Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. E6 and E7 Are Multifunctional Proteins
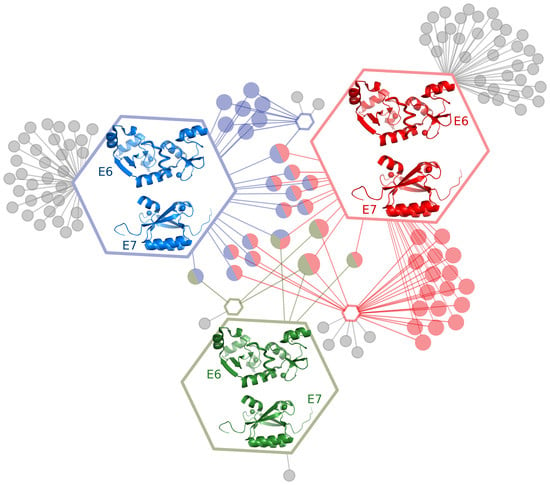
2.1. E6 and E7 Interact with Large Numbers of Host Target Proteins
2.2. Viral Domain-Motif Hijacking Strategies Explain E6 and E7 Multifunctionality
2.3. E6 and E7 Divert the Host Ubiquitination Machinery
2.4. E6 and E7 and Nucleic Acids
2.5. The Multifunctionality Issue: How to Make Sense of Complexity?
3. Sequence and Structure of E6 and E7 Oncoproteins
3.1. Amino Acid Sequence Features of E6 and E7
3.2. History of Progress towards E6 and E7 Tri-Dimensional Structures
3.3. Structure of the Zinc-Binding Domains of E6
3.4. Structure of the Zinc-Binding Domains of E7 and Comparison to E6 Domains
3.5. Conformation of Uncomplexed Mammalian E6 in Solution
4. Structure and Specificity of E6-Target Complexes
4.1. Structure of Full-Length Mammalian E6 Proteins Bound to Target LxxLL Motifs
4.2. Why Do Apparently Unrelated E6 Target Proteins Contain a Conserved E6-Binding LxxLL Motif? The CBP-P300 Hypothesis
4.3. Structure of the Ternary E6/E6AP/p53 Complex
4.4. Structural Basis of Hijacking of PDZ Domains and Rb Pocket Domains by High-Risk Mucosal HPVs
5. Exploitation of High-Resolution Structural Data for In Vivo Inhibition of E6 Oncogenic Activity
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human papillomavirus molecular biology. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Quint, W.; Banks, L.; Bravo, I.G.; Stoler, M.; Broker, T.R.; Stanley, M.A. The biology and life-cycle of human papillomaviruses. Vaccine 2012, 30, F55–F70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasino, M. The human papillomavirus family and its role in carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 26, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rector, A.; Van Ranst, M. Animal papillomaviruses. Virology 2013, 445, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Bueno, A.; Mavian, C.; Labella, A.M.; Castro, D.; Borrego, J.J.; Alcami, A.; Alejo, A. Concurrence of Iridovirus, Polyomavirus, and a Unique Member of a New Group of Fish Papillomaviruses in Lymphocystis Disease-Affected Gilthead Sea Bream. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8768–8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Ruoppolo, V.; Schmidt, A.; Lescroel, A.; Jongsomjit, D.; Elrod, M.; Kraberger, S.; Stainton, D.; Dugger, K.M.; Ballard, G.; et al. Unique genome organization of non-mammalian papillomaviruses provides insights into the evolution of viral early proteins. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, vex027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PaVE. PaVE: Papillomavirus Episteme. Available online: https://pave.niaid.nih.gov (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Li, Z.; Xirasagar, S.; Maes, P.; Kaminsky, D.; Liou, D.; Sun, Q.; Kaur, R.; Huyen, Y.; McBride, A.A. The Papillomavirus Episteme: A major update to the papillomavirus sequence database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D499–D506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egawa, N.; Doorbar, J. The low-risk papillomaviruses. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslund, O.; Johansson, H.; Madsen, K.G.; Kofoed, K. The nasal mucosa contains a large spectrum of human papillomavirus types from the Betapapillomavirus and Gammapapillomavirus genera. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasino, M. The biology of beta human papillomaviruses. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Banks, L. Molecular mechanisms underlying human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoprotein-induced cell transformation. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.A. Playing with fire: Consequences of human papillomavirus DNA replication adjacent to genetically unstable regions of host chromatin. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 26, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the first century of human tumour virology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.A. Oncogenic human papillomaviruses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Pol, S.B.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins. Virology 2013, 445, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, A.; Munger, K. The papillomavirus E7 proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 138–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingelhutz, A.J.; Roman, A. Cellular transformation by human papillomaviruses: Lessons learned by comparing high- and low-risk viruses. Virology 2012, 424, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Milner, J. Selective silencing of viral gene expression in HPV-positive human cervical carcinoma cells treated with siRNA, a primer of RNA interference. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6041–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butz, K.; Ristriani, T.; Hengstermann, A.; Denk, C.; Scheffner, M.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. siRNA targeting of the viral E6 oncogene efficiently kills human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5938–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonetta, A.C.; Mailly, L.; Robinet, E.; Trave, G.; Masson, M.; Deryckere, F. Artificial microRNAs against the viral E6 protein provoke apoptosis in HPV positive cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.; Poirson, J.; Foltz, C.; Chebaro, Y.; Schrapp, M.; Meyer, A.; Bonetta, A.; Forster, A.; Jacob, Y.; Masson, M.; et al. Targeting the Two Oncogenic Functional Sites of the HPV E6 Oncoprotein with a High-Affinity Bivalent Ligand. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 7958–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanier, K.; Stutz, C.; Kintscher, S.; Reinz, E.; Sehr, P.; Bulkescher, J.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Trave, G.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. The E6AP binding pocket of the HPV16 E6 oncoprotein provides a docking site for a small inhibitory peptide unrelated to E6AP, indicating druggability of E6. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutz, C.; Reinz, E.; Honegger, A.; Bulkescher, J.; Schweizer, J.; Zanier, K.; Trave, G.; Lohrey, C.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Intracellular Analysis of the Interaction between the Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Oncoprotein and Inhibitory Peptides. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dymalla, S.; Scheffner, M.; Weber, E.; Sehr, P.; Lohrey, C.; Hoppe-Seyler, F.; Hoppe-Seyler, K. A novel peptide motif binding to and blocking the intracellular activity of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtete, J.; Sibler, A.P.; Zeder-Lutz, G.; Dalkara, D.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Zuber, G.; Weiss, E. Suppression of cervical carcinoma cell growth by intracytoplasmic codelivery of anti-oncoprotein E6 antibody and small interfering RNA. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrange, M.; Boulade-Ladame, C.; Mailly, L.; Weiss, E.; Orfanoudakis, G.; Deryckere, F. Intracellular scFvs against the viral E6 oncoprotein provoke apoptosis in human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.J.; Rietz, A.; Malinkevich, A.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M.; Bartolowits, M.; Davisson, V.J.; Baleja, J.D.; Androphy, E.J. Structure based identification and characterization of flavonoids that disrupt human papillomavirus-16 E6 function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malecka, K.A.; Fera, D.; Schultz, D.C.; Hodawadekar, S.; Reichman, M.; Donover, P.S.; Murphy, M.E.; Marmorstein, R. Identification and Characterization of Small Molecule Human Papillomavirus E6 Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietz, A.; Petrov, D.P.; Bartolowits, M.; DeSmet, M.; Davisson, V.J.; Androphy, E.J. Molecular Probing of the HPV-16 E6 Protein Alpha Helix Binding Groove with Small Molecule Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.A.; Howley, P.M. Proteomic approaches to the study of papillomavirus-host interactions. Virology 2013, 435, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, M.; Munger, K. Proteomic analysis of the gamma human papillomavirus type 197 E6 and E7 associated cellular proteins. Virology 2017, 500, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveu, G.; Cassonnet, P.; Vidalain, P.O.; Rolloy, C.; Mendoza, J.; Jones, L.; Tangy, F.; Muller, M.; Demeret, C.; Tafforeau, L.; et al. Comparative analysis of virus-host interactomes with a mammalian high-throughput protein complementation assay based on Gaussia princeps luciferase. Methods 2012, 58, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Deo, R.C.; Padi, M.; Adelmant, G.; Calderwood, M.A.; Rolland, T.; Grace, M.; Dricot, A.; Askenazi, M.; Tavares, M.; et al. Interpreting cancer genomes using systematic host network perturbations by tumour virus proteins. Nature 2012, 487, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Dupuis, C.; Tyring, S.K.; Underbrink, M.P. Sterile alpha Motif Domain Containing 9 Is a Novel Cellular Interacting Partner to Low-Risk Type Human Papillomavirus E6 Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149859. [Google Scholar]
- White, E.A.; Kramer, R.E.; Tan, M.J.; Hayes, S.D.; Harper, J.W.; Howley, P.M. Comprehensive analysis of host cellular interactions with human papillomavirus E6 proteins identifies new E6 binding partners and reflects viral diversity. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13174–13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, N.E.; Trave, G.; Gibson, T.J. How viruses hijack cell regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diella, F.; Haslam, N.; Chica, C.; Budd, A.; Michael, S.; Brown, N.P.; Trave, G.; Gibson, T.J. Understanding eukaryotic linear motifs and their role in cell signaling and regulation. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6580–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemes, L.B.; de Prat-Gay, G.; Sanchez, I.E. Convergent evolution and mimicry of protein linear motifs in host-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 32, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Weiss, R.S.; Javier, R.T. Binding of human virus oncoproteins to hDlg/SAP97, a mammalian homolog of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6670–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyono, T.; Hiraiwa, A.; Fujita, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Ishibashi, M. Binding of high-risk human papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins to the human homologue of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11612–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Huibregtse, J.M. Human scribble (Vartul) is targeted for ubiquitin-mediated degradation by the high-risk papillomavirus E6 proteins and the E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8244–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaunsinger, B.A.; Lee, S.S.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L.; Javier, R. Interactions of the PDZ-protein MAGI-1 with adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5270–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javier, R.T.; Rice, A.P. Emerging theme: Cellular PDZ proteins as common targets of pathogenic viruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11544–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.D.; Roberts, S. Viral Interactions with PDZ Domain-Containing Proteins-An Oncogenic Trait? Pathogens 2016, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, L.; Pim, D.; Thomas, M. Human tumour viruses and the deregulation of cell polarity in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huibregtse, J.M.; Scheffner, M.; Howley, P.M. Localization of the E6-AP regions that direct human papillomavirus E6 binding, association with p53, and ubiquitination of associated proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4918–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Rustamzadeh, E.; Baleja, J.D.; Androphy, E.J. Identification of an alpha helical motif sufficient for association with papillomavirus E6. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13537–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Pol, S.B.; Brown, M.C.; Turner, C.E. Association of Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1 E6 oncoprotein with the focal adhesion protein paxillin through a conserved protein interaction motif. Oncogene 1998, 16, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohl, J.; Das, K.; Dasgupta, B.; Vande Pol, S.B. Competitive binding to a charged leucine motif represses transformation by a papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein. Virology 2000, 271, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.J.; White, E.A.; Sowa, M.E.; Harper, J.W.; Aster, J.C.; Howley, P.M. Cutaneous β-human papillomavirus E6 proteins bind Mastermind-like coactivators and repress Notch signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1473–E1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, J.M.; Spangle, J.M.; Munger, K. The human papillomavirus type 8 E6 protein interferes with NOTCH activation during keratinocyte differentiation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4762–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimer, N.; Lyons, C.; Wallberg, A.E.; Vande Pol, S.B. Cutaneous papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins associate with MAML1 to repress transactivation and NOTCH signaling. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4639–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, L.V.; Karpova, A.Y.; Vidal, M.; Howley, P.M. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 oncoprotein binds to interferon regulatory factor-3 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Whitaker, N.J. Human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis and the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003, 13, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, S. E3 ubiquitin ligases and human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2014, 42, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Vierstra, R.D.; Howley, P.M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell 1993, 75, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffner, M.; Nuber, U.; Huibregtse, J.M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature 1995, 373, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Thompson, D.A.; Münger, K. Destabilization of the RB tumor suppressor protein and stabilization of p53 contribute to HPV type 16 E7-induced apoptosis. Virology 1997, 239, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, S.N.; Wazer, D.E.; Band, V. E7 protein of human papilloma virus-16 induces degradation of retinoblastoma protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poirson, J.; Biquand, E.; Straub, M.L.; Cassonnet, P.; Nominé, Y.; Jones, L.; van der Werf, S.; Travé, G.; Zanier, K.; Jacob, Y.; et al. Mapping the interactome of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with the ubiquitin-proteasome system. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3171–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.T.; Danos, O. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the human papillomavirus type 18 genome. Phylogeny of papillomaviruses and repeated structure of the E6 and E7 gene products. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 193, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallon, R.G.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Defendi, V. DNA-binding activity of papillomavirus proteins. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Tsunokawa, Y.; Sugimura, T.; Terada, M. Purification and DNA-binding properties of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 164, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristriani, T.; Masson, M.; Nomine, Y.; Laurent, C.; Lefevre, J.F.; Weiss, E.; Trave, G. HPV oncoprotein E6 is a structure-dependent DNA-binding protein that recognizes four-way junctions. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristriani, T.; Nomine, Y.; Masson, M.; Weiss, E.; Trave, G. Specific recognition of four-way DNA junctions by the C-terminal zinc-binding domain of HPV oncoprotein E6. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomine, Y.; Masson, M.; Charbonnier, S.; Zanier, K.; Ristriani, T.; Deryckere, F.; Sibler, A.P.; Desplancq, D.; Atkinson, R.A.; Weiss, E.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of E6 oncoprotein: Insights in the molecular pathways of human papillomavirus-mediated pathogenesis. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomine, Y.; Charbonnier, S.; Ristriani, T.; Stier, G.; Masson, M.; Cavusoglu, N.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Weiss, E.; Kieffer, B.; Trave, G. Domain substructure of HPV E6 oncoprotein: Biophysical characterization of the E6 C-terminal DNA-binding domain. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 4909–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodaghi, S.; Jia, R.; Zheng, Z.M. Human papillomavirus type 16 E2 and E6 are RNA-binding proteins and inhibit in vitro splicing of pre-mRNAs with suboptimal splice sites. Virology 2009, 386, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Myers, M.P.; Massimi, P.; Guarnaccia, C.; Banks, L. Analysis of Multiple HPV E6 PDZ Interactions Defines Type-Specific PDZ Fingerprints that Predict Oncogenic Potential. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincentelli, R.; Luck, K.; Poirson, J.; Polanowska, J.; Abdat, J.; Blemont, M.; Turchetto, J.; Iv, F.; Ricquier, K.; Straub, M.L.; et al. Quantifying domain-ligand affinities and specificities by high-throughput holdup assay. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, R.J.; Herraez-Hernandez, E.; Fei, J.W.; Langbein, L.; Kaden, S.; Grone, H.J.; de Villiers, E.M. E7 oncoprotein of novel human papillomavirus type 108 lacking the E6 gene induces dysplasia in organotypic keratinocyte cultures. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; McBride, A.A. Molecular archeological evidence in support of the repeated loss of a papillomavirus gene. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipari, F.; McGibbon, G.A.; Wardrop, E.; Cordingley, M.G. Purification and biophysical characterization of a minimal functional domain and of an N-terminal Zn2+-binding fragment from the human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanier, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Sidi, A.O.; McEwen, A.G.; Ferrario, M.G.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Cura, V.; Brimer, N.; Babah, K.O.; Ansari, T.; et al. Structural Basis for Hijacking of Cellular LxxLL Motifs by Papillomavirus E6 Oncoproteins. Science 2013, 339, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlenschlager, O.; Seiboth, T.; Zengerling, H.; Briese, L.; Marchanka, A.; Ramachandran, R.; Baum, M.; Korbas, M.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Durst, M.; et al. Solution structure of the partially folded high-risk human papilloma virus 45 oncoprotein E7. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5953–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Alai, M.M.; Alonso, L.G.; de Prat-Gay, G. The N-terminal module of HPV16 E7 is an intrinsically disordered domain that confers conformational and recognition plasticity to the oncoprotein. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 10405–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Clements, A.; Zhao, K.; Marmorstein, R. Structure of the human Papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein and its mechanism for inactivation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Sidi, A.O.; Zanier, K.; Rybin, V.; Deryckere, F.; Rector, A.; Burk, R.D.; Lienau, E.K.; van Ranst, M.; Trave, G. Identification of unusual E6 and E7 proteins within avian papillomaviruses: Cellular localization, biophysical characterization, and phylogenetic analysis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8759–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, L.H.; Lenz, J.; van Doorslaer, K.; Chen, Z.; Stacy, B.A.; Wellehan, J.F., Jr.; Manire, C.A.; Burk, R.D. Genomic characterization of two novel reptilian papillomaviruses, Chelonia mydas papillomavirus 1 and Caretta caretta papillomavirus 1. Virology 2009, 383, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danos, O.; Georges, E.; Orth, G.; Yaniv, M. Fine structure of the cottontail rabbit papillomavirus mRNAs expressed in the transplantable VX2 carcinoma. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Georges, E.; Croissant, O.; Bonneaud, N.; Orth, G. Physical state and transcription of the cottontail rabbit papillomavirus genome in warts and transplantable VX2 and VX7 carcinomas of domestic rabbits. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarver, N.; Rabson, M.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Byrne, J.C.; Howley, P.M. Localization and analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 transforming functions. J. Virol. 1984, 52, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiller, J.T.; Vass, W.C.; Lowy, D.R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 7880–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.; Freese, U.K.; Gissmann, L.; Mayer, W.; Roggenbuck, B.; Stremlau, A.; zur Hausen, H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature 1985, 314, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androphy, E.J.; Schiller, J.T.; Lowy, D.R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science 1985, 230, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlashewski, G.; Banks, L.; Wu-Liao, J.; Spence, P.; Pim, D.; Crawford, L. The expression of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 protein in bacteria and the production of anti-E6 antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 1986, 67, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedorf, K.; Oltersdorf, T.; Krammer, G.; Rowekamp, W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smotkin, D.; Wettstein, F.O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4680–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cherry, J.J.; Dineen, J.V.; Androphy, E.J.; Baleja, J.D. Determinants of stability for the E6 protein of papillomavirus type 16. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanier, K.; ould M’hamed ould Sidi, A.; Boulade-Ladame, C.; Rybin, V.; Chappelle, A.; Atkinson, A.; Kieffer, B.; Trave, G. Solution structure analysis of the HPV16 E6 oncoprotein reveals a self-association mechanism required for E6-mediated degradation of p53. Structure 2012, 20, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomine, Y.; Ristriani, T.; Laurent, C.; Lefevre, J.F.; Weiss, E.; Trave, G. Formation of soluble inclusion bodies by HPV E6 oncoprotein fused to maltose-binding protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 23, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomine, Y.; Ristriani, T.; Laurent, C.; Lefevre, J.F.; Weiss, E.; Trave, G. A strategy for optimizing the monodispersity of fusion proteins: Application to purification of recombinant HPV E6 oncoprotein. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanier, K.; Nominé, Y.; Charbonnier, S.; Ruhlmann, C.; Schultz, P.; Schweizer, J.; Travé, G. Formation of well-defined soluble aggregates upon fusion to MBP is a generic property of E6 proteins from various human papillomavirus species. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 51, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidi, A.O.; Babah, K.O.; Brimer, N.; Nomine, Y.; Romier, C.; Kieffer, B.; Pol, S.V.; Trave, G.; Zanier, K. Strategies for bacterial expression of protein-peptide complexes: Application to solubilization of papillomavirus E6. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 80, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alai, M.M.; Dantur, K.I.; Smal, C.; Pietrasanta, L.; de Prat-Gay, G. High-risk HPV E6 oncoproteins assemble into large oligomers that allow localization of endogenous species in prototypic HPV-transformed cell lines. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanier, K.; Ruhlmann, C.; Melin, F.; Masson, M.; Ould M’hamed Ould Sidi, A.; Bernard, X.; Fischer, B.; Brino, L.; Ristriani, T.; Rybin, V.; et al. E6 proteins from diverse papillomaviruses self-associate both in vitro and in vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Zapien, D.; Ruiz, F.X.; Poirson, J.; Mitschler, A.; Ramirez, J.; Forster, A.; Cousido-Siah, A.; Masson, M.; Vande Pol, S.; Podjarny, A.; et al. Structure of the E6/E6AP/p53 complex required for HPV-mediated degradation of p53. Nature 2016, 529, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, S.; Gao, Q.; Androphy, E.J.; Band, V. Mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 demonstrates that p53 degradation is necessary for immortalization of mammary epithelial cells. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, B.; Schneider, S.; Bohl, J.; Jiang, Y.; Beaudet, A.; Vande Pol, S. Requirement of E6AP and the features of human papillomavirus E6 necessary to support degradation of p53. Virology 2003, 306, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischo, A.; Ohlenschläger, O.; Hortschansky, P.; Ramachandran, R.; Görlach, M. Structural insights into a wildtype domain of the oncoprotein E6 and its interaction with a PDZ domain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, L.G.; Garcia-Alai, M.M.; Nadra, A.D.; Lapena, A.N.; Almeida, F.L.; Gualfetti, P.; Prat-Gay, G.D. High-risk (HPV16) human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein is highly stable and extended, with conformational transitions that could explain its multiple cellular binding partners. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10510–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansma, A.L.; Martinez-Yamout, M.A.; Liao, R.; Sun, P.; Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. The high-risk HPV16 E7 oncoprotein mediates interaction between the transcriptional coactivator CBP and the retinoblastoma protein pRb. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 4030–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, M.O.; Hosek, T.; Calcada, E.O.; Castiglia, F.; Massimi, P.; Banks, L.; Felli, I.C.; Pierattelli, R. Monitoring HPV-16 E7 phosphorylation events. Virology 2017, 503, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.F.; Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L. Diversity and evolution of chromatin proteins encoded by DNA viruses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, N.V. Treble clef finger—A functionally diverse zinc-binding structural motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Subramanian, S. Classification of the treble clef zinc finger: Noteworthy lessons for structure and function evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporeale, G.; Lorenzo, J.R.; Thomas, M.G.; Salvatierra, E.; Borkosky, S.S.; Risso, M.G.; Sanchez, I.E.; de Prat Gay, G.; Alonso, L.G. Degenerate cysteine patterns mediate two redox sensing mechanisms in the papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemes, L.B.; Camporeale, G.; Sanchez, I.E.; de Prat-Gay, G.; Alonso, L.G. Cysteine-rich positions outside the structural zinc motif of human papillomavirus E7 provide conformational modulation and suggest functional redox roles. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smal, C.; Alonso, L.G.; Wetzler, D.E.; Heer, A.; de Prat Gay, G. Ordered self-assembly mechanism of a spherical oncoprotein oligomer triggered by zinc removal and stabilized by an intrinsically disordered domain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, L.G.; Garcia-Alai, M.M.; Smal, C.; Centeno, J.M.; Iacono, R.; Castano, E.; Gualfetti, P.; de Prat-Gay, G. The HPV16 E7 viral oncoprotein self-assembles into defined spherical oligomers. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 3310–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, M.L.; Alonso, L.G.; Tatti, S.; de Prat-Gay, G. Long-lasting immunoprotective and therapeutic effects of a hyperstable E7 oligomer based vaccine in a murine human papillomavirus tumor model. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikl, T.R.; Paul, F. Conformational selection in protein binding and function. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, M.; Hindelang, C.; Sibler, A.P.; Schwalbach, G.; Trave, G.; Weiss, E. Preferential nuclear localization of the human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein in cervical carcinoma cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbonnier, S.; Nominé, Y.; Ramírez, J.; Luck, K.; Chapelle, A.; Stote, R.H.; Travé, G.; Kieffer, B.; Atkinson, R.A. The Structural and Dynamic Response of MAGI-1 PDZ1 with Noncanonical Domain Boundaries to the Binding of Human Papillomavirus E6. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiley, K.Z.; Liban, T.J.; Felthousen, J.G.; Ramanan, P.; Litovchick, L.; Rubin, S.M. Structural mechanisms of DREAM complex assembly and regulation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Russo, A.A.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor pocket domain bound to a peptide from HPV E7. Nature 1998, 391, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Pol, S. Papillomavirus E6 Oncoproteins Take Common Structural Approaches to Solve Different Biological Problems. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plevin, M.J.; Mills, M.M.; Ikura, M. The LxxLL motif: A multifunctional binding sequence in transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catoe, H.W.; Nawaz, Z. E6-AP facilitates efficient transcription at estrogen responsive promoters through recruitment of chromatin modifiers. Steroids 2011, 76, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krois, A.S.; Ferreon, J.C.; Martinez-Yamout, M.A.; Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Recognition of the disordered p53 transactivation domain by the transcriptional adapter zinc finger domains of CREB-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1853–E1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallberg, A.E.; Pedersen, K.; Lendahl, U.; Roeder, R.G. p300 and PCAF Act Cooperatively to Mediate Transcriptional Activation from Chromatin Templates by Notch Intracellular Domains In Vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7812–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Y.; Liu, C.; Srinath, H.; Lam, S.S.; Correia, J.J.; Derynck, R.; Lin, K. Crystal structure of IRF-3 in complex with CBP. Structure 2005, 13, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; de Castro, I.; Defranco, D.B.; Deng, F.M.; Melamed, J.; Kapur, P.; Raj, G.V.; Rossi, R.; Hammes, S.R. Paxillin mediates extranuclear and intranuclear signaling in prostate cancer proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsen, M.; Sorensen, L.; Aabel, L.; Ledsaak, M.; Matre, V.; Gabrielsen, O.S. The adaptor protein ARA55 and the nuclear kinase HIPK1 assist c-Myb in recruiting p300 to chromatin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1860, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germaniuk-Kurowska, A.; Nag, A.; Zhao, X.; Dimri, M.; Band, H.; Band, V. Ada3 requirement for HAT recruitment to estrogen receptors and estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11789–11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Poetz, F.; Bruer, M.; Ly-Hartig, T.B.; Schott, J.; Seraphin, B.; Stoecklin, G. Acetylation-Dependent Control of Global Poly(A) RNA Degradation by CBP/p300 and HDAC1/2. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howie, H.L.; Koop, J.I.; Weese, J.; Robinson, K.; Wipf, G.; Kim, L.; Galloway, D.A. Beta-HPV 5 and 8 E6 promote p300 degradation by blocking AKT/p300 association. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.E.; Mossman, K.L. Recent advances in understanding viral evasion of type I interferon. Immunology 2013, 138, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottiger, M.O.; Nabel, G.J. Viral replication and the coactivators p300 and CBP. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Marshall, C.B.; Ikura, M. Transcriptional/epigenetic regulator CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis: Structural and functional versatility in target recognition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3989–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, D.M.; Hoare, S.; Hussain, S.; Parker, M.G.; Sheppard, H. Core LXXLL motif sequences in CREB-binding protein, SRC1, and RIP140 define affinity and selectivity for steroid and retinoid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6695–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, C.M.; Chitayat, S.; Plevin, M.J.; Wang, F.; Thompson, P.; Liu, S.; Spencer, H.L.; Ikura, M.; LeBrun, D.P.; Smith, S.P. Structural basis of CBP/p300 recruitment in leukemia induction by E2A-PBX1. Blood 2012, 120, 3968–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kalkum, M.; Yamamura, S.; Chait, B.T.; Roeder, R.G. E protein silencing by the leukemogenic AML1-ETO fusion protein. Science 2004, 305, 1286–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, T.; Brimer, N.; Vande Pol, S.B. Peptide Interactions Stabilize and Restructure Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 to Interact with p53. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11386–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. Structural biology of the tumor suppressor p53. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchi, V.P.; Klein, J.M.; Edwards, D.J.; Haas, A.L. The active form of E6-associated protein (E6AP)/UBE3A ubiquitin ligase is an oligomer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, F.; Schneider, D.; Barbic, T.; Sladewska-Marquardt, A.; Kuhnle, S.; Marx, A.; Scheffner, M. Role of ubiquitin and the HPV E6 oncoprotein in E6AP-mediated ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9872–9877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemak, A.; Yee, A.; Bezsonova, I.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Arrowsmith, C.H. Zn-binding AZUL domain of human ubiquitin protein ligase Ube3A. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 51, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Kinnucan, E.; Wang, G.; Beaudenon, S.; Howley, P.M.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of an E6AP-UbcH7 Complex: Insights into Ubiquitination by the E2-E3 Enzyme Cascade. Science 1999, 286, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dasgupta, J.; Ma, R.Z.; Banks, L.; Thomas, M.; Chen, X.S. Structures of a human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 polypeptide bound to MAGUK proteins: Mechanisms of targeting tumor suppressors by a high-risk HPV oncoprotein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3618–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amacher, J.F.; Cushing, P.R.; Brooks, L., 3rd; Boisguerin, P.; Madden, D.R. Stereochemical preferences modulate affinity and selectivity among five PDZ domains that bind CFTR: Comparative structural and sequence analyses. Structure 2014, 22, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournane, S.; Charbonnier, S.; Chapelle, A.; Kieffer, B.; Orfanoudakis, G.; Trave, G.; Masson, M.; Nomine, Y. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of the binding of high-risk mucosal HPV E6 oncoproteins to the PDZ1 domain of the tight junction protein MAGI-1. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, K.; Fournane, S.; Kieffer, B.; Masson, M.; Nomine, Y.; Trave, G. Putting into practice domain-linear motif interaction predictions for exploration of protein networks. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.N.; Bach, A.; Engstrom, A.; Stromgaard, K.; Lundstrom, P.; Ferguson, N.; Jemth, P. Biophysical characterization of the complex between human papillomavirus E6 protein and synapse-associated protein 97. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3597–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.; Recht, R.; Charbonnier, S.; Ennifar, E.; Atkinson, R.A.; Trave, G.; Nomine, Y.; Kieffer, B. Disorder-to-order transition of MAGI-1 PDZ1 C-terminal extension upon peptide binding: Thermodynamic and dynamic insights. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Trave, G. The emerging contribution of sequence context to the specificity of protein interactions mediated by PDZ domains. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2648–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, O.A.; Ramirez, J.; Oberg, D.; Malmqvist, T.; Engstrom, A.; Friberg, M.; Chi, C.N.; Widersten, M.; Trave, G.; Nilsson, M.T.; et al. Design of a PDZbody, a bivalent binder of the E6 protein from human papillomavirus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suarez, I.; Trave, G. Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins. Viruses 2018, 10, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010037
Suarez I, Trave G. Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins. Viruses. 2018; 10(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuarez, Irina, and Gilles Trave. 2018. "Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins" Viruses 10, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010037
APA StyleSuarez, I., & Trave, G. (2018). Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins. Viruses, 10(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10010037