GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape
Abstract
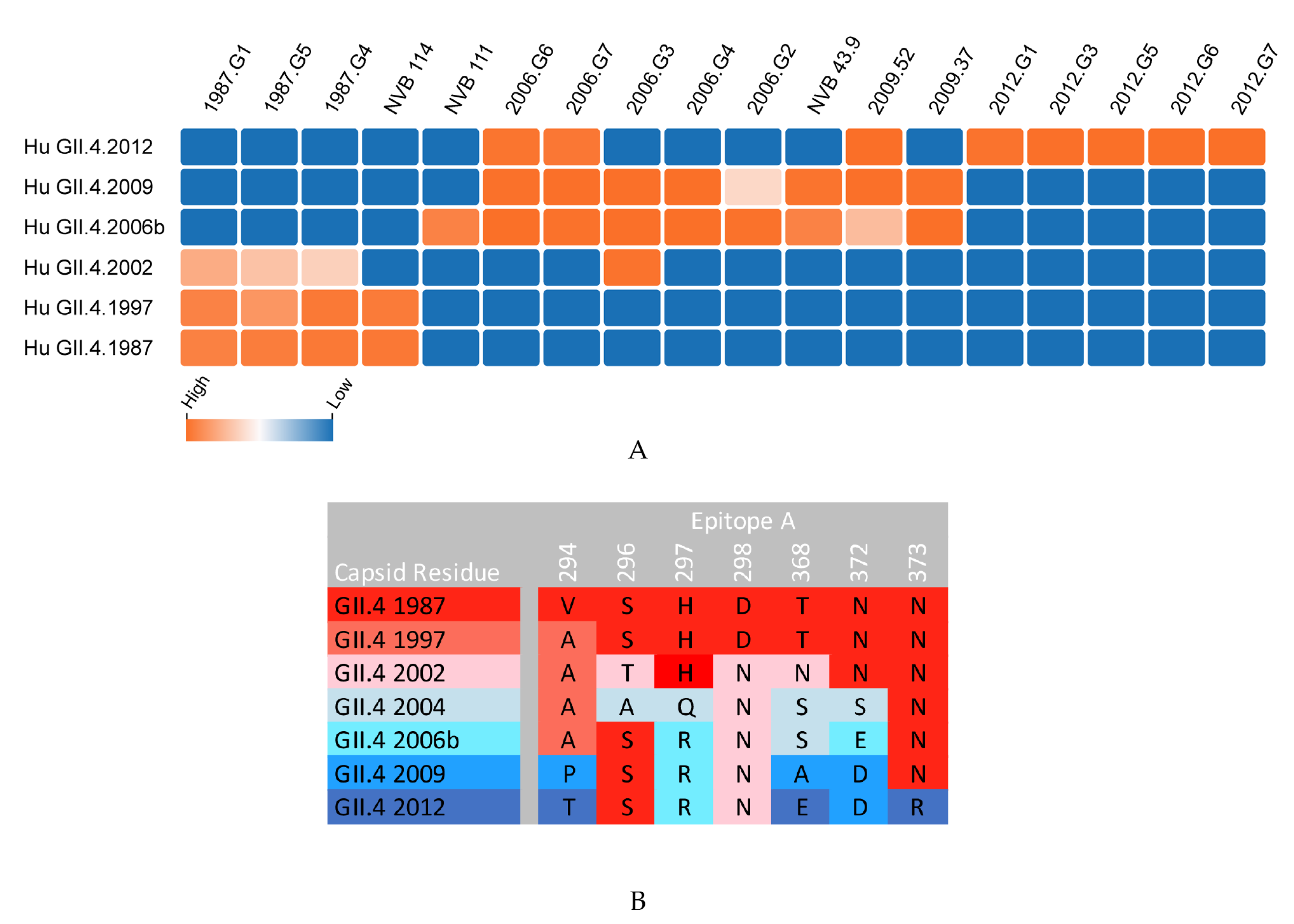
:1. Review Body
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Phan, K.; Teng, I.; Pu, J.; Watanabe, T. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis in developing countries. Medicine 2017, 96, e8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, M.M.; Widdowson, M.A.; Glass, R.I.; Akazawa, K.; Vinje, J.; Parashar, U.D. Systematic literature review of role of noroviruses in sporadic gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Ozawa, S.; Hall, A.J.; Lee, B.Y. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, E.; Parashar, U.; Tate, J. Rotavirus vaccines: Effectiveness, safety, and future directions. Paediatric Drugs 2018, 20, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Perez-Schael, I.; Velazquez, F.R.; Abate, H.; Breuer, T.; Clemens, S.C.; Cheuvart, B.; Espinoza, F.; Gillard, P.; Innis, B.L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Liebowitz, D.; Lin, K.; Kasparek, K.; Pasetti, M.F.; Garg, S.J.; Gottlieb, K.; Trager, G.; Tucker, S.N. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral tablet norovirus vaccine, a phase i randomized, placebo-controlled trial. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, R.L.; Bernstein, D.I.; Harro, C.D.; Al-Ibrahim, M.S.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Estes, M.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Opekun, A.R.; Richardson, C.; et al. Norovirus vaccine against experimental human norwalk virus illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Atmar, R.L.; Lyon, G.M.; Treanor, J.J.; Chen, W.H.; Jiang, X.; Vinje, J.; Gregoricus, N.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Moe, C.L.; et al. Norovirus vaccine against experimental human gii.4 virus illness: A challenge study in healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, J.F.; Debbink, K.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Graham, R.L.; Hugues, B.; Goodwin, R.R.; Baric, R.S. Noroviurs vaccines. In Plotkin’s vaccines, 7th ed.; Plotkin, S., Orenstein, W., Offit, P., Edwards, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 698–703. [Google Scholar]
- Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Correlates of protection against norovirus infection and disease-where are we now, where do we go? PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.; Moe, C.; Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Jiang, X.; Lindblad, L.; Stewart, P.; LePendu, J.; Baric, R. Human susceptibility and resistance to norwalk virus infection. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucardo, F.; Kindberg, E.; Paniagua, M.; Grahn, A.; Larson, G.; Vildevall, M.; Svensson, L. Genetic susceptibility to symptomatic norovirus infection in nicaragua. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Mallory, M.L.; Jones, T.A.; Richardson, C.; Goodwin, R.R.; Baehner, F.; Mendelman, P.M.; Bargatze, R.F.; Baric, R.S. Impact of pre-exposure history and host genetics on antibody avidity following norovirus vaccination. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Graham, D.; Wang, K.; Estes, M. Norwalk virus genome cloning and characterization. Science 1990, 250, 1580–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Estes, M.K. Sequence and genomic organization of norwalk virus. Virology 1993, 195, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baric, R.S.; Yount, B.; Lindesmith, L.; Harrington, P.R.; Greene, S.R.; Tseng, F.C.; Davis, N.; Johnston, R.E.; Klapper, D.G.; Moe, C.L. Expression and self-assembly of norwalk virus capsid protein from venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replicons. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3023–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Expression, self-assembly, and antigenicity of the norwalk virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6527–6532. [Google Scholar]
- Green, K.Y.; Lew, J.F.; Jiang, X.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Estes, M.K. Comparison of the reactivities of baculovirus-expressed recombinant norwalk virus capsid antigen with those of the native norwalk virus antigen in serologic assays and some epidemiologic observations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, B.V.; Hardy, M.E.; Dokland, T.; Bella, J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Estes, M.K. X-ray crystallographic structure of the norwalk virus capsid. Science 1999, 286, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Hegde, R.S.; Jiang, X. The p domain of norovirus capsid protein forms dimer and binds to histo-blood group antigen receptors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6233–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Fang, P.; Chachiyo, T.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Noroviral p particle: Structure, function and applications in virus-host interaction. Virology 2008, 382, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Lou, Z.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Rao, Z. Structural basis for the recognition of blood group trisaccharides by norovirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, S.; Choi, J.M.; Sankaran, B.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V. Structural analysis of hbga binding specificity in a norovirus gii.4 epidemic variant: Implications for epochal evolution. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8635–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Beltramello, M.; Donaldson, E.F.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Immunogenetic mechanisms driving norovirus gii.4 antigenic variation. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debbink, K.; Donaldson, E.F.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Baric, R.S. Genetic mapping of a highly variable norovirus gii.4 blockade epitope: Potential role in escape from human herd immunity. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinje, J.; Green, J.; Lewis, D.C.; Gallimore, C.I.; Brown, D.W.G.; Koopmans, M.P.G. Genetic polymorphism across regions of the three open reading frames of “norwalk-like viruses”. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.P.; Ando, T.; Fankhauser, R.L.; Beard, R.S.; Glass, R.I.; Monroe, S.S. Norovirus classification and proposed strain nomenclature. Virology 2006, 346, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.L.; Zhen, S.S.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, C.J.; Qiu, C.; Wang, S.M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.Y. Burden of acute gastroenteritis caused by norovirus in china: A systematic review. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa Tran, T.N.; Trainor, E.; Nakagomi, T.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Nakagomi, O. Molecular epidemiology of noroviruses associated with acute sporadic gastroenteritis in children: Global distribution of genogroups, genotypes and gii.4 variants. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.; van Beek, J.; Vennema, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Hewitt, J.; Bucardo, F.; Templeton, K.; Mans, J.; Nordgren, J.; Reuter, G.; et al. Emergence of a novel gii.17 norovirus - end of the gii.4 era? Euro. Surveill. 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Ji, L. Emergence of norovirus gii.P16-gii.2 strains in patients with acute gastroenteritis in huzhou, china, 2016-2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niendorf, S.; Jacobsen, S.; Faber, M.; Eis-Hubinger, A.M.; Hofmann, J.; Zimmermann, O.; Hohne, M.; Bock, C.T. Steep rise in norovirus cases and emergence of a new recombinant strain gii.P16-GII.2, germany, winter 2016. Euro. Surveill. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.M.; Shah, M.P.; Wikswo, M.E.; Barclay, L.; Kambhampati, A.; Marsh, Z.; Cannon, J.L.; Parashar, U.D.; Vinje, J.; Hall, A.J. The norovirus epidemiologic triad: Predictors of severe outcomes in us norovirus outbreaks, 2009–2016. J. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Lobue, A.D.; Cannon, J.L.; Zheng, D.P.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Mechanisms of gii.4 norovirus persistence in human populations. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebenga, J.J.; Vennema, H.; Renckens, B.; de Bruin, E.; van der Veer, B.; Siezen, R.J.; Koopmans, M. Epochal evolution of ggii.4 norovirus capsid proteins from 1995 to 2006. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9932–9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, J.S.; Fankhauser, R.L.; Ando, T.; Monroe, S.S.; Glass, R.I. Identification of a distinct common strain of "norwalk-like viruses" having a global distribution. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Baric, R.S. Norovirus gii.4 strain antigenic variation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbink, K.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Costantini, V.; Beltramello, M.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Emergence of new pandemic gii.4 sydney norovirus strain correlates with escape from herd immunity. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, P.R.; Lindesmith, L.; Yount, B.; Moe, C.L.; Baric, R.S. Binding of norwalk virus-like particles to abh histo-blood group antigens is blocked by antisera from infected human volunteers or experimentally vaccinated mice. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12335–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Ferris, M.T.; Mullan, C.W.; Ferreira, J.; Debbink, K.; Swanstrom, J.; Richardson, C.; Goodwin, R.R.; Baehner, F.; Mendelman, P.M.; et al. Broad blockade antibody responses in human volunteers after immunization with a multivalent norovirus vlp candidate vaccine: Immunological analyses from a phase i clinical trial. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Debbink, K.; Swanstrom, J.; Vinje, J.; Costantini, V.; Baric, R.S.; Donaldson, E.F. Monoclonal antibody-based antigenic mapping of norovirus gii.4-2002. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus and its histo-blood group antigen receptors: An answer to a historical puzzle. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeck, A.; Kavanagh, O.; Estes, M.K.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Atmar, R.L. Serological correlate of protection against norovirus-induced gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, M.; Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Vesikari, T.; Blazevic, V. High serum levels of norovirus genotype-specific blocking antibodies correlate with protection from infection in children. J. Infect Dis. 2014, 210, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costantini VP, M.E.; Browne, H.; Ettayebi, K.; Zeng, X.-L.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K.; Vinjé, J. Human norovirus replication in human intestinal enteroids as a model to evaluate virus inactivation. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, G.; Ettayebi, K.; Atmar, R.L.; Bombardi, R.G.; Kose, N.; Estes, M.K.; Crowe, J.E., Jr. Human monoclonal antibodies that neutralize pandemic gii.4 noroviruses. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, J.A.; Bar-On, Y.; Lu, C.L.; Fera, D.; Lockhart, A.A.K.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Nogueira, L.; Golijanin, J.; Scheid, J.F.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Non-neutralizing antibodies alter the course of hiv-1 infection in vivo. Cell 2017, 170, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry Dunand, C.J.; Leon, P.E.; Huang, M.; Choi, A.; Chromikova, V.; Ho, I.Y.; Tan, G.S.; Cruz, J.; Hirsh, A.; Zheng, N.Y.; et al. Both neutralizing and non-neutralizing human h7n9 influenza vaccine-induced monoclonal antibodies confer protection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.J.; Noad, R.; Samuel, D.; Gray, J.J.; Roy, P.; Iturriza-Gomara, M. Characterisation of a gii-4 norovirus variant-specific surface-exposed site involved in antibody binding. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Morozov, V.A.; Hefele, L.; Hansman, G.S. Human norovirus neutralized by a monoclonal antibody targeting the hbga pocket. J. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansman, G.S.; Taylor, D.W.; McLellan, J.S.; Smith, T.J.; Georgiev, I.; Tame, J.R.; Park, S.Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Gondaira, F.; Miki, M.; et al. Structural basis for broad detection of genogroup ii noroviruses by a monoclonal antibody that binds to a site occluded in the viral particle. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, S.E.; Ajami, N.; Parker, T.D.; Kitamoto, N.; Natori, K.; Takeda, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kou, B.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K. Mapping broadly reactive norovirus genogroup i and ii monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Huo, Y.; Qin, C.; Shen, S.; Wang, M. Characterization of a norovirus-specific monoclonal antibody that exhibits wide spectrum binding activities. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.I.; Azure, J.; Fischer, R.; Bok, K.; Sandoval-Jaime, C.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Sander, P.; Green, K.Y. Identification of a broadly cross-reactive epitope in the inner shell of the norovirus capsid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, R.; Tian, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of a cross-reactive monoclonal antibody against norovirus genogroups i, ii, iii and v. Virus Res. 2010, 151, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Hansman, G.S. Nanobodies targeting norovirus capsid reveal functional epitopes and potential mechanisms of neutralization. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Hansman, G.S. Nanobody binding to a conserved epitope promotes norovirus particle disassembly. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2718–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Mallory, M.L.; Debbink, K.; Swann, E.W.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Antigenic characterization of a novel recombinant gii.P16-gii.4 sydney norovirus strain with minor sequence variation leading to antibody escape. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Costantini, V.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Donaldson, E.F.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Emergence of a norovirus gii.4 strain correlates with changes in evolving blockade epitopes. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.I.; Abente, E.J.; Sandoval-Jaime, C.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Bok, K.; Green, K.Y. Multiple antigenic sites are involved in blocking the interaction of gii.4 norovirus capsid with abh histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7414–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rougemont, A.; Ruvoen-Clouet, N.; Simon, B.; Estienney, M.; Elie-Caille, C.; Aho, S.; Pothier, P.; Le Pendu, J.; Boireau, W.; Belliot, G. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the binding of gii.4 norovirus variants onto human blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4057–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Mallory, M.L.; Yount, B.; Collins, M.H.; Debbink, K.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. Human norovirus epitope d plasticity allows escape from antibody immunity without loss of capacity for binding cellular ligands. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Beltramello, M.; Pintus, S.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Jones, T.A.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Particle conformation regulates antibody access to a conserved GII.4 norovirus blockade epitope. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8826–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Mallory, M.L.; Debbink, K.; Donaldson, E.F.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Swann, E.W.; Sheahan, T.P.; Graham, R.L.; Beltramello, M.; Corti, D.; et al. Conformational occlusion of blockade antibody epitopes, a novel mechanism of gii.4 human norovirus immune evasion. mSphere 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Vicente, N.; Vila-Vicent, S.; Allen, D.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; Buesa, J.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J. Characterization of a novel conformational gii.4 norovirus epitope: Implications for norovirus-host interactions. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7703–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, T.; Okame, M.; Takanashi, S.; Khamrin, P.; Takagi, M.; Satou, K.; Masuoka, Y.; Yagyu, F.; Shimizu, Y.; Kohno, H.; et al. Characterization of a broadly reactive monoclonal antibody against norovirus genogroups i and ii: Recognition of a novel conformational epitope. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12298–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Terano, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Sakon, N.; Kuzuguchi, T.; Oda, H.; Tsukamoto, T. Precise characterization of norovirus (norwalk-like virus)-specific monoclonal antibodies with broad reactivity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Smith, H.Q.; Svoboda, S.A.; Lewis, M.S.; Sherman, M.B.; Lynch, G.C.; Pettitt, B.M.; Smith, T.J.; Wobus, C.E. Norovirus escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies is limited to allostery-like mechanisms. mSphere 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.D.; Bajic, G.; Ferdman, J.; Suphaphiphat, P.; Settembre, E.C.; Moody, M.A.; Schmidt, A.G.; Harrison, S.C. Conserved epitope on influenza-virus hemagglutinin head defined by a vaccine-induced antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, N.; Swem, L.R.; Reichelt, M.; Chen-Harris, H.; Luis, E.; Park, S.; Fouts, A.; Lupardus, P.; Wu, T.D.; Li, O.; et al. Two escape mechanisms of influenza a virus to a broadly neutralizing stalk-binding antibody. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, S.; Czako, R.; Sapparapu, G.; Alvarado, G.; Viskovska, M.; Sankaran, B.; Atmar, R.L.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V. Structural basis for norovirus neutralization by an hbga blocking human iga antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5830–E5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Kong, X.P. Antigenic landscape of the hiv-1 envelope and new immunological concepts defined by hiv-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 42, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieltjens, T.; Willems, B.; Coppens, S.; Van Nieuwenhove, L.; Humbert, M.; Dietrich, U.; Heyndrickx, L.; Vanham, G.; Janssens, W. Unravelling the antigenic landscape of the hiv-1 subtype a envelope of an individual with broad cross-neutralizing antibodies using phage display peptide libraries. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonville, J.M.; Wilks, S.H.; James, S.L.; Fox, A.; Ventresca, M.; Aban, M.; Xue, L.; Jones, T.C.; Le, N.M.H.; Pham, Q.T.; et al. Antibody landscapes after influenza virus infection or vaccination. Science 2014, 346, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Hogerkorp, C.M.; Schief, W.R.; Seaman, M.S.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, S.D.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.; et al. Rational design of envelope identifies broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to HIV-1. Science 2010, 329, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingens, A.S.; Acharya, P.; Haddox, H.K.; Rawi, R.; Xu, K.; Chuang, G.Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, B.; Mascola, J.R.; Carragher, B.; et al. Complete functional mapping of infection- and vaccine-elicited antibodies against the fusion peptide of hiv. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Wilson, I.A. Structural characterization of viral epitopes recognized by broadly cross-reactive antibodies. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 386, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahay, B.; Nguyen, C.Q.; Yamamoto, J.K. Conserved hiv epitopes for an effective hiv vaccine. J. Clin. Cell. Immunology 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Boutz, D.R.; Chromikova, V.; Joyce, M.G.; Vollmers, C.; Leung, K.; Horton, A.P.; DeKosky, B.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lavinder, J.J.; et al. Molecular-level analysis of the serum antibody repertoire in young adults before and after seasonal influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaumik, S.K.; Priyamvada, L.; Kauffman, R.C.; Lai, L.; Natrajan, M.S.; Cho, A.; Rouphael, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Mulligan, M.J.; Wrammert, J. Pre-existing dengue immunity drives a denv-biased plasmablast response in zikv-infected patient. Viruses 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wine, Y.; Horton, A.P.; Ippolito, G.C.; Georgiou, G. Serology in the 21st century: The molecular-level analysis of the serum antibody repertoire. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| VP1 Epitope | VP1 Domain | Features | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epitope A: 294–298, 368, 372, 373 | P2 | Hypervariable: immunodominant blocking; predictive of new strain | [25,26,39,51,60,61,62] |
| Epitope D: 391, 393–396 | P2 | Variable; blocking; regulates HBGA affinity | [24,35,39,63,64] |
| Epitope E: 407, 412, 413 | P2 | Variable; Ab access particle conformation-dependent | [42] |
| Epitope F: 327, 404 | P2 | Conserved GII.4 1987–2015 blocking; Ab access particle conformation-dependent | [65,66] |
| 3C3G3 Epitope: 245, 247, 389, 390, 397, 435, 443–446, 448 | P2/P1 | Variable; blocking; Residue 397 modulates HBGA interaction | [67] |
| 10E9 Epitope Chain A: 391, 394, 395, 397, 341, 435, 444, 446, 448, 504, 506; Chain B: 340–343, 345 | P2/P1 | Blocking and neutralizing; spans both monomers of the dimer | [52] |
| Nanobody-26 Epitope Chain A: 231, 488. Chain B 269, 271, 272, 274, 276, 316, 470–472, 475 a | P2/P1 | GII cross-reactive; spans both monomers of the dimer; nanobody binding induces particle disassembly b | [58] |
| Nanobody-85 Epitope: 520–522, 524‒526 | P1 | GII cross-reactive; site occluded on intact particles; nanobody binding induces particle disassembly | [58,59] |
| 5B18 Epitope: 433, 496, 530, 533–535 a | P1 | GII cross-reactive; site occluded on intact particles | [53] |
| NV23, NS22 Epitope: 453–472 | P1 | GI, GII cross-reactive | [54] |
| MAB 14-1 Epitope: 418 to 426 and 526 to 534 | P1 | GI, GII cross-reactive | [68] |
| 1B4, 1f6, 8D8 and 10B11 Epitope: 31–60 | Shell | GI, GII cross-reactive; site occluded on intact particles | [55,69] |
| TV20 Epitope: 52–56 | Shell | GI, GII cross-reactive; non-blocking | [56] |
| N2C3 Epitope: 55–60 | Shell | Human and animal norovirus cross-reactive | [57] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallory, M.L.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses 2019, 11, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020177
Mallory ML, Lindesmith LC, Graham RL, Baric RS. GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses. 2019; 11(2):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020177
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallory, Michael L., Lisa C. Lindesmith, Rachel L. Graham, and Ralph S. Baric. 2019. "GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape" Viruses 11, no. 2: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020177
APA StyleMallory, M. L., Lindesmith, L. C., Graham, R. L., & Baric, R. S. (2019). GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses, 11(2), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020177





