Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Amino Acid Analysis of ACE Inhibitory Peptides with Different Molecular Weights (MWs)
2.2. ACE Inhibitory Activity with Different Molecular Weights
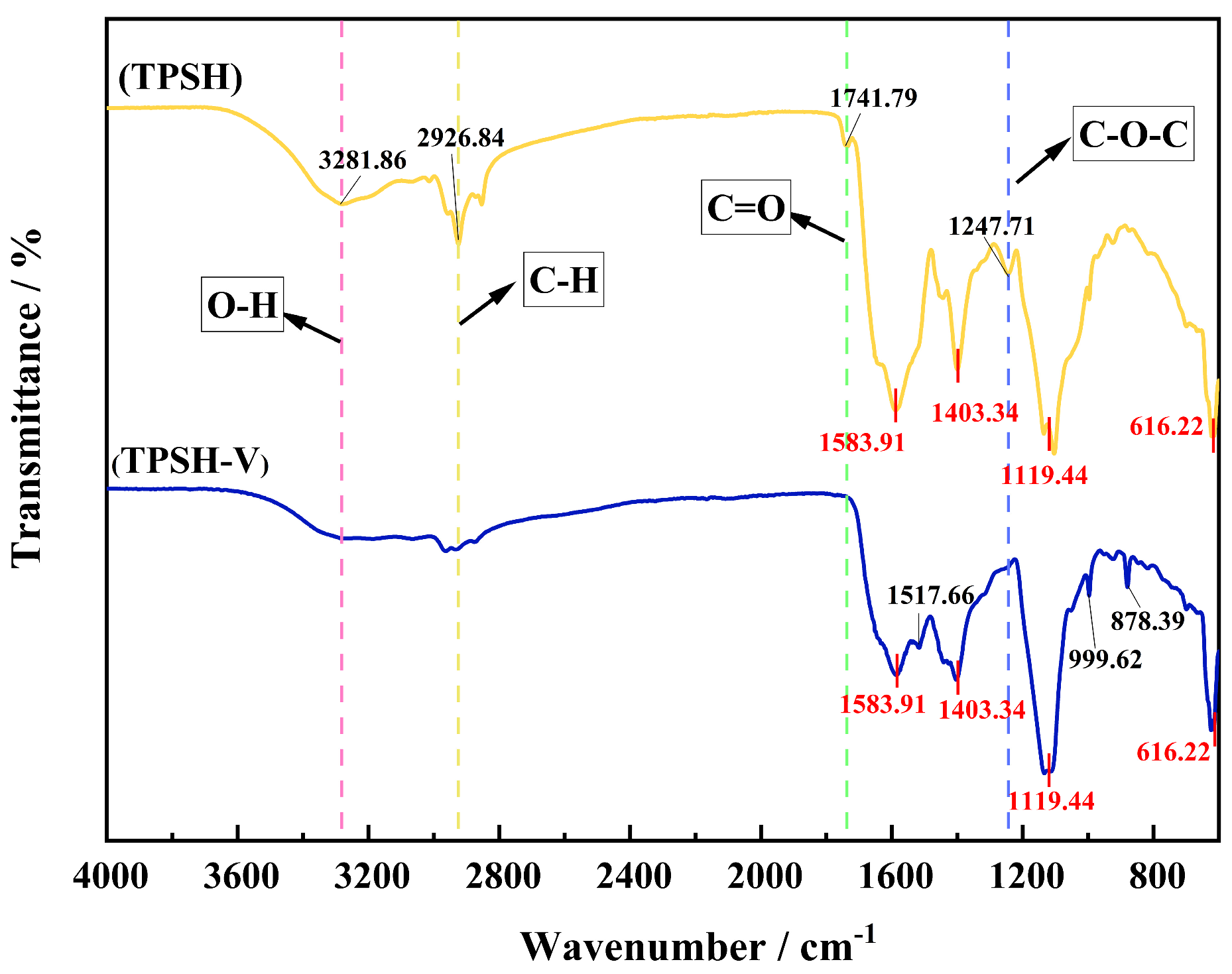
2.3. Secondary Structure of TPSH and TPSH-V
2.4. TPSH-V Stability Analysis
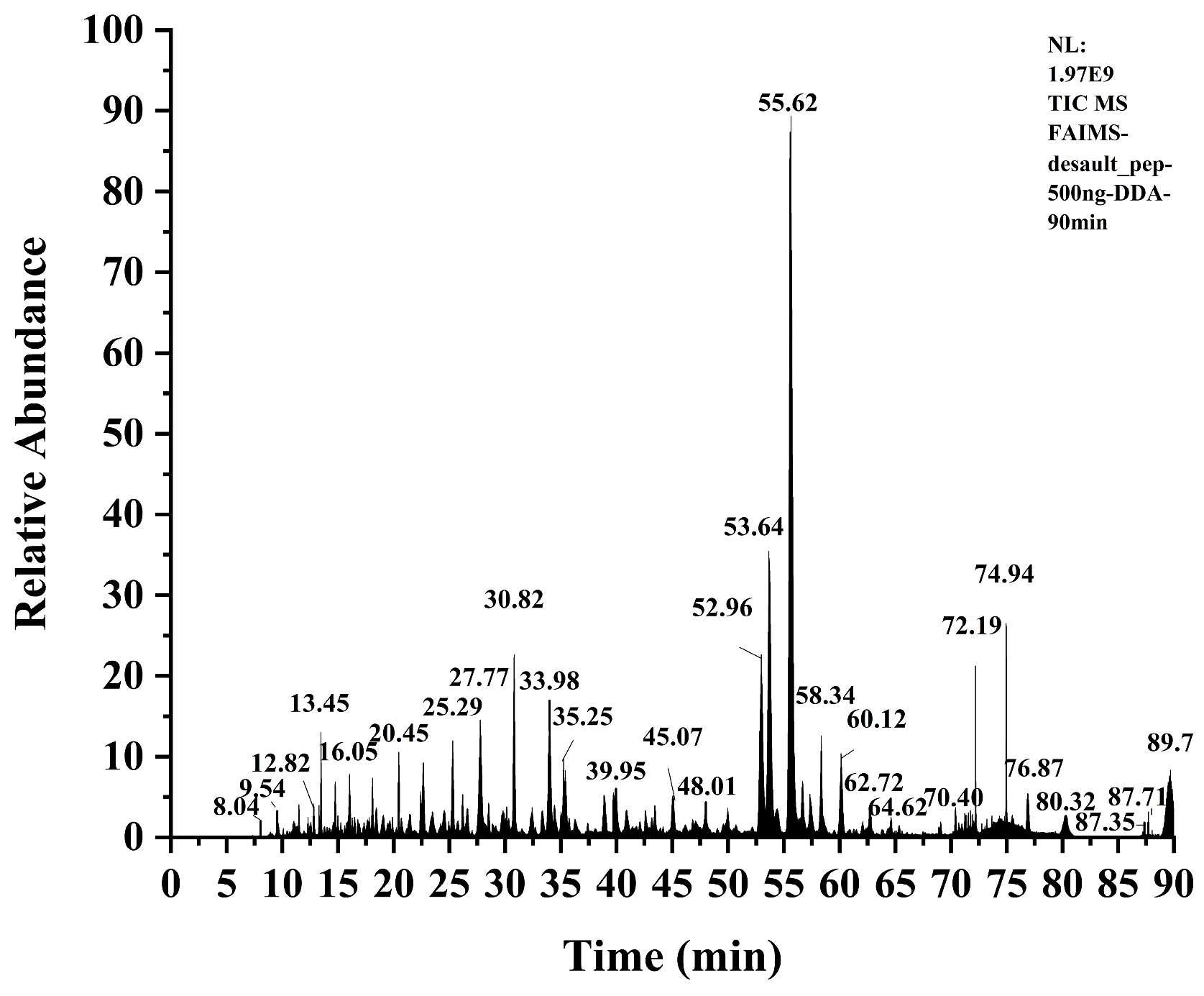
2.5. Peptide Identification
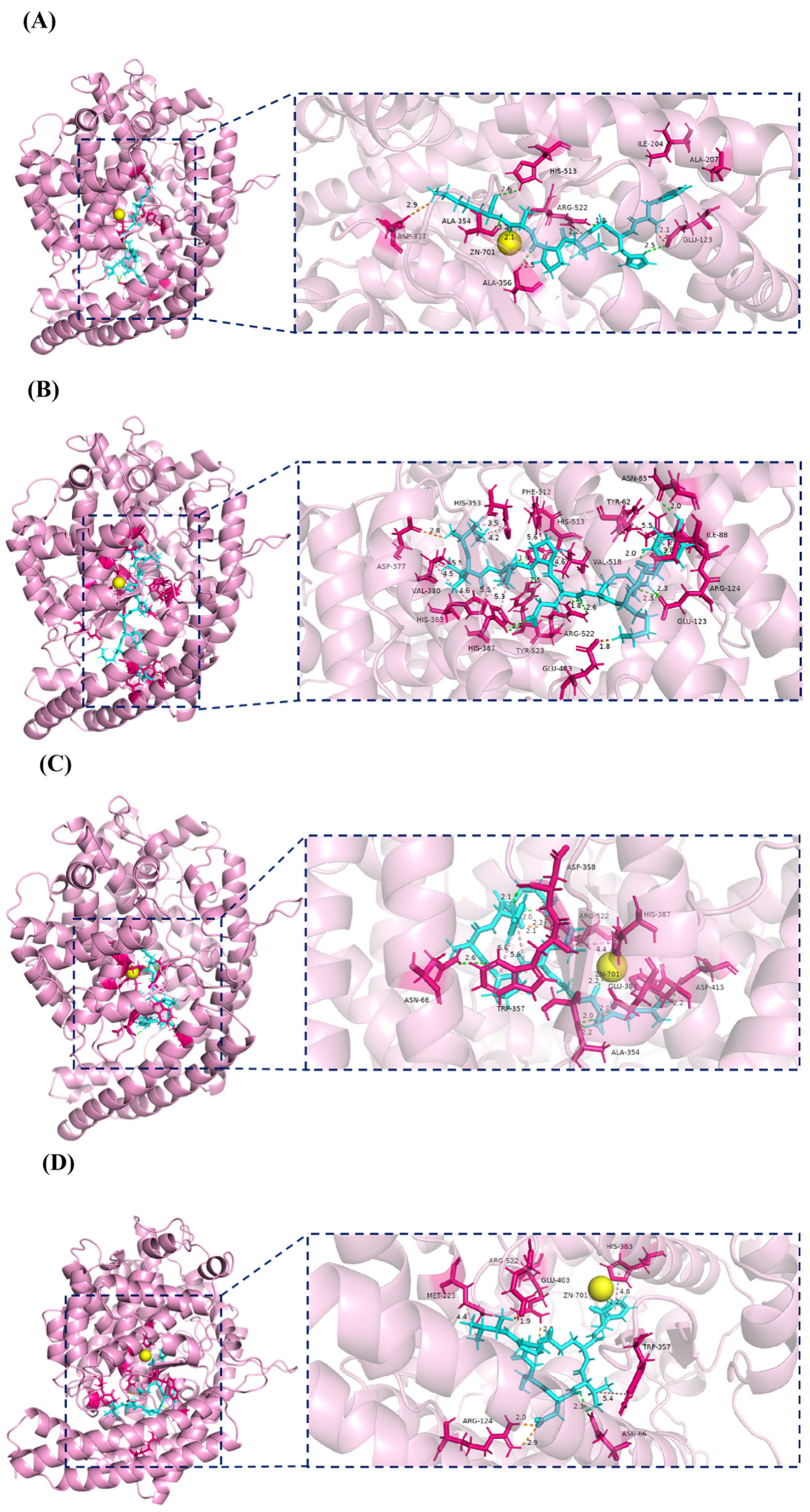
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis of Four Potential Novel ACEI Peptides Bound to ACE
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Ultrafiltration of TPSH
3.3. Determination of Total Amino Acids
3.4. In Vitro ACEI Activity Assay
3.5. Determination of Peptides’ Secondary Structure Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.6. Temperature Stability Analysis
3.7. pH Stability Analysis
3.8. Identification of the Sequence of TPSH-V via Nano LC-MS/MS
3.9. Peptide In Silico Screening
3.10. Molecular Docking Between Four Novel Peptides and ACE
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, S.I.; Park, S.Y.; Yoon, I.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, I.S.; Heu, M.S. Purification and characterization of leucyl aminopeptidase from the Todarodes pacificus hepatopancreas. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Dai, W.; Zhu, S.; Ding, Y. Mechanisms of alkali pH-shifted colour changes in squid (Uroteuthis edulis) subjected to frozen storage. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 134977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Aubourg, S.P. Recent trends for the employment of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) by-products as a source of bioactive compounds with nutritional, functional and preservative applications: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, A.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Montero, P. Identification of ace-inhibitory peptides from squid skin collagen after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Aubourg, S.P. Characterization of the Jumbo Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Skin By-Product by Shotgun Proteomics and Protein-Based Bioinformatics. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, H.S.; Yan, J.X.; Shi, Q.; Yang, H.; Cao, S.Q.; Qi, X.Y. Identification and molecular mechanism of novel antioxidant peptides from squid skin protein hydrolysates: In silico and in vitro analysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 214, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.Q.; Cai, J.X.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhou, K.N.; Liu, L.; He, L.Y.; Qi, X.Y.; Yang, H. Cryoprotective effect of collagen hydrolysates from squid skin on frozen shrimp and characterizations of its antifreeze peptides. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 174, 114443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, H.; Sila, A.; Bougatef, A.; Martínez-Alvarez, O. Protein Hydrolysis as a Way to Valorise Squid-Processing Byproducts: Obtaining and Identification of ACE, DPP-IV and PEP Inhibitory Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromfield, S.; Muntner, P. High Blood Pressure: The Leading Global Burden of Disease Risk Factor and the Need for Worldwide Prevention Programs. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, S.M.; Metzger, R.; Klieser, E.; Sotlar, K.; Trakht, I.N.; Garcia, J.G.N. Tissue ACE phenotyping in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.J.; Chen, X.; Huang, M.C.; Yang, Q.; Cai, X.X.; Chen, X.; Du, M.; Huang, J.L.; Wang, S.Y. Molecular characteristics and structure-activity relationships of food-derived bioactive peptides. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2313–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Takano, T. Antihypertensive Effect of Sour Milk and Peptides Isolated from It That Are Inhibitors to Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitors from Sour Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Wang, Y.M.; Ye, R.; Wu, Y.N.; Xia, W.S. Comparison of analytical methods to assay inhibitors of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamamoto, N. Study of the mechanism of antihypertensive peptides VPP and IPP in spontaneously hypertensive rats by DNA microarray analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 620, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamata, Y.; Watson, K.A.; Jauregi, P. Whey-Derived Peptides Interactions with ACE by Molecular Docking as a Potential Predictive Tool of atural ACE Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Wu, C.P.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.X.; Zhao, T.T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.M.; Su, G.W. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwal, S.M.; Abidin, N.Z.; Zarei, M.; Tan, C.P.; Saari, N. Identification, structure-activity relationship and in silico molecular docking analyses of five novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from stone fish (Actinopyga lecanora) hydrolysates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0197644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, K.; Suresh, K.; Anbalagan, S.; Ragini, Y.P.; Kadirvel, V. Investigating the nutritional viability of marine-derived protein for sustainable future development. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Process Biochem. 2001, 36, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, N.H.; Shaik, M.I.; Yellapu, N.K.; Howell, N.K.; Sarbon, N.M. Purification, characterization and molecular docking study of angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from shortfin scad (Decapterus macrosoma) protein hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2021, 58, 4567–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.L.; Pan, N.; Xu, M.; Su, Y.C.; Qiao, K.; Chen, B.; Zheng, B.D.; Xiao, M.T.; Liu, Z.Y. ACE Inhibitory Peptide from Skin Collagen Hydrolysate of Takifugu bimaculatus as Potential for Protecting HUVECs Injury. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lv, S.; Li, B. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory and antihypertensive properties of squid skin gelatin hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, I.; Mora, L.; Barkia, A.; Aristoy, M.C.; Nasri, M.; Toldrá, F. Bioactive peptides identified in thornback ray skin’s gelatin hydrolysates by proteases from Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Keskin Ulug, S.; Hong, H.; Wu, J. Regulatory requirements of bioactive peptides (protein hydrolysates) from food proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, W.C.; Ma, H.L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Structural characterization and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory mechanism of Stropharia rugosoannulata mushroom peptides prepared by ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Tarafdar, A.; Dass, S.L.; Pareek, S.; Badgujar, P.C. Antioxidant potential and amino acid profile of ultrafiltration derived peptide fractions of spent hen meat protein hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2023, 60, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famuwagun, A.A.; Alashi, A.M.; Gbadamosi, S.O.; Taiwo, K.A.; Oyedele, J.D.; Adebooye, O.C.; Aluko, R.E. In Vitro Characterization of Fluted Pumpkin Leaf Protein Hydrolysates and Ultrafiltration of Peptide Fractions: Antioxidant and Enzyme-Inhibitory Properties. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2020, 70, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanggang, A.B.; Putri, J.E.; Palupi, N.S.; Hatzakis, E.; Syamsir, E.; Budijanto, S. Enzymatic Preparation of Bioactive Peptides Exhibiting ACE Inhibitory Activity from Soybean and Velvet Bean: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.Z.; Sheikh, A.R.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.Z.; Sun, N.Z.; Su, X.D.; Luo, L.; Ma, H.L.; He, R.H. Understanding the Mechanism for the Structure-Activity Relationship of Food-Derived ACEI Peptides. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1751–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.L.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Mao, F.J.; Cheng, S.Z.; Lu, W.H.; Du, M. Analysis and Evaluation of the Inhibitory Mechanism of a Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide Derived from Casein Hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4139–4144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.S.; Guo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.; Bassey, A.P.; Ali, A.; Huang, M.; Huang, J.C. ACE Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Muscovy Duck (Cairina moschata) Plasma. Foods 2023, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Jeon, J.K.; Byun, H.G. Effect of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide purified from skate skin hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Ravallec-Plé, R.; Leroy, Y.; Guillochon, D.; Barkia, A.; Nasri, M. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, Y.S.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; El Halawany, A.M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.W. Production of Dual Inhibitory Hydrolysate by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Squid Processing By-Product. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.X.; Shao, S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Qi, H.Y.; Xiao, F.Q.; Shen, Y.X.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.D.; Zhao, D.Q.; Li, G.Z.; et al. Physico-chemical properties, antioxidant activity, and ACE inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates from wild jujube seed. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2484–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavarasan, K.; Shamasundar, B.A.; Badii, F.; Howell, N. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity and structural properties of oven- and freeze-dried protein hydrolysate from fresh water fish (Cirrhinus mrigala). Food Chem. 2016, 206, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Xu, L.; Fan, C.; Cao, L.L.; Guo, X.F. Structural Characteristics and Antioxidant Mechanism of Donkey-Hide Gelatin Peptides by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, S. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by casein. Evidence of molecular encapsulation of 1,4-pentadiene fatty acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 792, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.Y.; He, R.; Huang, A.X.; Wang, X.F. Identification, structural characterization, and molecular dynamic simulation of ACE inhibitory peptides in whey hydrolysates from Chinese Rushan cheese by-product. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzadehpanah, H.; Asoodeh, A.; Mahaki, H.; Mostajabodave, Z.; Chamani, J.; Mojallal-Tabatabaei, Z.; Emtenani, S.; Emtenani, S.; Moradi, M.R. Bioactive and ACE binding properties of three synthetic peptides assessed by various spectroscopy techniques. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, W.; Gao, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Leng, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. A combined in vitro and in silico study of the inhibitory mechanism of angiotensin-converting enzyme with peanut peptides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Vij, S. In vitro stability of bioactive peptides derived from fermented soy milk against heat treatment, pH and gastrointestinal enzymes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Hu, H.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhu, H.T.; Zhang, W.H.; Tai, Z.Y.; Yu, X.D.; He, Q.Y. A novel ACE inhibitory peptide from Douchi hydrolysate: Stability, inhibition mechanism, and antihypertensive potential in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, P.; Sharma, S.; Surasani, V.K.R. Influence of processing and pH on amino acid profile, morphology, electrophoretic pattern, bioactive potential and functional characteristics of alfalfa protein isolates. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Shi, P.Q.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Y.L.; You, L.Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, W. A novel ACE-inhibitory hexapeptide from camellia glutelin-2 hydrolysates: Identification, characterization and stability profiles under different food processing conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S. Peptide toxicity prediction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1268, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.Q.; Liu, M.; Duan, S.S.; Sun, X. The Antihypertensive Effects and Potential Molecular Mechanism of Microalgal Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Like Peptides: A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-Originating ACE Inhibitors, Including Antihypertensive Peptides, as Preventive Food Components in Blood Pressure Reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Gao, X.C.; Zhou, T.Y.; Cao, J.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Dang, Y.L.; Pan, D.D. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activity of Umami Peptides after In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8232–8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Qiu, Z.C.; Zhao, R.J.; Zheng, Z.J.; Qiao, X.G. Advancement and prospects of production, transport, functional activity and structure-activity relationship of food-derived angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1437–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.Y.; Miao, Y.L.; Hao, X.; Gao, B.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; He, X.; Zhang, L.J. Investigation on the characteristics and mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides by a thorough analysis of all 8000 tripeptides via binding free energy calculation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2943–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.-M.; Khan, F.; Park, S.-K.; Ko, S.-C.; Kim, K.W.; Yang, D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, G.-W.; Choi, G.; Lee, D.-S.; et al. From Sea to Lab: Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibition by Marine Peptides-Mechanisms and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, M. Basic and recent advances in marine antihypertensive peptides: Production, structure-activity relationship and bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X. Study of the binding mechanism between hydroxytyrosol and bovine serum albumin using multispectral and molecular docking. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadkaria, A.; Narvekar, D.T.; Nagar, D.P.; Sah, S.P.; Srivastava, N.; Bhagyawant, S.S. Purification, molecular docking and in vivo analyses of novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia (Jacq.) Màrechal) seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, A.S.; Roque, A.C.A. Studies on the molecular recognition between bioactive peptides and angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Mol. Recognit. 2009, 22, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Wang, H. Research on the screening and inhibition mechanism of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from tuna dark muscle. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.Z.; Li, J.R.; Liu, J.B.; Chen, F. Identification and molecular docking study of novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Salmo salar using in silico methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.D.; Cao, J.X.; Guo, H.Q.; Zhao, B. Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Gui, Z. Purification and molecular docking study of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from alcalase hydrolysate of ultrasonic-pretreated silkworm pupa (Bombyx mori) protein. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.L.; Chai, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.G. Separation and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from cashew nut (Anacardium occidentale Linnaeus) protein. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S981–S991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Safavi, M.; Hadizadeh, M. In vitro and in silico studies of novel synthetic ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein hydrolysate. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, N.Y.; Du, Y.F.; Feng, Q.; Shi, W.Z. Changes in Gel Structure and Chemical Interactions of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Surimi Gels: Effect of Setting Process and Different Starch Addition. Foods 2022, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Luo, Y.K. Production and identification of antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) muscle hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.X.; Liu, H.P.; Zu, S.Y.; Tang, B.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Cao, M.F.; Quek, S.Y.; He, N. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment: Identification and characterization of snakehead-muscle-protein-based angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitory peptides. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 194, 115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Amino Acid | Content (g/100 g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPSH | TPSH-Ⅰ | TPSH-Ⅱ | TPSH-Ⅲ | TPSH-Ⅳ | TPSH-Ⅴ | |
| Asp | 5.14 ± 0.35 d | 3.80 ± 0.16 e | 4.10 ± 0.05 e | 7.87 ± 0.09 a | 5.63 ± 0.12 c | 7.13 ± 0.16 b |
| Thr # | 1.98 ± 0.08 c | 1.23 ± 0.06 d | 1.96 ± 0.02 c | 2.48 ± 0.00 a | 2.27 ± 0.08 b | 2.54 ± 0.04 a |
| Ser | 2.32 ± 0.13 c | 1.47 ± 0.04 d | 2.69 ± 0.04 b | 2.77 ± 0.05 b | 2.81 ± 0.08 b | 2.98 ± 0.02 a |
| Glu | 6.51 ± 0.39 c | 4.13 ± 0.03 e | 5.93 ± 0.05 d | 8.81 ± 0.10 a | 7.68 ± 0.27 b | 8.70 ± 0.28 a |
| Gly | 5.64 ± 0.61 c | 3.73 ± 0.11 d | 5.88 ± 0.07 c | 8.75 ± 0.10 a | 7.36 ± 0.26 b | 8.77 ± 0.24 a |
| Ala * | 3.35 ± 0.20 c | 1.95 ± 0.04 d | 4.32 ± 0.07 b | 4.24 ± 0.03 b | 4.34 ± 0.11 b | 4.65 ± 0.14 a |
| Cys | 0.21 ± 0.05 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.30 ± 0.00 a | 0.16 ± 0.05 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 b | 0.20 ± 0.00 b |
| Val *#1 | 2.23 ± 0.09 c | 1.27 ± 0.09 d | 2.37 ± 0.02 c | 2.62 ± 0.05 b | 2.60 ± 0.07 b | 2.85 ± 0.08 a |
| Met *#1 | 1.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.46 ± 0.19 b | 0.08 ± 0.02 c | 0.52 ± 0.20 b | 0.65 ± 0.08 b | 1.22 ± 0.23 a |
| Ile *#1 | 1.98 ± 0.09 c | 1.19 ± 0.08 d | 1.97 ± 0.03 c | 2.33 ± 0.05 ab | 2.26 ± 0.07 b | 2.49 ± 0.08 a |
| Leu *# | 3.17 ± 0.15 b | 1.79 ± 0.09 c | 3.83 ± 0.07 a | 3.40 ± 0.05 b | 3.72 ± 0.10 a | 3.81 ± 0.08 a |
| Tyr 2 | 1.88 ± 0.20 b | 1.08 ± 0.04 c | 2.01 ± 0.05 ab | 2.09 ± 0.05 ab | 2.11 ± 0.04 ab | 2.23 ± 0.04 a |
| Phe *#2 | 2.23 ± 0.16 d | 1.20 ± 0.06 e | 3.00 ± 0.05 a | 2.39 ± 0.09 cd | 2.61 ± 0.05 bc | 2.63 ± 0.06 b |
| Lys | 2.81 ± 0.09 c | 1.45 ± 0.06 d | 3.55 ± 0.06 a | 2.85 ± 0.08 c | 3.10 ± 0.09 b | 3.10 ± 0.10 b |
| His | 1.00 ± 0.01 b | 0.62 ± 0.03 c | 1.03 ± 0.03 b | 1.02 ± 0.04 b | 1.13 ± 0.04 ab | 1.29 ± 0.20 a |
| Arg | 3.78 ± 0.13 d | 1.74 ± 0.08 e | 5.10 ± 0.03 a | 4.14 ± 0.12 c | 4.42 ± 0.14 b | 4.37 ± 0.10 bc |
| Pro * | 3.30 ± 0.09 c | 2.21 ± 0.05 e | 2.80 ± 0.07 d | 4.90 ± 0.08 a | 3.89 ± 0.10 b | 5.06 ± 0.07 a |
| AAA | 4.11 ± 0.37 c | 2.28 ± 0.10 d | 5.01 ± 0.10 a | 4.48 ± 0.14 bc | 4.71 ± 0.09 ab | 4.86 ± 0.10 ab |
| BCAA | 6.39 ± 0.23 b | 3.44 ± 0.36 d | 5.88 ± 0.12 c | 6.25 ± 0.10 bc | 6.63 ± 0.09 b | 7.52 ± 0.07 a |
| HAA | 17.49 ± 0.78 c | 10.08 ± 0.38 d | 18.38 ± 0.19 c | 20.40 ± 0.15 b | 20.06 ± 0.42 b | 22.70 ± 0.14 a |
| TAA | 48.75 ± 2.71 c | 29.49 ± 0.90 d | 50.91 ± 0.53 c | 61.34 ± 0.44 a | 56.72 ± 1.45 b | 64.01 ± 1.31 a |
| Number | Peptide Sequence | Molecular Weight | AHT-SVM | Toxin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CDFEIQFE | 1086.4328 | −1.39 | Non-Toxin |
| 2 | EKPDFGK | 819.4126 | −0.44 | Non-Toxin |
| 3 | EQPALGK | 741.4021 | −0.53 | Non-Toxin |
| 4 | FHGLPAK | 768.4282 | 1.38 | Non-Toxin |
| 5 | NALRTAM | 775.4010 | −2.11 | Non-Toxin |
| 6 | RGLPAYE | 804.4130 | 0.67 | Non-Toxin |
| 7 | TLRVDIK | 843.5178 | −1.1 | Non-Toxin |
| 8 | VPSDVEF | 791.3701 | 1.17 | Non-Toxin |
| 9 | YTDANGE | 768.2926 | −1.27 | Non-Toxin |
| 10 | LIGGHQK | 751.4340 | −0.69 | Non-Toxin |
| 11 | PWHFDRNY | 1133.5043 | −0.27 | Non-Toxin |
| 12 | IIAPPERKY | 1085.6233 | 1.51 | Non-Toxin |
| 13 | LRVAPEE | 812.4392 | −0.01 | Non-Toxin |
| 14 | WWNTSNIY | 1082.4821 | −0.2 | Non-Toxin |
| 15 | HYDRYYF | 1062.4559 | −0.19 | Non-Toxin |
| 16 | SARVDGK | 731.3926 | −2.02 | Non-Toxin |
| 17 | VLHTLGF | 785.4435 | −0.96 | Non-Toxin |
| Time (min) | Liquid A | Liquid B |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 98% | 2% |
| 10.0 | 92% | 8% |
| 55.0 | 73% | 27% |
| 65.0 | 63% | 37% |
| 70.0 | 2% | 98% |
| 75.0 | 2% | 98% |
| 78.0 | 95% | 5% |
| 81.0 | 95% | 5% |
| 85 | 2% | 98% |
| 90 | 2% | 98% |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Ion mode | Positive ion mode |
| Primary scanning range | 350–1500 Da |
| Secondary scanning range | Automatic control based on parent ion mass-to-charge ratio |
| Capillary temperature | 320 °C |
| Ion source spray voltage | 2200 V |
| Fragmentation conditions | HCD |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| The mass range of the parent ion | 350–1500 Da |
| The minimum number of peaks in the secondary mass spectra | 10 |
| S/N threshold | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gu, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, W. Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020081
Li M, Liang Q, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Gu Y, Song X, Wang X, Shi W. Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(2):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mingyuan, Qianqian Liang, Yurui Zhang, Xin Jiang, Yuan Gu, Xin Song, Xichang Wang, and Wenzheng Shi. 2025. "Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition" Marine Drugs 23, no. 2: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020081
APA StyleLi, M., Liang, Q., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., Gu, Y., Song, X., Wang, X., & Shi, W. (2025). Screening of Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides in Squid (Todarodes pacificus) Skin Hydrolysates: Preliminary Study of Its Mechanism of Inhibition. Marine Drugs, 23(2), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020081





