Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Baculovirus as a Vector for Gene Delivery
2.1. Genome Structure and Very-Late Gene Expression of Baculovirus
2.2. Genetic Modification of Baculovirus for Minimum Vector
3. Baculovirus-Mediated Gene Delivery into Mammalian Cells
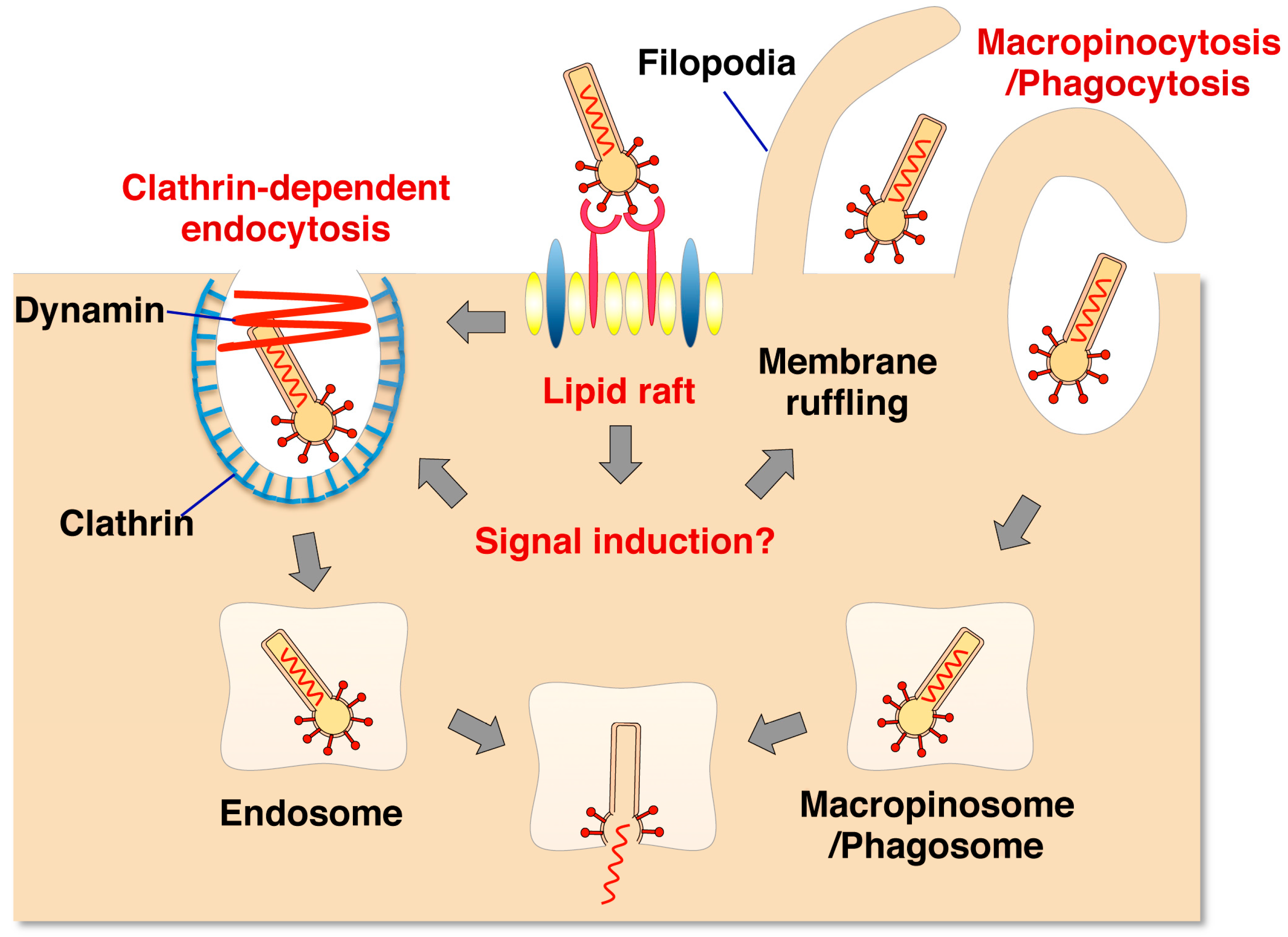
3.1. GP64-Mediated Entry into Mammalian Cells
3.2. Modification of Envelope Proteins on Recombinant Baculovirus
4. Immune Responses Induced by Baculovirus Infection in Mammalian Cells
4.1. Toll-Like Receptor-Dependent Pathway
4.2. Toll-Like Receptor-Independent Pathway
5. Baculovirus for Gene Therapy
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carbonell, L.F.; Klowden, M.J.; Miller, L.K. Baculovirus-mediated expression of bacterial genes in dipteran and mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1985, 56, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, C.; Sandig, V.; Jennings, G.; Rudolph, M.; Schlag, P.; Strauss, M. Efficient gene transfer into human hepatocytes by baculovirus vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10099–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, F.M.; Bucher, N.L. Baculovirus-mediated gene transfer into mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2348–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, I.; Aizaki, H.; Tani, H.; Ishii, K.; Chiba, T.; Saito, I.; Miyamura, T.; Matsuura, Y. Efficient gene transfer into various mammalian cells, including non-hepatic cells, by baculovirus vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 10, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Limn, C.K.; Yap, C.C.; Onishi, M.; Nozaki, M.; Nishimune, Y.; Okahashi, N.; Kitagawa, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Mochizuki, R.; et al. In vitro and in vivo gene delivery by recombinant baculoviruses. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9799–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, H.; Nishijima, M.; Ushijima, H.; Miyamura, T.; Matsuura, Y. Characterization of cell-surface determinants important for baculovirus infection. Virology 2001, 279, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckow, V.A.; Lee, S.C.; Barry, G.F.; Olins, P.O. Efficient generation of infectious recombinant baculoviruses by site-specific transposon-mediated insertion of foreign genes into a baculovirus genome propagated in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4566–4579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hamazaki, H.; Miyano-Kurosaki, N.; Matsuura, Y.; Takaku, H. Baculovirus induces an innate immune response and confers protection from lethal influenza virus infection in mice. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Hemmi, H.; Miyamoto, H.; Moriishi, K.; Tamura, S.; Takaku, H.; Akira, S.; Matsuura, Y. Involvement of the toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway in the induction of innate immunity by baculovirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2847–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Kaname, Y.; Wen, X.; Tani, H.; Moriishi, K.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Ishii, K.J.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S.; et al. Baculovirus induces type I interferon production through toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent pathways in a cell-type-specific manner. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7629–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronowski, A.M.; Hilbert, D.M.; Sheehan, K.C.; Garotta, G.; Schreiber, R.D. Baculovirus stimulates antiviral effects in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9944–9951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, M.; Takaku, H. Induction of antitumor acquired immunity by baculovirus Autographa californica multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection in mice. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrmann, G.F. Baculovirus Molecular Biology, 3rd ed.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013.
- Matsuura, Y.; Possee, R.D.; Overton, H.A.; Bishop, D.H. Baculovirus expression vectors: The requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 1233–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Kawai, T.; Obinata, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Saeki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Furusawa, M. Production of human alpha-interferon in silkworm using a baculovirus vector. Nature 1985, 315, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, P.D.; Miller, L.K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1986, 131, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leisy, D.J.; Rohrmann, G.; Beaudreau, G. The nucleotide sequence of the polyhedrin gene region from the multicapsid baculovirus of Orgyia pseudotsugata. Virology 1986, 153, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisy, D.J.; Rohrmann, G.F.; Neson, M.; Beaudreau, G.S. Nucleotide sequencing and transcriptional mapping of the Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus p10 gene. Virology 1986, 153, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Miller, L.K. Activation of baculovirus very late promoters by interaction with very late factor 1. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guarino, L.A.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Summers, M.D. Complete sequence and enhancer function of the homologous DNA regions of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J. Virol. 1986, 60, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Passarelli, A.L.; Miller, L.K. Three baculovirus genes involved in late and very late gene expression: Ie-1, ie-n, and lef-2. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blissard, G.W.; Quant-Russell, R.L.; Rohrmann, G.F.; Beaudreau, G.S. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional mapping, and temporal expression of the gene encoding p39, a major structural protein of the multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Orgyia pseudotsugata. Virology 1989, 168, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissard, G.W.; Rohrmann, G.F. Location, sequence, transcriptional mapping, and temporal expression of the gp64 envelope glycoprotein gene of the Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology 1989, 170, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabihi, H.; Ogliastro, M.H.; Martin, M.; Giraud, C.; Devauchelle, G.; Cerutti, M. Competition between baculovirus polyhedrin and p10 gene expression during infection of insect cells. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nobiron, I.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Olszewski, J.A. Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of spodoptera frugiperda cells: A global analysis of host gene regulation during infection, using a differential display approach. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayachandran, L.S.; Thimiri Govinda Raj, D.B.; Edelweiss, E.; Gupta, K.; Maier, J.; Gordeliy, V.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Berger, I. Gene gymnastics: Synthetic biology for baculovirus expression vector system engineering. Bioengineered 2013, 4, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, C.; Kamagata, T.; Taka, H.; Sahara, K.; Asano, S.; Bando, H. Phenotypic grouping of 141 BmNPVs lacking viral gene sequences. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodgson, J.J.; Arif, B.M.; Krell, P.J. Interaction of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus cathepsin protease progenitor (proV-CATH) with insect baculovirus chitinase as a mechanism for proV-CATH cellular retention. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3918–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Salem, T.Z.; Campbell, D.J.; Turney, C.M.; Kumar, C.M.; Cheng, X.W. Characterization of a virion occlusion-defective Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus mutant lacking the p26, p10 and p74 genes. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hitchman, R.B.; Possee, R.D.; Crombie, A.T.; Chambers, A.; Ho, K.; Siaterli, E.; Lissina, O.; Sternard, H.; Novy, R.; Loomis, K.; et al. Genetic modification of a baculovirus vector for increased expression in insect cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2010, 26, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noad, R.J.; Stewart, M.; Boyce, M.; Celma, C.C.; Willison, K.R.; Roy, P. Multigene expression of protein complexes by iterative modification of genomic bacmid DNA. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taka, H.; Ono, C.; Sato, M.; Asano, S.-I.; Bando, H. Complex genetic interactions among non-essential genes of BmNPV revealed by multiple gene knockout analysis. J. Insect Biotechnol. Sericol. 2013, 82, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loo, N.D.; Fortunati, E.; Ehlert, E.; Rabelink, M.; Grosveld, F.; Scholte, B.J. Baculovirus infection of nondividing mammalian cells: Mechanisms of entry and nuclear transport of capsids. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duisit, G.; Saleun, S.; Douthe, S.; Barsoum, J.; Chadeuf, G.; Moullier, P. Baculovirus vector requires electrostatic interactions including heparan sulfate for efficient gene transfer in mammalian cells. J. Gene Med. 1999, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, S. A pH-sensitive heparin-binding sequence from Baculovirus gp64 protein is important for binding to mammalian cells but not to Sf9 insect cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkonen, K.E.; Turkki, P.; Laakkonen, J.P.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Marjomäki, V.; Airenne, K.J. 6-o- and N-sulfated syndecan-1 promotes baculovirus binding and entry into mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11148–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, C.; Kaname, Y.; Taguwa, S.; Abe, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Tani, H.; Moriishi, K.; Matsuura, Y. Baculovirus GP64-mediated entry into mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.; Pan, X.; Kormelink, R.; Vlak, J.M. Functional entry of baculovirus into insect and mammalian cells is dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8830–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matilainen, H.; Rinne, J.; Gilbert, L.; Marjomäki, V.; Reunanen, H.; Oker-Blom, C. Baculovirus entry into human hepatoma cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15452–15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakkonen, J.P.; Mäkelä, A.R.; Kakkonen, E.; Turkki, P.; Kukkonen, S.; Peränen, J.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Airenne, K.J.; Oker-Blom, C.; Vihinen-Ranta, M.; et al. Clathrin-independent entry of baculovirus triggers uptake of E. coli in non-phagocytic human cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, S.D.; Jones, I.M. Non-polar distribution of green fluorescent protein on the surface of Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus using a heterologous membrane anchor. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, A.R.; Oker-Blom, C. Baculovirus display: A multifunctional technology for gene delivery and eukaryotic library development. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 68, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borg, J.; Nevsten, P.; Wallenberg, R.; Stenstrom, M.; Cardell, S.; Falkenberg, C.; Holm, C. Amino-terminal anchored surface display in insect cells and budded baculovirus using the amino-terminal end of neuraminidase. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 114, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, I.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Robinson, J.H.; Lung, O. Transduction of vertebrate cells with Spodoptera exigua multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus F protein-pseudotyped gp64-null Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinn, P.L.; Hwang, B.Y.; Li, N.; Ortiz, J.L.S.; Shirazi, E.; Parekh, K.R.; Cooney, A.L.; Schaffer, D.V.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Novel GP64 envelope variants for improved delivery to human airway epithelial cells. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Wu, C.P.; Chao, Y.C.; Liu, C.Y. Membrane penetrating peptides greatly enhance baculovirus transduction efficiency into mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhong, J. A surface-modified baculovirus vector with improved gene delivery to B-lymphocytic cells. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 129, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, N.; Cho, H.J.; Yoon, J.K.; Van, N.D.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, Y.B. Development of a novel viral DNA vaccine against human papillomavirus: AcHERV-HP16L1. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitidee, K.; Nangola, S.; Gonzalez, G.; Boulanger, P.; Tayapiwatana, C.; Hong, S.S. Baculovirus display of single chain antibody (scFv) using a novel signal peptide. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyn, J.C.; Cardin, A.J.; Wines, B.D.; Cendron, A.; Li, S.; Mackenzie, J.; Powell, M.; Gowans, E.J. Surface display of IgG Fc on baculovirus vectors enhances binding to antigen-presenting cells and cell lines expressing Fc receptors. Arch Virol. 2009, 154, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciabene, A.; Aurisicchio, L.; La Monica, N. Baculovirus vectors elicit antigen-specific immune responses in mice. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8663–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Raty, J.K.; Airenne, K.J.; Wirth, T.; Heikura, T.; Yla-Herttuala, S. Truncated vesicular stomatitis virus G protein improves baculovirus transduction efficiency in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, H.; Suzuki, H.; Abe, T.; Miyano-Kurosaki, N.; Takaku, H. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein pseudotyped baculovirus vector-transduced ribozyme in mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Tani, H.; Limn, C.K.; Matsunaga, T.M.; Moriishi, K.; Matsuura, Y. Ligand-directed gene targeting to mammalian cells by pseudotype baculoviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3639–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Ho, Y.; Kwang, J. Suppression of porcine arterivirus replication by baculovirus-delivered shRNA targeting nucleoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Blissard, G.W. Display of heterologous proteins on gp64null baculovirus virions and enhanced budding mediated by a vesicular stomatitis virus G-stem construct. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, N.B.; Sidhu, J.S.; Omiecinski, C.J. Baculovirus vectors repress phenobarbital-mediated gene induction and stimulate cytokine expression in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, C.; Ninomiya, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Abe, T.; Wen, X.; Fukuhara, T.; Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Saitoh, T.; Satoh, T.; et al. Innate immune response induced by baculovirus attenuates transgene expression in mammalian cells. J.Virol. 2014, 88, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Du, F.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science 2013, 339, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.D.; Wu, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects. Science 2013, 341, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; MacDuff, D.A.; Imanaka, N.; Gainey, M.D.; Shrestha, B.; Eitson, J.L.; Mar, K.B.; Richardson, R.B.; Ratushny, A.V.; Litvak, V.; et al. Pan-viral specificity of IFN-induced genes reveals new roles for cGAS in innate immunity. Nature 2014, 505, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahama, M.; Fukuda, M.; Ohbayashi, N.; Kozaki, T.; Misawa, T.; Okamoto, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Akira, S.; Saitoh, T. The RAB2b-GARIL5 complex promotes cytosolic DNA-induced innate immune responses. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2944–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.Y.; Wu, C.X.; Wang, S. Recombinant baculovirus containing the diphtheria toxin A gene for malignant glioma therapy. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5798–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balani, P.; Boulaire, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. High mobility group box2 promoter-controlled suicide gene expression enables targeted glioblastoma treatment. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Tian, X.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhong, J.; Yu, L.F.; Hu, S.P.; Li, B. Suppression of gastric cancer growth by baculovirus vector-mediated transfer of normal epithelial cell specific-1 gene. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5810–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.D.; Sun, L.; Seth, R.B.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17717–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Reilly, L.A.; Cullen, L.; Visvader, J.; Lindeman, G.J.; Print, C.; Bath, M.L.; Huang, D.C.; Strasser, A. The proapoptotic BH3-only protein bim is expressed in hematopoietic, epithelial, neuronal, and germ cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinimaki, S.; Tamminen, K.; Malm, M.; Vesikari, T.; Blazevic, V. Live baculovirus acts as a strong B and T cell adjuvant for monomeric and oligomeric protein antigens. Virology 2017, 511, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenoutis, C.; Efrose, R.C.; Swevers, L.; Lavdas, A.A.; Gaitanou, M.; Matsas, R.; Iatrou, K. Baculovirus-mediated gene delivery into mammalian cells does not alter their transcriptional and differentiating potential but is accompanied by early viral gene expression. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, J.C.; Chao, Y.C. Stimulation of baculovirus transcriptome expression in mammalian cells by baculoviral transcriptional activators. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tung, H.; Wei, S.C.; Lo, H.R.; Chao, Y.C. Baculovirus IE2 stimulates the expression of heat shock proteins in insect and mammalian cells to facilitate its proper functioning. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Hsiao, W.K.; Lo, H.R.; Wu, C.P.; Chao, Y.C. RING and coiled-coil domains of baculovirus IE2 are critical in strong activation of the cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3604–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ono, C.; Okamoto, T.; Abe, T.; Matsuura, Y. Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy. Viruses 2018, 10, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090510
Ono C, Okamoto T, Abe T, Matsuura Y. Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy. Viruses. 2018; 10(9):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090510
Chicago/Turabian StyleOno, Chikako, Toru Okamoto, Takayuki Abe, and Yoshiharu Matsuura. 2018. "Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy" Viruses 10, no. 9: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090510
APA StyleOno, C., Okamoto, T., Abe, T., & Matsuura, Y. (2018). Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy. Viruses, 10(9), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090510



