EEG-Based Person Identification during Escalating Cognitive Load
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study presents a biometric identification method based on a novel paradigm with unique data for EEG-based person identification. A unique set of EEG data was used, which covers the entire spectrum of the brain load from when the subject was relaxed with closed eyes to solving a difficult task.
- The ability to identify a person was investigated separately for no brain load, low, medium, and high loads, and the combination of these loads with high accuracy.
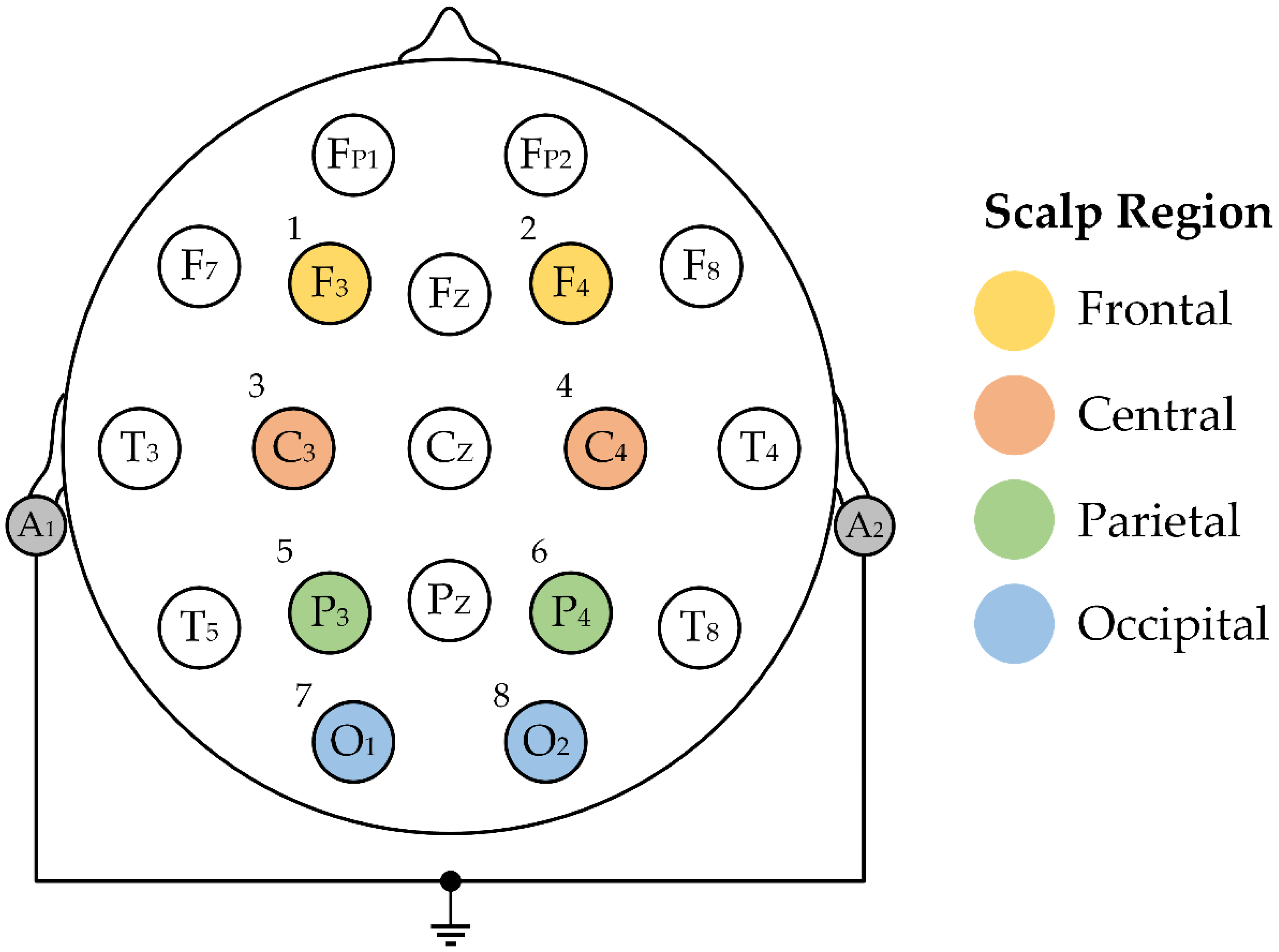
- This research deals with modeling the effects of reducing channel numbers by using a relatively low number of achieved channels, in comparison to person identification accuracy with other studies using a larger number of channels. This can lead to a reduction in cost and time funding in the real-life adoption of the proposed approach.
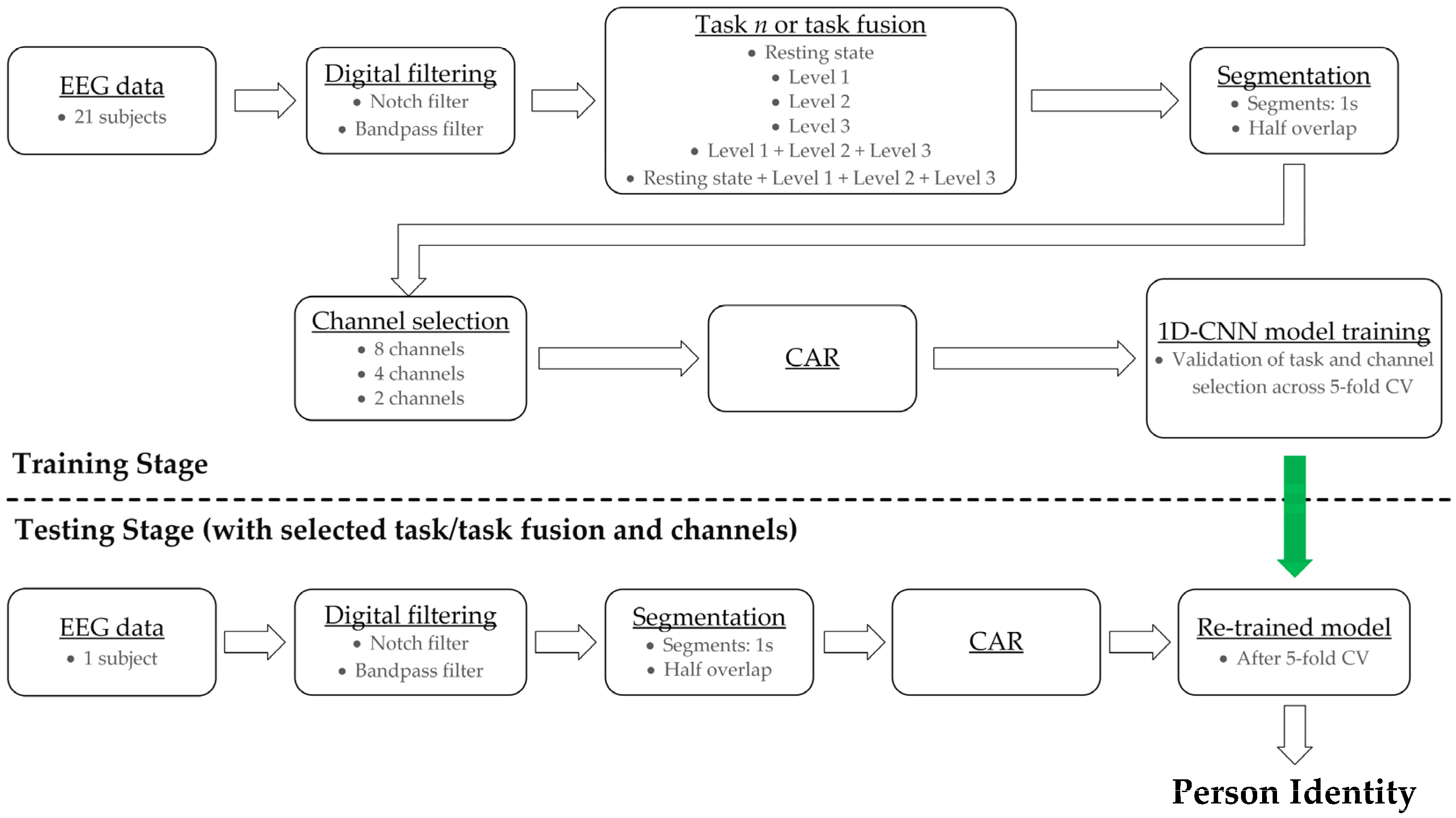
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EEG Data
- Task 1: Close eyes for approximately 60 s;
- Task 2: The first level (easy) of the serious game;
- Task 3: The second level (medium) of the serious game;
- Task 4: The third level (hard) of the serious game. Eight students were unable to complete this level, so the end of the game was subsequently considered the end of this task in all cases.
2.2. Serious Game
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
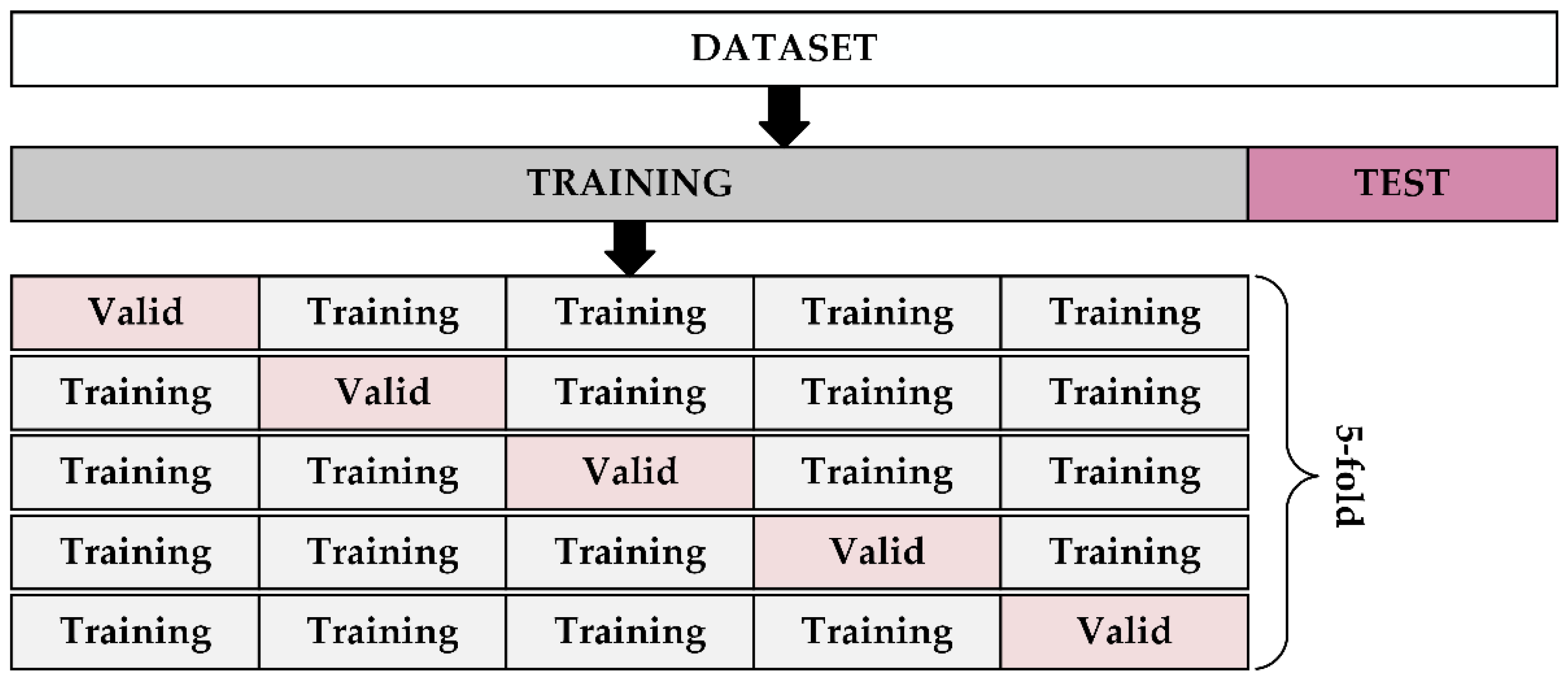
2.4. Dataset Preparation
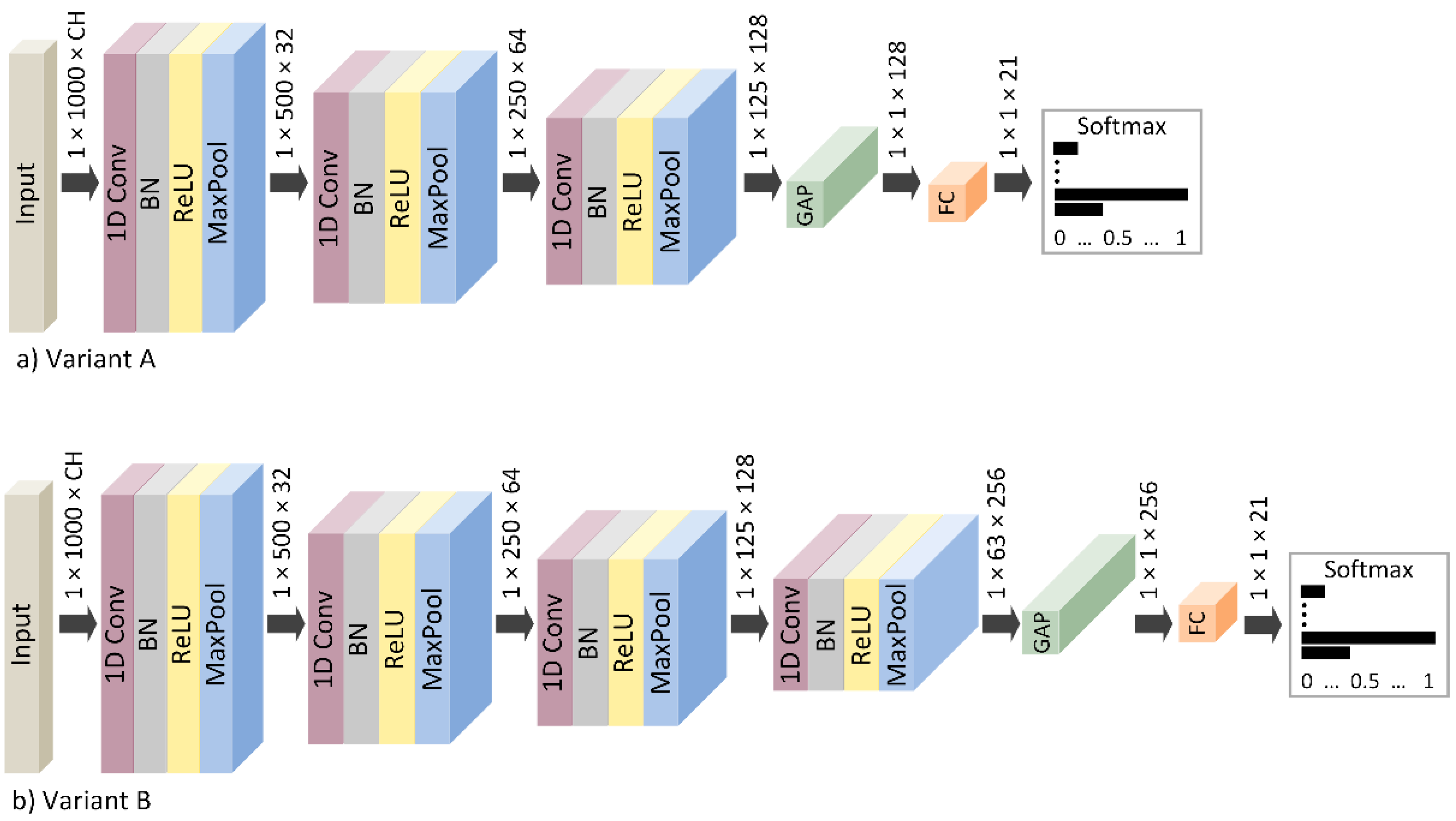
2.5. Feature Extraction and Classification
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouamo, S.; Tangha, C. Fingerprint Recognition with Artificial Neural Networks: Application to E-Learning. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2016, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, R.; Lu, J.; Tan, Y.P. Robust Point Set Matching for Partial Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Hand Image Biometric Based Personal Authentication System. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2017, 660, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirchi, V.R.E.; Waghmare, L.M.; Chirchi, E.R. Iris Biometric Recognition for Person Identification in Security Systems. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, M.; Krishnakumari, K. A Novel Retina Based Biometric Privacy Using Visual Cryptography. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2016, 16, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowski, M.; Sroczyński, A.; Bogdanis, G.; Czyżewski, A. An Automated Method for Biometric Handwritten Signature Authentication Employing Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.N.M.; Ab Rashid, M.Z.; Abdollah, M.F.; Kamarudin, M.N.; Lin, C.K.; Kamis, Z. Biometric Voice Recognition in Security System. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, L.R.; Bhavani, D.R. Bhavani Biometric Authorization System Using Gait Biometry. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1108.6294. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, M.O.; Seif, A.; Sabbah, M.; El-Abed, M.; Aloulou, N. A Review on ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Systems. In Hidden Biometrics; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Raurale, S.A.; McAllister, J.; del Rincon, J.M. EMG Biometric Systems Based on Different Wrist-Hand Movements. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 12256–12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zahhad, M.; Ahmed, S.M.; Abbas, S.N. A Novel Biometric Approach for Human Identification and Verification Using Eye Blinking Signal. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, R.B.; Mahovsky, J.; Benedicenti, L.; Koles, Z. The Electroencephalogram as a Biometric. Can. Conf. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2001, 2, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F.; Sree, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ng, K.H.; Suri, J.S. Automated Diagnosis of Epileptic EEG Using Entropies. Biomed. Signal Process Control 2012, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzallas, A.T.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Fotiadis, D.I. Epileptic Seizure Detection in EEGs Using Time-Frequency Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiouris, Κ.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Zervakis, M.; Konitsiotis, S.; Koutsouris, D.D.; Fotiadis, D.I. A Long Short-Term Memory Deep Learning Network for the Prediction of Epileptic Seizures Using EEG Signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 99, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Park, S.J. HealthSOS: Real-Time Health Monitoring System for Stroke Prognostics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 213574–213586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.A.; Park, S.J.; Jun, J.A.; Pyo, C.S.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Yu, J.H. Deep Learning-Based Stroke Disease Prediction System Using Real-Time Bio Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeibi, A.; Sadeghi, D.; Moridian, P.; Ghassemi, N.; Heras, J.; Alizadehsani, R.; Khadem, A.; Kong, Y.; Nahavandi, S.; Zhang, Y.D.; et al. Automatic Diagnosis of Schizophrenia in EEG Signals Using CNN-LSTM Models. Front. Neuroinform. 2021, 15, 777977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, M.S.; Safi, S.M.M. Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease from EEG Signals Using Hjorth Parameters. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 65, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Raghavendra, U.; Yuvaraj, R.; Arunkumar, N.; Murugappan, M.; Acharya, U.R. A Deep Learning Approach for Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis from EEG Signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10927–10933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, H. Automatic Identification of Insomnia Based on Single-Channel EEG Labelled with Sleep Stage Annotations. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 104281–104291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, R.; Tang, N.; Chew, E.; Chua, K.S.G.; Ang, K.K.; Quek, C.; Guan, C.; Phua, K.S.; Kuah, C.W.K.; Deshmukh, V.A.; et al. Assessment of the Efficacy of EEG-Based MI-BCI with Visual Feedback and EEG Correlates of Mental Fatigue for Upper-Limb Stroke Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarou, I.; Nikolopoulos, S.; Petrantonakis, P.C.; Kompatsiaris, I.; Tsolaki, M. EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces for Communication and Rehabilitation of People with Motor Impairment: A Novel Approach of the 21st Century. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.S.; Chen, J.L.; Hsu, H.C. Novel Upper-Limb Rehabilitation System Based on Attention Technology for Post-Stroke Patients: A Preliminary Study. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 2720–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Lian, J.; Jie, K.; Lai, R.; Liu, Y. A Speed and Direction-Based Cursor Control System with P300 and SSVEP. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 14, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Chung, W.Y. A Single-Channel SSVEP-Based BCI Speller Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Hong, K.; Zhang, L. Design of Assistive Wheelchair System Directly Steered by Human Thoughts. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2013, 23, 1350013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.K.; Chaurasiya, R.K.; Verma, S. Performance Improvement of P300-Based Home Appliances Control Classification Using Convolution Neural Network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Hossain, M.A.; Jany, R.; Bari, M.A.; Uddin, M.; Kamal, A.R.M.; Ku, Y.; Kim, J.-S. Quantitative Evaluation of EEG-Biomarkers for Prediction of Sleep Stages. Sensors 2022, 22, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Young, S.; Park, S.J. Driving-Induced Neurological Biomarkers in an Advanced Driver-Assistance System. Sensors 2021, 21, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Bhardwaj, S.; Agarwal, R. Classification of EEG Signals Using Hybrid Combination of Features for Lie Detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Young, S.; Kim, C.H.; Benjamin, H.C.M.; Park, S.J. Quantifying Physiological Biomarkers of a Microwave Brain Stimulation Device. Sensors 2021, 21, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Kuo, P.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chen, Y.S. Challenges and Future Perspectives on Electroencephalogram-Based Biometrics in Person Recognition. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Abbass, H.A. BrainPrint: EEG Biometric Identification Based on Analyzing Brain Connectivity Graphs. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 105, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, R.; Mandic, D.P. Biometrics from Brain Electrical Activity: A Machine Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Minett, J.W.; Blu, T.; Wang, W.S.Y. Resting State EEG-Based Biometrics for Individual Identification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, Q. CNN-Based Personal Identification System Using Resting State Electroencephalography. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 1160454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lo, F.P.W.; Lo, B. EEG-Based User Identification System Using 1D-Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 125, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moctezuma, L.A.; Torres-García, A.A.; Villaseñor-Pineda, L.; Carrillo, M. Subjects Identification Using EEG-Recorded Imagined Speech. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 118, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.; Jin, Z.; Xu, W. Exploring EEG-Based Biometrics for User Identification and Authentication. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium, IEEE SPMB 2014-Proceedings, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarathne, I.; Cohen, M.; Amarakeerthi, S. BrainID: Development of an EEG-Based Biometric Authentication System. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference, IEEE IEMCON 2016, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 13–15 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.Y.; Choo, Y.H.; Mohd Yusoh, Z.I.; Khoh, W.H. Person Authentication Based on Eye-Closed and Visual Stimulation Using EEG Signals. Brain Inf. 2021, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas Seha, S.N.; Hatzinakos, D. A New Approach for EEG-Based Biometric Authentication Using Auditory Stimulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Biometrics, ICB 2019, Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Attallah, O. Multi-Tasks Biometric System for Personal Identification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-22nd IEEE International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering and 17th IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing, CSE/EUC 2019, New York, NY, USA, 1–3 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hema, C.R.; Elakkiya, A.; Paulraj, M.P. Biometric Identification Using Electroencephalography. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 106, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zeynali, M.; Seyedarabi, H. EEG-Based Single-Channel Authentication Systems with Optimum Electrode Placement for Different Mental Activities. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babusiak, B.; Hostovecky, M.; Smondrk, M.; Huraj, L. Spectral Analysis of Electroencephalographic Data in Serious Games. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Medical Instrumentation: Application and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon, S.P.; Pope, K.J.; MacKenzie, L.; Clark, C.R.; Willoughby, J.O. Cognitive Tasks Augment Gamma EEG Power. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moctezuma, L.A.; Molinas, M. Towards a Minimal EEG Channel Array for a Biometric System Using Resting-State and a Genetic Algorithm for Channel Selection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seha, S.N.A.; Hatzinakos, D. EEG-Based Human Recognition Using Steady-State AEPs and Subject-Unique Spatial Filters. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3901–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Atnafu, A.D.; Schlattner, I.; Weldtsadik, W.T.; Roh, M.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Blankertz, B.; Fazli, S. A High-Security EEG-Based Login System with RSVP Stimuli and Dry Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 2635–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, C.M.; Grace Mary Kanaga, E. Probing on Classification Algorithms and Features of Brain Signals Suitable for Cancelable Biometric Authentication. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, ICCIC 2017, Coimbatore, India, 14–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Y.; An, X.; Zhong, W.; Liu, S.; Ming, D. The Time-Robustness Analysis of Individual Identification Based on Resting-State EEG. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, H.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, L.; Wan, B.; Wang, C.; et al. Individual Feature Extraction and Identification on EEG Signals in Relax and Visual Evoked Tasks. In Proceedings of the Communications in Computer and Information Science, Aizu-Wakamatsu, Japan, 16–17 September 2013; Volume 404. [Google Scholar]
- Schons, T.; Moreira, G.J.P.; Silva, P.H.L.; Coelho, V.N.; Luz, E.J.S. Convolutional Network for EEG-Based Biometric. In Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics, Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Valparaíso, Chile, 7–10 November 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10657 LNCS. [Google Scholar]
- Arnau-González, P.; Katsigiannis, S.; Ramzan, N.; Tolson, D.; Arevalillo-Herráez, M. ES1D: A Deep Network for EEG-Based Subject Identification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, BIBE 2017, Washington, DC, USA, 23–25 October 2017; Volume 2018-January. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Saini, R.; Kaur, B.; Roy, P.P.; Scheme, E. Fusion of Neuro-Signals and Dynamic Signatures for Person Authentication. Sensors 2019, 19, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilaiprasitporn, T.; Ditthapron, A.; Matchaparn, K.; Tongbuasirilai, T.; Banluesombatkul, N.; Chuangsuwanich, E. Affective EEG-Based Person Identification Using the Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 12, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, E. Learning Deep Features for Task-Independent EEG-Based Biometric Verification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 143, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, Ö.; Tosun, M. Biometric Authentication from Photic Stimulated EEG Records. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wei, C.S.; Chiang, K.J.; Nakanishi, M.; Jung, T.P. EEG-Based User Authentication Using a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, NER, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–23 March 2019; Volume 2019-March. [Google Scholar]
- Jijomon, C.M.; Vinod, A.P. Person-Identification Using Familiar-Name Auditory Evoked Potentials from Frontal EEG Electrodes. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandini, M.; Bagli, E.; Visani, G. Metrics for Multi-Class Classification: An Overview. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.05756. [Google Scholar]
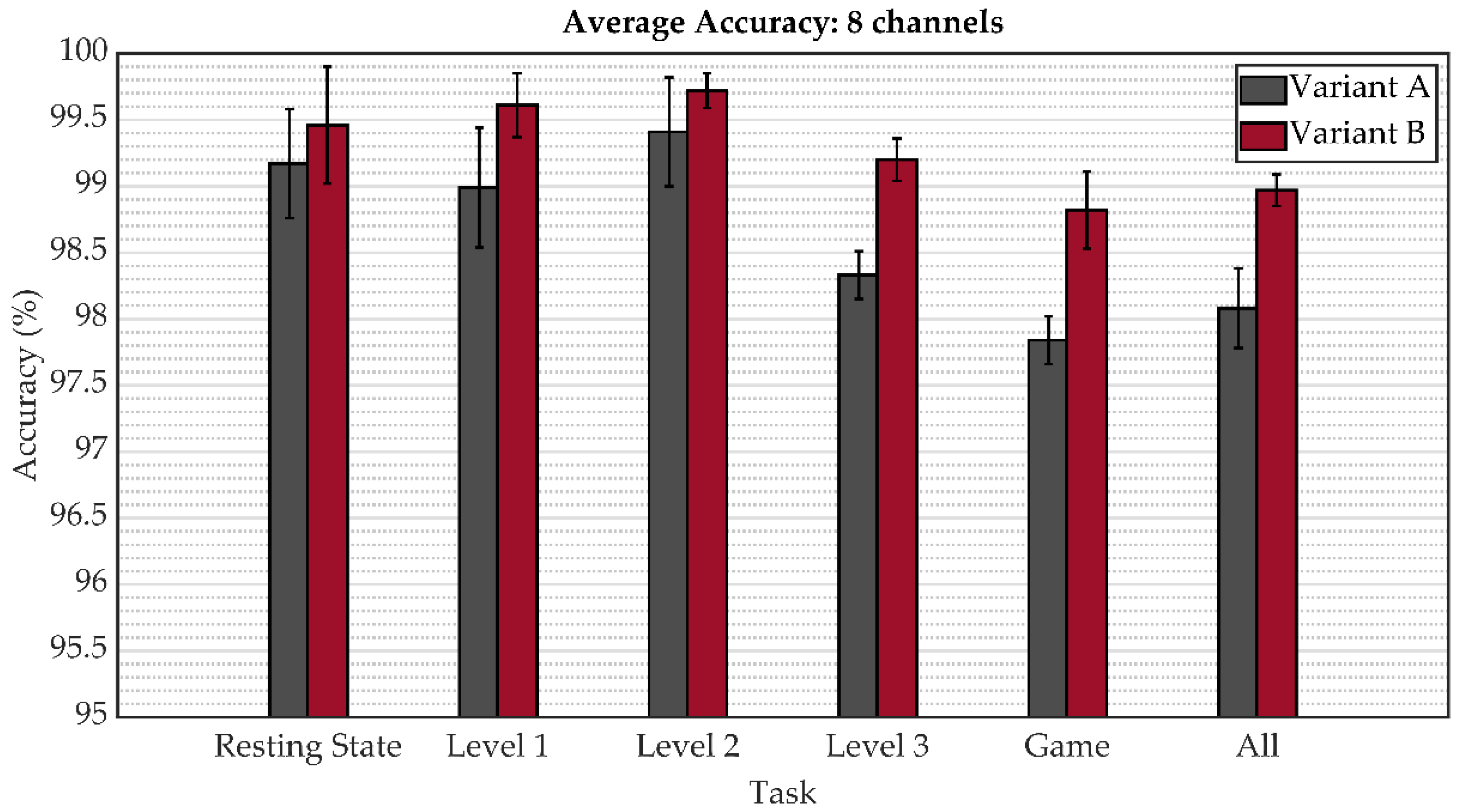
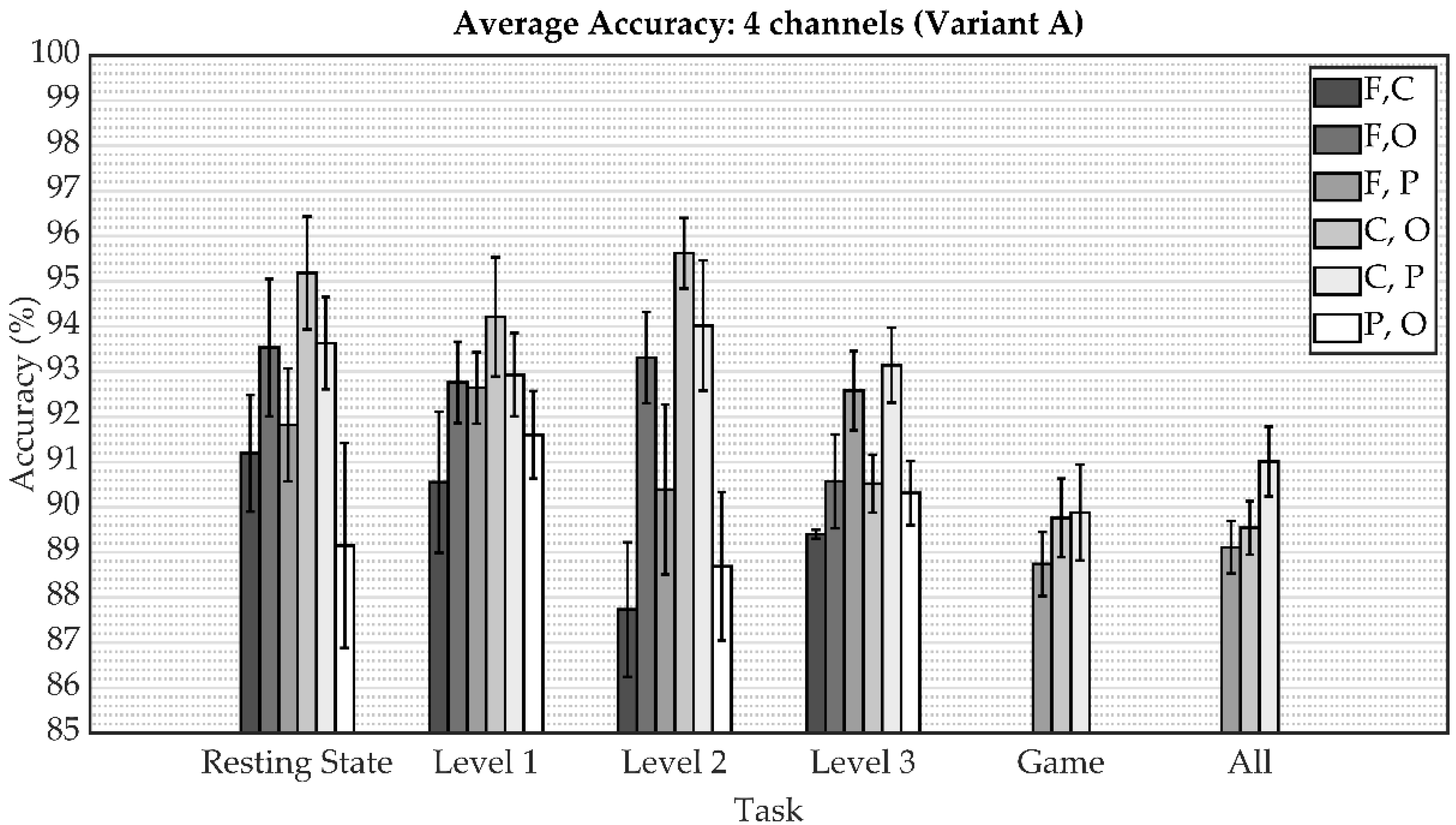

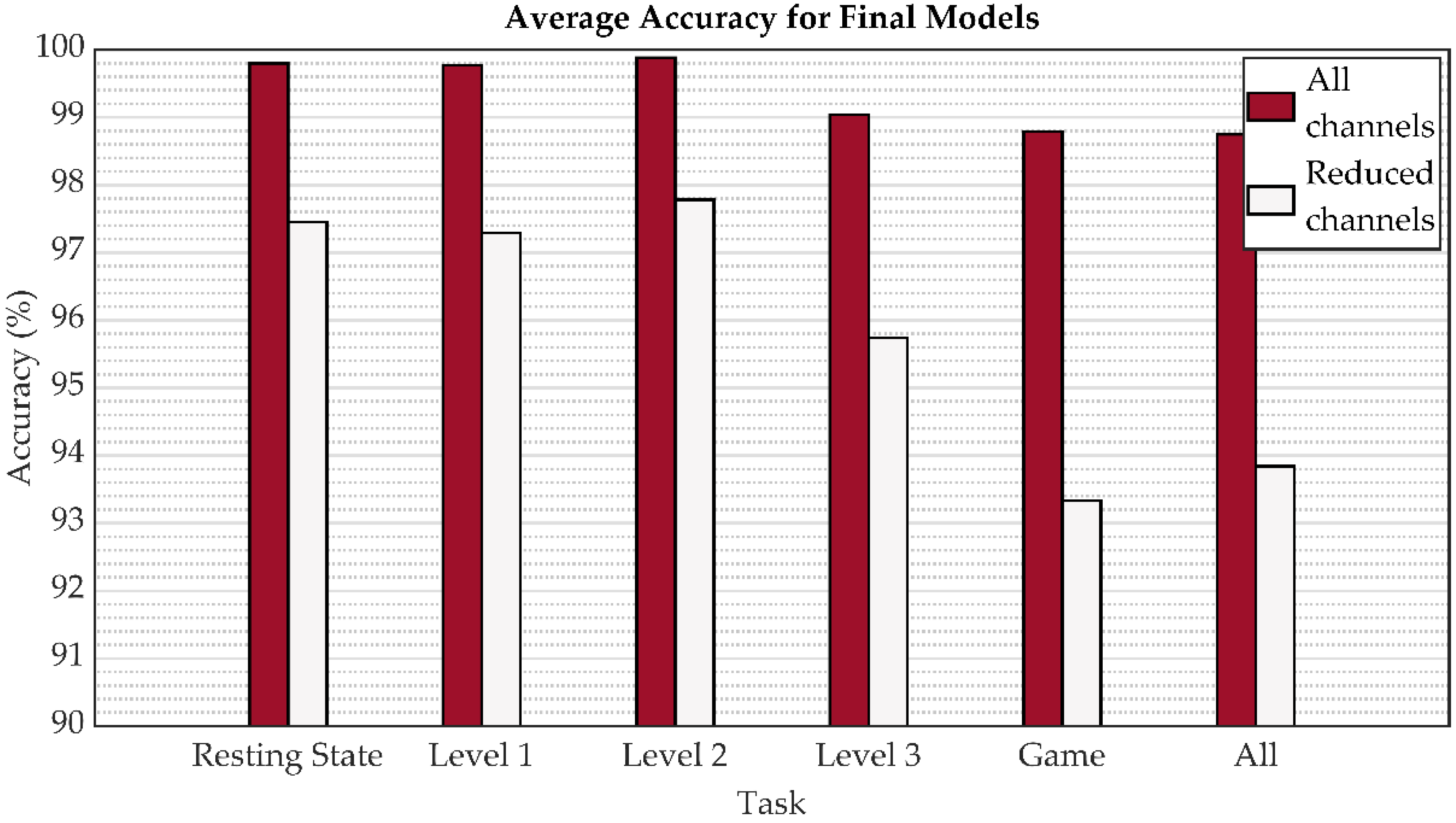
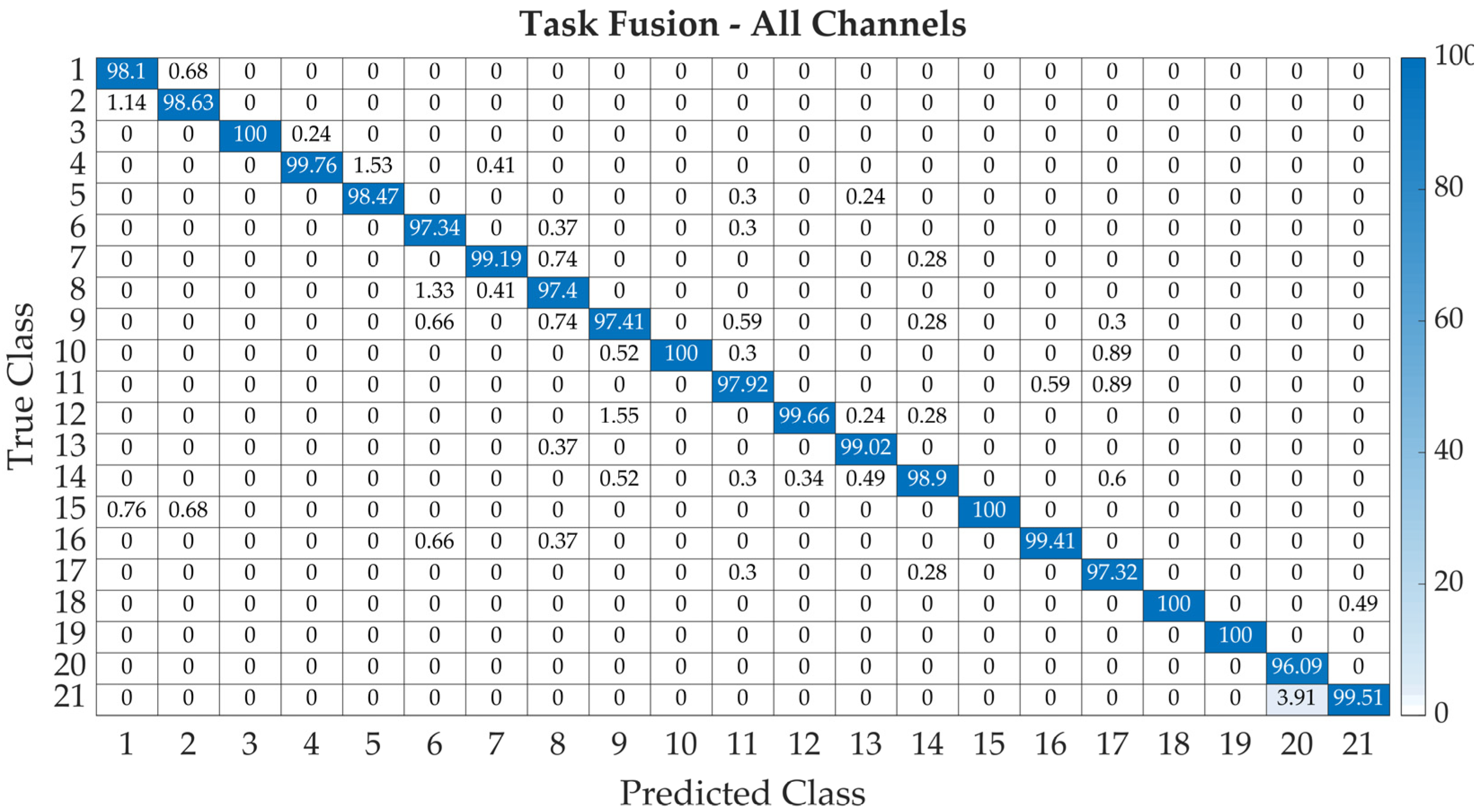
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 99.17 ± 0.41 | 99.13 ± 0.37 | 99.32 ± 0.31 | 99.22 ± 0.34 | 99.46 ± 0.44 | 99.37 ± 0.61 | 99.53 ± 0.35 | 99.45 ± 0.44 |
| F, C | 91.19 ± 1.29 | 91.43 ± 1.27 | 91.40 ± 1.63 | 91.41 ± 1.43 | 96.40 ± 0.85 | 96.47 ± 0.76 | 96.46 ± 0.62 | 96.46 ± 0.68 |
| F, O | 93.53 ± 1.52 | 93.68 ± 1.46 | 93.67 ± 1.27 | 93.67 ± 1.36 | 97.32 ± 0.67 | 97.41 ± 0.72 | 97.39 ± 0.59 | 97.40 ± 0.65 |
| F, P | 91.82 ± 1.25 | 92.10 ± 1.67 | 91.84 ± 1.65 | 91.97 ± 1.66 | 96.01 ± 1.94 | 95.93 ± 1.97 | 96.20 ± 1.76 | 96.06 ± 1.86 |
| C, O | 95.18 ± 1.25 | 95.17 ± 1.22 | 95.23 ± 1.24 | 95.20 ± 1.23 | 97.52 ± 1.01 | 97.45 ± 1.02 | 97.58 ± 1.00 | 97.51 ± 1.01 |
| C, P | 93.63 ± 1.02 | 94.04 ± 0.92 | 93.79 ± 1.35 | 93.91 ± 1.09 | 97.37 ± 0.92 | 97.31 ± 0.88 | 97.54 ± 0.84 | 97.42 ± 0.86 |
| P, O | 89.15 ± 2.27 | 89.93 ± 2.06 | 89.15 ± 2.13 | 89.54 ± 2.09 | 95.38 ± 1.39 | 95.47 ± 1.21 | 95.69 ± 1.37 | 95.58 ± 1.29 |
| F | 57.86 ± 2.77 | 56.81 ± 2.93 | 57.29 ± 2.51 | 57.05 ± 2.70 | 64.28 ± 3.45 | 63.50 ± 3.66 | 64.02 ± 3.48 | 63.76 ± 3.57 |
| C | 60.19 ± 2.89 | 61.14 ± 3.88 | 59.69 ± 2.81 | 60.41 ± 3.26 | 69.83 ± 1.05 | 70.40 ± 1.20 | 69.95 ± 0.50 | 70.17 ± 0.71 |
| P | 58.83 ± 4.34 | 61.43 ± 4.01 | 59.05 ± 4.35 | 60.22 ± 4.17 | 67.25 ± 1.11 | 68.64 ± 2.65 | 67.47 ± 1.41 | 68.05 ± 1.84 |
| O | 59.17 ± 2.84 | 58.51 ± 2.95 | 58.96 ± 2.48 | 58.73 ± 2.69 | 65.45 ± 2.06 | 65.94 ± 1.60 | 65.03 ± 1.26 | 65.48 ± 1.41 |
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 98.99 ± 0.45 | 99.02 ± 0.45 | 98.92 ± 0.33 | 98.97 ± 0.38 | 99.61 ± 0.24 | 99.53 ± 0.38 | 99.57 ± 0.21 | 99.55 ± 0.27 |
| F, C | 90.55 ± 1.56 | 90.69 ± 1.34 | 89.24 ± 1.79 | 89.96 ± 1.53 | 94.40 ± 1.29 | 94.23 ± 1.73 | 93.58 ± 1.39 | 93.90 ± 1.54 |
| F, O | 92.76 ± 0.90 | 92.36 ± 0.89 | 91.72 ± 0.92 | 92.04 ± 0.90 | 95.99 ± 0.54 | 95.49 ± 0.81 | 95.18 ± 0.56 | 95.33 ± 0.66 |
| F, P | 92.64 ± 0.79 | 92.61 ± 1.03 | 92.73 ± 0.86 | 92.67 ± 0.94 | 96.11 ± 0.68 | 95.88 ± 0.91 | 95.98 ± 0.86 | 95.93 ± 0.88 |
| C, O | 94.21 ± 1.32 | 93.87 ± 1.50 | 93.62 ± 1.66 | 93.74 ± 1.58 | 96.50 ± 0.86 | 96.49 ± 0.94 | 96.07 ± 1.12 | 96.28 ± 1.02 |
| C, P | 92.93 ± 0.92 | 93.53 ± 0.85 | 93.14 ± 0.91 | 93.33 ± 0.88 | 96.71 ± 0.67 | 96.81 ± 0.95 | 96.75 ± 0.40 | 96.78 ± 0.56 |
| P, O | 91.60 ± 0.97 | 91.84 ± 1.09 | 90.19 ± 1.05 | 91.01 ± 1.07 | 95.45 ± 0.27 | 95.47 ± 0.50 | 94.62 ± 0.49 | 95.04 ± 0.49 |
| F | 56.05 ± 1.74 | 51.55 ± 2.15 | 49.87 ± 1.65 | 50.70 ± 1.87 | 61.22 ± 1.80 | 59.36 ± 1.53 | 56.17 ± 2.05 | 57.72 ± 1.75 |
| C | 57.56 ± 1.94 | 56.52 ± 1.93 | 53.62 ± 2.13 | 55.03 ± 2.03 | 64.10 ± 1.56 | 62.56 ± 0.98 | 59.80 ± 0.92 | 61.15 ± 0.95 |
| P | 46.82 ± 3.35 | 45.46 ± 3.64 | 40.92 ± 3.19 | 43.07 ± 3.40 | 48.05 ± 3.86 | 48.76 ± 2.62 | 42.24 ± 4.39 | 45.27 ± 3.28 |
| O | 58.61 ± 2.83 | 57.71 ± 1.92 | 53.25 ± 2.46 | 55.39 ± 2.16 | 64.88 ± 1.50 | 64.93 ± 0.89 | 60.47 ± 1.07 | 62.62 ± 0.97 |
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 99.41 ± 0.41 | 99.42 ± 0.49 | 99.24 ± 0.57 | 99.33 ± 0.53 | 99.72 ± 0.13 | 99.67 ± 0.17 | 99.72 ± 0.18 | 99.69 ± 0.17 |
| F, C | 87.73 ± 1.49 | 89.05 ± 0.98 | 85.78 ± 2.18 | 87.38 ± 1.35 | 93.53 ± 0.72 | 93.69 ± 0.59 | 92.27 ± 1.34 | 92.97 ± 0.82 |
| F, O | 93.31 ± 1.01 | 92.63 ± 1.24 | 92.50 ± 1.76 | 92.56 ± 1.45 | 97.32 ± 0.68 | 97.05 ± 0.81 | 97.07 ± 0.94 | 97.06 ± 0.87 |
| F, P | 90.39 ± 1.88 | 90.52 ± 1.51 | 90.17 ± 2.18 | 90.34 ± 1.78 | 96.21 ± 1.22 | 95.68 ± 1.17 | 96.07 ± 1.38 | 95.87 ± 1.27 |
| C, O | 95.62 ± 0.78 | 94.98 ± 0.86 | 94.78 ± 1.05 | 94.88 ± 0.95 | 97.50 ± 0.73 | 97.42 ± 0.75 | 96.90 ± 1.22 | 97.16 ± 0.93 |
| C, P | 94.02 ± 1.44 | 94.17 ± 1.61 | 93.13 ± 1.17 | 93.65 ± 1.36 | 97.44 ± 0.77 | 97.45 ± 0.71 | 97.12 ± 1.34 | 97.28 ± 0.93 |
| P, O | 88.69 ± 1.64 | 88.49 ± 1.34 | 87.45 ± 1.23 | 87.97 ± 1.28 | 94.98 ± 1.80 | 94.41 ± 1.85 | 94.35 ± 2.45 | 94.38 ± 2.11 |
| F | 39.69 ± 4.03 | 39.58 ± 2.05 | 37.39 ± 3.56 | 38.45 ± 2.60 | 45.61 ± 6.16 | 49.87 ± 6.48 | 44.87 ± 6.99 | 47.24 ± 6.73 |
| C | 57.53 ± 1.28 | 57.53 ± 5.04 | 50.15 ± 0.86 | 53.59 ± 1.47 | 65.27 ± 2.47 | 63.87 ± 4.07 | 60.81 ± 2.79 | 62.30 ± 3.31 |
| P | 25.92 ± 2.32 | 27.33 ± 4.52 | 22.51 ± 2.65 | 24.69 ± 3.34 | 26.41 ± 4.15 | 29.97 ± 3.44 | 24.23 ± 3.77 | 26.80 ± 3.60 |
| O | 61.42 ± 2.05 | 60.23 ± 3.01 | 55.27 ± 2.02 | 57.64 ± 2.42 | 67.80 ± 1.71 | 65.04 ± 1.61 | 62.97 ± 2.51 | 63.99 ± 1.96 |
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 98.33 ± 0.18 | 98.29 ± 0.19 | 98.15 ± 0.25 | 98.22 ± 0.22 | 99.20 ± 0.16 | 99.07 ± 0.24 | 99.11 ± 0.19 | 99.09 ± 0.21 |
| F, C | 89.40 ± 0.10 | 89.14 ± 0.60 | 86.73 ± 0.98 | 87.92 ± 0.74 | 93.71 ± 0.57 | 93.19 ± 0.78 | 92.53 ± 0.70 | 92.86 ± 0.74 |
| F, O | 90.57 ± 1.04 | 90.74 ± 0.79 | 89.62 ± 1.05 | 90.18 ± 0.90 | 93.80 ± 0.96 | 93.83 ± 0.77 | 93.33 ± 1.16 | 93.58 ± 0.93 |
| F, P | 92.58 ± 0.88 | 92.27 ± 0.49 | 92.05 ± 0.96 | 92.16 ± 0.65 | 95.84 ± 0.45 | 95.81 ± 0.80 | 95.31 ± 0.72 | 95.56 ± 0.76 |
| C, O | 90.52 ± 0.64 | 91.18 ± 0.73 | 89.81 ± 1.10 | 90.49 ± 0.88 | 93.83 ± 0.79 | 94.17 ± 0.71 | 93.36 ± 0.81 | 93.76 ± 0.76 |
| C, P | 93.14 ± 0.83 | 92.73 ± 1.18 | 92.87 ± 1.32 | 92.80 ± 1.25 | 95.68 ± 0.52 | 95.65 ± 0.59 | 95.57 ± 0.68 | 95.61 ± 0.63 |
| P, O | 90.31 ± 0.71 | 91.10 ± 0.62 | 88.95 ± 0.70 | 90.01 ± 0.66 | 93.98 ± 1.01 | 94.24 ± 1.10 | 93.06 ± 1.33 | 93.65 ± 1.20 |
| F | 53.41 ± 1.82 | 49.70 ± 1.76 | 47.92 ± 1.93 | 48.79 ± 1.84 | 59.86 ± 0.91 | 57.52 ± 0.57 | 55.21 ± 0.77 | 56.34 ± 0.66 |
| C | 57.38 ± 1.78 | 57.60 ± 2.34 | 52.59 ± 1.19 | 54.98 ± 1.58 | 64.80 ± 0.92 | 64.23 ± 1.47 | 60.10 ± 1.02 | 62.10 ± 1.20 |
| P | 48.02 ± 2.84 | 51.53 ± 2.69 | 44.25 ± 2.70 | 47.61 ± 2.69 | 54.13 ± 3.36 | 55.60 ± 3.36 | 49.83 ± 3.17 | 52.56 ± 3.26 |
| O | 53.53 ± 1.34 | 56.26 ± 0.94 | 50.53 ± 2.29 | 53.24 ± 1.33 | 57.61 ± 0.81 | 59.87 ± 0.77 | 55.67 ± 0.74 | 57.69 ± 0.75 |
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 97.84 ± 0.18 | 97.63 ± 0.13 | 97.66 ± 0.31 | 97.64 ± 0.18 | 98.82 ± 0.29 | 98.65 ± 0.26 | 98.77 ± 0.30 | 98.71 ± 0.28 |
| F, P | 88.74 ± 0.71 | 88.70 ± 0.63 | 88.12 ± 0.64 | 88.41 ± 0.63 | 92.58 ± 0.49 | 92.27 ± 0.57 | 92.09 ± 0.46 | 92.18 ± 0.51 |
| C, O | 89.76 ± 0.87 | 89.70 ± 0.86 | 89.18 ± 1.19 | 89.44 ± 1.00 | 91.99 ± 0.67 | 91.81 ± 0.40 | 91.50 ± 0.70 | 91.65 ± 0.51 |
| C, P | 89.88 ± 1.06 | 89.45 ± 0.91 | 89.46 ± 1.09 | 89.45 ± 0.99 | 92.54 ± 0.59 | 92.11 ± 0.83 | 92.12 ± 0.86 | 92.11 ± 0.84 |
| Channels | Variant A | Variant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) | |
| all | 98.08 ± 0.30 | 98.06 ± 0.29 | 98.04 ± 0.32 | 98.05 ± 0.30 | 98.97 ± 0.12 | 98.91 ± 0.18 | 98.93 ± 0.10 | 98.92 ± 0.13 |
| F, P | 89.11 ± 0.58 | 89.30 ± 0.76 | 88.64 ± 0.70 | 88.97 ± 0.73 | 92.40 ± 0.49 | 92.39 ± 0.44 | 91.99 ± 0.60 | 92.19 ± 0.51 |
| C, O | 89.54 ± 0.59 | 89.54 ± 0.62 | 88.88 ± 0.58 | 89.21 ± 0.60 | 92.22 ± 0.86 | 92.15 ± 0.94 | 91.94 ± 0.80 | 92.04 ± 0.86 |
| C, P | 91.01 ± 0.77 | 90.75 ± 0.62 | 90.68 ± 0.73 | 90.71 ± 0.67 | 93.39 ± 0.42 | 93.17 ± 0.45 | 93.09 ± 0.40 | 93.13 ± 0.42 |
| Channels | Task | Average Accuracy (%) | Macro Average Precision (%) | Macro Average Recall (%) | Macro Average F1 Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Resting State | 99.80 | 99.78 | 99.82 | 99.80 |
| Level 1 | 99.77 | 99.67 | 99.70 | 99.68 | |
| Level 2 | 99.88 | 99.83 | 99.74 | 99.78 | |
| Level 3 | 99.04 | 99.00 | 99.09 | 99.04 | |
| Game | 98.79 | 98.79 | 98.72 | 98.75 | |
| Task fusion | 98.75 | 98.77 | 98.68 | 98.72 | |
| Reduced | Resting State (C, O) | 97.45 | 97.68 | 97.35 | 97.51 |
| Level 1 (C, P) | 97.29 | 97.65 | 97.64 | 97.64 | |
| Level 2 (C, O) | 97.78 | 97.55 | 97.24 | 97.39 | |
| Level 3 (F, P) | 95.74 | 95.97 | 95.28 | 95.62 | |
| Game (F, P) | 93.33 | 93.17 | 93.17 | 93.17 | |
| Task Fusion (C, P) | 93.84 | 93.68 | 93.39 | 93.53 |
| Ref. | Paradigm | Database | No. of Subjects | No. of Channels | Segment Length | Classifier, Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | Resting state | Physionet | 109 | 14 reduced | 0.5 s | 2D-CNN 99.32% |
| [38] | Resting state, opening, and closing fists and feet both physically and imaginarily | Physionet | 109 | 16 reduced | 1 s | 1D-CNN LSTM 99.58% |
| [56] | Resting state | Physionet | 109 | 64 | 12 s | 1D-CNN 99.81% |
| [57] | Watching film clips | DREAMER | 23 | 14 | 1 s | CNN 94.01% |
| [58] | Signed subject signatures on mobile phone screen | Own | 33 genuine and 25 forged users | 14 | - | BLSTM-NN 98.78% |
| [59] | Watching affective elicited music videos | DEAP | 32 | 5 reduced | 1 s | CNN-GRU 99.17% (CRR) |
| [60] | Eyes close, open, motor speech imaginarily, visual stimulation, mathematical calculation | Own | 45 | 19 | 5 s | 1D-CNN 95.2% (eyes open) |
| [61] | Photic stimulation | Own | 16 | 16 | 3 s | 1D-CNN 97.17% |
| [62] | Steady-state visual-evoked potentials | Own | 8 | 9 | - | CNN 96.78% |
| [63] | Auditory evoked potentials | Own | 20 | 2/1 reduced | 2 s | 1D-CNN LSTM 99.53% (2 channels) 96.93% (1 channel) |
| 8 | 1D-CNN | |||||
| Rest | 99.80% | |||||
| L1 | 99.77% | |||||
| L2 | 99.88% | |||||
| L3 | 99.04% | |||||
| GAME | 98.79% | |||||
| ALL | 98.75% | |||||
| Prop. | Own | 21 | 1 s | |||
| 4 reduced | 1D-CNN | |||||
| Rest | 97.45% | |||||
| L1 | 97.29% | |||||
| L2 | 97.78% | |||||
| L3 | 95.74% | |||||
| GAME | 93.33% | |||||
| ALL | 93.84% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kralikova, I.; Babusiak, B.; Smondrk, M. EEG-Based Person Identification during Escalating Cognitive Load. Sensors 2022, 22, 7154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197154
Kralikova I, Babusiak B, Smondrk M. EEG-Based Person Identification during Escalating Cognitive Load. Sensors. 2022; 22(19):7154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197154
Chicago/Turabian StyleKralikova, Ivana, Branko Babusiak, and Maros Smondrk. 2022. "EEG-Based Person Identification during Escalating Cognitive Load" Sensors 22, no. 19: 7154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197154
APA StyleKralikova, I., Babusiak, B., & Smondrk, M. (2022). EEG-Based Person Identification during Escalating Cognitive Load. Sensors, 22(19), 7154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197154








