Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Matrix Protein Reduces Viral RNA Synthesis of HPIV3 by Regulating Inclusion Body Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Plasmid Constructs
2.3. In Vitro Minigenome Assay of HPIV3
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.6. Transfection and Recovery of Recombinant HPIV3
3. Results
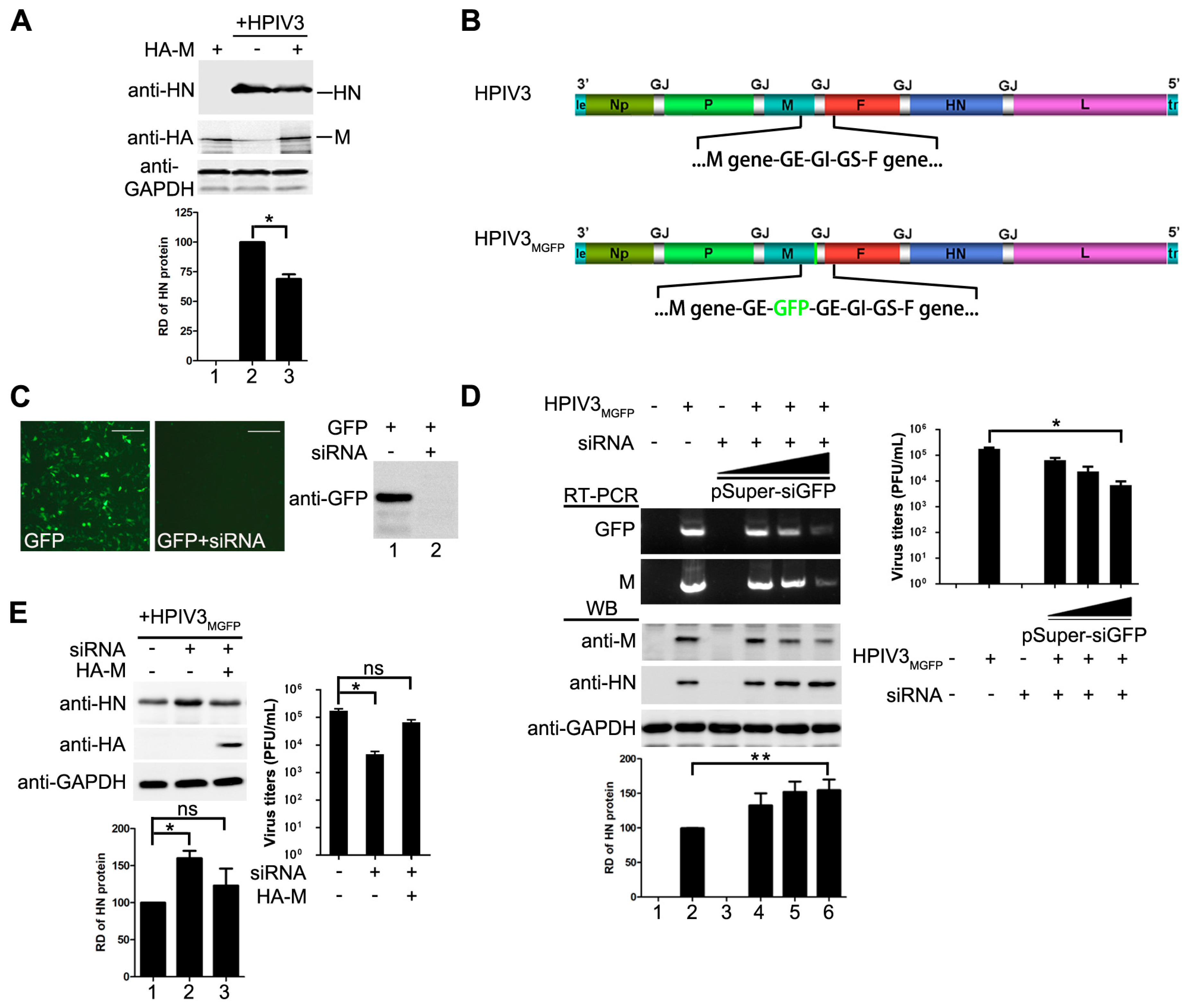
3.1. M Reduces HPIV3 Mingenome-Encoded Reporter Activity
3.2. M Restricts the Replication of HPIV3
3.3. The Inhibitory Activity of M Is Independent of Its Budding Ability
3.4. M Reduces the IB Formation via M–N Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPIV3 | human parainfluenza virus type 3 |
| M | matrix protein |
| VLP | virus like particle |
| N | nucleoprotein |
| IBs | inclusion bodies |
| NNSV | non-segmented, negative-strand RNA virus |
| P | phosphoprotein |
| L | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| F | fusion protein |
| HN | hemagglutinin-neuraminidase |
| RNP | ribonucleoprotein |
| GS | gene start |
| GE | gene end |
| GJ | gene junction |
| VSV | vesicular stomatitis virus |
| RSV | respiratory syncytial virus |
| NiV | Nipah virus |
| EBOV | Ebola virus |
| MeV | measles virus |
| PIV5 | parainfluenza virus type 5 |
| IFN-I | type-I interferon |
| RABV | rabies virus |
| MARV | Marburg virus |
| MOI | multiplicity of infection |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| vTF7-3 | Recombinant vaccinia virus |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
References
- Moscona, A. Entry of parainfluenza virus into cells as a target for interrupting childhood respiratory disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.K.; Barik, S.; De, B.P. Gene expression of nonsegmented negative strand RNA viruses. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 51, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.A.; Banerjee, A.K. Precise mapping of the replication and transcription promoters of human parainfluenza virus type 3. Virology 2000, 269, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, S.; Receveur-Brechot, V.; Karlin, D.; Johansson, K.; Darbon, H.; Bhella, D.; Yeo, R.; Finet, S.; Canard, B. The C-terminal domain of the measles virus nucleoprotein is intrinsically disordered and folds upon binding to the C-terminal moiety of the phosphoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18638–18648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, T.M.; Pieters, A.; Moyer, S.A. A highly conserved region of the Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein contributes to the NP-NP binding domain. Virology 1997, 229, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, C.J.; Retzler, C.; Homann, H.E.; Neubert, W.J. The carboxy-terminal domain of Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein is involved in complex formation between phosphoprotein and nucleocapsid-like particles. Virology 1994, 204, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, E.A., Jr.; Favier, A.; Gerard, F.C.; Leyrat, C.; Brutscher, B.; Blondel, D.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Blackledge, M.; Jamin, M. Solution structure of the C-terminal nucleoprotein-RNA binding domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.K.; Malur, A.G.; Huo, Y.; De, B.P.; Banerjee, A.K. Characterization of the oligomerization domain of the phosphoprotein of human parainfluenza virus type 3. Virology 2002, 302, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Q.; Yang, X.; Ding, B.; Tang, Q.; Sun, S.; Hu, Z.; Chen, M. An amino acid of human parainfluenza virus type 3 nucleoprotein is critical for template function and cytoplasmic inclusion body formation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12457–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chen, M. Inclusion Body Fusion of Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Regulated by Acetylated alpha-Tubulin Enhances Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebatsion, T.; Weiland, F.; Conzelmann, K.K. Matrix protein of rabies virus is responsible for the assembly and budding of bullet-shaped particles and interacts with the transmembrane spike glycoprotein G. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cathomen, T.; Mrkic, B.; Spehner, D.; Drillien, R.; Naef, R.; Pavlovic, J.; Aguzzi, A.; Billeter, M.A.; Cattaneo, R. A matrix-less measles virus is infectious and elicits extensive cell fusion: Consequences for propagation in the brain. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3899–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, E.O. Viral late domains. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4679–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, R.N.; Paragas, J.; Sudol, M.; Palese, P. A proline-rich motif within the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus interacts with WW domains of cellular proteins: Implications for viral budding. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baviskar, P.S.; Hotard, A.L.; Moore, M.L.; Oomens, A.G. The respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein targets to the perimeter of inclusion bodies and facilitates filament formation by a cytoplasmic tail-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10730–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patch, J.R.; Crameri, G.; Wang, L.F.; Eaton, B.T.; Broder, C.C. Quantitative analysis of Nipah virus proteins released as virus-like particles reveals central role for the matrix protein. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmins, J.; Scianimanico, S.; Schoehn, G.; Weissenhorn, W. Vesicular release of ebola virus matrix protein VP40. Virology 2001, 283, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runkler, N.; Pohl, C.; Schneider-Schaulies, S.; Klenk, H.D.; Maisner, A. Measles virus nucleocapsid transport to the plasma membrane requires stable expression and surface accumulation of the viral matrix protein. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.P.; Leser, G.P.; Waning, D.L.; Lamb, R.A. Requirements for budding of paramyxovirus simian virus 5 virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3952–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Schmitt, P.T.; Li, Z.; McCrory, T.S.; He, B.; Schmitt, A.P. Mumps virus matrix, fusion, and nucleocapsid proteins cooperate for efficient production of virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7261–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Ding, B.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, M. A leucine residue in the C terminus of human parainfluenza virus type 3 matrix protein is essential for efficient virus-like particle and virion release. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13173–13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chen, M. Interaction of Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Nucleoprotein with Matrix Protein Mediates Internal Viral Protein Assembly. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, B.P.; Thornton, G.B.; Luk, D.; Banerjee, A.K. Purified matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus blocks viral transcription in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 7137–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, S.; Mueller-Waldeck, R.; Conzelmann, K.K. Rabies virus matrix protein regulates the balance of virus transcription and replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 6, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Takeda, M.; Shirogane, Y.; Nakatsu, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yanagi, Y. The matrix protein of measles virus regulates viral RNA synthesis and assembly by interacting with the nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10374–10383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenen, T.; Jung, S.; Herwig, A.; Groseth, A.; Becker, S. Both matrix proteins of Ebola virus contribute to the regulation of viral genome replication and transcription. Virology 2010, 403, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jans, D.A.; Bardin, P.G.; Meanger, J.; Mills, J.; Ghildyal, R. Association of respiratory syncytial virus M protein with viral nucleocapsids is mediated by the M2-1 protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8863–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis-Ruth, F.X.; Dessen, A.; Timmins, J.; Bracher, A.; Kolesnikowa, L.; Becker, S.; Klenk, H.D.; Weissenhorn, W. The matrix protein VP40 from Ebola virus octamerizes into pore-like structures with specific RNA binding properties. Structure 2003, 11, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.F.; McCarthy, S.E.; Godlewski, P.J.; Harty, R.N. Ebola virus VP35-VP40 interaction is sufficient for packaging 3E-5E minigenome RNA into virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5135–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, P.; Lieber, D.; Meyer, S.; Dautel, P.; Kerth, A.; Kraus, I.; Garten, W.; Stubbs, M.T. Crystal structure of the Borna disease virus matrix protein (BDV-M) reveals ssRNA binding properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3710–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacamo, R.; Lopez, N.; Wilda, M.; Franze-Fernandez, M.T. Tacaribe virus Z protein interacts with the L polymerase protein to inhibit viral RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10383–10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, B.L.; Lyles, D.S. Vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein inhibits host cell-directed transcription of target genes in vivo. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4058–4064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wenigenrath, J.; Kolesnikova, L.; Hoenen, T.; Mittler, E.; Becker, S. Establishment and application of an infectious virus-like particle system for Marburg virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91 Pt 5, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Protein | VLP Formation | M–N Interaction | M–P Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | + | + | + |
| ML302A | - | + | + |
| ML305A | + | - | + |
| Category | Size (Mean Cross-Sectional Area) |
|---|---|
| Large | Greater than 8 μm2 |
| Medium | Between 3 μm2 and 8 μm2 |
| Small | Less than 3 μm2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Cheng, Q.; Luo, C.; Qin, Y.; Chen, M. Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Matrix Protein Reduces Viral RNA Synthesis of HPIV3 by Regulating Inclusion Body Formation. Viruses 2018, 10, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030125
Zhang S, Cheng Q, Luo C, Qin Y, Chen M. Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Matrix Protein Reduces Viral RNA Synthesis of HPIV3 by Regulating Inclusion Body Formation. Viruses. 2018; 10(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shengwei, Qi Cheng, Chenxi Luo, Yali Qin, and Mingzhou Chen. 2018. "Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Matrix Protein Reduces Viral RNA Synthesis of HPIV3 by Regulating Inclusion Body Formation" Viruses 10, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030125
APA StyleZhang, S., Cheng, Q., Luo, C., Qin, Y., & Chen, M. (2018). Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 Matrix Protein Reduces Viral RNA Synthesis of HPIV3 by Regulating Inclusion Body Formation. Viruses, 10(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10030125




