Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Reveals a Lung Oxidative Stress Response in Murine Herpesvirus-68 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and cell Cultures
2.2. Mouse Infections with MHV-68 and MHV68/IL6 Viruses
2.3. BAL Fluid Processing
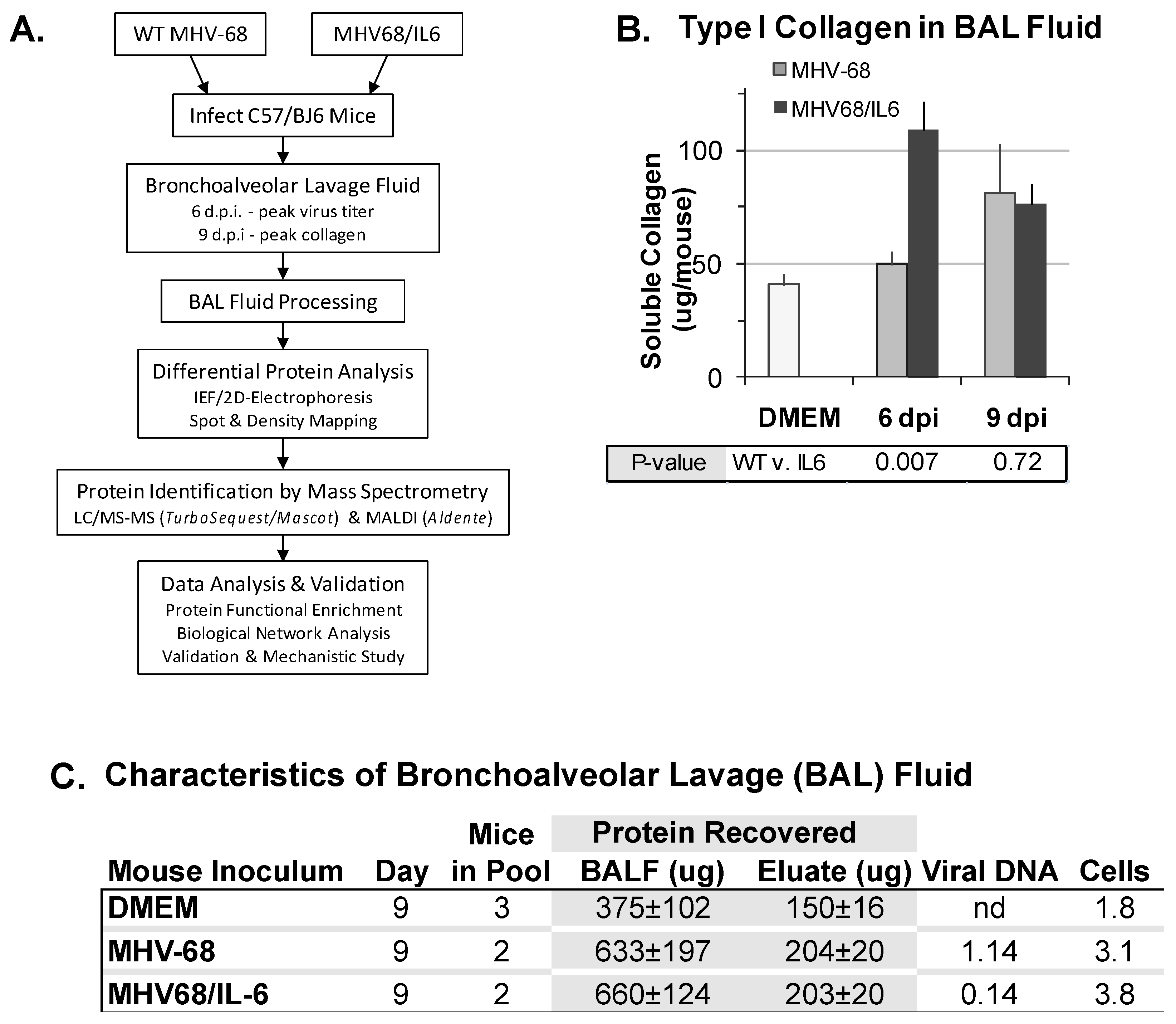
2.4. Sircol Collagen Assay
2.5. Catalase Assay and Immunoblotting
2.6. PCR
2.7. IEF, 2D-PAGE, Spot Mapping and Densitometry
2.8. Mass Spectrometry
2.9. Bioinformatics Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Recovery and Characterization of BAL Fluid from Mouse Lungs Infected with MHV-68
3.2. Differential Proteomics Analysis of BAL Fluid
3.3. Functions of Proteins Induced by MHV-68 in Lungs
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Acute Phase and Oxidative Stress Gene Expression in the MHV-68 Infected Lung
3.6. Lytic MHV-68 Infection Induces Oxidative Stress in Cultured Fibroblasts
3.7. An Oxidative Stress Response Network Induced in Mouse Lungs by MHV-68 Infection
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Co-Expressing IL6
4.2. Oxidative Stress Response Proteins Are Induced in MHV-68 Infection of the Mouse Lung
4.2.1. Sources of Oxidative Stress
4.2.2. Oxidative Damage to Surfactant Phospholipids
4.2.3. Comparison to other Respiratory Diseases and Role of Nrf2
4.3. Modeling a Complex Relationship
4.3.1. Acute Phase Response
4.3.2. Other Immunomodulatory Proteins in BAL Fluid
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Experimental MHV-68 Infection of the Mouse as a Model for Lung Diseases
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belser, J.A.; Maines, T.R.; Tumpey, T.M.; Katz, J.M. Influenza A virus transmission: Contributing factors and clinical implications. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2010, 12, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Carmo Debur, M.; Raboni, S.M.; Flizikowski, F.B.; Chong, D.C.; Persicote, A.P.; Nogueira, M.B.; Rosele, L.V.; de Almeida, S.M.; de Noronha, L. Immunohistochemical assessment of respiratory viruses in necropsy samples from lethal non-pandemic seasonal respiratory infections. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Dong, L.; Dong, J.; Wen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Feng, Z.; Chen, M.; Tan, Y.; Mo, Z.; et al. A systematic molecular pathology study of a laboratory confirmed H5N1 human case. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, M.; Skidmore, S.; Osman, H.; Weinbren, M.; Warren, R. Surveillance of respiratory virus infections in adult hospital admissions using rapid methods. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenburg, J.; Boivin, G. The distinguishing features of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.L.; Palacios, G.; Jabado, O.J.; Conlan, S.; Hirschberg, D.L.; Pozo, F.; Jack, P.J.; Cisterna, D.; Renwick, N.; Hui, J.; et al. Detection of respiratory viruses and subtype identification of influenza A viruses by GreeneChipResp oligonucleotide microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estenssoro, E.; Rios, F.G.; Apezteguia, C.; Reina, R.; Neira, J.; Ceraso, D.H.; Orlandi, C.; Valentini, R.; Tiribelli, N.; Brizuela, M.; et al. Pandemic 2009 influenza A in Argentina: A study of 337 patients on mechanical ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koegelenberg, C.F.; Irusen, E.M.; Cooper, R.; Diacon, A.H.; Taljaard, J.J.; Mowlana, A.; von Groote-Bidlingmaier, F.; Bolliger, C.T. High mortality from respiratory failure secondary to swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in South Africa. QJM 2010, 103, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, A.; Chandra, S.; Agarwal, D.; Guleria, R.; Broor, S.; Gaur, B.; Pandey, R.M. Prevalence of viral infection detected by PCR and RT-PCR in patients with acute exacerbation of COPD: A systematic review. Respirology 2010, 15, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterwhite, L.; Mehta, A.; Martin, G.S. Novel findings from the second wave of adult pH1N1 in the United States. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoopat, L.; Rangkakulnuwat, S.; Okonogi, R.; Wannasai, K.; Bhoopat, T. Cell reservoirs of the Epstein-Barr virus in biopsy-proven lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis in HIV-1 subtype E infected children: Identification by combined in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2010, 18, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, J.A.; Hayashi, S.; Hegele, R.G.; Hogg, J.C. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia by in situ hybridization. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.; Franzen, C.; Klussmann, P.; Wagner, M.; Diehl, V.; Fatkenheuer, G.; Salzberger, B.; Ablashi, D.V.; Krueger, G.R. Human herpesvirus type 8 in HIV-infected patients with interstitial pneumonitis. J. Infect. 2000, 40, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.L.; Torres-Gonzalez, E.; Rojas, M.; Xu, J.; Ritzenthaler, J.; Speck, S.H.; Roman, J.; Brigham, K.; Stecenko, A. Control of virus reactivation arrests pulmonary herpesvirus-induced fibrosis in IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.J.; Kipar, A.; Sample, J.T.; Stewart, J.P. Pathogenesis of a model gammaherpesvirus in a natural host. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3949–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weslow-Schmidt, J.L.; Jewell, N.A.; Mertz, S.E.; Simas, J.P.; Durbin, J.E.; Flano, E. Type I interferon inhibition and dendritic cell activation during gammaherpesvirus respiratory infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9778–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Cool, C.D.; van Dyk, L.F. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 infection of gamma interferon-deficient mice on a BALB/c background results in acute lethal pneumonia that is dependent on specific viral genes. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11397–11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarawar, S.R.; Cardin, R.D.; Brooks, J.W.; Mehrpooya, M.; Hamilton-Easton, A.M.; Mo, X.Y.; Doherty, P.C. Gamma interferon is not essential for recovery from acute infection with murine gammaherpesvirus 68. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3916–3921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarawar, S.R.; Lee, B.J.; Anderson, M.; Teng, Y.C.; Zuberi, R.; Von Gesjen, S. Chemokine induction and leukocyte trafficking to the lungs during murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68) infection. Virology 2002, 293, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarawar, S.R.; Cardin, R.D.; Brooks, J.W.; Mehrpooya, M.; Tripp, R.A.; Doherty, P.C. Cytokine production in the immune response to murine gammaherpesvirus 68. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3264–3268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dutia, B.M.; Allen, D.J.; Dyson, H.; Nash, A.A. Type I interferons and IRF-1 play a critical role in the control of a gammaherpesvirus infection. Virology 1999, 261, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehtisham, S.; Sunil-Chandra, N.P.; Nash, A.A. Pathogenesis of murine gammaherpesvirus infection in mice deficient in CD4 and CD8 T cells. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 5247–5252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuse, S.; Obar, J.J.; Bellfy, S.; Leung, E.K.; Zhang, W.; Usherwood, E.J. CD80 and CD86 control antiviral CD8+ T-cell function and immune surveillance of murine gammaherpesvirus 68. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9159–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.B.; Holmes, K.L.; Fredrickson, T.N.; Hartley, J.W.; Morse, H.C., 3rd. Characteristics of a murine gammaherpesvirus infection immunocompromised mice. In Vivo 1997, 11, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.; Shea, A.L.; Inglis, C.; Giannoni, F.; Lee, L.N.; Sarawar, S.R. Primary clearance of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 by PKCtheta-/- CD8 T cells is compromised in the absence of help from CD4 T cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11970–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, T.R.; Moore, B.B.; Weinberg, J.B.; Vannella, K.M.; Fields, W.B.; Christensen, P.J.; van Dyk, L.F.; Toews, G.B. Exacerbation of established pulmonary fibrosis in a murine model by gammaherpesvirus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Lin, C.F.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, C.W.; Lin, Y.S. Prediction of outcome in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome by bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory mediators. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.H.; Law, H.K.; Wang, L.J.; Li, X.; Yang, X.Q.; Liu, E.M. Lipopolysaccharide induces IL-6 production in respiratory syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells through the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarawar, S.R.; Brooks, J.W.; Cardin, R.D.; Mehrpooya, M.; Doherty, P.C. Pathogenesis of murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Virology 1998, 249, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Osborne, J.; Bestetti, G.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Viral IL-6-induced cell proliferation and immune evasion of interferon activity. Science 2002, 298, 1432–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Nicholas, J. Signal transduction by human herpesvirus 8 viral interleukin-6 (vIL-6) is modulated by the nonsignaling gp80 subunit of the IL-6 receptor complex and is distinct from signaling induced by human IL-6. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10874–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, S.A.; Nguyen, E.; Altemeier, W.A.; Shaffer, S.A.; Doneanu, C.E.; Goodlett, D.R.; Schnapp, L.M. Of mice and men: Comparative proteomics of bronchoalveolar fluid. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 35, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattiez, R.; Falmagne, P. Proteomics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 815, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Torre, C.; Ying, S.X.; Munson, P.J.; Meduri, G.U.; Suffredini, A.F. Proteomic analysis of inflammatory biomarkers in bronchoalveolar lavage. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnapp, L.M.; Donohoe, S.; Chen, J.; Sunde, D.A.; Kelly, P.M.; Ruzinski, J.; Martin, T.; Goodlett, D.R. Mining the acute respiratory distress syndrome proteome: Identification of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)/IGF-binding protein-3 pathway in acute lung injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottoli, P.; Magi, B.; Perari, M.G.; Liberatori, S.; Nikiforakis, N.; Bargagli, E.; Cianti, R.; Bini, L.; Pallini, V. Cytokine profile and proteome analysis in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis associated with systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plymoth, A.; Lofdahl, C.G.; Ekberg-Jansson, A.; Dahlback, M.; Broberg, P.; Foster, M.; Fehniger, T.E.; Marko-Varga, G. Protein expression patterns associated with progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in bronchoalveolar lavage of smokers. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Umstead, T.M.; Freeman, W.M.; Floros, J.; Phelps, D.S. The impact of surfactant protein-A on ozone-induced changes in the mouse bronchoalveolar lavage proteome. Proteome Sci. 2009, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Kang, X.; Boontheung, P.; Li, N.; Nel, A.E.; Loo, J.A. Oxidative stress and asthma: Proteome analysis of chitinase-like proteins and FIZZ1 in lung tissue and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, M.A.; Bradbury, J.A.; Rebolloso, Y.D.; Graves, J.P.; Zeldin, D.C.; Germolec, D.R. Pharmacologic inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 in influenza A viral infection in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.N.; Estep, R.D.; Lopez-Ferrer, D.; Brewer, H.M.; Clauss, T.R.; Manes, N.P.; O’Connor, M.; Li, H.; Adkins, J.N.; Wong, S.W.; et al. Characterization of macaque pulmonary fluid proteome during monkeypox infection: Dynamics of host response. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosakote, Y.M.; Liu, T.; Castro, S.M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Respiratory syncytial virus induces oxidative stress by modulating antioxidant enzymes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, C.L.; Higdon, R.; Hohmann, L.; Martin, D.; Kolker, E.; Liggitt, H.D.; Skerrett, S.J.; Rubens, C.E. Staphylococcus aureus elicits marked alterations in the airway proteome during early pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5862–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, C.L.; Higdon, R.; Kolker, E.; Skerrett, S.J.; Rubens, C.E. Host airway proteins interact with Staphylococcus aureus during early pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Umstead, T.M.; Haque, R.; Mikerov, A.N.; Freeman, W.M.; Floros, J.; Phelps, D.S. Differences in the BAL proteome after Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in wild type and SP-A-/- mice. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoolman, J.S.; Vannella, K.M.; Coomes, S.M.; Wilke, C.A.; Sisson, T.H.; Toews, G.B.; Moore, B.B. Latent Infection by Gammaherpesvirus Stimulates Pro-fibrotic Mediator Release from Multiple Cell Types. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 300, L274–L285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, C.E.; Xu, W.; Pullarkat, R.K.; Kascsak, R. Retinoic acid reduces the yield of herpes simplex virus in Vero cells and alters the N-glycosylation of viral envelope proteins. Antiviral Res. 2000, 47, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Galvan, M.; Santoni, F.; Alvarez, S.; de Lera, A.R.; Ivanova, D.; Gronemeyer, H.; Caruso, A.; Guidoboni, M.; Cassai, E.; et al. Retinoic acid analogues inhibit human herpesvirus 8 replication. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Stephensen, C.B. High-level dietary vitamin A enhances T-helper type 2 cytokine production and secretory immunoglobulin A response to influenza A virus infection in BALB/c mice. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, C.; Kadokawa, Y.; Tabata, R.; Takahashi, M.; Okoshi, K.; Sakai, Y.; Mishima, M.; Kubo, H. All-trans-retinoic acid prevents radiation- or bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Dutia, B.M.; Brownstein, D.G.; Nash, A.A. Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection causes multi-organ fibrosis and alters leukocyte trafficking in interferon-gamma receptor knockout mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symensma, T.L.; Martinez-Guzman, D.; Jia, Q.; Bortz, E.; Wu, T.T.; Rudra-Ganguly, N.; Cole, S.; Herschman, H.; Sun, R. COX-2 induction during murine gammaherpesvirus 68 infection leads to enhancement of viral gene expression. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12753–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, C.; Kubo, H.; Tabata, R.; Wada, M.; Sakuma, K.; Ichikawa, M.; Fujita, S.; Mio, T.; Mishima, M. All-trans retinoic acid modulates radiation-induced proliferation of lung fibroblasts via IL-6/IL-6R system. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L597–L606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Gong, S.; Carmody, R.J.; Hilliard, A.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Kong, L.; Xu, L.; Hilliard, B.; Hu, S.; et al. TIPE2, a negative regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune homeostasis. Cell 2008, 133, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaofei, E.; Hwang, S.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Gwack, Y.; Kowalik, T.F.; Sun, R.; Jung, J.U.; Liang, C. Viral Bcl-2-mediated evasion of autophagy aids chronic infection of gammaherpesvirus 68. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000609. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Druhan, L.J.; Zweier, J.L. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase function shifting the balance of nitric oxide and superoxide production. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 494, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, I. Oxidative stress in pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 43, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglott, D.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T. Entrez Gene: Gene-centered information at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D52–D57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, S.S.; Haider, Y.; Howell, D.; Stewart, J.P.; Hasleton, P.S.; Egan, J.J. Murine gammaherpes virus as a cofactor in the development of pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin resistant mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.N.; Palermo, R.E.; Baskin, C.R.; Gritsenko, M.; Sabourin, P.J.; Long, J.P.; Sabourin, C.L.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Albrecht, R.; et al. Macaque proteome response to highly pathogenic avian influenza and 1918 reassortant influenza virus infections. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12058–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortz, E.; Wang, L.; Jia, Q.; Wu, T.T.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Sun, R. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF52 encodes a tegument protein required for virion morphogenesis in the cytoplasm. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10137–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Wu, T.T.; Tong, L.M.; Kim, K.S.; Martinez-Guzman, D.; Colantonio, A.D.; Uittenbogaart, C.H.; Sun, R. Persistent gammaherpesvirus replication and dynamic interaction with the host in vivo. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12498–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.T.; Liao, H.I.; Tong, L.; Leang, R.S.; Smith, G.; Sun, R. Construction and characterization of an infectious murine gammaherpesivrus-68 bacterial artificial chromosome. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 926258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.S.; Coleman, H.M.; Boname, J.M.; Stevenson, P.G. Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 ORF28 encodes a non-essential virion glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Chernishof, V.; Bortz, E.; McHardy, I.; Wu, T.T.; Liao, H.I.; Sun, R. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 open reading frame 45 plays an essential role during the immediate-early phase of viral replication. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5129–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortz, E.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Jia, Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; Stewart, J.P.; Wu, T.T.; Sun, R. Identification of proteins associated with murine gammaherpesvirus 68 virions. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13425–13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, S.M.; Bil, K.Y.; Aguilera, R.; Nishio, J.N.; Faull, K.F.; Whitelegge, J.P. Transit peptide cleavage sites of integral thylakoid membrane proteins. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, L.D.; Orozco, N.M.; Geschwind, D.H.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Faull, K.F.; Kornblum, H.I. Identification of differentially expressed proteins in murine embryonic and postnatal cortical neural progenitors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagi, P.M.; Lisacek, F.; Appel, R.D. Database interrogation algorithms for identification of proteins in proteomic separations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 519, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskin, C.R.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Tumpey, T.M.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Carter, V.S.; Nistal-Villan, E.; Katze, M.G. Integration of clinical data, pathology, and cDNA microarrays in influenza virus-infected pigtailed macaques (Macaca nemestrina). J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10420–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Drai, D.; Elmer, G.; Kafkafi, N.; Golani, I. Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, G., Jr.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, L.T.; Torres-Gonzalez, E.; Qin, Q.; Sorescu, D.; Rojas, M.; Stecenko, A.; Speck, S.H.; Mora, A.L. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling reduces virus load and gammaherpesvirus-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenstra, T.D.; Conrads, T.P.; Hood, B.L.; Avellino, A.M.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Morrison, R.S. Biomarkers: Mining the biofluid proteome. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, S.A.; Vaisar, T.; Aitken, M.L.; Park, D.R.; Heinecke, J.W.; Fu, X. Mapping the lung proteome in cystic fibrosis. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3020–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.W.; Hayashi, S.; Gharib, S.A.; Vaisar, T.; King, S.T.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ruzinski, J.T.; Park, D.R.; Matute-Bello, G.; Wurfel, M.M.; et al. Proteomic and computational analysis of bronchoalveolar proteins during the course of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Chang, Y.W.; Yao, C.W.; Chiueh, T.S.; Huang, S.C.; Chien, K.Y.; Chen, A.; Chang, F.Y.; Wong, C.H.; Chen, Y.J. Plasma proteome of severe acute respiratory syndrome analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17039–17044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Neely, G.G.; Yaghubian-Malhami, R.; Perkmann, T.; van Loo, G.; Ermolaeva, M.; Veldhuizen, R.; Leung, Y.H.; Wang, H.; et al. Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury. Cell 2008, 133, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolliputi, N.; Waxman, A.B. IL-6 cytoprotection in hyperoxic acute lung injury occurs via suppressor of cytokine signaling-1-induced apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 degradation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, C.A.; McClellan, J.L.; Maassab, H.F.; Smitka, C.W.; Majde, J.A.; Kluger, M.J. Cytokines and the acute phase response to influenza virus in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, R78–R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinton, L.J.; Jones, M.R.; Robson, B.E.; Mizgerd, J.P. Mechanisms of the hepatic acute-phase response during bacterial pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.J.; Song, M.J.; Deng, H.; Wu, T.T.; Cheng, G.; Sun, R. NF-kappaB inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8532–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S.; Taga, T. IL-6 receptor and mechanism of signal transduction. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1992, 14, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J.; Zahlten, J.; Pollok, I.; Lippmann, J.; Scharf, S.; N’Guessan, P.D.; Opitz, B.; Flieger, A.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S.; et al. Legionella pneumophila induced IκBζ-dependent expression of Il-6 in lung epithelium. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, E.C.; Gage, J.R.; Guo, B.; Magpantay, L.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Miles, S.; Martinez-Maza, O. Viral interleukin 6 stimulates human peripheral blood B cells that are unresponsive to human interleukin 6. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 212, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Chu, J.T.; Rettig, M.B.; Martinez-Maza, O.; Sun, R. Rta of the human herpesvirus 8/Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus up-regulates human interleukin-6 gene expression. Blood 2002, 100, 1919–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Z.; Kearney, P.; Plaisance, K.; Parsons, C.H. Pivotal advance: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-encoded microRNA specifically induce IL-6 and IL-10 secretion by macrophages and monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Imani, F.; Miller-DeGraff, L.; Walters, D.; Melendi, G.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Polack, F.P.; Kleeberger, S.R. Antiviral activity of Nrf2 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.M.; Knobil, K.; Otterbein, S.L.; Eastman, D.A.; Jacoby, D.B. Oxidant stress responses in influenza virus pneumonia: Gene expression and transcription factor activation. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, L383–L391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, S.; Khanna, M.; Raj, H.G. Effect of Quercetin on lipid peroxidation and changes in lung morphology in experimental influenza virus infection. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2003, 84, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, H.B.; Ryan, L.K.; Bishop, L.; Folz, R.J. Prevention of influenza-induced lung injury in mice overexpressing extracellular superoxide dismutase. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L69–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, S.M.; Guerrero-Plata, A.; Suarez-Real, G.; Adegboyega, P.A.; Colasurdo, G.N.; Khan, A.M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Antioxidant treatment ameliorates respiratory syncytial virus-induced disease and lung inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Ganesan, S.; Comstock, A.T.; Meldrum, C.A.; Mahidhara, R.; Goldsmith, A.M.; Curtis, J.L.; Martinez, F.J.; Hershenson, M.B.; Sajjan, U. Increased cytokine response of rhinovirus-infected airway epithelial cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavouras, J.H.; Prandovszky, E.; Valyi-Nagy, K.; Kovacs, S.K.; Tiwari, V.; Kovacs, M.; Shukla, D.; Valyi-Nagy, T. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection induces oxidative stress and the release of bioactive lipid peroxidation by-products in mouse P19N neural cell cultures. J. Neurovirol. 2007, 13, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.S.; Bryant, P.W.; Burch, A.D. Accumulation of oxidized proteins in Herpesvirus infected cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaul, P.; Singh, I.; Turner, R.B. Effect of rhinovirus challenge on antioxidant enzymes in respiratory epithelial cells. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; van Breemen, R.B. DNA oxidation induced by cyclooxygenase-2. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, K.L. Role of surfactant protein A and D (SP-A and SP-D) in human antiviral host defense. Front. Biosci. 2009, 2, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.B.; Dodia, C.; Chander, A. Inhibition of lung calcium-independent phospholipase A2 by surfactant protein A. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, L335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manevich, Y.; Fisher, A.B. Peroxiredoxin 6, a 1-Cys peroxiredoxin, functions in antioxidant defense and lung phospholipid metabolism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.B.; Dodia, C.; Yu, K.; Manevich, Y.; Feinstein, S.I. Lung phospholipid metabolism in transgenic mice overexpressing peroxiredoxin 6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Feinstein, S.I.; Wang, Y.; Dodia, C.; Fisher, D.; Yu, K.; Ho, Y.S.; Fisher, A.B. Comparison of glutathione peroxidase 1 and peroxiredoxin 6 in protection against oxidative stress in the mouse lung. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bocchino, M.; Agnese, S.; Fagone, E.; Svegliati, S.; Grieco, D.; Vancheri, C.; Gabrielli, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Avvedimento, E.V. Reactive oxygen species are required for maintenance and differentiation of primary lung fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, W.; Lindholm, P.; Vuorinen, K.; Myllarniemi, M.; Salmenkivi, K.; Kinnula, V.L. Cell-specific elevation of NRF2 and sulfiredoxin-1 as markers of oxidative stress in the lungs of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and non-specific interstitial pneumonia. APMIS 2010, 118, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuorinen, K.; Ohlmeier, S.; Lepparanta, O.; Salmenkivi, K.; Myllarniemi, M.; Kinnula, V.L. Peroxiredoxin II expression and its association with oxidative stress and cell proliferation in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Salwinski, L.; Zhang, C.; Chu, D.; Sampankanpanich, C.; Reyes, N.A.; Vangeloff, A.; Xing, F.; Li, X.; Wu, T.T.; et al. An integrated approach to elucidate the intra-viral and viral-cellular protein interaction networks of a gamma-herpesvirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.; Filipe, J.; Seldon, M.P.; Fonseca, L.; Anrather, J.; Soares, M.P.; Simas, J.P. Termination of NF-kappaB activity through a gammaherpesvirus protein that assembles an EC5S ubiquitin-ligase. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Feng, J.; Sun, R. Oxidative stress induces reactivation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and death of primary effusion lymphoma cells. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monton, C.; Torres, A. Lung inflammatory response in pneumonia. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 1998, 53, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Jong, H.K.; van der Poll, T.; Wiersinga, W.J. The systemic pro-inflammatory response in sepsis. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.B.; Lavender, K.J.; Qin, L.; Stacey, A.R.; Liu, M.K.; di Gleria, K.; Simmons, A.; Gasper-Smith, N.; Haynes, B.F.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. Elevation of intact and proteolytic fragments of acute phase proteins constitutes the earliest systemic antiviral response in HIV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.; Kalsheker, N.A. Regulation of the serine proteinase inhibitor (SERPIN) gene alpha 1-antitrypsin: A paradigm for other SERPINs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 and NF-IL6 in acute-phase response and viral infection. Immunol. Rev. 1992, 127, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasnacht, N.; Muller, W. Conditional gp130 deficient mouse mutants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Cordero, E.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Aguilar, L.D.; Orozco, E.H.; Hernandez Pando, R. Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, its local production and immunopathological participation in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, H.M.; Newcomer, M.E. The structure of human retinol-binding protein (RBP) with its carrier protein transthyretin reveals an interaction with the carboxy terminus of RBP. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Spot a | BAL Protein Identification | Symbol | GO:Terms b | Function | Lung Disease Finding c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Phase Response and Inflammation | |||||
| 1 | α1-acid glycoprotein 1B | A1AG1 | 0002682 | Lipocalin-like immune regulator | APR; TB; IAV |
| 2 | α1-anti-trypsin (serpin A1) | A1AT6 | 0004867 | Serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor | APR; ARDS; COPD; SARS; IAV |
| 3 | α2-macroglobulin | A2MP | 0004867 | Serum-type endopeptidase inhibitor | APR; ARDS; IPF |
| 11 | Haptoglobin | Hp | 0004252 | Serine-type endopeptidase | APR; SARS |
| 12 | IL1 family member 10 | IL1f10 | 0005152 | IL1-receptor antagonist | APR; IPF |
| 21 | TNF α-induced protein 8-like 2 | Tnfaip8l2 | 0050728 | Negative immune regulator | Anti-proliferative |
| Oxidative Stress Response | |||||
| 19 | Superoxide dismutase 3 [Cu-Zn], ex. | EC-SOD | 0006979 | Response to oxidative stress | ARDS; NFκB; antioxidant |
| 10 | Glutathione-S-transferase, mu1 | GSTm1 | 0004364 | Response to oxidative stress | Antioxidant |
| 14 | Peroxiredoxin 2 | Pdx2 | 0006979 | Response to oxidative stress | ARDS; SARS; IAV; antioxidant |
| 15 | Peroxiredoxin 6 | Pdx6 | 0000302 | Response to reactive oxygen species | Sf-PhL; IAV; antioxidant |
| 20 | Thioredoxin-like 4B | TXNL4B | 0030612 | Thioredoxin activity | Antioxidant |
| Phospholipid Metabolism and Signaling | |||||
| 8 | Calcyclin | S100a6 | 0048146 | Fibroblast proliferation | Growth factor |
| 9 | Clara cell protein 10 | CC10 | 0019834 | Phospholipase A2 inhibitor | Sf-PhL |
| 13 | Oxytocin receptor | OxtR | 0004990 | Oxytocin receptor activity | |
| 16 | Phospholipase A2, secreted | PLA2G12A | 0004623 | Phospholipase A2 activity | SARS; IAV; Sf-PhL |
| 12 | Hydrocephalus-inducing protein | Hydin | 0003341 | Movement of tracheal cilia | |
| Molecular Transport/Serum | |||||
| 5 | Albumin | Alb | 0006810 | Molecular transport in serum | |
| 6 | Annexin A5 | Anxa5 | 0050819 | Negative regulation of coagulation | Anticoagulant |
| 4 | α2-u-globulin (mj urinary protein 6) | Mup6 | 0005550 | Lipocalin-like pheromone transport | Allergen |
| 7 | Apolipoprotein E | ApoE | 0017127 | Cholesterol, lipid transport in serum | Sf-PhL |
| 17 | Plasma retinol binding protein | RBP4 | 0001972 | Plasma retinol and vitamin A carrier | SARS; VA; APR (negative) |
| 18 | Retinoic acid binding protein 2 | CRABP2 | 0001972 | Retinoic acid (retinol) binding | APR; VA |
| 22 | Transthyretin | TTR | 0005179 | Vitamin A and T4/thyroxine transport | APR; VA |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bortz, E.; Wu, T.-T.; Patel, P.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Sun, R. Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Reveals a Lung Oxidative Stress Response in Murine Herpesvirus-68 Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120670
Bortz E, Wu T-T, Patel P, Whitelegge JP, Sun R. Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Reveals a Lung Oxidative Stress Response in Murine Herpesvirus-68 Infection. Viruses. 2018; 10(12):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120670
Chicago/Turabian StyleBortz, Eric, Ting-Ting Wu, Parthive Patel, Julian P. Whitelegge, and Ren Sun. 2018. "Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Reveals a Lung Oxidative Stress Response in Murine Herpesvirus-68 Infection" Viruses 10, no. 12: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120670
APA StyleBortz, E., Wu, T.-T., Patel, P., Whitelegge, J. P., & Sun, R. (2018). Proteomics of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Reveals a Lung Oxidative Stress Response in Murine Herpesvirus-68 Infection. Viruses, 10(12), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120670






