The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-Terminal Arginine-Rich Motif
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Transfection
2.4. Reporter Assay and Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
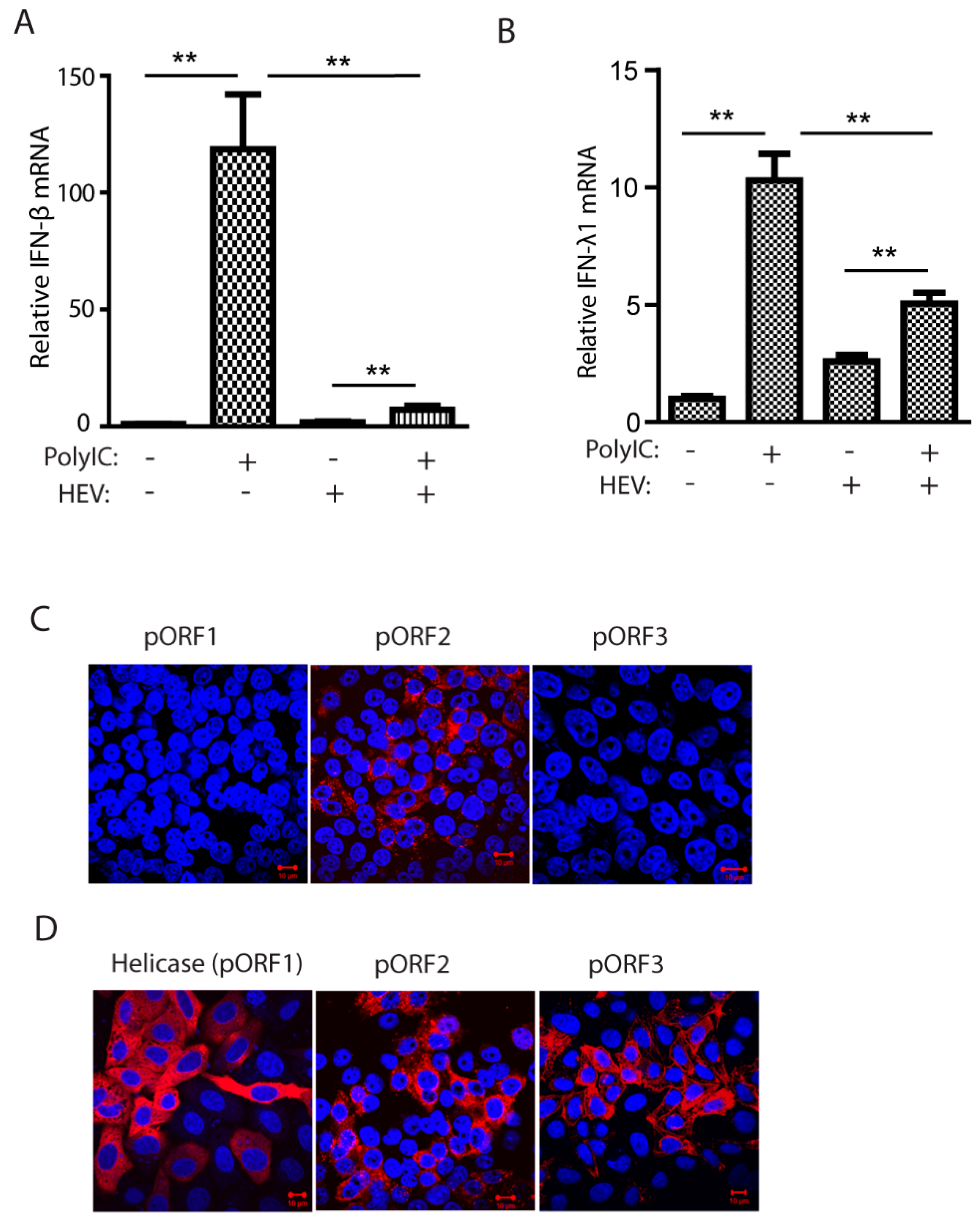
3.1. HEV Kernow-C1 Strain Inhibits Poly(I:C)-Induced IFN Production, and Only the Capsid Protein Is Detectable in Infected HepG2/C3A Cells
3.2. The Capsid Proteins of Both Genotype 1 and 3 HEV Strains Impair Poly(I:C)-Induced IFN Production
3.3. The Capsid Protein Inhibits TBK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of IRF3
3.4. The Capsid Protein Interacts with TBK1 to Inhibit the IRF3 Activation
3.5. The Capsid Protein Blocks the Phosphorylation and Dissociation of IRF3 from MAVS
3.6. The First 111 Residues of the Capsid Protein Are Responsible for the Inhibition of TBK1-Induced IRF3 Phosphorylation
3.7. The Arginine-Rich-Motif (ARM) within the N Terminus of the Capsid Protein Is Indispensable for Blocking IRF3 Phosphorylation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Pavio, N.; Aggarwal, R.; Labrique, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankcorn, M.J.; Ijaz, S.; Poh, J.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Smit, E.; Cramb, R.; Ravi, S.; Martin, K.; Tedder, R.; Neuberger, J. Toward Systematic Screening for Persistent Hepatitis E Virus Infections in Transplant Patients. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Harrison, T.J.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Smith, D.B.; ICTV Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2645–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Nayak, B.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Synthesis of a Novel Viral Factor Mediates Efficient Replication of Genotype-1 Hepatitis E Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, P.; Bremer, B.; Todt, D.; Brown, R.J.; Heim, A.; Manns, M.P.; Steinmann, E.; Wedemeyer, H. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) ORF2 Antigen Levels Differentiate Between Acute and Chronic HEV Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Gass, S.; Giersch, K.; Groth, A.; Kah, J.; Volz, T.; Rapp, G.; Schobel, A.; Lohse, A.W.; Polywka, S.; et al. Human liver chimeric mice as a new model of chronic hepatitis E virus infection and preclinical drug evaluation. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenggenhager, D.; Gouttenoire, J.; Malehmir, M.; Bawohl, M.; Honcharova-Biletska, H.; Kreutzer, S.; Semela, D.; Neuweiler, J.; Hurlimann, S.; Aepli, P.; et al. Visualization of hepatitis E virus RNA and proteins in the human liver. J. Hepatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Li, X.; Ambardekar, C.; Hu, Z.; Lhomme, S.; Feng, Z. Hepatitis E virus persists in the presence of a type III interferon response. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, Y.-M.; Gale, M. Immune signaling by RIG-I-like receptors. Immunity 2011, 34, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, K.; Bowie, A.G. Activation of host pattern recognition receptors by viruses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.T.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS recruits multiple ubiquitin E3 ligases to activate antiviral signaling cascades. eLife 2013, 2, e00785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Khattar, S.K.; Fredericksen, B.; Zhang, Y.J. Hepatitis E virus inhibits type I interferon induction by ORF1 products. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11924–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Kannan, H.; Fredericksen, B.; Zhang, Y.J. Enhancement of interferon induction by ORF3 product of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8696–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Cepko, C.L. Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojima, Y.; Fujimoto, A.; Delhase, M.; Chen, Y.; Hatakeyama, S.; Nakayama, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Nimura, Y.; Motoyama, N.; Ikeda, K.; et al. NAK is an IkappaB kinase-activating kinase. Nature 2000, 404, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Opriessnig, T.; Stein, D.A.; Halbur, P.G.; Meng, X.J.; Iversen, P.L.; Zhang, Y.J. Peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers inhibit porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication. Antivir. Res. 2008, 77, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Wang, R.; Shen, M.; Faaberg, K.S.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, Y.J. Induction of type I interferons by a novel porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolate. Virology 2012, 432, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panne, D.; McWhirter, S.M.; Maniatis, T.; Harrison, S.C. Interferon regulatory factor 3 is regulated by a dual phosphorylation-dependent switch. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22816–22822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, P.A.; Marshall, D.; Schneemann, A. Dual Roles for an Arginine-Rich Motif in Specific Genome Recognition and Localization of Viral Coat Protein to RNA Replication Sites in Flock House Virus-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2872–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, A.D.; Young, J.A. HIV-1: Fifteen proteins and an RNA. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casu, F.; Duggan, B.M.; Hennig, M. The arginine-rich RNA-binding motif of HIV-1 Rev is intrinsically disordered and folds upon RRE binding. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Cheng, J.C.; Kou, Y.H.; Kao, C.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Chang, M.F. Roles of the AX(4)GKS and Arginine-Rich Motifs of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Helicase in ATP- and Viral RNA-Binding Activity. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9732–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Li, X.; Kong, X.Q.; Luo, C.; Chang, C.C.; Chung, Y.; Shih, H.M.; Li, K.K.; Ann, D.K. An arginine-rich motif of ring finger protein 4 (RNF4) oversees the recruitment and degradation of the phosphorylated and SUMOylated Kruppel-associated box domain-associated protein 1 (KAP1)/TRIM28 protein during genotoxic stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20757–20772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surjit, M.; Varshney, B.; Lal, S.K. The ORF2 glycoprotein of hepatitis E virus inhibits cellular NF-kappaB activity by blocking ubiquitination mediated proteasomal degradation of IkappaBalpha in human hepatoma cells. BMC Biochem. 2012, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, L.; Thomas, S.; Herchenroder, O.; Putzer, B.M.; Schaefer, S. Hepatitis E virus ORF2 protein activates the pro-apoptotic gene CHOP and anti-apoptotic heat shock proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, X.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, F.; Fan, Y.; Shen, T.; Xiao, M.; Xia, Z.; et al. PPM1A silences cytosolic RNA sensing and antiviral defense through direct dephosphorylation of MAVS and TBK1. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Guan, Y.; Tao, J.; Xi, J.; Feng, J.M.; Jiang, Z. MAVS activates TBK1 and IKKε through TRAFs in NEMO dependent and independent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, F.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kato, T.; Narita, Y.; Furuya, A.; Ogawa, T.; Sakurai, H.; Joh, T.; Itoh, M.; Delhase, M.; et al. Identification of NAP1, a regulatory subunit of IkappaB kinase-related kinases that potentiates NF-kappaB signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7780–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, A.; Burckstummer, T.; Dixit, E.; Scheicher, R.; Gorna, M.W.; Karayel, E.; Sugar, C.; Stukalov, A.; Berg, T.; Kralovics, R.; et al. Functional dissection of the TBK1 molecular network. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larabi, A.; Devos, J.M.; Ng, S.L.; Nanao, M.H.; Round, A.; Maniatis, T.; Panne, D. Crystal structure and mechanism of activation of TANK-binding kinase 1. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Cheng, G. Modulation of the interferon antiviral response by the TBK1/IKKi adaptor protein TANK. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11817–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Kato, N.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes through interference with interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and dampening of the interaction between TBK1/IKKepsilon and DDX3. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.A.; Narayana, N. RNA recognition by arginine-rich peptide motifs. Biopolymers 1998, 48, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Primer a | Sequence (5′ to 3′) b | Target |
|---|---|---|
| ORF2-T1F | CCGCTCGAGGTCGCTCCGGCCCATGACA | T1 ORF2 |
| ORF2-T1R | GGCGGCCGCTTACTATAACTCCCGAGTTTTAC | T1 ORF2 |
| ORF2-T3F | GCTCGAGTGCCCTAGGGTTGTTCTGCTGCTGTTC | T3 ORF2 |
| ORF2-T3R | GGCGGCCGCTTAAGACTCCCGGGTTTTGCCTACCTCCG | T3 ORF2 |
| ORF2-D1F | ATCTGCTCGAATTCGCCACCATGTGCCCTAGGGTTGTTC | ORF2 D1 |
| ORF2-D1R | GCCTCGAGAGGGCGGGAGTAGAACA | ORF2 D1 |
| ORF2-D2F | CCTCGAGGTTGTCTCGGCCAATGGCGA | ORF2 D2 |
| ORF2-D2R | AGCGGCCGCTTAAGACTCCCGGGTTTTGCC | ORF2 D2 |
| ORF2-D3F | TCTCGAGGTTAGGATTTTGGTCCAGCC | ORF2 D3 |
| ORF2-D3R | AGCGGCCGCTTAGGCTAATACACCCACCGC | ORF2 D3 |
| ORF2-D4F | TCTCGAGGCTGTATCACCAGCCCCTGA | ORF2 D4 |
| ORF2-D4R | AGCGGCCGCTTAGCTAATACACCCACCGCGGAGA | ORF2 D4 |
| ORF2-D7-R | ACCTCGAGAGTCAACGGCGCAGCCCCAG | ORF2 D7 |
| ORF2-D8-R | ACTCGAGGGGCTGAGAATCAACCCTGT | ORF2 D8 |
| ORF2-D9-F | TGAATTCGCCACCATGTTCGCCCTCCCCTATATTCA | ORF2 D9 |
| ORF2-D10-F | AGAATTCGCCACCATGGGCGGTGCCGGCGGTGGTTTC | ORF2 D10 |
| mIRF3-F1 | CGAATTCGGAACCCCAAAGCCACGGATCC | Mutant IRF3 |
| mIRF3-R1 | CTCCAGGGCGGCGGCACCCCCTACCCGGGCCATTTCTA | Mutant IRF3 |
| mIRF3-F2 | GGTAGGGGGTGCCGCCGCCCTGGAGAATACTGTGGACCTGC | Mutant IRF3 |
| mIRF3-R2 | ACTCGAGTCAGCTCTCCCCAGGGCCCT | Mutant IRF3 |
| TBK1-F | AACGTCTCGAATTCCAGAGCACTTCTAATCATCTG | TBK1 |
| TBK1-R | CCTCGAGCTAAAGACAGTCAACGTTGCGAAG | TBK1 |
| ORF2-N-M1F | CAGCCGTCTGGCGCTGCTCGTGGGCGGCGCAGCGGCGGTGC | ORF2-D7-M1 |
| ORF2-N-M1R | CTGCGCCGCCCACGAGCAGCGCCAGACGGCTGGCCGGCCGGT | ORF2-D7-M1 |
| ORF2-N-M2F | GTCTGGCCGTCGTGCTGGGGCTCGCAGCGGCGGTGCCGGCGGT | ORF2-D7-M2 |
| ORF2-N-M2R | ACCGCCGCTGCGAGCCCCAGCACGACGGCCAGACGGCTGGCCG | ORF2-D7-M2 |
| ORF2-N-M3F | TGGCCGTCGTCGTGGGGCCGCCAGCGGCGGTGCCGGCGGTGGT | ORF2-D7-M3 |
| ORF2-M1-F1 | CTGCCCGCGCCACCGGCCGGCCAGCCGTCTGGCGCTCGTCGTGGGC GGGCCAGCGGCGGTGC | ORF2-M1 |
| ORF2-M1-F3 | ACCGTCTCGAATTCGCCACCATGTGCCCTAGGGTTGTTCTGCTGCT GTTCTTCGTGTTTCTGCCTATGCTGCCCGCGCCACCGGCCGGCCAG | ORF2-M1 |
| KORF2-R5 | ACTCGAGAGACTCCCGGGTTTTGCCTACCTCCGTT | ORF2 |
| ORF2-N-M3R | CCGGCACCGCCGCTGGCGGCCCCACGACGACGGCCAGACGGC | ORF2-D7-M3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Yang, Y.; Nan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.-J. The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-Terminal Arginine-Rich Motif. Viruses 2019, 11, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111050
Lin S, Yang Y, Nan Y, Ma Z, Yang L, Zhang Y-J. The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-Terminal Arginine-Rich Motif. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111050
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shaoli, Yonglin Yang, Yuchen Nan, Zexu Ma, Liping Yang, and Yan-Jin Zhang. 2019. "The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-Terminal Arginine-Rich Motif" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111050
APA StyleLin, S., Yang, Y., Nan, Y., Ma, Z., Yang, L., & Zhang, Y.-J. (2019). The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-Terminal Arginine-Rich Motif. Viruses, 11(11), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111050





