Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metagenomic Assembly and Genomic Analysis
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. K-mer Analysis
2.4. Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The CV-Can Metagenome
3.2. Predicted Gene Products of CV-Can
3.2.1. Replicase (nt 276 to 7007)
3.2.2. Helicase (nt 7014–8192)
3.2.3. Possible Movement Protein (nt 8197–9117)
3.2.4. Coat protein (CP) (nt 9197–9631)
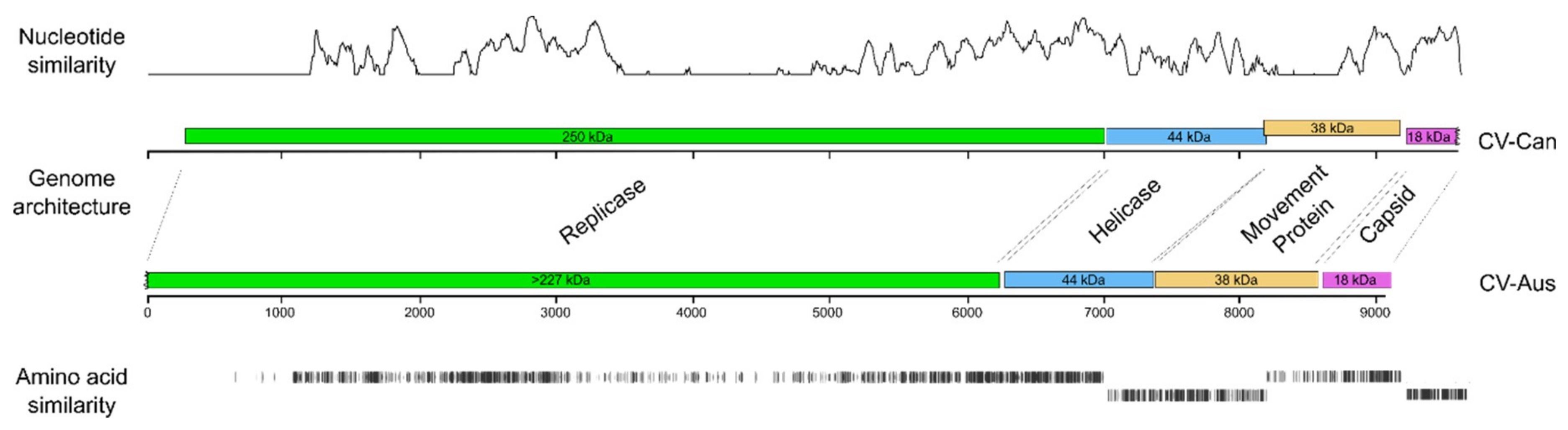
3.3. Divergence of CV-Aus and CV-Can
3.4. CV-Can in British Columbia
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubinstein, C.V.; Gerrienne, P.; de la Puente, G.S.; Astini, R.A.; Steemans, P. Early middle Ordovician evidence for land plants in Argentina (eastern Gondwana). New Phytol. 2010, 188, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delwiche, C.F.; Cooper, E.D. The Evolutionary Origin of a Terrestrial Flora. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R899–R910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.; Skotnicki, A.H.; Gardiner, J.E.; Walker, E.S.; Hollings, M. A tobamovirus of a green alga. Virology 1975, 64, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Torronen, M.; Mackenzie, A.M.; Wood, J.T.; Armstrong, J.S.; Kondo, H.; Tamada, T.; Keese, P.L. The enigmatic genome of Chara australis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Wood, J.; Garcia-Arenal, F.; Ohshima, K.; Armstrong, J.S. Tobamoviruses have probably co-diverged with their eudicotyledonous hosts for at least 110 million years. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicki, A.; Gibbs, A.; Wrigley, G. Further studies on Chara corallina virus. Virology 1976, 75, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, I.; Bistolas, K.S.I.; Button, J.B.; Jackson, E.W. Occurrence and seasonal dynamics of RNA viral genotypes in three contrasting temperate lakes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rossum, T.; Uyaguari-Diaz, M.I.; Vlok, M.; Peabody, M.A.; Tian, A.; Cronin, K.I.; Chan, M.; Croxen, M.A.; Hsiao, W.W.; Isaac-Renton, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of river viruses, bacteria and microeukaryotes. bioRxiv 2018, 259861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyaguari-Diaz, M.I.; Chan, M.; Chaban, B.L.; Croxen, M.A.; Finke, J.F.; Hill, J.E.; Peabody, M.A.; Van Rossum, T.; Suttle, C.A.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; et al. A comprehensive method for amplicon-based and metagenomic characterization of viruses, bacteria, and eukaryotes in freshwater samples. Microbiome 2016, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rossum, T.; Peabody, M.A.; Uyaguari-Diaz, M.I.; Cronin, K.I.; Chan, M.; Slobodan, J.R.; Nesbitt, M.J.; Suttle, C.A.; Hsiao, W.W.; Tang, P.K.; et al. Year-long metagenomic study of river microbiomes across land use and water quality. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Genome analysis Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. Genome analysis PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Brudno, M.; Do, C.B.; Cooper, G.M.; Kim, M.F.; Davydov, E.; Green, E.D.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, C.; Brudno, M.; Schwartz, J.R.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.S.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Visualizing global DNA sequence alignments of arbitrary length. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Viol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanmougin, F.; Thompson, J.D.; Gouy, M.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, msw054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuelo, A. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Multiple Comparisons of Log-Likelihoods with Applications to Phylogenetic Inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourment, M.; Gibbs, M.J. PATRISTIC: A program for calculating patristic distances and graphically comparing the components of genetic change. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, H.; Aboyoun, P.; Gentleman, R.; DebRoy, S. Biostrings: Efficient Manipulation of Biological Strings. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/Biostrings.html (accessed on 24 September 2017).
- R Studio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- Hirschfeld, H. A connection between correlation and contingency. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1935, 31, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzécri, J.P. L’Analyse des Données: Leçons sur L’analyse Factorielle et la Reconnaissace des Formes et Travaux de Laboratoire; Benzécri, J.P., Ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 24 September 2017).
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Simpson, G.L. vegan3d: Statid and Dynamic 3D Plots for the “Vegan” Package. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan3d (accessed on 24 September 2017).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rozanov, M.N.; Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Conservation of the putative methyltransferase domain: A hallmark of the “Sindbis-like” supergroup of positive-strand RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Chumakov, K.M. Tentative identification of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of dsRNA viruses and their relationship to positive strand RNA viral polymerases. FEBS Lett. 1989, 252, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotto, P.M.; Gibbs, M.J.; Gould, E.A.; Holmes, E.C. A reevaluation of the higher taxonomy of viruses based on RNA polymerases. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6083–6096. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, H.; Hirano, S.; Chiba, S.; Andika, I.B.; Hirai, M.; Maeda, T.; Tamada, T. Characterization of burdock mottle virus, a novel member of the genus Benyvirus, and the identification of benyvirus-related sequences in the plant and insect genomes. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, N.; Luria, N.; Yaari, M.; Prusky, D.; Dombrovsky, A. Genome Sequence of a Potential New Benyvirus Isolated from Mango RNA-seq Data. Genome Announc. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Kondo, H.; Chiba, S. Genetic Diversity of Beet Necrotic Yellow Vein Virus. In Rhizomania; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, G.; Dobbs, E.; Bennett, J.M.; Jones, I.M.; Grogan, H.M.; Burton, K.S. Multiple viral infections in Agaricus bisporus—Characterisation of 18 unique RNA viruses and 8 ORFans identified by deep sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magae, Y. Molecular characterization of a novel mycovirus in the cultivated mushroom, Lentinula edodes. Virol. J. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Koonin, E.V.; Donchenko, A.P.; Blinov, V.M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 4713–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.J.; Antoniw, J.F.; Kreuze, J. Virgaviridae: A new family of rod-shaped plant viruses. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró, A.; Martínez-Gil, L.; Tamborero, S.; Pallás, V.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.A.; Mingarro, I. The Tobacco mosaic virus movement protein associates with but does not integrate into biological membranes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3016–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomo, K.; Smith, J.F.; Feild, T.S.; Samain, M.-S.; Bond, L.; Davidson, C.; Zimmers, J.; Neinhuis, C.; Wanke, S. The Emergence of Earliest Angiosperms May be Earlier than Fossil Evidence Indicates. Syst. Bot. 2017, 42, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallon, S.; Gomez-Acevedo, S.; Sanchez-Reyes, L.L.; Hernandez-Hernandez, T. A metacalibrated time-tree documents the early rise of flowering plant phylogenetic diversity. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakayama, H.; Kasai, F.; Nozaki, H.; Watanabe, M.M.; Kawachi, M.; Shigyo, M.; Nishihiro, J.; Washitani, I.; Krienitz, L.; Ito, M. Taxonomic reexamination of Chara globularis (Charales, Charophyceae) from Japan based on oospore morphology and rbcL gene sequences, and the description of C. leptospora sp. nov. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, W.; Hall, J.D.; McCourt, R.M.; Karol, K.G. Phylogeny of North American Tolypella (Charophyceae, Charophyta) based on plastid DNA sequences with a description of Tolypella ramosissima sp. nov. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subak-Sharpe, H.; Burk, R.R.; Crawford, L.V.; Morrison, M.; Hay, J.; Keir, H.M. An approach to evolutionary relationships of mammalian DNA viruses through analysis of the pattern of nearest neighbor base sequences. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. 1966, 31, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.; Subak-Sharpe, H. Analysis of nearest neighbour base frequencies in the RNA of a mammalian virus: Encephalomyocarditis Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1968, 2, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Lipkin, W.I.; Zaidi, S.; Delwart, E. Use of nucleotide composition analysis to infer hosts for three novel picorna-like viruses. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10322–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.R.; Papmichail, D.; Skiena, S.; Futcher, B.; Wimmer, E.; Mueller, S. Virus attenuation by genome-scale changes in codon pair bias. Science 2008, 320, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Anna, B.S.; Branco, J.O.; de Oliveira, M.M.; Boos, H.; Turra, A. Diet and population biology of the invasive crab Charybdis hellerii in southwestern Atlantic waters. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, A.; Henningsen, L.; Schubert, H.; Blindow, I. Encrustations and element composition of charophytes from fresh or brackish water sites—Habitat- or species-specific differences? Aquat. Bot. 2018, 148, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. National University of Ireland, Galway. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 19 November 2017).
- Scribailo, R.W.; Alix, M.S.A. A Checklist of North American Characeae. Charophytes 2010, 2, 38–52. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, V.W. Taxonomy of Chara Braunii: An experimental approach. J. Phycol. 1970, 6, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.H.; Li, H.; Sivasithamparam, K.; Admiraal, R.; Jones, M.G.K.; Wylie, S.J. Evolution of a wild-plant tobamovirus passaged through an exotic host: Fixation of mutations and increased replication. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, vex001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A. What is a Quasispecies? Trends Ecol. Evol. 1992, 7, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltman, B.; Allegrini, C. Restoration of lost aquatic plant communities: New habitats for Chara. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1997, 30, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, M.S.; Coops, H.; Simons, J. Propagule bank buildup of Chara aspera and its significance for colonization of a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 2001, 462, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariosa, Y.; Quesada, A.; Aburto, J.; Carrasco, D.; Legane, F.; Ferna, E. Epiphytic cyanobacteria on Chara vulgaris are the main contributors to N2 fixation in rice fields. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5391–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlok, M.; Suttle, C.A. University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. Unpublished work. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Kazlauskas, D.; Iranzo, J.; Lucía-sanz, A.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, V.; Krupovic, M. Origins and Evolution of the Global RNA Virome. MBio 2018, 9, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldbach, R. Genome similarities between plant and animal RNA viruses. Microbiol. Sci. 1987, 4, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldbach, R.; Wellink, J. Evolution of plus-strand RNA viruses. Intervirology 1988, 29, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.J. How ancient are the tobamoviruses? Intervirology 1980, 14, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauquet, H.; von Balthazar, M.; Magallón, S.; Doyle, J.A.; Endress, P.K.; Bailes, E.J.; Barroso de Morais, E.; Bull-Hereñu, K.; Carrive, L.; Chartier, M.; et al. The ancestral flower of angiosperms and its early diversification. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.D.; Powell, C.M.; Veevers, J.J. Spreading history of the eastern Indian Ocean and Greater India’s northward flight from Antarctica and Australia. GSA Bull. 1976, 87, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakey, R.C. Gondwana paleogeography from assembly to breakup—A 500 m.y. odyssey. In Resolving the Late Paleozoic Ice Age in Time and Space; Fielding, C.R., Frank, T.D., Isbell, J.L., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780813724416. [Google Scholar]
- Kidston, R.; Lang, W.H. XXXII—On Old Red Sandstone plants showing structure, from the Rhynie Chert Bed, Aberdeenshire. Part IV. Restorations of the vascular cryptogams, and discussion of their bearing on the general morphology of the Pteridophyta and the origin of the organisat. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1921, 52, 831–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, J.R.; Mestre, P.; Lu, R.; Malcuit, I.; Baulcombe, D.C. NRG1, a CC-NB-LRR Protein, together with N, a TIR-NB-LRR Protein, Mediates Resistance against Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor, H.H. Current status of the gene-fob-gene concept. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1971, 9, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, C.; Chen, J.Z.; Coureux, P.; Stroupe, M.E.; Fändrich, M.; Grigorieff, N. High-resolution Electron Microscopy of Helical Specimens: A Fresh Look at Tobacco Mosaic Virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 812–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstein, R.; Bollschweiler, D.; Engelhardt, H.; Lawrence, C.M.; Young, M. Large tailed spindle viruses of Archaea: A new way of doing viral business. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9146–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlok, M.; Gibbs, A.J.; Suttle, C.A. Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030299
Vlok M, Gibbs AJ, Suttle CA. Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses. Viruses. 2019; 11(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlok, Marli, Adrian J. Gibbs, and Curtis A. Suttle. 2019. "Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses" Viruses 11, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030299
APA StyleVlok, M., Gibbs, A. J., & Suttle, C. A. (2019). Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses. Viruses, 11(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030299




