Feline Foamy Virus is Highly Prevalent in Free-Ranging Puma concolor from Colorado, Florida and Southern California
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
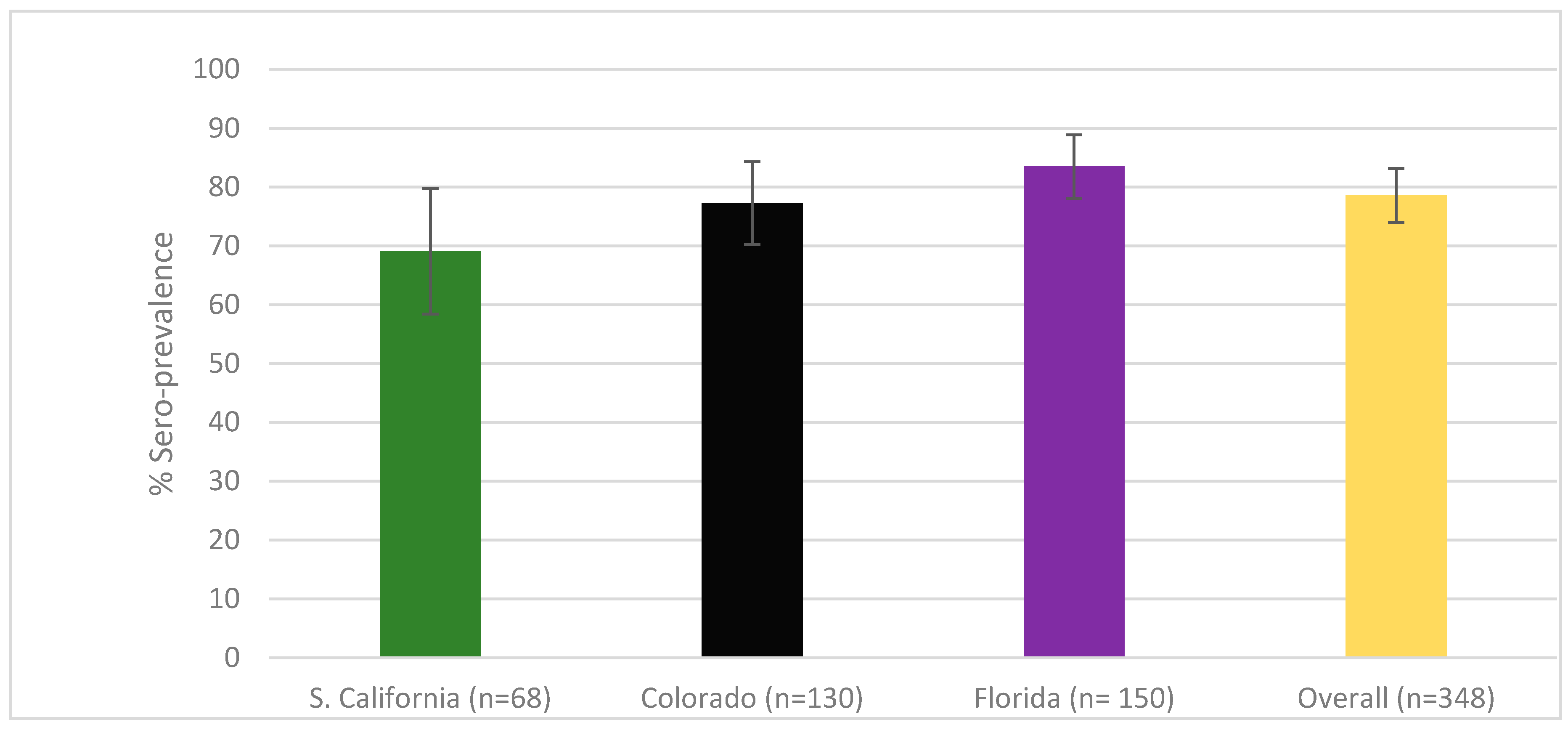
3.1. Sero-Prevalence
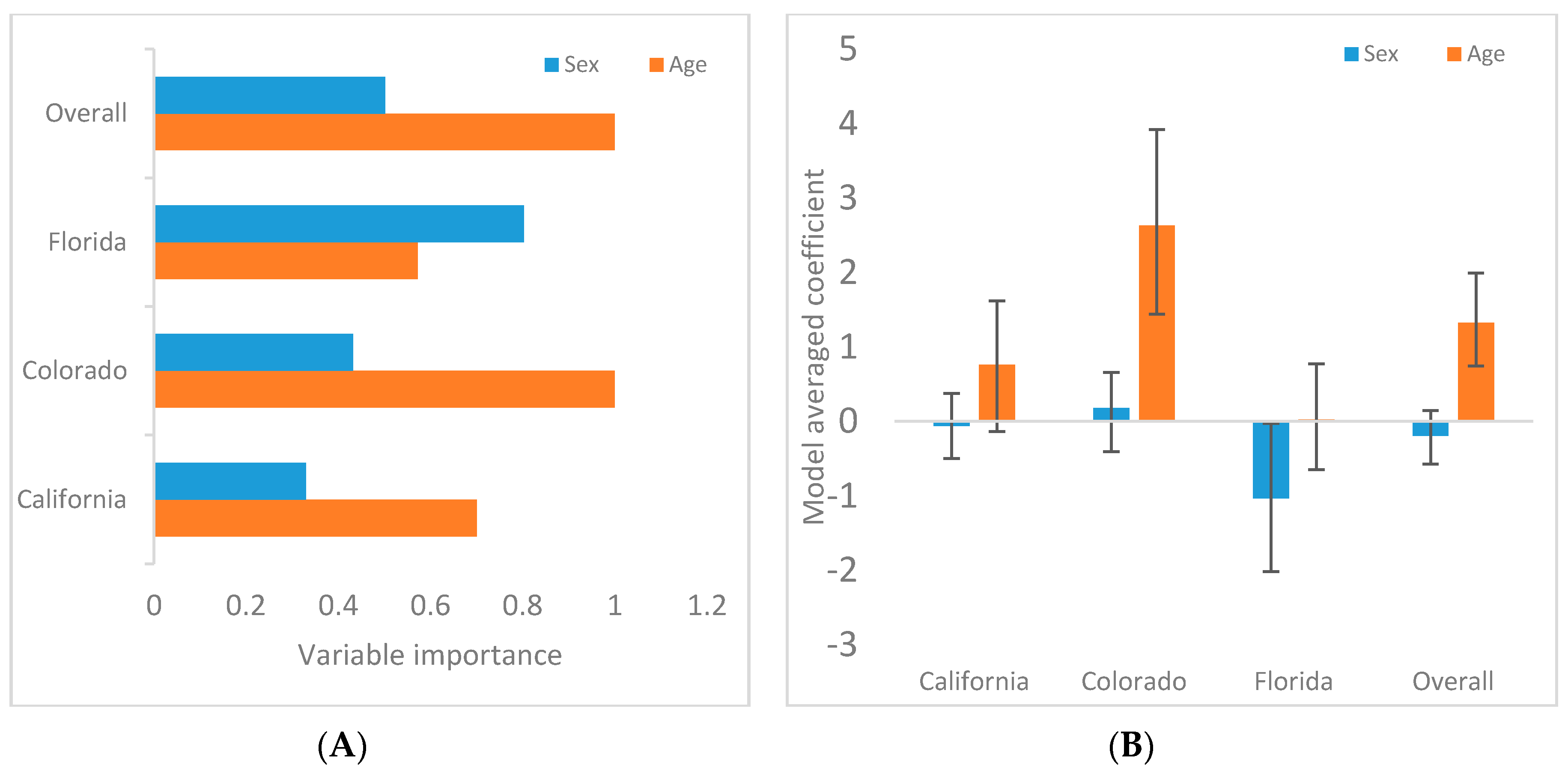
3.2. Demographic Associations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fields, B.N.; Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M.; Griffin, D.E. Foamy Viruses. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Rethwilm, A., Lindemann, D., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; p. 1614. [Google Scholar]
- Linial, M. Why aren’t foamy viruses pathogenic? Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, J.L.; Oshiro, L.S.; Taylor, D.O.N.; Lenette, E.H. Syncytium-forming agent isolated from domestic cats. Nature 1969, 11, 1190–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linial, M.L. Foamy Viruses are Unconventional Retroviruses. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.A.; Cheng, M.C.; Inoshima, Y.; Tomonaga, K.; Miyazawa, T.; Tohya, Y.; Toh, K.; Lu, Y.S.; Mikami, T. Seroepidemiological survey of feline retrovirus infections in cats in Taiwan in 1993 and 1994. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1995, 57, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, I.G.; Lochelt, M.; Flower, R.L.P. Epidemiology of Feline Foamy virus and Feline Immunodeficiency virus infections in domestic and feral cats: a seroepidemiological study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2848–2851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, M.; Akuzawa, M.; Nagatomo, H. Serological Survey of the Iriomote Cat (Felis-Iriomotensis) in Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 1990, 26, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Maeda, K.; Horimoto, T.; Tohya, Y.; Mochizuki, M.; Vu, D.; Vu, G.D.; Cu, D.X.; Ono, K.; et al. Seroepidemiological survey of feline retrovirus infections in domestic and leopard cats in northern Vietnam in 1997. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1998, 60, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, M.J.; Golder, M.C.; Jarrett, O.; MacDonald, D.W. Feline viruses in wildcats from Scotland. J. Wildl. Dis. 1999, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleaveland, S.; Mlengeya, T.; Kaare, M.; Haydon, D.; Lembo, T.; Luarenson, M.K.; Packer, C. The conservation relevance of epidemiological research into carnivore viral diseases in the Serengeti. Conservation Biol. 2007, 21, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, A.C.; Harbour, D.A.; Helps, C.R.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J. Is feline foamy virus really apathogenic? Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Wang, Y.; Wilmers, C. Spatial characteristics of residential development shift large carnivore prey habits. J. Wildl. Manage. 2016, 80, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, S.; Bevins, S.N.; Lappin, M.R.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Alldredge, M.; Logan, K.; Sweanor, L.L.; Riley, S.P.D.; Serieys, L.E.K.; et al. Pathogen exposure varies widely among sympatric populations of wild and domestic felids across the United States. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Hagen, S.; Troyer, R.; Zheng, X.; Musselman, E.; Slavkovic, L.D.; Franke, A.-M.; Maeda, D.; Zielonka, J.; Munk, C.; et al. Replacement of feline fomay virus bet by feline immunodeficiency virus vif yields replicative virus with novel vaccine candidate potential. Retrovirology 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleiholder, A.; Muhle, M.; Hechler, T.; Bevins, S.; VandeWoude, S.; Denner, J.; Lochelt, M. Pattern of seroreactivity against feline foamy virus proteins in domestic cats from Germany. Vet. Immunol. Immunop. 2011, 143, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romen, F.; Pawlita, M.; Sehr, P.; Bachmann, S.; Schröder, J.; Lutz, H.; Löchelt, M. Antibodies against Gag are diagnostic markers for feline foamy virus infections while Env and Bet reactivity is undetectable in a substantial fraction of infected cats. Virology 2006, 345, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bevins, S.N.; Carver, S.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Alldredge, M.; Logan, K.A.; Riley, S.P.D.; Fisher, R.N.; Vickers, T.W.; Boyce, W.; et al. Three pathogens in sympatric populations of pumas, bobcats, and domestic cats: implications for infectious disease transmission. PLoS ONE 2006, 7, 31403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, I.; Bodem, J.; Haas, L.; Zemba, M.; Delius, H.; Flower, R.; Flugel, R.M.; Löchelt, M. Characterization of the genome of feline foamy virus virus and its proteins shows distinct features different from those of primate spumaviruses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6727–6741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kehl, T.; Bleiholder, A.; Roßmann, F.; Rupp, S.; Lei, J.; Lee, J.; Boyce, W.; Vickers, W.; Crooks, K.; VandeWoude, S. Complete Genome Sequences of Two Novel Puma concolor Foamy Viruses from California. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e0020112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraberger, S.; Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA. Personal communication, 2019.
- Lardeux, F.; Torrico, G.; Aliaga, C. Calculation of ELISA’s cut-off based on the change-point analysis method for detection of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in Bolivian dogs in the absence of controls. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, K.A. Assessing Effects of Hunting on a Puma Population on the Uncompahgre Plateau, Colorado. Wildlife Research Report; Colorado Parks and Wildlife: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015.
- Seidensticker, J.; Hornocker, M.; Wiles, W.; Messick, J. Mountain Lion Social Organization in the Idaho Primitive Area. Wildl. Monogr. 1973, 35, 3–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hemker, T.; Lindzey, F.; Ackerman, B. Population Characteristics and Movement Patterns of Cougars in Southern Utah. J. Wildl. Manage. 1984, 48, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, K.A.; Sweanor, L. Behavior and social organization of a solitary carnivore. In Cougar: Ecology and Conservation; Hornocker, M., Negri, S., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Elbroch, M.; Levy, M.; Lubell, M.; Quigley, H.; Caragiulo, A. Adaptive social strategies in a solitary carnivore. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1701218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Pearse, W.D.; Escobar, L.E.; Alba-Casals, A.; Carver, S.; Davies, T.J.; Kraberger, S.; Papes, M.; Vandegrift, K.; Worsley-Tonks, K.; et al. Towards an eco-phylogenetic framework for infectious disease ecology. Biol. Reviews. 2017, 93, 950–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kechejian, S.; Dannemiller, N.; Kraberger, S.; Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Löchelt, M.; Carver, S.; VandeWoude, S. Feline foamy virus sero-prevalence and demographic risk factors in United States stray domestic cat populations. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, L.T.F.; Muniz, C.P.; Jia, H.; Augusto, A.; Troccoli, F.; Medeiros, S.; Dias, C.; Switzer, W.; Soares, M.; Santos, A. Clinical and Molecular Features of Feline Foamy Virus and Feline Leukemia Virus Co-Infection in Naturally-Infected Cats. Viruses 2018, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saib, A. Non-primate foamy viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 277, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.; Galvin, T.A.; Williams, D.K.; Beren, J.; Bryant, M.A.; Khan, A.S. Influence of naturally occurring simian foamy viruses (SFVs) on SIV disease progression in the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) model. Viruses 2013, 5, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.A.; Chiu, E.S.; Kraberger, S.; Roelke-Parker, M.; Lowery, I.; Erbeck, K.; Troyer, R.; Carver, S.; VandeWoude, S. Feline leukemia virus disease outcomes in a domestic cat breeding colony: Relationship to endogenous FeLV and other chronic viral infections. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00649-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biek, R.; Real, L.A. The landscape genetics of infectious disease emergence and spread. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3515–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Model | AIC | ΔAIC | Model Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA | |||
| Age | 63.39 | 0.00 | 0.46 |
| Null | 64.98 | 1.59 | 0.21 |
| Sex + Age | 65.34 | 1.94 | 0.18 |
| Sex | 66.7 | 3.38 | 0.09 |
| Sex + Age + Sex*Age | 67.34 | 3.94 | 0.06 |
| COLORADO | |||
| Age | 62.09 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| Sex + Age | 63.87 | 1.78 | 0.23 |
| Sex + Age + Sex*Age | 64.20 | 2.11 | 0.20 |
| Null | 77.69 | 15.60 | 0.00 |
| Sex | 79.23 | 17.14 | 0.00 |
| FLORIDA | |||
| Sex | 111.53 | 0.00 | 0.32 |
| Sex + Age + Sex*Age | 111.77 | 0.24 | 0.29 |
| Sex + Age | 112.55 | 1.02 | 0.19 |
| Null | 113.77 | 2.24 | 0.11 |
| Age | 114.02 | 2.49 | 0.09 |
| OVERALL | |||
| Age | 240.22 | 0.00 | 0.50 |
| Sex + Age | 240.84 | 0.62 | 0.37 |
| Sex + Age + Sex*Age | 242.83 | 2.61 | 0.14 |
| Sex | 254.40 | 14.18 | 0.00 |
| Null | 256.12 | 15.90 | 0.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kechejian, S.R.; Dannemiller, N.; Kraberger, S.; Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Malmberg, J.; Roelke Parker, M.; Cunningham, M.; McBride, R.; Riley, S.P.D.; Vickers, W.T.; et al. Feline Foamy Virus is Highly Prevalent in Free-Ranging Puma concolor from Colorado, Florida and Southern California. Viruses 2019, 11, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040359
Kechejian SR, Dannemiller N, Kraberger S, Ledesma-Feliciano C, Malmberg J, Roelke Parker M, Cunningham M, McBride R, Riley SPD, Vickers WT, et al. Feline Foamy Virus is Highly Prevalent in Free-Ranging Puma concolor from Colorado, Florida and Southern California. Viruses. 2019; 11(4):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040359
Chicago/Turabian StyleKechejian, Sarah R., Nick Dannemiller, Simona Kraberger, Carmen Ledesma-Feliciano, Jennifer Malmberg, Melody Roelke Parker, Mark Cunningham, Roy McBride, Seth P. D. Riley, Winston T. Vickers, and et al. 2019. "Feline Foamy Virus is Highly Prevalent in Free-Ranging Puma concolor from Colorado, Florida and Southern California" Viruses 11, no. 4: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040359
APA StyleKechejian, S. R., Dannemiller, N., Kraberger, S., Ledesma-Feliciano, C., Malmberg, J., Roelke Parker, M., Cunningham, M., McBride, R., Riley, S. P. D., Vickers, W. T., Logan, K., Alldredge, M., Crooks, K., Löchelt, M., Carver, S., & VandeWoude, S. (2019). Feline Foamy Virus is Highly Prevalent in Free-Ranging Puma concolor from Colorado, Florida and Southern California. Viruses, 11(4), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11040359





