Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid in the Seabream Sparus aurata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fish maintenance
2.3. Experimental design
2.4. Examination of DA neurotoxicity
2.5. Light microscopy and immunohistochemistry
2.6. DA levels in brain and liver
3. Results
3.1. DA neurotoxicity
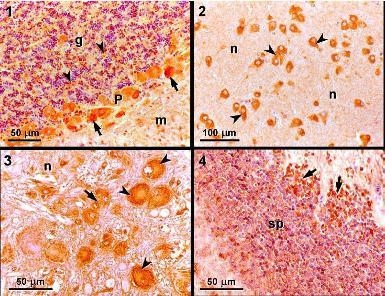
3.2. Light microscopy and immunohistochemistry
3.3. DA levels in the brain and liver
4. Discussion
Acknowledgements
References
- Takemoto, T; Daigo, K. Constituents of Chondria armata. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1958, 6, 578–580. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, SS. Domoic acid-producing diatoms: another genus added. J. Phycol 2000, 36, 978–983. [Google Scholar]
- Clayden, J; Read, B; Hebditch, KR. Chemistry of domoic acid, isodomoic acids, and their analogues. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 5713–5724. [Google Scholar]
- Hald, H; Naur, P; Pickering, DS; Sprogoe, D; Madsen, U; Timmermann, DB; Ahring, PK; Liljefors, T; Schousboe, A; Egebjerg, J; Gajhede, M; Kastrup, JS. Partial agonism and antagonism of the ionotropic glutamate receptor iGLuR5: structures of the ligand-binding core in complex with domoic acid and 2-amino-3-[5-tert-butyl-3-(phosphonomethoxy)-4-isoxazolyl]propionic acid. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 25726–25736. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, DR; Manalo, JL. The activation of Glutamate receptors by kainic acid and domoic acid. J. Nat. Toxins 1998, 6, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, SS; Bird, CJ; de Freitas, ASW; Foxall, R; Gilgan, M; Hanic, LA; Johnson, GR; McCulloch, AW; Odense, P; Pocklington, R; et al. Pennate diatom Nitzschia pungens as the primary source of domoic acid, a toxin in shellfish from Eastern Prince Edward Island, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci 1989, 46, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, BA; Palafox-Uribe, M; Grajales-Montiel, J; Cruz-Villacorta, A; Ochoa, JL. Sea bird mortality at Cabo San Lucas, Mexico: evidence that toxic diatom blooms are spreading. Toxicon 1997, 35, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, KA; Powell, CL; Busman, M; Doucette, GJ; Moeller, PDR; Silver, JB; Miller, PE; Hughes, MP; Singaram, S; Silver, MW; Tjeerdema, RS. Detection of domoic acid in northern anchovies and California sea lions associated with an unusual mortality event. J. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Silvagni, PA; Lowestine, LJ; Spraker, T; Lipscomb, TP; Gulland, FMD. Pathology of domoic acid toxicity in california sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol 2005, 42, 184–191. [Google Scholar]
- Busse, LB; Venrick, EL; Antrobus, R; Miller, PE; Vigilant, V; Silver, MW; Mengelt, C; Mydlarz, L; Prezelin, BB. Domoic acid in phytoplankton and fish in San Diego. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, MA; Wright, JLC. The amnesic shellfish poisoning mystery. Anal. Chem 1989, 61, 1053A–1060A. [Google Scholar]
- Bargu, S; Powell, C; Coale, S; Busman, M; Doucette, G; Silver, M. Krill: a potential vector for domoic acid in marine food webs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser 2002, 237, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bargu, S; Silver, M. Field evidence of krill grazing on the toxic diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia spp. in Monterey Bay, California. Bull. Mar. Sci 2003, 72, 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer, P; Reeves, C; Casper, DR; Davis, CR. Absence of neurotoxic effects in leopard sharks, Triakis semifasciata, following domoic acid exposure. Toxicon 2006, 47, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, KA; Dovel, SL; Silver, MW. Tissue distribution and neurotoxic effects of domoic acid in a prominent vector species, the northern anchovy Engraulis mordax. Mar. Biol 2001, 138, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Salierno, JD; Snyder, NS; Murphy, AZ; Poli, M; Hall, S; Baden, D; Kane, AS. Harmful algal bloom toxins alter c-Fos protein expression in the brain of killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Aquat. Toxicol 2006, 78, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, KA; Noren, DP; Schultz, IR; Bogard, SM; Wilson, J; Eberhart, BTL. Uptake, tissue distribution and excretion of domoic acid after oral exposure in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquat. Toxicol 2007, 81, 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Bakke, MJ; Horsberg, TE. Effects of algal-produced neurotoxins on metabolic activity in telencephalon, optic tectum and cerebellum of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquat. Toxicol 2007, 85, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Begout, ML; Lagardere, JP. An acoustic telemetry study of seabream (Sparus aurata L.): first results on activity rhythm, effects of environmental variables and space utilization. Hydrobiologia 1995, 301, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido, OM. Domoic acid toxicologic pathology: A review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 180–219. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, MA; Xie, M; Hardstaff, WR. A Rapid Extraction and Clean-Up Procedure for Determination of Domoic Acid in Tissue Sample; Technical Report 64 (NRCC No 3301); National Research Council Canada, Institute of Marine Bioscence: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes, CRC; Alfonso, PM; Duran, BR; Vidal, L; Leao, M; Gago, M. Application of precolumn oxidation HPLC method with fluorescence detection to evaluate saxitoxin levels in discrete brain regions of rats. Toxicon 2007, 49, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tasker, R; Connell, B; Strain, S. Pharmacology of systemically administered domoic acid in mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol 1991, 69, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- Larm, JA; Beart, PM; Cheung, NS. Neurotoxin domoic acid produces cytotoxicity via kainate-and ampa sensitive receptors in cultured cortical neurones. Neurochem. Int 1997, 31, 677–682. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, FW; Murray, TF. Domoic acid neurotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule neurons is mediated predominantly by NMDA receptors that are activated as a consequence of excitatory amino acid release. J. Neurochem 1997, 69, 693–703. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, D; Ramsdell, JS. Glutamate receptors and calcium entry mechanisms for domoic acid in hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, GR; Zorumski, CF; Price, MT; Olney, JW. Domoic acid: a dementia-inducing excitotoxic food poison with kainic acid receptor specificity. Exp. Neurol 1990, 110, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas, L; Iverson, F. Neuropathology of excitatory neurotoxins: The domoic acid model. Toxicol. Pathol 1990, 27, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas, L; Truelove, J; Iverson, F. Acute parenteral neurotoxicity of domoic acid in cynomolgous monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Toxicol. Pathol 1990, 18, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka, TJ; Brown, R; Quander, DY; Jackson, R; Smith, M; Long, SA; Barton, CN; Rountree, RL; Hall, S; Eilers, P; Johannessen, JN; Scallet, AC. Domoic acid: neurobehavioral and neurohistological effects of low-dose exposure in adult rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol 1996, 18, 659–670. [Google Scholar]
- Truelove, J; Mueller, J; Pulido, O; Iverson, F. Subchronic toxicity study of domoic acid in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol 1996, 34, 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Truelove, J; Mueller, R; Pulido, O; Martin, L; Fernie, S; Iverson, F. 30-day oral toxicity study of domoic acid in cynomolgus monkeys: lack of overt toxicity at doses approaching the acute toxic dose. Nat. Toxins 1997, 5, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kardong, KV. Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution, 3rd ed; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 609–653. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, AB; Mortensen, L; Poppe, TT. Histology Atlas, Normal Structure of Salmonids; Akvapatologisk Laboratorium AS: Bodǿ, Norway, 1992. [Google Scholar]


| Experimental setup | Time (hours) | Number of fish per aquarium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Examination of DA neurotoxicity | Behavioral observations | 0.5 and 2 | 6 |
| Mortality | 24 | 6 | |
| Light microscopy and immunohistochemistry | 24 | 2 | |
| DA analyses | 1, 2, and 4 | 3 | |
| HPLC Instrument | PV-980 Jasco |
| Column | Reversed Phase Phenomenex luna C18, 5 μm, 100A ODS3, 250 × 4.6 mm |
| Mobile Phase | Acetonitrile:Water 12% (v/v) with formic acid 0.2% (v/v) |
| Flow rate | 1 mL min−1 |
| UV detector | Jasco UV-1575 |
| Wavelength | 242 nm |
| Injection Volume | 20 μL |
| Data Analysis | Borwin software |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nogueira, I.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; Afonso, A.; Rivera, S.; Azevedo, J.; Monteiro, R.; Cervantes, R.; Gago-Martinez, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid in the Seabream Sparus aurata. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2721-2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102721
Nogueira I, Lobo-da-Cunha A, Afonso A, Rivera S, Azevedo J, Monteiro R, Cervantes R, Gago-Martinez A, Vasconcelos V. Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid in the Seabream Sparus aurata. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(10):2721-2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102721
Chicago/Turabian StyleNogueira, Isabel, Alexandre Lobo-da-Cunha, António Afonso, Socorro Rivera, Joana Azevedo, Rogério Monteiro, Rosa Cervantes, Ana Gago-Martinez, and Vítor Vasconcelos. 2010. "Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid in the Seabream Sparus aurata" Marine Drugs 8, no. 10: 2721-2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102721
APA StyleNogueira, I., Lobo-da-Cunha, A., Afonso, A., Rivera, S., Azevedo, J., Monteiro, R., Cervantes, R., Gago-Martinez, A., & Vasconcelos, V. (2010). Toxic Effects of Domoic Acid in the Seabream Sparus aurata. Marine Drugs, 8(10), 2721-2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102721