Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins Isolated from the Octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of San Andrés and Providencia Islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cytotoxic Activity
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Octocoral Collection
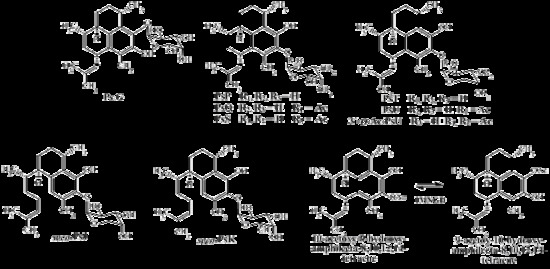
3.3. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Compounds from P. elisabethae
3.4. Cell Lines
3.5. Cytotoxic Assay
3.6. Microbial Strains and Culture Media
3.7. Antimicrobial Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Marrero, J; Rodriguez, II; Rodriguez, AD. The natural products chemistry of the gorgonian genus Pseudopterogorgia (Octocorallia:Gorgoniidae). In Comprehensive Natural Products II: Chemistry and Biology, 1st ed; Mander, L, Liu, H-W, Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 363–428. [Google Scholar]
- Heckrodt, TJ; Mulzer, J. Marine Natural Products from Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae: structures, biosynthesis, pharmacology, and total synthesis. In Natural Products Synthesis II, 1st ed; Mulzer, J, Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 244, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Look, SA; Fenical, W; Jacobs, RS; Clardy, J. The pseudopterosins: anti-inflammatory and analgesic natural products from the sea whip Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986, 83, 6238–6240. [Google Scholar]
- Roussis, V; Wu, Z; Fenical, W; Strobel, SA; van-Duyne, D; Clardy, J. New antiinflammatory pseudopterosins from the marine octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. J Org Chem 1990, 55, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar]
- Ata, A; Win, HY; Holt, D; Holloway, P; Segstro, EP; Jayatilake, GS. New antibacterial diterpenes from Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Helv Chim Acta 2004, 87, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Hoarau, C; Day, D; Moya, C; Wu, G; Hackim, A; Jacobs, RS; Little, RD. iso-PsE, a new pseudopterosin. Tetrahedron Lett 2008, 49, 4604–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, C; Puyana, M; Narvaez, G; Paz, A; Osorno, O; Hara, N; Fujimoto, Y. Pseudopterosins P-V.New compounds from the gorgonian octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae from Providencia Island, Colombian Caribbean. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 10627–10635. [Google Scholar]
- Ata, A; Kerr, RG; Moya, CE; Jacobs, RS. Identification of anti-inflammatory diterpenes from the marine gorgonian Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar]
- Puyana, M; Narvaez, G; Paz, A; Osorno, O; Duque, C. Pseudopterosin content variability of the purple sea whip Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae at the Islands of San Andrés and Providencia (SW Caribbean). J Chem Ecol 2004, 30, 1183–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, C; Puyana, M; Castellanos, L; Arias, A; Correa, H; Osorno, O; Asai, T; Hara, N; Fujimoto, Y. Further studies on the constituents of gorgonian octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae collected in San Andrés and Providencia islands, Colombian Caribbean: isolation of a putative biosynthetic intermediate leading to erogorgiane. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, II; Shi, Y-P; García, OJ; Rodríguez, AD; Mayer, AMS; Sánchez, JA; Ortega, E; González, J. New pseudopterosin and seco-pseudopterosin diterpene glycosides from two Colombian isolates of Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae and their diverse biological activities. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Look, SA; Fenical, W. The seco-pseudopterosins: new anti-inflammatory diterpene-glycosides from a Caribbean gorgonian octocoral of the genus Pseudopterogorgia. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 3363–3370. [Google Scholar]
- Ferns, TA; Kerr, RG. Identification of amphilectosins as key intermediates in pseudopterosin biosynthesis. J Org Chem 2005, 70, 6152–6152. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, C. Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae de San Andrés y Providencia, una pluma de mar con excelente potencial como fuente de productos naturales con aplicación industrial. Rev Acad Colomb Cienc 2010, 34, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, BC; Faulkner, DJ. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors from marine organisms. J Nat Prod 1992, 55, 1707–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Jacobson, PB; Fenical, W; Jacobs, RS; Glaser, KB. Pharmacological characterization of the pseudopterosins: novel anti-inflammatory natural products isolated from the Caribbean soft coral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Life Sci 1998, 62, PL 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kijoa, A; Sawanwong, P. Drugs and cosmetics from the sea. Mar Drugs 2004, 2, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, H; König, GM. Terpenoids from marine organisms: unique structures and their pharmacological potential. Phytochem Rev 2006, 5, 115–141. [Google Scholar]
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Glaser, KB; Cuevas, C; Jacobs, RS; Kem, W; Little, RD; McIntosh, JM; Newman, DJ; Potts, B; Shuster, DE. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: a current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, H; Valenzuela, AL; Ospina, LF; Duque, C. Anti-inflammatory effects of the gorgonian Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae collected at the Islands of Providencia and San Andrés (SW Caribbean). J Inflamm 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, TJ. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bugelski, PJ; Atif, U; Molton, S; Toeg, I; Lord, PG; Morgan, G. A strategy for primary high throughput cytotoxicity screening in pharmaceutical toxicology. Pharm Res 2000, 17, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Vasková, Z; Stachová, P; Krupkováa, L; Hudecováa, D; Valigura, D. Bis(nitrobenzoato)copper(II) complexes with nicotinamide, preparation, structure and properties. Acta Chim Slov 2009, 2, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, LHG; Greenway, DLA; Gaylarde, CC; Surman, SB. Consideration of some implications of the resistance of biofilms to biocides. Int Biodeter Biodegr 1998, 41, 247–259. [Google Scholar]

| Compounds | GI50 ± S.E (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | PC-3 | HCT116 | MCF7 | BJ | |
| PsG | 9.22 ± 0.45 | 8.83 ± 0.54 | 12.04 ± 0.36 | 9.42 ± 0.43 | 7.62 ± 0.38 |
| PsP | 10.31 ± 0.49 | 13.77 ± 0.58 | 17.89 ± 0.45 | 12.58 ± 0.45 | 10.40 ± 0.42 |
| PsQ | 5.82 ± 0.33 | 7.81 ± 0.35 | 7.66 ± 0.27 | 8.44 ± 0.41 | 4.47 ± 0.31 |
| PsS | 13.79 ± 0.39 | 52.05 ± 0.31 | 33.50 ± 0.33 | 26.25 ± 0.45 | 29.14 ± 0.45 |
| PsT | 14.58 ± 0.35 | 21.99 ± 0.46 | 24.24 ± 0.42 | 14.72 ± 0.46 | 12.94 ± 0.37 |
| PsU | 15.63 ± 0.32 | 24.81 ± 0.34 | 23.44 ± 0.40 | 26.46 ± 0.46 | 9.35 ± 0.34 |
| 3-O-Ac-PsU | 44.61 ± 0.35 | 26.45 ± 0.31 | 20.48 ± 0.48 | 83.93 ± 0.39 | 62.03 ± 0.45 |
| seco-PsJ | 21.08 ± 0.37 | 37.21 ± 0.41 | 31.68 ± 0.32 | 28.02 ± 0.51 | 15.00 ± 0.35 |
| seco-PsK | 15.83 ± 0.18 | 13.57 ± 0.38 | 13.28 ± 0.27 | 11.45 ± 0.36 | 8.28 ± 0.29 |
| IMNGD* | 11.20 ± 0.15 | 12.11 ± 0.20 | 19.90 ± 0.19 | 9.67 ± 0.15 | 7.91 ± 0.17 |
| Staurosporine** | 105.6 ± 0.41 | 61.82 ± 0.38 | 45.56 ± 0.45 | 176.6 ± 0.38 | 13.56 ± 0.35 |
| Compounds | IC50 ± S.E (μM) * | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | |
| PsG | 4.48 ± 0.18 | 3.14 ± 0.22 |
| PsP | 14.91 ± 0.20 | 37.35 ± 0.29 |
| PsQ | 3.30 ± 0.20 | 7.38 ± 0.16 |
| PsS | 3.89 ± 0.23 | 20.20 ± 0.25 |
| PsT | 5.39 ± 0.25 | 4.38 ± 0.16 |
| PsU | 2.97 ± 0.17 | 3.19 ± 0.25 |
| 3-O-Ac-PsU | 20.23 ± 0.19 | 7.64 ± 0.16 |
| seco-PsJ | 6.52 ± 0.12 | 4.08 ± 0.19 |
| seco-PsK | 4.20 ± 0.16 | 3.82 ± 0.21 |
| IMNGD** | 2.33 ± 0.09 | 3.47 ± 0.15 |
| Penicillin G | 1.61 ± 0.08 | - |
| Vancomycin | - | 4.21 ± 0.11 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Correa, H.; Aristizabal, F.; Duque, C.; Kerr, R. Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins Isolated from the Octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of San Andrés and Providencia Islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea). Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 334-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9030334
Correa H, Aristizabal F, Duque C, Kerr R. Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins Isolated from the Octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of San Andrés and Providencia Islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea). Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(3):334-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrea, Hebelin, Fabio Aristizabal, Carmenza Duque, and Russell Kerr. 2011. "Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins Isolated from the Octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of San Andrés and Providencia Islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea)" Marine Drugs 9, no. 3: 334-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9030334
APA StyleCorrea, H., Aristizabal, F., Duque, C., & Kerr, R. (2011). Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins Isolated from the Octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of San Andrés and Providencia Islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea). Marine Drugs, 9(3), 334-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9030334