New Lobane and Cembrane Diterpenes from Two Comorian Soft Corals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
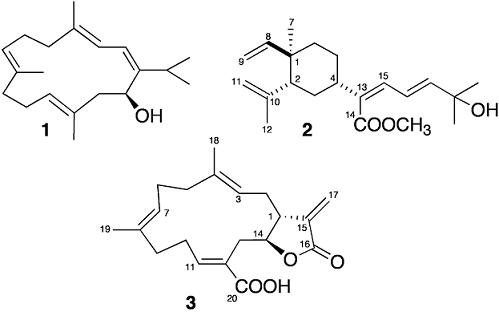
2.1. Sarcophyton
2.2. Lobophytum
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Brine Shrimp Lethality Test
3.5. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Test
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Blunt, JW; Copp, BR; Hu, W.-P; Munro, MHG; Northcote, PT; Princep, MR. Marine Natural products. Nat Prod Rep 2009, 26, 170–244, and earlier references in this series cited therein. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J; Fenical, W. Fuscosides A-D: Antiinflammatory diterpenoid glycosides of new structural classes from the Caribbean gorgonian Eunicea fusca. J Org Chem 1991, 56, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, RW; Wells, RJ. Isolation of some novel diterpenes from a soft coral of the genus Lobophytum. Aust J Chem 1979, 32, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Edrada, RA; Proksch, P; Wray, V; Witte, L; van Ofwegen, L. Four new bioactive lobane diterpenes of the soft coral Lobophytum pauciflorum from Mindoro, Philippines. J Nat Prod 1998, 61, 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, ASR; Raju, KVS. A new lobane diterpene acid from the soft coral Lobophytum microlobulatum of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indian J Chem 1996, 35B, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, ASR; Kameswara Rao, NS. Four new lobane diterpenoids from the soft coral Lobophytum microlobulatum of the Havellock island of the Andaman and Nicobar group of Islands. Indian J Chem 1996, 35B, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, T; Kusumi, T; Ishitsuka, MO; Kakisawa, H. Structures and absolute configurations of the new lobane diterpenoids from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Chem Lett 1992, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi, T; Hamada, T; Ishitsuka, MO; Ohtani, I; Kakisawa, H. Elucidation of the relative and absolute stereochemistry of lobatriene, a marine diterpene, by a modified Mosher method. J Org Chem 1992, 57, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, M.-C; Wang, S.-K; Dai, C.-F; Duh, C.-Y. A cytotoxic lobane diterpene from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia inelegans. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 843–844. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, MA; Gustafson, KR; Boyd, MR. HIV-inhibitory cembrane derivatives from a Philippines collection of the soft coral Lobophytum species. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 531–533. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, AF; Shiue, R.-T; Wang, G.-H; Dai, C.-F; Kuo, Y.-H; Sheu, J.-H. Five novel norcembranoids from Sinularia leptoclados and S parva. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 7337–7344. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, ASR; Venkateswara Rao, GJ. Chemical Constituents of the Soft Coral Species of Sarcophyton Genus: A Review. J Indian Chem Soc 1997, 74, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, JC. The chemistry and the chemical ecology of octocorals (Coelenterata, Anthozoa, Octocorallia). Chem Rev 1992, 92, 613–631. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, BN; Ferrigni, NR; Putnam, JE. Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Medica 1982, 45, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Marston, A; Kissling, J; Hostettmann, K. A rapid TLC bioautographic method for the detection of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors in plants. Phytochem Anal 2002, 13, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Blennow, K; de Leon, MJ; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, RS; Lee, HG; Xiongwei, Z; Perry, G; Smith, MA; Castellani, RJ. Current approaches in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2008, 62, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M; Nakagawa, T; Mitsuhashi, H. Marine terpene and terpenoids. I. Structures of four cembrane-type diterpenes; sarcophytol-A, sarcophytol-A acetate, sarcophytol-B, and sarcophytonin-A, from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Chem Pharm Bull 1979, 27, 2382–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Yokomatsu, H; Satake, K; Hiura, A; Tsutsumi, M; Suganuma, M. Sarcophytol A: A new chemotherapeutic and chemopreventive agent for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 1994, 9, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma, M; Okabe, S; Sueoka, E; Iida, N; Komori, A; Kim, S-J; Fujiki, H. A new process of cancer prevention mediated through inhibition of tumor necrosis factor a expression. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 3711–3715. [Google Scholar]
- Gopichand, Y; Schmitz, FJ. Marine natural products: Fuscol, a new elemene-type diterpene alcohol from the gorgonian Eunicea fusca. Tetrahedron Lett 1978, 19, 3641–3644. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, JC; Bowden, BF; König, GM; Braslau, R; Price, IR. Studies of Australian soft corals. XXXX. The natural products chemistry of Alcyonacean soft corals with special reference to the genus Lobophytum. Bull Soc Chim Belg 1986, 95, 815–834. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, ASR; Venkateswara Rao, G; Raju, KVS; Krishna Murthy, MVR. Two new lobane derivatives from the soft coral Lobophytum pauciflorum of the Havelock Island of the Indian Ocean. Indian J Chem 1995, 34B, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmana Raju, B; Subbaraju, GV; Bheemasankara Rao, C; Trimurtulu, G. Two new oxygenated lobanes from a soft coral of Lobophytum species of the Andaman and Nicobar coasts. J Nat Prod 1993, 56, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, V; Nageswara Rao, K; Appa Rao, KMC. Isolation of loba-8,10,15-triene-13,17,18- triol-17,18-diacetate from a soft coral of Lobophytum species of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indian J Chem 1995, 34B, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmana Raju, B; Subbaraju, GV; Vasavi Reddy, K; Bheemasankara Rao, C. Alcyonacean metabolites : part 5. Further metabolites from a soft coral of Lobophytum genus of the Andaman and Nicobar coasts. Indian J Chem 1994, 33B, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar]
- A lobane has been reported isolated from Sclerophytum sp. but the coral was subsequently reidentified as part of a variable Lobophytum pauciflorum complex (cf. reference 23).
- Stothers, JB. Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; Volume Chapter 11. [Google Scholar]
- Uchio, Y; Toyota, J; Nozaki, H; Nakayama, M; Nishizono, Y; Hase, T. Lobohedleolide and (7Z)-lobohedleolide, new cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum hedleyi Whitelegge. Tetrahedron Lett 1981, 22, 4089–4092. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, JC; Mitchell, SJ; Stokie, GJ. Studies of Australian soft corals. II. A novel cembranoid diterpene from Lobophytum michaelae. Aust J Chem 1977, 30, 1859–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, BF; Brittle, JA; Coll, JC; Liyanage, N; Mitchell, SJ; Stokie, GJ. Studies of Australian soft corals. VI. A new cembranolide diterpene from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Tetrahedron Lett 1977, 41, 3661–3662. [Google Scholar]
- Ahond, A; Bowden, BF; Coll, JC; Fourneron, J-D; Mitchell, SJ. Studies of Australian soft corals. XII. Further cembranolide diterpenes from Lobophytum crassospiculatum and a correction of a previous stereochemical assignment. Aust J Chem 1979, 32, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W; Krohn, K; Ding, J; Miao, Z.-H; Zhou, X.-H; Chen, S.-H; Pescitelli, G; Salvadori, P; Kurtan, T; Guo, Y.-W. Structural and stereochemical studies of a α-methylene-γ-lactonebearing cembrane diterpenoids from a south China Sea soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Duh, C.-Y; Wang, S.-K; Huang, B.-K; Dai, C.-F. Cytotoxic cembrenolide diterpenes from the Formosan soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 884–885. [Google Scholar]
- Duh, C.-Y; Wang, S.-K; Chung, S.-G; Chou, G.-C; Dai, C.-F. Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassaule. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Kinamoni, Z; Grosweiss, A; Carmely, S; Kashman, Y; Loya, Y. Several new cembranoid diterpenes from three soft corals of the Red Sea. Tetrahedron 1983, 39, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-K; Duh, C.-Y; Wu, Y.-C; Wang, Y; Cheng, M.-C; Soong, K; Fang, L.-S. Studies on Formosan soft corals, II. Cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. J Nat Prod 1992, 55, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, C.-H; Wen, Z.-H; Wu, Y.-C; Yeh, H.-C; Sheu, J.-H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Bheemasankara Rao, C; Ramanan, KV; Kalidindi Raju, SHSN; Sreenivasa Rao, D; Venkata Rao, D; Trimurtulu, G; Faulkner, DJ. Cembrane diterpenes from a new species of the genus Lobophytum of the Indian Ocean. Indian J Chem 1994, 33B, 1004–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Ata, A; Ackerman, J; Bayoud, A; Radhika, P. Bioactive Chemical Constituents of Cladiella Species. Helv Chim Acta 2004, 87, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, T; Macek, P; Suput, D. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by a pseudozoanthoxanthin-like compound isolated from the zoanthid Parazoanthus axinellae (O. Schmidt). Toxicon 1995, 33, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, SN; Radic, Z; Manker, D; Faulkner, DJ; Taylor, P. Onchidal: A naturally occurring irreversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase with a novel mechanism of action. Mol Pharmacol 1989, 36, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, K; Singh, R; Kaushik, MP; Gupta, AK. Acute toxicity of synthetic Gymnodinium brevetoxin metabolite and its analogues in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 1996, 35, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kem, WR. Alzheimer’s drug design based upon an invertebrate toxin (anabaseine) which is a potent nicotinic receptor agonist. Invert Neurosci 1997, 3, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sepcic, K; Marcel, V; Klaebe, A; Turk, T; Suput, D; Fournier, D. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by an alkylpyridinium polymer from the marine sponge Reniera sarai. Biochemica Biophysica Acta 1998, 1387, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, T; Frangez, R; Sepcic, K. Mechanisms of toxicity of 3-alkylpyridinium polymers from marine sponge Raniera sarai. Mar Drugs 2007, 5, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Sepcic, K; Mancini, I; Vidic, I; Jovan, U; Frassanito, R; Pietra, F; Macek, P; Turk, T. Antibacterial and anticholinesterase activities of aplysamine-4, a bromotyrosine-derived metabolite of a Red Sea marine sponge. J Nat Toxins 2001, 10, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, GA; Alonso, GD; Dorronsoro, DI; Garcia, PE; Austria, LC; Usan, EP; Del, MMM; Median, PM. Marine compounds with calcium channel blocking properties for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. European Patent 2005, EP 1609783. [Google Scholar]
- Kigoshi, H; Kanematsu, K; Yokota, K; Uemura, D. Turbotoxins A and B, novel diiodotyramine derivatives from the Japanese gastropod Turbo marmorata. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 9063–9070. [Google Scholar]
- Nukoolkarn, VS; Saen-oon, S; Rungrotmongkol, T; Hannongbua, S; Ingkaninan, K; Suwanborirux, K. Petrosamine, a potent anticholinesterase pyridoacridine alkaloid from a Thai marine sponge Petrosia n. sp. Bioorg Med Chem 2008, 16, 6560–6567. [Google Scholar]
- Ferchmin, PA; Pagan, OR; Ulrich, H; Szeto, AC; Hann, RM; Eterovic, VA. Actions of octocoral and tobacco cembranoids on nicotinic receptors. Toxicon 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Atom n° | 1H NMR | 13C NMRc | COSY | HMBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.8 | Cq | |||
| 2 | 2,20 m | 52.7 | CH | 3 | |
| 3 | 1,56 m | 33.4 | CH2 | 2, 4 | |
| 4 | 2,02 m | 41.5 | CH | 3 | |
| 5 | 1,60–1,57 mb | 27.2 | CH2 | ||
| 6 | 1,50–1,45 mb | 39.7 | CH2 | ||
| 7 | 1.08 s | 16.6 | CH3 | 8 | |
| 8 | 5.82 dd (11.0, 18.0) | 150.0 | CH | 9a, 9b | 7 |
| 9a | 4.91 d (18.0) | 110.0 | CH2 | 8 | 1, 8 |
| 9b | 4.90 d (11.0) | 8 | 1, 8 | ||
| 10 | 147.4 | Cq | |||
| 11a | 4.82 br s | 112.3 | CH2 | 2, 12 | |
| 11b | 4.58 br s | 2, 12 | |||
| 12 | 1.70 s | 24.8 | CH3 | 11a, 11b | 10, 11 |
| 13 | 136.8 | Cq | |||
| 14 | 168.7 | Cq | |||
| 15 | 6.33 d (14.0) | 134.3 | CH | 16 | 4, 14, 17 |
| 16 | 6.97 dd (14.0, 15.0) | 123.6 | CH | 15, 17 | |
| 17 | 6.05 d (15.0) | 146.7 | CH | 16 | 15, 18, 19/20 |
| 18 | 71.0 | Cq | |||
| 19 | 1.36 s | 29.6 | CH3 | 17, 18 | |
| 20 | 1.36 s | 29.6 | CH3 | 17, 18 | |
| 21 | 3.79 s | 51.6 | CH3 | 14 | |
| Atom n° | 1H NMR | 13C NMRb | COSY | HMBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.97 ddd (2.3, 4.3, 11.2) | 43.7 | CH | 2a, 2b, 17a, 17b | |
| 2a | 2.18 m | 33.6 | CH2 | 1, 2b, 3 | 1 |
| 2b | 2.25 m | 1, 2a, 3 | |||
| 3 | 4.84 dd (4.0, 10.0) | 122.0 | CH | 2a, 2b, 18 | 18 |
| 4 | 137.6 | Cq | |||
| 5 | 1.95 m | 39.1 | CH2 | 6 | 6, 18 |
| 6 | 2.15 m | 24.1 | CH2 | 5, 7 | 5 |
| 7 | 4.95 dd (7.0, 8.0) | 124.0 | CH | 6, 19 | 9, 19 |
| 8 | 133.9 | Cq | |||
| 9 | 2.22 m | 37.5 | CH2 | ||
| 10a | 2.30 m | 27.3 | CH2 | 11 | 9 |
| 10b | 2.50 m | 11 | 9 | ||
| 11 | 7.03 dd (4.8, 9.0) | 151.5 | CH | 10a, 10b | 13, 20 |
| 12 | 125.5 | Cq | |||
| 13a | 2.57 m | 31.7 | CH2 | 13b, 14 | 1, 11, 12, 14, 20 |
| 13b | 2.68 m | 13a, 14 | 1, 11, 12, 14, 20 | ||
| 14 | 4.11 ddd (2.3, 5.1, 9.6) | 80.8 | CH | 2, 16 | |
| 15 | 138.7 | Cq | |||
| 16 | 170.3 | Cq | |||
| 17a | 5.67 d (1.9) | 123.3 | CH2 | 1, 16 | |
| 17b | 6.29 d (1.9) | 1, 15, 16 | |||
| 18 | 1.53 s | 15.5 | CH3 | 3 | 3, 4, 5 |
| 19 | 1.58 s | 17.0 | CH3 | 7 | 7, 8, 9 |
| 20 | 172.4 | Cq | |||
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonnard, I.; Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S.B.; Bontemps, N.; Banaigs, B.; Aknin, M. New Lobane and Cembrane Diterpenes from Two Comorian Soft Corals. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 359-372. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8020359
Bonnard I, Jhaumeer-Laulloo SB, Bontemps N, Banaigs B, Aknin M. New Lobane and Cembrane Diterpenes from Two Comorian Soft Corals. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(2):359-372. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8020359
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonnard, Isabelle, Sabina B. Jhaumeer-Laulloo, Nataly Bontemps, Bernard Banaigs, and Maurice Aknin. 2010. "New Lobane and Cembrane Diterpenes from Two Comorian Soft Corals" Marine Drugs 8, no. 2: 359-372. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8020359
APA StyleBonnard, I., Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S. B., Bontemps, N., Banaigs, B., & Aknin, M. (2010). New Lobane and Cembrane Diterpenes from Two Comorian Soft Corals. Marine Drugs, 8(2), 359-372. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8020359