, E.R.; Lefebvre, K.A. ELISA Methods for Domoic Acid Quantification in Multiple Marine Mammal Species and Sample Matrices; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NWFSC-122; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; 20p. [Google Scholar]
- Seubert, E.L.; Howard, M.D.; Kudela, R.M.; Stewart, T.N.; Litaker, R.W.; Evans, R.; Caron, D.A. Development, Comparison, and Validation Using ELISAs for the Determination of Domoic Acid in California Sea Lion Body Fluids. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulland, F.M.; Hall, A.J.; Greig, D.J.; Frame, E.R.; Colegrove, K.M.; Booth, R.K.; Wasser, S.K.; Scott-Moncrieff, J.C.R. Evaluation of Circulating Eosinophil Count and Adrenal Gland Function in California Sea Lions Naturally Exposed to Domoic Acid. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 241, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.M. Clinical Values of Blood Variables in Wild and Stranded California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) and Blood Sample Storage Stability. Master’s Thesis, California State University Monterey Bay and Moss Landing Marine Laboratories, Moss Landing, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, V.C.; Fernández Ajó, A.; Degrati, M.; Krock, B.; Hunt, K.E.; Uhart, M.M.; Buck, C.L. Potential Endocrine Correlation with Exposure to Domoic Acid in Southern Right Whale (Eubalaena australis) at the Península Valdés Breeding Ground. Oecologia 2022, 198, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arufe, M.; Arias, B.; Duran, R.; Alfonso, M. Effects of Domoic Acid on Serum Levels of TSH and Thyroid Hormones. Endocr. Res. 1995, 21, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, M.; Duran, R.; Arufe, M. Effect of Excitatory Amino Acids on Serum TSH and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Freely Moving Rats. Horm. Res. 2000, 54, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, L.; Knowles, S.; Lefebvre, K.; St. Martin, M.; Murray, M.; Kloecker, K.; Monson, D.; Weitzman, B.; Ballachey, B.; Coletti, H. Divergent Gene Expression Profiles in Alaskan Sea Otters: An Indicator of Chronic Domoic Acid Exposure? Oceans 2022, 3, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joblon, M.J.; Flower, J.E.; Thompson, L.A.; Biddle, K.E.; Burt, D.A.; Zabka, T.S.; Adkesson, M.J.; Halaska, B.; Goertz, C.E.; Rouse, N. Investigation of the Use of Serum Biomarkers for the Detection of Cardiac Disease in Marine Mammals. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2022, 53, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, M.E.; Miller, M.A.; Murray, M.J.; Duignan, P.J.; Gunther-Harrington, C.T.; Field, C.L.; Adams, L.M.; Schmitt, T.L.; Johnson, C.K. Exploration of Serum Cardiac Troponin I as a Biomarker of Cardiomyopathy in Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 82, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther-Harrington, C.T.; Moriarty, M.E.; Field, C.L.; Adams, L.M.; Johnson, C.K.; Murray, M.J. Transthoracic Echocardiographic Evaluation and Serum Cardiac Troponin Values in Anesthetized Healthy Female Southern Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2021, 52, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.C.; Haulena, M.; Dennison, S.; Waugh, L.; Goldstein, T.; Nutter, F.; Bonn, B.V.; Hoard, V.; Laxer, K.D.; Buckmaster, P.S. Pinniped Electroencephalography: Methodology and Findings in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1040125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yonemasu, Y.; Cendes, F.; Cashman, N.R.; Andermann, F. Electroclinical and Pathological Studies after Parenteral Administration of Domoic Acid in Freely Moving Nonanesthetized Rats: An Animal Model of Excitotoxicity. J. Epilepsy 1996, 9, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.; Murias, M.; Grant, K.; Crouthamel, B.; McKain, N.; Shum, S.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N.; Burbacher, T. Power Spectrum Analysis of EEG in a Translational Nonhuman Primate Model after Chronic Exposure to Low Levels of the Common Marine Neurotoxin, Domoic Acid. Neurotoxicology 2020, 80, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjedde, A.; Evans, A. PET Studies of Domoic Acid Poisoning in Humans: Excitotoxic Destruction of Brain Glutamatergic Pathways, Revealed in Measurements of Glucose Metabolism by Positron Emission Tomography. Can. Dis. Wkly. Rep.=Rapp. Hebd. Des Mal. Au Can. 1990, 16, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.F.; Reichmuth, C.; Rouse, A.A.; Libby, L.A.; Dennison, S.E.; Carmichael, O.T.; Kruse-Elliott, K.T.; Bloom, J.; Singh, B.; Fravel, V.A. Algal Toxin Impairs Sea Lion Memory and Hippocampal Connectivity, with Implications for Strandings. Science 2015, 350, 1545–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krucik, D.D.; Cook, P.; Cathey, M.; Meegan, J.M.; Gomez, F.M.; Van Bonn, W.; Le-Bert, C. Adult-Onset Epilepsy and Hippocampal Pathology in a California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus): A Case Study of Suspected in Utero Exposure to Domoic Acid. Neurotoxicology 2023, 96, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, P.F.; Berns, G.S.; Colegrove, K.; Johnson, S.; Gulland, F. Postmortem DTI Reveals Altered Hippocampal Connectivity in Wild Sea Lions Diagnosed with Chronic Toxicosis from Algal Exposure. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.; Harvey, J.T.; Goldstein, T.; Barakos, J.; Gulland, F. Movement, Dive Behavior, and Survival of California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) Posttreatment for Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2010, 26, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorre, R. Memory Loss Following Domoic Acid Intoxication from Ingestion of Toxic Mussels. Can. Dis. Wkly. Rep.=Rapp. Hebd. Des Mal. Au Can. 1990, 16, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.; Reichmuth, C.; Gulland, F. Rapid Behavioural Diagnosis of Domoic Acid Toxicosis in California Sea Lions. Biol. Lett. 2011, 7, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, L.M.; Cook, P.F.; Reichmuth, C.; Gulland, F.M. The Evaluation of Olfaction in Stranded California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) and Its Relevance to Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Potvin, J.L. Neural and Behavioural Effects of Domoic Acid, an Amnesic Shellfish Toxin, in the Rat. Can. J. Psychol./Rev. Can. De Psychol. 1992, 46, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Pinsky, C.; Standish, N.; Bose, R.; Glavin, G. Parenteral Domoic Acid Impairs Spatial Learning in Mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1992, 41, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobotka, T.; Brown, R.; Quander, D.; Jackson, R.; Smith, M.; Long, S.; Barton, C.; Rountree, R.; Hall, S.; Eilers, P. Domoic Acid: Neurobehavioral and Neurohistological Effects of Low-Dose Exposure in Adult Rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1996, 18, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiotani, M.; Cole, T.B.; Hong, S.; Park, J.J.Y.; Griffith, W.C.; Burbacher, T.M.; Workman, T.; Costa, L.G.; Faustman, E.M. Neurobehavioral Assessment of Mice Following Repeated Oral Exposures to Domoic Acid during Prenatal Development. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 64, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panlilio, J.M.; Aluru, N.; Hahn, M.E. Developmental Neurotoxicity of the Harmful Algal Bloom Toxin Domoic Acid: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Altered Behavior in the Zebrafish Model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallet, A.C.; Schmued, L.C.; Johannessen, J.N. Neurohistochemical Biomarkers of the Marine Neurotoxicant, Domoic Acid. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.; Hoesing, J.; Whishaw, I. Domoic Acid, an Environmental Toxin, Produces Hippocampal Damage and Severe Memory Impairment. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 120, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckmaster, P.S.; Wen, X.; Toyoda, I.; Gulland, F.M.; Van Bonn, W. Hippocampal Neuropathology of Domoic Acid–Induced Epilepsy in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 1691–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryphonas, L.; Truelove, J.; Iverson, F. Acute Parenteral Neurotoxicity of Domoic Acid in Cynomolgus Monkeys (M. fascicularis). Toxicol. Pathol. 1990, 18, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossart, G.D. Marine Mammals as Sentinel Species for Oceans and Human Health. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, B.A.; Soper, J.L.; Gulland, F.M.; Bell, P.D.; Kindy, M.; Arthur, J.M.; Janech, M.G. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) with Domoic Acid Toxicosis Identifies Proteins Associated with Neurodegeneration. Proteomics 2015, 15, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, A.; Ryan, J.C.; Chapman, R.W.; Wu, Q.; Warr, G.W.; Gulland, F.M.; Van Dolah, F.M. Health Status, Infection and Disease in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) Studied Using a Canine Microarray Platform and Machine-Learning Approaches. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiolski, E.M.; Kendrick, P.S.; Frame, E.R.; Myers, M.S.; Bammler, T.K.; Beyer, R.P.; Farin, F.M.; Wilkerson, H.; Smith, D.R.; Marcinek, D.J. Chronic Low-Level Domoic Acid Exposure Alters Gene Transcription and Impairs Mitochondrial Function in the CNS. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, B.A.; Ferrante, J.A.; Chaves, J.M.; Soper, J.L.; Almeida, J.S.; Arthur, J.M.; Gulland, F.M.; Janech, M.G. Proteomic Analysis of Plasma from California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) Reveals Apolipoprotein E as a Candidate Biomarker of Chronic Domoic Acid Toxicosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Tilton, S.C.; Bammler, T.K.; Beyer, R.P.; Srinouanprachan, S.; Stapleton, P.L.; Farin, F.M.; Gallagher, E.P. Gene Expression Profiles in Zebrafish Brain after Acute Exposure to Domoic Acid at Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Doses. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 107, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, B.A.; Soper, J.L.; Greig, D.J.; Carlin, K.P.; Favre, E.G.; Gulland, F.M.; Almeida, J.S.; Janech, M.G. Serum Profiling by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry as a Diagnostic Tool for Domoic Acid Toxicosis in California Sea Lions. Proteome Sci. 2012, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Morey, J.; Ramsdell, J.; Van Dolah, F. Acute Phase Gene Expression in Mice Exposed to the Marine Neurotoxin Domoic Acid. Neuroscience 2005, 136, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, S.; Delcourt, N. Marine Neurotoxins’ Effects on Environmental and Human Health: An OMICS Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, A.S.; Lefebvre, K.A.; MacDonald, J.; Bammler, T.; Aluru, N. Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Domoic Acid Exposure in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Revealed Distinct Non-Overlapping Gene Expression Patterns in the Brain. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 252, 106310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G. Identification of Candidate Protein Biomarkers Associated with Domoic Acid Toxicosis in Cerebrospinal Fluid of California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, C.A.; Scott, G.; Navarro, R.A.; Procter, D. Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Oceans 2022, 3, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, C.A.; Andrews, J.P.; Johnson, S.P.; Casalia, M.; Kochanski, R.; Chang, E.F.; Cameron, D.; Dennison, S.; Inglis, B.; Scott, G. Xenotransplantation of Porcine Progenitor Cells in an Epileptic California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus): Illustrative Case. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, C.A.; Stoskopf, M.K. Pharmaceuticals and Formularies. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 607–674. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, J. BSAVA Small Animal Formulary. Part B: Exotic Pets; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 1-910443-71-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dakshinamurti, K.; Sharma, S.; Geiger, J.D. Neuroprotective Actions of Pyridoxine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2003, 1647, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M. Troxerutin Counteracts Domoic Acid–Induced Memory Deficits in Mice by Inhibiting CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein β–Mediated Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3466–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M. Ursolic Acid Improves Domoic Acid-Induced Cognitive Deficits in Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 271, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananth, C.; Dheen, S.T.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Kaur, C. Distribution of NADPH-diaphorase and Expression of nNOS, N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor (NMDAR1) and non-NMDA Glutamate Receptor (GlutR2) Genes in the Neurons of the Hippocampus after Domoic Acid-induced Lesions in Adult Rats. Hippocampus 2003, 13, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z. Purple Sweet Potato Color Attenuates Domoic Acid-Induced Cognitive Deficits by Promoting Estrogen Receptor-α-Mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis Signaling in Mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, G.; White, C.C.; Mohar, I.; Kavanagh, T.J.; Costa, L.G. Glutathione Levels Modulate Domoic Acid–Induced Apoptosis in Mouse Cerebellar Granule Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 100, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, G. Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid on Caenorhabditis elegans and the Underlying Mechanism. Int. J. Biol. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golechha, M.; Chaudhry, U.; Bhatia, J.; Saluja, D.; Arya, D.S. Naringin Protects against Kainic Acid-Induced Status Epilepticus in Rats: Evidence for an Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Intervention. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.F.; Hou, C.-W.; Yao, P.-W.; Wu, S.-P.; Peng, Y.-F.; Shen, M.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Chang, M.-H.; Jeng, K.-C. Sesamin Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Mortality in Kainic Acid-Induced Status Epilepticus by Inhibition of MAPK and COX-2 Activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsky, C.; Giavim, G.B.; Bose, R. Kynurenic Acid Protects against Neurotoxicity and Lethality of Toxic Extracts from Contaminated Atlantic Coast Mussels. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavin, G.B.; Pinsky, C. Kynurenic Acid Attenuates Experimental Ulcer Formation and Basal Gastric Acid Secretion in Rats. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1989, 64, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glavin, G.B.; Bose, R.; Pinsky, C. Kynurenic Acid Protects against Gastroduodenal Ulceration in Mice Injected with Extracts from Poisonous Atlantic Shellfish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavin, G.B.; Pinsky, C.; Bose, R. Domoic Acid-Induced Neuro Visceral Toxic Syndrome: Characterization of an Animal Model and Putative Antidotes. Brain Res. Bull. 1990, 24, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M. Small Interfering RNA–Mediated Knockdown of Protein Kinase C Zeta Attenuates Domoic Acid–Induced Cognitive Deficits in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 128, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Dakshinamurti, K. Suppression of Domoic Acid Induced Seizures by 8-(OH)-DPAT. J. Neural Transm./Gen. Sect. JNT 1993, 93, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.L.; Whoriskey, S.T.; Zhao, X.; Papich, M.G. Pharmacokinetics of Subcutaneous Alpha Lipoic Acid, a Proposed Therapeutic Aid for Domoic Acid Intoxication in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2021, 52, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Duignan, P.; Martinez, M.; Papich, M.G.; Field, C. Meloxicam-Associated Nephrotoxicity in Three Adult Female California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) in Treatment for Domoic Acid Toxicosis. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Conference of the International Association of Aquatic Animal Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 20–24 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Simeone, C.; Fauquier, D.; Skidmore, J.; Cook, P.; Colegrove, K.; Gulland, F.; Dennison, S.; Rowles, T.K. Clinical Signs and Mortality of Non-released Stranded California Sea Lions Housed in Display Facilities: The Suspected Role of Prior Exposure to Algal Toxins. Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Tabor, G.M. Introduction: Marine Vertebrates as Sentinels of Marine Ecosystem Health. EcoHealth 2004, 1, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H.L.; Hansen, L.J.; Sweeney, J.C.; Townsend, F.I.; Stone, R.; Casper, D.R.; Scott, M.D.; Hohn, A.A.; Rowles, T.K. Bottlenose Dolphins as Marine Ecosystem Sentinels: Developing a Health Monitoring System. EcoHealth 2004, 1, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.; Scheuhammer, A.M.; Bursian, S.J.; Elliott, J.; Rouvinen-Watt, K.; Chan, H.M. Mink as a Sentinel Species in Environmental Health. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.E. Marine Mammals as Ecosystem Sentinels. J. Mammal. 2008, 89, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, E.L.; Abrahms, B.; Brodie, S.; Carroll, G.; Jacox, M.G.; Savoca, M.S.; Scales, K.L.; Sydeman, W.J.; Bograd, S.J. Marine Top Predators as Climate and Ecosystem Sentinels. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 17, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Cram, J.A.; Berndt, M.P.; Hoard, V.; Shultz, D.; Deming, A.C. Quantifying the linkages between California sea lion (Zalophus californianus) strandings and particulate domoic acid concentrations at piers across Southern California. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1278293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Prabhakar, M.; Kumar, P.; Deshmukh, R.; Sharma, P. Excitotoxicity: Bridge to Various Triggers in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I. Environmental Risk Factors for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy–Is Prenatal Exposure to the Marine Algal Neurotoxin Domoic Acid a Potentially Preventable Cause? Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A. Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Kidney Damage and Possible Mechanisms: A Mini-Review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahvis, G.P. What California Sea Lions Exposed to Domoic Acid Might Teach Us about Autism: Lessons for Predictive and Preventive Medicine. EPMA J. 2017, 8, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Shangloo, P.; Gupte, B.; Gupta, S. Effect Of AJI-NO-MOTO On Kidney Of Adult Albino Rat: A Histopathological Evaluation. Perspect. Med. Res. 2022, 10, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwubiko, G.N.; Nwankwo, N.E.; Egbuonu, A.C.C.; Soribe, B.A.; Okeke, E.S.; Eze, C.J. Amelioration of High Levels of Serum Kidney Function Biomarkers by Vernonia Amygdalina in Monosodium Glutamate Induced Rats. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. (IJNPR)[Former. Nat. Prod. Radiance (NPR)] 2022, 13, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, D.A.; Ramsay, S.L.; Tasker, R.A. Selective Reductions in Subpopulations of GABAergic Neurons in a Developmental Rat Model of Epilepsy. Brain Res. 2010, 1331, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | Exposure | Population-Level | Individual-Level | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinnipeds | ||||
| California sea lion (Zalophus californianus) | C | C | C | [40,93] |
| Stellar sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus) | C | - | S | [9,136] |
|
Guadalupe fur seal (Arctocephalus townsendi) | C | S | C | [137,138] |
| South American sea lion (Otaria byronia) | C | - | - | [10] |
| Peruvian fur seal (Arctocephalus australis) | C | - | - | [10] |
| Northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus) | C | C | C | [9,139] |
| Harbor seal – Pacific, Scottish (Phoca vitulina) | C, C | -, S | C, S | [9,95,140,141,142] |
| Ringed seal (Phoca hispida) | C | - | - | [9,143] |
| Bearded seal (Erignathus barbatus) | C | - | - | [9,143] |
| Spotted seal (Phoca largha) | C | - | - | [9,143] |
| Ribbon seal (Histriophoca fasciata) | C | - | - | [9,143] |
| Pacific walrus (Odobenus rosmarus) | C | - | - | [9] |
| Fissipeds | ||||
| Sea otter— Southern, Northern (Enhydra lutra) | C, C | C, - | C, - | [9,41,42] |
| Cetaceans | ||||
| Bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) | C | - | - | [9,144] |
| Right whale- Northern, Southern (Eubalaena glacialis, australis) | C, C | S, S | -,- | [46,47,50] |
| Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus) | C | - | - | [9,44] |
| Pygmy sperm whale (Kogia breviceps) | C | - | - | [45] |
| Dwarf sperm whale (Kogia sima) | C | - | - | [45] |
| Long-beaked common dolphin (Delphinus capensis) | C | - | C | [11,43] |
| Short-beaked common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) | C | - | C | [11,43] |
| Bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) | C | - | C | [8,11,43,67,145,146,147] |
| Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) | C | - | - | [11,43] |
| Harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) | C | - | C | [9,11,95] |
| Dall’s porpoise (Phocoenoides dalli) | C | - | - | [11] |
| Minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) | C | - | C | [11,89] |
| Humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) | C | - | - | [9,11,43,44] |
| Cuvier’s beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris) | C | - | - | [11,43] |
| Gray whale (Eschrichtius robustus) | C | - | S | [11,43] |
| Fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus) | C | - | - | [11] |
| Northern right whale dolphin (Lissodelphis borealis) | C | - | - | [11] |
| Pacific white sided dolphin (Lagenorhyncus obliquidens) | C | - | - | [11] |
| Beluga whale (Delphinapterus leucas) | C | - | - | [9,148] |
|
Long-finned pilot whale (Globicephala macrocephalus) | S | S | S | [49] |
| Seabirds | ||||
| Brandt’s cormorant (Phalacrocorax penicillatus) | C | S | C | [34,39] |
|
Brown pelican (Pelecanus occidentalis) | C | S | C | [34,35,39] |
| Clark’s grebe (Aechmophorus clarkii) | C | - | C | [39] |
| Pacific loon (Gavia pacifica) | C | - | C | [39] |
| Red-throated loon (Gavia stellata) | C | - | C | [39] |
| Surf scoter (Melanitta perspicillata) | C | - | S | [39] |
| Common murre (Uria aalge) | C | - | C | [39,149] |
| White-winged scoter (Melanitta deglandi) | C | - | S | [39] |
| Double-crested cormorant (Phalacrocorax auratus) | C | - | C | [39] |
|
Ring-billed gull (Larus delawarensis) | C | - | S | [39] |
|
Cassin’s auklet (Ptychoramphus aleuticus) | C | - | C | [39,149] |
|
Northern fulmar (Fulmarus glacialis) | C | - | S | [39,149] |
| Sooty shearwater (Puffinus griseus) | S | - | S | [150] |
| Marbled murrelet (Brachyramphus marmoratus) | C | S | C | [151] |
| Marine Reptiles | ||||
| Green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas) | C | - | S | [52,54] |
| Leatherback sea turtle (Dermochelys coriacea) | C | - | S | [53] |
| Blood Variable | Anomaly | Species | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | |||
| Red Blood Cell (RBC) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| White Blood Cell (WBC) | ↑ | H, BND, CSL, GFS | [26,67,137,145,197,218] |
| Hemoglobin (HGB) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Platelet (PLT) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| Neutrophils | ↑ | CSL | [141,218] |
| Lymphocytes | ↓ | HS | [141] |
| Monocytes | ↑ | HS | [141] |
| Eosinophils | ↑ | CSL, BND | [67,145,209,217] |
| Hematocrit (HCT) | ↑ | CSL, GFS | [40,137,209] |
| Serum Biochemistry | |||
| Serum Creatinine (sCr) | ↑ or ↓ | H, GFS, CSL | [26,137,197,218] |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) | ↑ or ↓ | H, SB, CSL, GFS, CSL | [26,34,40,137,197,218] |
| Uric Acid (UA) | ↑ | SB | [34] |
| Creatine Kinase (CK)/ Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) | ↑ | H, SB, CSL | [26,34,40,197] |
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| Alanine transaminase (ALT) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| Cholesterol (CHOL) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Glucose (GLU) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Total Bilirubin (TBili) | ↑ | CSL | [218] |
| Phosphorous (PHOS) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Total Iron (TIRON) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Calium (Ca2+) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Sodium (Na+) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Albumin (ALB) | ↓ | CSL | [218] |
| Total Protein (TP) | ↑ | GFS | [137] |
| Method | Species | Matrix | Findings | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene microarray | CSL | Whole blood | Discriminated CSLs with DA toxicosis vs. other illnesses; Identified upregulation of inflammatory mediators and TNFAIP6 as a candidate biomarker of DA toxicosis | [248] |
| Peptidomics (MALDI-TOF with artificial neural networks) | CSL | Serum | This method can be a sensitive or specific diagnostic test for acute DA toxicosis | [252] |
| Proteomics (2D-GE/MS) | CSL | Plasma | Apolipoprotein E is a sensitive, but not specific biomarker of chronic DA toxicosis | [250] |
| Shotgun proteomics (LC-MS/MS) | CSL | CSF | Identified candidate biomarkers of DA toxicosis, as well as molecular mechanisms for neurodegeneration | [247] |
| Proteomics (MS) | CSL | CSF | Identified candidate biomarkers to diagnose and differentiate acute vs. chronic DA toxicosis | [256] |
| Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | NSO | Whole blood | Evidence of persistent, low-level DA exposure to Kachemak Bay, Alaska sea otters; Noted differences in neurologic, cardiac, immune, and detoxification function gene expression in DA exposed vs. reference population | [222] |
| Immuno-histochemistry (IHC) + PCR | CSL | Heart | Pathway of DA-induced cardiac damage may involve direct activation of local GluRs and apoptosis | [100,104] |
| Immuno-fluorescence (IF) | CSL | Brain | Fluoro-jade staining did not identify ischemic neuronal degeneration per-acutely before standard HE staining | [101] |
| Immuno-fluorescence (IF) | CSL | Hippocampus | Correlated increased oxidative stress and glial activation with disease severity and glial activation and nitric oxide with the development of chronic toxicosis; Gliosis and alterations in glutamine synthetase may be part of mechanism for DA-induced seizures | [113] |
| Immuno-histochemistry (IHC) | CSL | Hippocampus | Oxidative stress is involved in acute and chronic DA toxicosis, whereas glutamine synthetase redistribution is only involved in chronic toxicosis | [117] |
| Immuno-cytochemistry (ICC) | CSL | Hippocampus | Supported similarity between human temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) and chronic toxicosis | [244] |
| Acute DA Toxicosis | Chronic DA Toxicosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Brain histopathology | None-hippocampal necrosis +/− involvement of other limbic system regions | Hippocampal atrophy +/− gliosis +/− involvement of other limbic system regions |
| Clinical signs | Ataxia, head weaving, seizures, tremors, coma, decreased responsiveness to stimuli, scratching behavior +/− good BCS | Intermittent seizures, episodic lethargy and inappetence, vomiting, central blindness, abnormal behaviors (stereotypic scratching, conspecific or human-directed aggression) +/− poor BCS |
| Case history | Strand in clusters (≥5 individuals within 48 h and 80 km) concurrent with a DA-producing bloom | Strand individually, possibly in an atypical location without a concurrent DA-producing bloom +/− previous treatment for acute toxicosis |
| DA levels | Not detectable-detectable | Not detectable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krasner, A.E.; Martinez, M.E.; Field, C.L.; Fire, S.E. The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020061
Krasner AE, Martinez ME, Field CL, Fire SE. The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrasner, Ami E., Margaret E. Martinez, Cara L. Field, and Spencer E. Fire. 2025. "The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife" Marine Drugs 23, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020061
APA StyleKrasner, A. E., Martinez, M. E., Field, C. L., & Fire, S. E. (2025). The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife. Marine Drugs, 23(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020061







