Quantitative Measurements of Pharmacological and Toxicological Activity of Molecules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Indicators of Toxicity and Pharmacological Activity
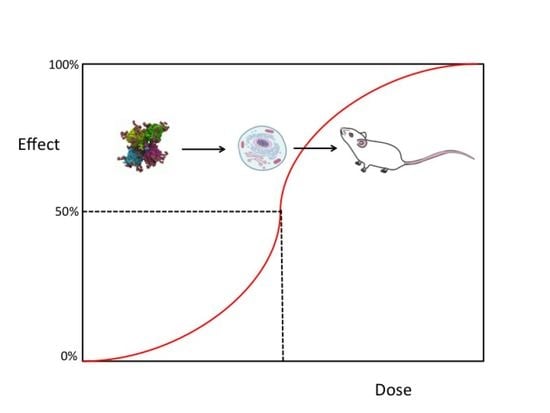
2.1. The Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50)
2.2. Lethal Dose-50 (LD50)
3. Relations between Indicators: From Practical Descriptors to Empirical Relationship
3.1. Relationships between IC50, the Median Effective Dose (ED50), and LD50
3.1.1. Relationship between LD50 and IC50
3.1.2. Therapeutic Index (TI)
3.1.3. Therapeutic Window
3.2. Structure–Activity Relationships and In Silico Approaches
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: Why it is important to toxicology and toxicologists. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louizos, C.; Yáñez, J.A.; Forrest, M.L.; Davies, N.M. Understanding the Hysteresis Loop Conundrum in Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Relationships. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 17, 34–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lawrence, P.J.; Ma, A.; Zhu, J.; Xu, D.; Ma, Q. Single-Cell Techniques and Deep Learning in Predicting Drug Response. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametgalieva, A.R.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Aglyamova, A.R.; Masson, P. Steady-state kinetic analysis of human cholinesterases over wide concentration ranges of competing substrates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2022, 1870, 140733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, P.; Lushchekina, S.V. Slow-binding inhibition of cholinesterases, pharmacological and toxicological relevance. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 593, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Evolution of the drug-target residence time model. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.W.; Chung, B.; Yoo, S.H.; Chang, P.S. Heterologous expression of a papain-like protease inhibitor (SnuCalCpI17) in the E. coli and its mode of inhibition. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 4563–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, H. Hill coefficients, dose–response curves and allosteric mechanisms. J. Chem. Biol. 2010, 3, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buker, S.M.; Boriack-Sjodin, P.A.; Copeland, R.A. Enzyme–Inhibitor Interactions and a Simple, Rapid Method for Determining Inhibition Modality. SLAS Discov. 2019, 24, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colović, M.B.; Krstić, D.Z.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.D.; Bondžić, A.M.; Vasić, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Petter, R.C.; Baillie, T.A.; Whitty, A. The resurgence of covalent drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, T.S.; Tabrizi-Fard, M.A.; Fung, H.L. Impact of mechanism-based enzyme inactivation on inhibitor potency: Implications for rational drug discovery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierse, J.K.; Koboldt, C.M.; Walker, M.C.; Seibert, K.; Isakson, P.C. Kinetic basis for selective inhibition of cyclo-oxygenases. Biochem. J. 1999, 339, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, R.J. Chapter 4—Toxicant interactions with macromolecular targets. In An Introduction to Interdisciplinary Toxicology; Pope, C.N., Liu, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarensen, A.; Balbo, P.; Banker, M.E.; Czerwinski, R.M.; Kuhn, M.; Maurer, T.S.; Telliez, J.B.; Vincent, F.; Wittwer, A.J. The advantages of describing covalent inhibitor in vitro potencies by IC50 at a fixed time point. IC50 determination of covalent inhibitors provides meaningful data to medicinal chemistry for SAR optimization. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, T.S.; Smith, D.; Beaumont, K.; Di, L. Dose Predictions for Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6423–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevan, J.W. The error of determination of toxicity. Proc. Royal Soc. B 1927, 101, 483–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden, G.; Flury-Roversi, M. Significance of the LD50-test for the toxicological evaluation of chemical substances. Arch. Toxicol. 1981, 47, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), 6th ed.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Colerangle, J.B. Chapter 25—Preclinical Development of Nononcogenic Drugs (Small and Large Molecules). In A Comprehensive Guide to Toxicology in Nonclinical Drug Development, 2nd ed.; Faqi, A.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, O.L.; Smoliga, J.M. Translating dosages from animal models to human clinical trials—Revisiting body surface area scaling. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, J.C.; Hewitt, M. Prediction of Human Lethal Doses and Concentrations of MEIC Chemicals from Rodent LD50 Values: An Attempt to Make Some Reparation. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2021, 49, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashirova, T.; Shaihutdinova, Z.; Mansurova, M.; Kazakova, R.; Shambazova, D.; Bogdanov, A.; Tatarinov, D.; Daudé, D.; Jacquet, P.; Chabrière, E.; et al. Enzyme Nanoreactor for In Vivo Detoxification of Organophosphates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 19241–19252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, W.; Spielmann, H. Two Procedures for the Prediction of Acute Toxicity (LD50) from Cytotoxicity Data. Altern. Lab. Anim. 1992, 20, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Stated. ICCVAM Test Method Evaluation Report: In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test Methods for Estimating Starting Doses for Acute Oral Systemic Toxicity Testing; NIH Publication No. 07-4519; United Stated: New York, NY, USA, 2006.
- Rosenkranz, H.S.; Cunningham, A.R. Lack of Predictivity of the Rat Lethality (LD50) Test for Ecological and Human Health Effects. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005, 3, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePass, L.R. Alternative approaches in median lethality (LD50) and acute toxicity testing. Toxicol. Lett. 1989, 49, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005.
- Peris, J. Drug-Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics. In Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology, 7th ed.; Whalen, K., Field, C., Radhakrishnan, R., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yartsev, A. Therapeutic Index, ED50, TD50 and LD50. 2022. Available online: https://derangedphysiology.com/cicm-primary-exam/required-reading/pharmacodynamics/Chapter%20413/therapeutic-index-ed50-td50-and-ld50 (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Hansch, C.; Rockwell, S.D.; Jow, P.Y.; Leo, A.; Steller, E.E. Substituent constants for correlation analysis. J. Med. Chem. 1977, 20, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, R.W. A survey of Hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z. Atom surface fragment contribution method for predicting the toxicity of ionic liquids. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 421, 126705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhanga, H.; Chenb, Z. Application of atomic electrostatic potential descriptors for predicting the eco-toxicity of ionic liquids towards leukemia rat cell line. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 260, 117941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Kang, Y.; Leung, E.L.; Lei, T.; Shen, C.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Z.; Cao, D.; Hou, T. Do we need different machine learning algorithms for QSAR modeling? A comprehensive assessment of 16 machine learning algorithms on 14 QSAR data sets. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, A.Z.; Arodz, T.; Gálvez, J. Computational Methods in Developing Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships (QSAR): A Review. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2006, 9, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chang, L.J.; Yang, J.-M. An integrated approach with new strategies for QSAR models and lead optimization. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Jiménez, E.H.; Zárate-Hernández, L.A.; Camacho-Mendoza, R.L.; González-Montiel, S.; Alvarado-Rodríguez, J.G.; Gómez-Castro, C.Z.; Pescador-Rojas, M.; Meneses-Viveros, A.; Cruz-Borbolla, J. QSTR Modeling to Find Relevant DFT Descriptors Related to the Toxicity of Carbamates. Molecules 2022, 27, 5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfenati, E. Silico Methods for Predicting Drug Toxicity; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Roy, K. Prediction of aquatic toxicity of chemical mixtures by the QSAR approach using 2D structural descriptors. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 408, 124936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, L.; Plener, L.; Daudé, D.; Chabrière, E. Enzymatic decontamination of paraoxon-ethyl limits long-term effects in planarians. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a Model Vertebrate for Investigating Chemical Toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.V.; Herst, P.M.; Tan, A.S. Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: New insights into their cellular reduction. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Test No. 498: In Vitro Phototoxicity—Reconstructed Human Epidermis Phototoxicity test method, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Musso, N.; Grasso, M.; Costantino, A.; Lazzarino, G.; Tascedda, F.; Gulisano, M.; Lunte, S.M.; Caraci, F. Microfluidics as a Novel Tool for Biological and Toxicological Assays in Drug Discovery Processes: Focus on Microchip Electrophoresis. Micromachines 2020, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, S.C.; Kriel, F.H.; Ivask, A.; Tong, Z.; Lombi, E.; Voelcker, N.H.; Priest, C. The Use of Microfluidics in Cytotoxicity and Nanotoxicity Experiments. Micromachines 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandenius, C.F.; Ross, J.A. Cell-Based Assays Using iPSCs for Drug Development and Testing; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Imprint Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]





| Type of Inhibitor | IC50 | IC50 vs. [S]/KM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Competitive | if [S] << KM, Ki = IC50 | Linear ascending plot | |
| Non-competitive | Ki | α = 1 | Linear horizontal plot |
| Mixed type | if α = 1, Ki = IC50 | α > 1: curvilinear ascending plot α < 1: curvilinear descending plot | |
| Uncompetitive | if [S] >> KM, αKi ≈ IC50 | Curvilinear descending plot | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazakova, R.R.; Masson, P. Quantitative Measurements of Pharmacological and Toxicological Activity of Molecules. Chemistry 2022, 4, 1466-1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040097
Kazakova RR, Masson P. Quantitative Measurements of Pharmacological and Toxicological Activity of Molecules. Chemistry. 2022; 4(4):1466-1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazakova, Renata R., and Patrick Masson. 2022. "Quantitative Measurements of Pharmacological and Toxicological Activity of Molecules" Chemistry 4, no. 4: 1466-1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040097
APA StyleKazakova, R. R., & Masson, P. (2022). Quantitative Measurements of Pharmacological and Toxicological Activity of Molecules. Chemistry, 4(4), 1466-1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040097