Structures, Biological Activities and Phylogenetic Relationships of Terpenoids from Marine Ciliates of the Genus Euplotes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
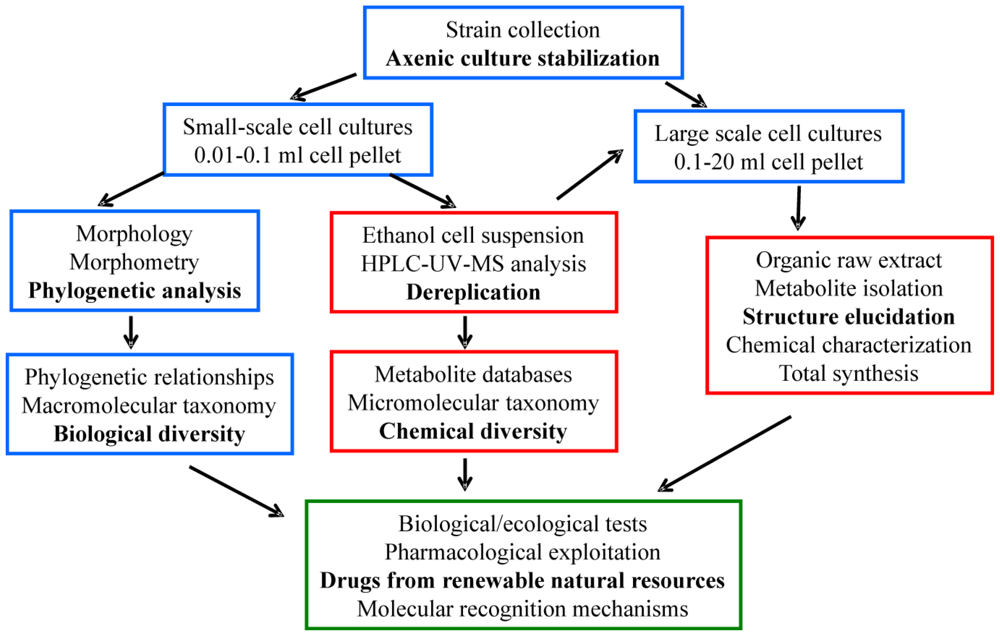
2. Generalities on Biological and Chemical Methodologies
2.1. Cell cultures, ecological tests and phylogenetic analysis
2.2. Cell extracts, de-replication analysis, isolation and structure elucidation of secondary metabolites
3. Terpenoids from Euplotes crassus
3.1. Structures, chemical reactivity and total synthesis
3.2. Inclusion complexes
3.3. Biogenetic considerations
3.4. Intra-morphospecies phylogenetic analysis
3.5. Ecological role and biological activities
4. Terpenoids from Euplotes raikovi
4.1. Structures, chemical reactivity and synthesis
4.2. Biogenetic considerations
4.3. Intra-morphospecies phylogenetic analysis
4.4. Ecological role and biological activities
5. Terpenoids from Euplotes vannus
5.1. Structures, chemical reactivity and synthesis
5.2. Biogenetic considerations
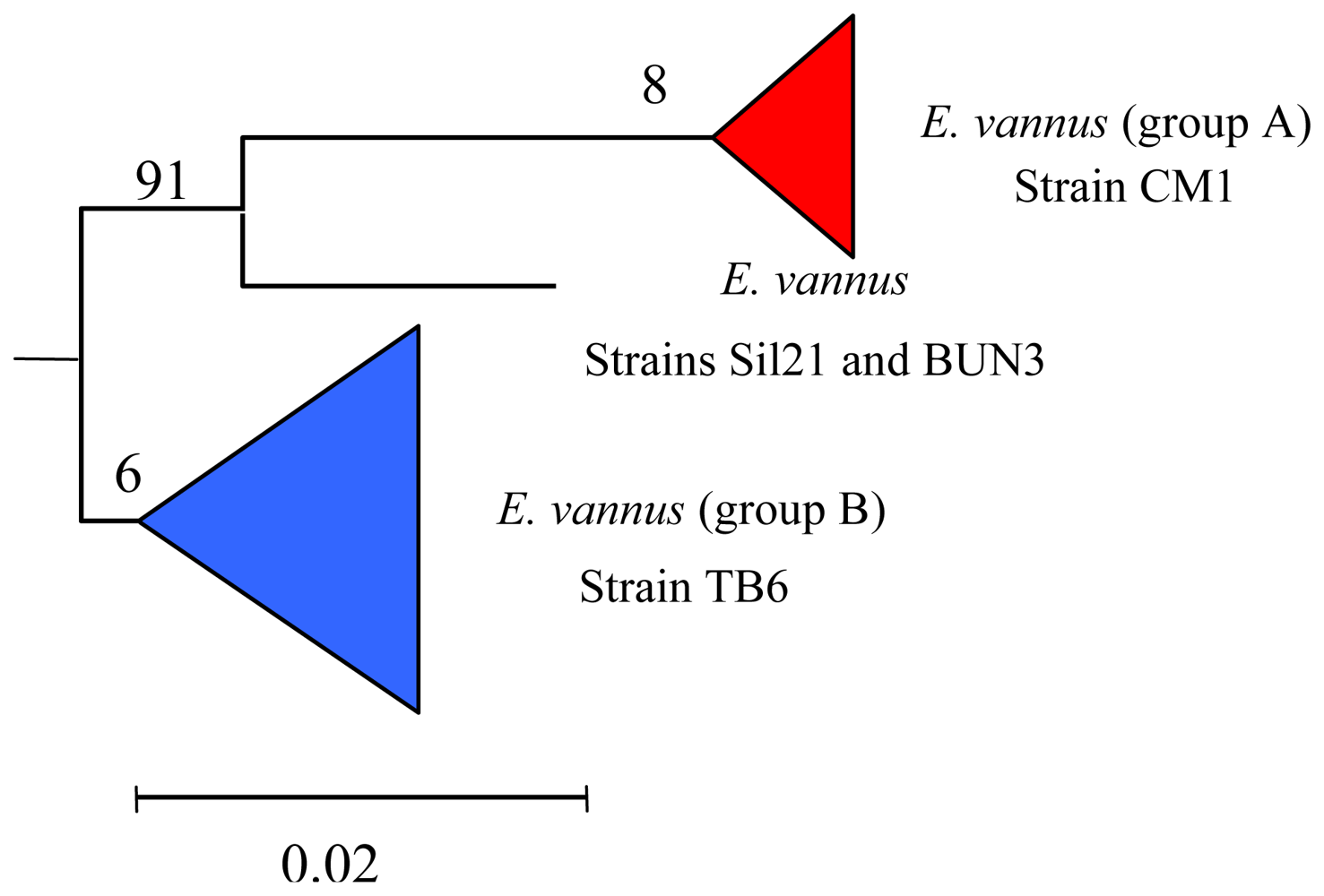
5.3. Intra-morphospecies phylogenetic analysis
6. Terpenoids from Euplotes rariseta
6.1. Structures, chemical reactivity and synthesis
6.2. Biogenetic considerations
6.3. Intra-morphospecies phylogenetic analysis
6.4. Biological activities
7. Terpenoids from Euplotes focardii
7.1. Structures, chemical reactivity and synthesis
7.2. Biogenetic considerations
7.3. Intra-morphospecies phylogenetic analysis
7.4. Biological activities
8. Functional Role and Phylogenetic Significance
9. Conclusions
References
- Finlay, BJM; Fenchel, T. Divergent perspective on Protist species richness. Protist 1999, 150, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Finlay, BJM; Corliss, JO; Esteban, GF; Fenchel, T. Biodiversity at the microbial level: the number of free-living ciliates in the biosphere. Quart. Rev. Biol 1996, 72, 221–237. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, JJ; Leedale, GF; Bradbury, P. The Illustrated Guide to the Protozoa, 2nd ed; Wiley-Blackwell: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2000; pp. 1–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Nanney, DL. Experimental Ciliatology: An Introduction to Genetic and Developmental Analysis in Ciliates; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 1–230. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, F; Nyberg, D. Gwynfryn, JJ, Ed.; Sex in ciliates. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 13, pp. 85–153. [Google Scholar]
- Petroni, G; Rosati, G; Vannini, C; Modeo, L; Dini, F; Verni, F. In situ identification by fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes of morphologically similar, closely related ciliate species. Microb. Ecol 2003, 45, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G. Terpenoids from marine ciliates: structure, biological activity, ecological role and phylogenetic relationship. Invited Lecture to 3rd European Conference on Marine Natural Products, Munich, Germany, September 2002.
- Luporini, P; Alimenti, C; Ortenzi, C; Vallesi, A. Ciliate mating types and their specific protein pheromones. Acta Protozool 2005, 44, 89–101, and references therein. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, N; Orlando, M; Hyon, J; Gross, M; Song, P. A new photoreceptor molecule from Stentor coeruleus. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1993, 115, 2526–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Checcucci, G; Shoemaker, RS; Bini, E; Cerny, R; Tao, N; Hyon, J; Gioffre, D; Ghetti, F; Lenci, F; Song, P. Chemical structure of blepharismin, the photosensor pigment for Blepharisma japonicum. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1997, 119, 5762–5763. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, M; Naoki, H; Matsuoka, T; Kato, Y; Kotsuki, H; Utsumi, K; Tanaka, T. Blepharismin 1–5, novel photoreceptor from the unicellular organism Blepharisma japonicum. Tetrahedron Lett 1997, 38, 7411–7414. [Google Scholar]
- Höfle, G; Pohlan, S; Uhlig, G; Kabbe, K; Schumacher, D. Keronopsins A and B, chemical defense substances of the marine ciliate Pseudokeronopsis rubra (Protozoa): identification by Ex vivo HPLC. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 1994, 33, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Frassanito, R; Mancini, I; Sandron, T; Modeo, L; Verni, F; Dini, F; Petroni, G. Keronopsamides, a new class of pigments from marine ciliates. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2010, 3, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Masaki, ME; Harumoto, T; Terazima, MN; Miyake, A; Usuki, Y; Iio, H. Climacostol, a defense toxin of the heterotrich ciliate Climacostomum virens against predators. Tetrahedron Lett 1999, 40, 8227–8229. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, I; Rohmer, M. Enyzmatic cyclization of 2,3-dihydrosqualene into euph-7-ene by a cell-free system from the protozoon Tetrahymena pyriformis. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun 1991, 13, 902–903. [Google Scholar]
- Foissner, W; Berger, H; Schaumburg, J. Identification and Ecology of limnetic plankton ciliates; Bavarian State Office for Water Management: Munich, Germany, 1999; pp. 1–793. [Google Scholar]
- Medlin, L; Elwood, HJ; Stickel, S; Sogin, ML. The characterization of enzymatically amplified 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene 1988, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Petroni, G; Dini, F; Verni, F; Rosati, G. A molecular approach to the tangled intrageneric relationships underlying phylogeny in Euplotes (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol 2002, 22, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, JD; Gibson, TJ; Plewniak, F; Jeanmougin, F; Higgins, DG. The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 1997, 4, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, TA. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids Symp 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Peer, Y; Baldauf, SL; Doodlittle, WF; Meyer, A. An updated and comprehensive rRNA phylogeny of (Crown) eukaryotes based on rate-calibrated evolutionary distances. J. Mol. Evol 2000, 51, 565–576. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, DL. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods); Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, D; Crandall, KA. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Ann. Rev. Genet 1988, 22, 521–565. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, F; Guella, G; Giubbilini, P; Mancini, I; Pietra, F. Control of interspecific relationships in marine ciliate protists by most evolved natural-products. Naturwissenschaften 1993, 80, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Tomei, A; Pietra, F. Preuplotin, a putative biogenetic precursor of the euplotins, bioactive sesquiterpenoids of the marine ciliated protist Euplotes crassus. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. I 1994, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu, T; Ravi, BN; Faulkner, DJ. Antimicrobial constituents of Udotea flabellum. J. Org. Chem 1981, 46, 2435–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Pietra, F. Hydrolytic breakdown of the euplotins, highly strained, adaptive, hemiacetal esters of the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus: A mimic of degradative pathways in nature and a trick for the assignment of the absolute configuration. Helv Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 710–717. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, JA; Mosher, HS. Nuclear magnetic resonance enantiomer reagents. Configurational correlations via nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts of diastereomeric mandelate, O-methylmandelate, and α-methoxy-α-trifluoromethylphenylacetate (MTPA) esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1973, 95, 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, I; Kusumi, T; Kashman, Y; Kakisawa, H. High-field FT NMR application of Mosher’s method. The absolute configurations of marine terpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1991, 113, 4092–4096. [Google Scholar]
- Tascioglu, S. Micellar solutions as reaction media. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 11113–11152. [Google Scholar]
- Aungst, RA, Jr; Funk, RL. Synthesis of (Z)-2-acyl-2-enals via retrocycloadditions of 5-acyl-4-alkyl-4H-1,3-dioxins: Application in the total synthesis of the cytotoxin (±)-euplotin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2001, 123, 9455–9456. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Callone, E; Mancini, I; Uccello-Barretta, G; Balzano, F; Dini, F. Chemical and structural properties of the inclusion complex of euplotin C with heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin through NMR spectroscopy, electrospray mass spectrometry and molecular mechanics investigations. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2004, 6, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Rohmer, M; Knani, M; Simonin, P; Sutter, B; Sahm, H. Isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria: A novel pathway for the early steps leading to isopentenyl diphosphate. Biochem. J 1993, 295, 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, BM; Rujan, T; Martin, W; Croteau, R. Isoprenoid biosynthesis: The evolution of two ancient and distinct pathways across genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13172–13177. [Google Scholar]
- Trapp, SC; Croteau, RB. Genomic organization of plant terpene synthases and molecular evolutionary implications. Genetics 2001, 158, 811–832. [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Franklin, JN; Butler, A. Vanadium bromoperoxidase-catalyzed biosynthesis of halogenated marine natural products. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 15060–15066. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, F. On the evolutionary significance of autogamy in the marine Euplotes (Ciliophora: Hypotrichida). Am. Nat 1984, 123, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer, JW; Machemer, H. Osmotic tolerance of Ca-dependent excitability in the marine ciliate Paramecium calkinsi. J. Exp. Biol 1982, 97, 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Savoia, D; Avanzini, C; Allice, T; Callone, E; Guella, G; Dini, F. Antimicrobial activity of euplotin C, the sesquiterpene taxonomic marker from the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemoth 2004, 48, 3828–3833. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoino, P; Usai, C; Maccione, S; Beltrame, F; Diaspro, A; Fato, M; Guella, G; Dini, F. Effect of the bioactive metabolite euplotin C on phagocytosis and fluid-phase endocytosis in the single-celled eukaryote Paramecium. Aquat. Toxicol 2007, 85, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoino, P; Dini, F; Bianchini, P; Diaspro, A; Guella, G; Usai, C. Biophysical effects of the natural product euplotin C on the Paramecium membrane. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2009, 195, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Cervia, D; Martini, D; Garcia-Gil, M; Di Giuseppe, G; Guella, G; Dini, F; Bagnoli, P. Cytotoxic effects and apoptotic signalling mechanisms of the sesquiterpenoid euplotin C, a secondary metabolite of the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus, in tumor cells. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 829–843. [Google Scholar]
- Cervia, D; Garcia-Gil, M; Simonetti, E; Di Giuseppe, G; Guella, G; Bagnoli, P; Dini, F. Molecular mechanisms of euplotin C-induced apoptosis: Involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and proteases. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Trielli, F; Cervia, D; Di Giuseppe, G; Ristori, C; Kruppel, T; Burlando, B; Guella, G; Viarengo, A; Bagnoli, P; Corrado, MU; Dini, F. Action mechanisms of the secondary metabolite euplotin C: signaling and functional role in Euplotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol 2008, 55, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Erra, F; Pietra, F. Raikovenal, a new sesquiterpenoid favoring adaptive radiation of the marine ciliate Euplotes raikovi, and its putative biogenetic precursor, preraikovenal. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Comm 1994, 22, 2585–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Pietra, F. From epiraikovenal, an instrumental niche-exploitation sesquiterpenoid of some strains of the marine ciliated protist Euplotes raikovi, to an unusual intramolecular tele-dienone-olefin [2+2] photocycloaddition. Helv. Chim. Acta 1995, 78, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Pietra, F. Photochemical conversion of the xenicane into crenulatane skeleton with diterpenoids of the brown seaweed Dictyota sp. of the coasts of Senegal. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun 1993, 20, 1539–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Chiasera, G; Ndiaye, I; Pietra, F. Xenicane diterpenes revisited - Thermal (E)→(Z) isomerization and conformational motions - A unifying picture. Helv. Chim. Acta 1994, 77, 1203–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Snider, BB; Lu, Q. Syntheses of (±)-raikovenal, (±)-preraikovenal, and (±)-epiraikovenal. Synth. Commun 1997, 27, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Rosini, G; Gonfalonieri, G; Marotta, E; Rama, F; Righi, P. Preparation of bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-ones: 1,4-dimethylbicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-one (Bicyclo[3.2.0]hept-3-en-6-one, 1,4-dimethyl-, cis-(±)-). Org. Synth 1997, 74, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Pietra, F. Metabolites with a novel C30-backbone from marine ciliates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 1999, 38, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Callone, E; Di Giuseppe, G; Frassanito, R; Frontini, F; Mancini, I; Dini, F. Hemivannusal and prevannusadials, new sesquiterpenoids from the marine ciliate protist, Euplotes vannus, the putative biogenetic precursors of vannusals dimeric terpenoids. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2007, 31, 5226–5234. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Ortiz, A; Zhang, H. The true structures of the vannusals, part 2: Total synthesis and revised structure of vannusal b. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2009, 48, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Zhang, H; Ortiz, A. The true structures of the vannusals, part 1: Initial forays into suspected structures and intelligence gathering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2009, 48, 5642–5647. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Zhang, H; Ortiz, A; Dagneau, P. Total synthesis of the originally assigned structure of vannusal B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 8605–8610. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Tang, W; Dagneau, P; Faraoni, R. A catalytic asymmetric three-component 1,4-addition/aldol reaction: Enantioselective synthesis of the spirocyclic system of vannusal A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2005, 44, 3874–3879. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Jennings, MP; Dagneau, P. An expedient entry into the fused polycyclic skeleton of vannusal A. Chem. Commun 2002, 8, 2480–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Ortiz, A; Zhang, H; Dagneau, P; Lanver, A; Jennings, MP; Arseniyadis, S; Faraoni, R; Lizos, DE. Total synthesis and structural revision of vannusal A and B: synthesis of the originally assigned structure of vannusal B. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 7138–7152. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou, KC; Ortiz, A; Zhang, H; Guella, G. Total synthesis and structural revision of vannusal A and B: synthesis of the true structures of vannusal B. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 7153–7176. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ; Fenical, W. Bioactive terpenoids from caribbean marine-algae of the genera Penicillus and Udotea (Chlorophyta). Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2913–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorusso, E; Magno, S; Mayol, L; Novellino, F. Petiodial, a new monocyclic diterpenoid from the mediterranean green-alga Udotea-petiolata. Experientia 1983, 39, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Snider, BB. Fleming, I, Ed.; Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1991; Volume 2, p. 527. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Pietra, F. Rarisetenolide, epoxyrarisetenolide, and epirarisetenolide, new-skeleton sesquiterpene lactones as taxonomic markers and defensive agents of the marine ciliated morphospecies Euplotes rariseta. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 2180–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Guella, G; Dini, F; Pietra, F. Epoxyfocardin and its putative biogenetic precursor, focardin, bioactive, new-skeleton diterpenoids of the marine ciliate Euplotes focardii from Antarctica. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Pietra, F. Evolution of the secondary metabolite versus evolution of the species. Pure Appl. Chem 2002, 74, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ; Puglisi, MP; Ritson-Williams, R. Marine chemical ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep 2006, 23, 153–180. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, V; Pohnert, W. Rapid wound-activated transformation of the green algal defensive metabolites caulerpenyne. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 7169–7172. [Google Scholar]
- Gavagnin, M; Fontana, A. Diterpenes from maribe opisthobranch mollusks. Curr. Org. Chem 2000, 4, 1201–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, MA; Clardy, J. One pathway, many products. Nature Chem. Biol 2007, 3, 353–355. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, MJ; Williams, DH. On the evolution of functional secondary metabolites (natural products). Mol. Microbiol 1992, 6, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, DH; Stone, MJ; Hauck, PR; Rahman, SK. Why are secondary metabolites (natural products) biosynthesized? J. Nat. Prod 1989, 52, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Firn, RD; Jones, CG. The evolution of secondary metabolism-a unifying model. Mol. Microbiol 2000, 37, 989–994. [Google Scholar]
- Firn, RD; Jones, CG. Natural products–a simple model to explain chemical diversity. Nat. Prod. Rep 2003, 20, 382–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lesburg, CA; Caruthers, JM; Paschall, CM; Christianson, DW. Managing and manipulating carbocations in biology: Terpenoid cyclase structure and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 1998, 8, 695–703. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, EM; Croteau, R. Cyclization enzymes in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and diterpenes. In Biosynthesis Aromatic Polyketides Isoprenoids Alkaloids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; Volume 209, pp. 53–95. [Google Scholar]
























© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Guella, G.; Skropeta, D.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Dini, F. Structures, Biological Activities and Phylogenetic Relationships of Terpenoids from Marine Ciliates of the Genus Euplotes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2080-2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8072080
Guella G, Skropeta D, Di Giuseppe G, Dini F. Structures, Biological Activities and Phylogenetic Relationships of Terpenoids from Marine Ciliates of the Genus Euplotes. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(7):2080-2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8072080
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuella, Graziano, Danielle Skropeta, Graziano Di Giuseppe, and Fernando Dini. 2010. "Structures, Biological Activities and Phylogenetic Relationships of Terpenoids from Marine Ciliates of the Genus Euplotes" Marine Drugs 8, no. 7: 2080-2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8072080
APA StyleGuella, G., Skropeta, D., Di Giuseppe, G., & Dini, F. (2010). Structures, Biological Activities and Phylogenetic Relationships of Terpenoids from Marine Ciliates of the Genus Euplotes. Marine Drugs, 8(7), 2080-2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8072080




