Hepatitis E Virus Drug Development
Abstract
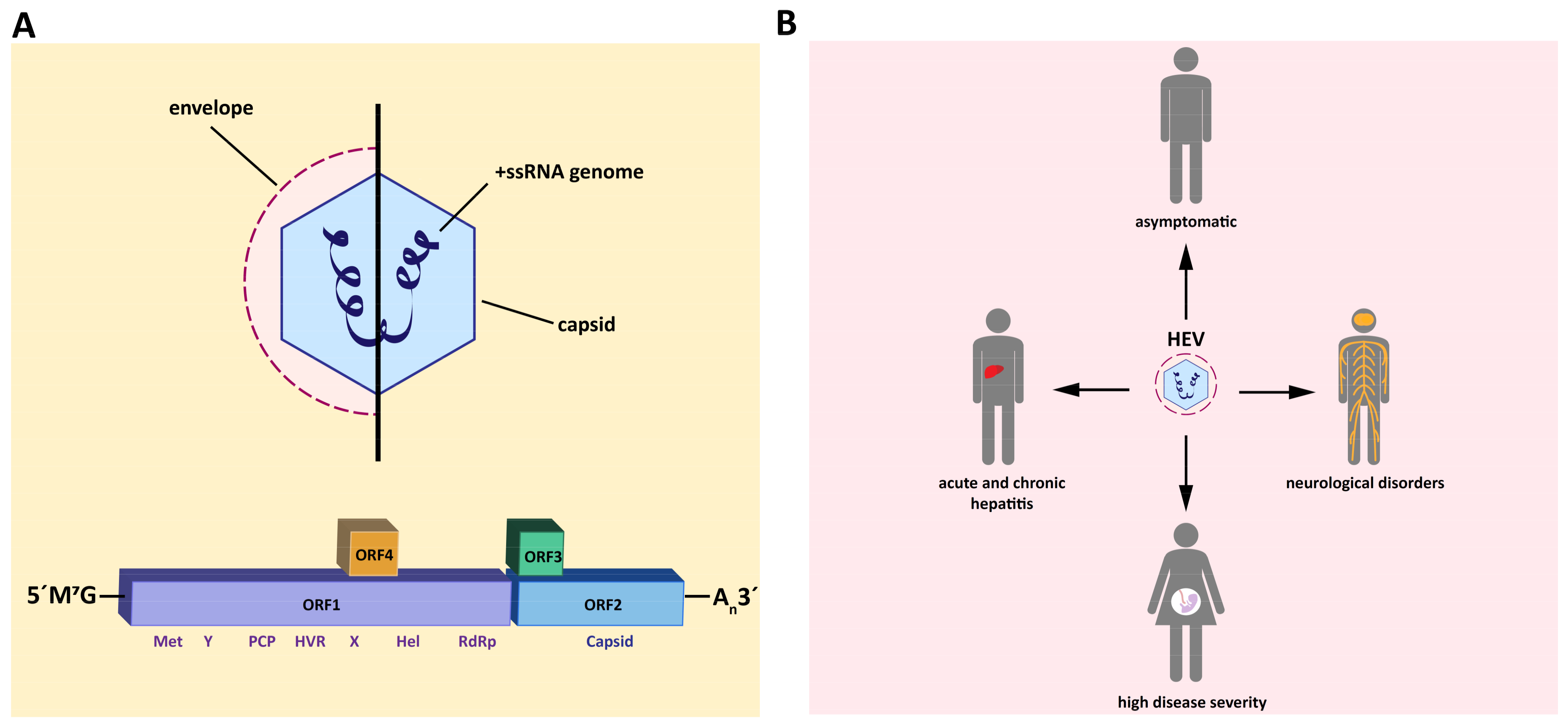
:1. Introduction
2. Strategies to Find Novel Therapy Options
3. Drug Repurposing
3.1. 2’-C-Methylcytidine
3.2. NITD008 and GPC-N114
3.3. Ciprofloxacin and IFN-λ
3.4. Sofosbuvir
4. Screening
4.1. Plant Ethanol Extracts
4.2. Zinc
4.3. 66E2
5. Basic Research/Structure-Guided
5.1. Hammerhead Ribozymes
5.2. Peptide Conjugated Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers
5.3. MG132
5.4. CP11
5.5. Inhibitors of Inosine-5′-Monophosphate Dehydrogenase
5.6. Silvestrol
6. Vaccine
7. Limitations, Needs, and Hopes for HEV Drug Development
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Izopet, J.; Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Johne, R.; Koenig, M.; Jameel, S.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.-J.; et al. Proposed reference sequences for hepatitis E virus subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Akanbi, O.A.; Harms, D.; Adesina, O.; Osundare, F.A.; Naidoo, D.; Deveaux, I.; Ogundiran, O.; Ugochukwu, U.; Mba, N.; et al. A new hepatitis E virus genotype 2 strain identified from an outbreak in Nigeria, 2017. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.; Lenglet, A.; Beversluis, D.; de Jong, M.; Vernier, L.; Spencer, C.; Andayi, F.; Kamau, C.; Vollmer, S.; Hogema, B.; et al. A large outbreak of Hepatitis E virus genotype 1 infection in an urban setting in Chad likely linked to household level transmission factors, 2016–2017. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, F.; Banu, S.S.; Ara, K.; Chowdhury, I.A.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Kamili, S.; Rahman, M.; Luby, S.P. An outbreak of hepatitis E in an urban area of Bangladesh. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izopet, J.; Lhomme, S.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Mansuy, J.-M.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F. HEV and transfusion-recipient risk. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2017, 24, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-H.; Tan, B.-H.; Teo, E.C.-Y.; Lim, S.-G.; Dan, Y.-Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.K.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.-K.; et al. Chronic Infection With Camelid Hepatitis E Virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355-7.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A.J.-X.; Leung, K.-H.; Chung, T.W.H.; Chan, J.F.W.; Chan, W.-M.; Teng, J.L.L.; et al. Rat Hepatitis E Virus as Cause of Persistent Hepatitis after Liver Transplant. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andonov, A.; Robbins, M.; Borlang, J.; Cao, J.; Hattchete, T.; Stueck, A.; Deschaumbault, Y.; Murnaghan, K.; Varga, J.; Johnston, B. Rat hepatitis E virus linked to severe acute hepatitis in an immunocompetent patient. J. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Pavio, N.; Aggarwal, R.; Labrique, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-García, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis E virus. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Rostaing, L.; Abravanel, F.; Garrouste, C.; Esposito, L.; Cardeau-Desangles, I.; Mansuy, J.M.; Selves, J.; Peron, J.M.; Otal, P.; et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha for treating chronic hepatitis E virus infection after liver transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, e30–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagsma, E.B.; Riezebos-Brilman, A.; van den Berg, A.P.; Porte, R.J.; Niesters, H.G.M. Treatment of chronic hepatitis E in liver transplant recipients with pegylated interferon α-2b. Liver Transplantation 2010, 16, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Garrouste, C.; Cardeau-Desangles, I.; Mansuy, J.M.; Weclawiak, H.; Izopet, J.; Rostaing, L. Three-month pegylated interferon-alpha-2a therapy for chronic hepatitis E virus infection in a haemodialysis patient. NDT 2010, 25, 2792–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalton, H.R.; Kamar, N.; Baylis, S.A.; Moradpour, D.; Wedemeyer, H.; Negro, F.; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Tripon, S.; Bismuth, M.; Hillaire, S.; Dumortier, J.; Radenne, S.; Coilly, A.; Garrigue, V.; D’Alteroche, L.; et al. Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis E virus infection in transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.T. Ribavirin and RSV: A new approach to an old disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1985, 1, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Clercq, E.; Li, G. Approved Antiviral Drugs over the Past 50 Years. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 695–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todt, D.; Meister, T.L.; Steinmann, E. Hepatitis E virus treatment and ribavirin therapy: Viral mechanisms of nonresponse. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 32, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.P.F.; Hsu, C.-W. Drug Repurposing for Ebola Virus Disease: Principles of Consideration and the Animal Rule. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, B.; Palù, G.; Loregian, A. Drug Repurposing for Viral Infectious Diseases: How Far Are We? Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schor, S.; Einav, S. Repurposing of Kinase Inhibitors as Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Drugs. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, T.L.; Bruening, J.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E. Cell culture systems for the study of hepatitis E virus. Antiviral Res. 2019, 163, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-C.; Wakita, T. Small Animal Models of Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Wu, X.; Rice, C.M.; Neyts, J.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Sofosbuvir Inhibits Hepatitis E Virus Replication In Vitro and Results in an Additive Effect When Combined With Ribavirin. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 82–85.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, C.; Xu, L.; Yin, Y.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q.; Wang, W. Nucleoside analogue 2’-C-methylcytidine inhibits hepatitis E virus replication but antagonizes ribavirin. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierra, C.; Amador, A.; Benzaria, S.; Cretton-Scott, E.; D’Amours, M.; Mao, J.; Mathieu, S.; Moussa, A.; Bridges, E.G.; Standring, D.N.; et al. Synthesis and pharmacokinetics of valopicitabine (NM283), an efficient prodrug of the potent anti-HCV agent 2’-C-methylcytidine. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6614–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.A. Progress towards improving antiviral therapy for hepatitis C with hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitors. Part I: Nucleoside analogues. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.J.; Sharma, S.D.; Feng, J.Y.; Ray, A.S.; Smidansky, E.D.; Kireeva, M.L.; Cho, A.; Perry, J.; Vela, J.E.; Park, Y.; et al. Sensitivity of mitochondrial transcription and resistance of RNA polymerase II dependent nuclear transcription to antiviral ribonucleosides. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzler, N.E.; Tuipulotu, D.E.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Mackenzie, J.M.; White, P.A. Antiviral candidates for treating hepatitis E virus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, L.; Vives-Adrián, L.; Selisko, B.; Ferrer-Orta, C.; Liu, X.; Lanke, K.; Ulferts, R.; de Palma, A.M.; Tanchis, F.; Goris, N.; et al. The RNA template channel of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a target for development of antiviral therapy of multiple genera within a virus family. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, J.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y.; Nong, J.; Wu, M.; Shao, Y.; Tang, R.; Yu, X.; Yin, Z.; Sun, Y. Resistance analysis and characterization of NITD008 as an adenosine analog inhibitor against hepatitis C virus. Antiviral Res. 2016, 126, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.; Roe, K.; Orillo, B.; Shi, P.-Y.; Verma, S. Combined treatment of adenosine nucleoside inhibitor NITD008 and histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat represents an immunotherapy strategy to ameliorate West Nile virus infection. Antiviral Res. 2015, 122, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.-Q.; Zhang, N.-N.; Li, C.-F.; Tian, M.; Hao, J.-N.; Xie, X.-P.; Shi, P.-Y.; Qin, C.-F. Adenosine Analog NITD008 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Zika Virus. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.-L.; Schul, W.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Gu, F.; Duraiswamy, J.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Niyomrattanakit, P.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Goh, A.; et al. An adenosine nucleoside inhibitor of dengue virus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Jirintai, S.; Kii, I.; Nagashima, S.; Prathiwi Primadharsini, P.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Screening of novel drugs for inhibiting hepatitis E virus replication. J. Virol. Methods 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V. Sofosbuvir: A novel oral agent for chronic hepatitis C. Annals Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Liu, P.; Takacs, C.N.; Xiang, K.; Andrus, L.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D.; Rice, C.M. Pan-Genotype Hepatitis E Virus Replication in Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocellular Systems. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hakim, M.S.; Nair, V.P.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Huang, F.; Sprengers, D.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Surjit, M.; Pan, Q. Distinct Antiviral Potency of Sofosbuvir Against Hepatitis C and E Viruses. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.-C.; Bai, H.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Genotype 5 Hepatitis E Virus Produced by a Reverse Genetics System Has the Potential for Zoonotic Infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, M.C.; Imlach, S.N.; Abravanel, F.; Ramalingam, S.; Johannessen, I.; Petrik, J.; Fraser, A.R.; Campbell, J.D.M.; Bramley, P.; Dalton, H.R.; et al. Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir Anti-Viral Therapy Fails to Clear HEV Viremia and Restore Reactive T Cells in a HEV/HCV Co-Infected Liver Transplant Recipient. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todesco, E.; Mazzola, A.; Akhavan, S.; Abravanel, F.; Poynard, T.; Roque-Afonso, A.-M.; Peytavin, G.; Marcelin, A.-G.; Calmus, Y.; Lecuyer, L.; et al. Chronic hepatitis E in a heart transplant patient: Sofosbuvir and ribavirin regimen not fully effective. Antivir. Ther. (Lond) 2018, 23, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Papp, C.P.; Bock, C.-T.; Hofmann, J.; Gerlach, U.A.; Maurer, M.M.; Eurich, D.; Mueller, T. Combination therapy of sofosbuvir and ribavirin fails to clear chronic hepatitis E infection in a multivisceral transplanted patient. J. Hepatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Valk, M.; Zaaijer, H.L.; Kater, A.P.; Schinkel, J. Sofosbuvir shows antiviral activity in a patient with chronic hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliotti, E.; Franchi, C.; Spaziante, M.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Volpicelli, L.; Palazzo, D.; de Angelis, M.; Esvan, R.; Taliani, G. Autochthonous acute hepatitis E: Treatment with sofosbuvir and ribavirin. Infection 2018, 46, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinane, M.; Jing Wang, X.; Watt, K. Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin Eradication of Refractory Hepatitis E in an Immunosuppressed Kidney Transplant Recipient. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2297–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornberg, M.; Pischke, S.; Müller, T.; Behrendt, P.; Piecha, F.; Benckert, J.; Smith, A.; Koch, A.; Lohse, A.; Hardtke, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir monotherapy in patients with chronic hepatitis E—The HepNet SofE pilot study. In Proceedings of the International Liver Congress™, Vienna, Austria, 10–14 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, M.P. High-throughput screening (HTS) for the identification of novel antiviral scaffolds. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2014, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarron, R.; Banks, M.N.; Bojanic, D.; Burns, D.J.; Cirovic, D.A.; Garyantes, T.; Green, D.V.S.; Hertzberg, R.P.; Janzen, W.P.; Paslay, J.W.; et al. Impact of high-throughput screening in biomedical research. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.E.; Kim, J.-E.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, B.J.; Song, Y.-J. An ethanol extract of Lysimachia mauritiana exhibits inhibitory activity against hepatitis E virus genotype 3 replication. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Parveen, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, B.J.; Song, Y.-J. Spicatoside A derived from Liriope platyphylla root ethanol extract inhibits hepatitis E virus genotype 3 replication in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, Y.; Sakurai, H.; Hussain, S.; Anner, B.M.; Hoshino, H. Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by zinc group metal compounds. Antiviral Res. 1999, 43, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Velthuis, A.J.W.; van den Worm, S.H.E.; Sims, A.C.; Baric, R.S.; Snijder, E.J.; van Hemert, M.J. Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.; Subramani, C.; Anang, S.; Muthumohan, R.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Zinc Salts Block Hepatitis E Virus Replication by Inhibiting the Activity of Viral RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, V.H.; Stammers, A.-L.; Medina, M.W.; Patel, S.; Dykes, F.; Souverein, O.W.; Dullemeijer, C.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Serra-Majem, L.; Nissensohn, M.; et al. The relationship between zinc intake and serum/plasma zinc concentration in children: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Nutrients 2012, 4, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Failure to respond to ribavirin despite elevated intra-erythrocyte zinc level in transplant-patients with chronic hepatitis E virus infection. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 21, e13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhvi, A.; Hingane, S.; Srivastav, R.; Joshi, N.; Subramani, C.; Muthumohan, R.; Khasa, R.; Varshney, S.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S.; et al. A screen for novel hepatitis C virus RdRp inhibitor identifies a broad-spectrum antiviral compound. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Mori, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Cheng, R.H.; Yoshimura, M.; Unno, H.; Shima, R.; Moriishi, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Li, T.C.; et al. Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis E virus-like particles based on the crystal structure. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guu, T.S.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Mata, D.A.; Li, K.; Yin, C.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.J. Structure of the hepatitis E virus-like particle suggests mechanisms for virus assembly and receptor binding. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Chandra, V.; Rahman, S.A.; Sehgal, D.; Jameel, S. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are required for cellular binding of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 capsid protein and for viral infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12714–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, C.; Luptak, A.; Perreault, J.; de La Peña, M. The ubiquitous hammerhead ribozyme. RNA 2012, 18, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukushima, A.; Fukuda, N.; Lai, Y.; Ueno, T.; Moriyama, M.; Taguchi, F.; Iguchi, A.; Shimizu, K.; Kuroda, K. Development of a chimeric DNA-RNA hammerhead ribozyme targeting SARS virus. Intervirology 2009, 52, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-López, C.; Díaz-González, R.; Barroso-delJesus, A.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication and internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation by an RNA molecule. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lewin, A.S.; Tuli, S.S.; Ghivizzani, S.C.; Schultz, G.S.; Bloom, D.C. Reduction in severity of a herpes simplex virus type 1 murine infection by treatment with a ribozyme targeting the UL20 gene RNA. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7467–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, B.; Thakral, D.; Panda, S.K. Targeted cleavage of hepatitis E virus 3’ end RNA mediated by hammerhead ribozymes inhibits viral RNA replication. Virology 2003, 312, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J. Antisense Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers as Novel Antiviral Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Kannan, H.; Stein, D.A.; Iversen, P.I.; Meng, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.-J. Inhibition of hepatitis E virus replication by peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers. Antiviral Res. 2015, 120, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome inhibitors: Valuable new tools for cell biologists. Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, Y.A.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis E virus replication requires an active ubiquitin-proteasome system. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5948–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, X.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Inhibition of hepatitis E virus replication by proteasome inhibitor is nonspecific. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrus, J.E.; von Schwedler, U.K.; Pornillos, O.W.; Morham, S.G.; Zavitz, K.H.; Wang, H.E.; Wettstein, D.A.; Stray, K.M.; Côté, M.; Rich, R.L.; et al. Tsg101 and the Vacuolar Protein Sorting Pathway Are Essential for HIV-1 Budding. Cell 2001, 107, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surjit, M.; Oberoi, R.; Kumar, R.; Lal, S.K. Enhanced alpha1 microglobulin secretion from Hepatitis E virus ORF3-expressing human hepatoma cells is mediated by the tumor susceptibility gene 101. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8135–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is essential for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai; Tanaka, T.; Yamada, K.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. A PSAP motif in the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is necessary for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornillos, O.; Alam, S.L.; Davis, D.R.; Sundquist, W.I. Structure of the Tsg101 UEV domain in complex with the PTAP motif of the HIV-1 p6 protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavassoli, A.; Lu, Q.; Gam, J.; Pan, H.; Benkovic, S.J.; Cohen, S.N. Inhibition of HIV budding by a genetically selected cyclic peptide targeting the Gag-TSG101 interaction. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anang, S.; Kaushik, N.; Hingane, S.; Kumari, A.; Gupta, J.; Asthana, S.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Potent Inhibition of Hepatitis E Virus Release by a Cyclic Peptide Inhibitor of the Interaction between Viral Open Reading Frame 3 Protein and Host Tumor Susceptibility Gene 101. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Bushell, S.; Qing, M.; Xu, H.Y.; Bonavia, A.; Nunes, S.; Zhou, J.; Poh, M.K.; Florez de Sessions, P.; Niyomrattanakit, P.; et al. Inhibition of dengue virus through suppression of host pyrimidine biosynthesis. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6548–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schläpfer, E.; Fischer, M.; Ott, P.; Speck, R.F. Anti-HIV-1 activity of leflunomide: A comparison with mycophenolic acid and hydroxyurea. AIDS 2003, 17, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Stiefel, P.; Franz, B.; Bremer, B.; Suneetha, P.V.; Heim, A.; Ganzenmueller, T.; Schlue, J.; Horn-Wichmann, R.; Raupach, R.; et al. Chronic hepatitis E in heart transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant 2012, 12, 3128–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Debing, Y.; Chen, K.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Neyts, J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Metselaar, H.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Calcineurin inhibitors stimulate and mycophenolic acid inhibits replication of hepatitis E virus. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Cointault, O.; Esposito, L.; Cardeau-Desangles, I.; Del Bello, A.; Dörr, G.; Lavayssière, L.; Nogier, M.B.; et al. An Early Viral Response Predicts the Virological Response to Ribavirin in Hepatitis E Virus Organ Transplant Patients. Transplantation 2015, 99, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Zhou, X.; Shokrollahi, E.; Felczak, K.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Pankiewicz, K.W.; Sprengers, D.; Raat, N.J.H.; et al. Cross Talk between Nucleotide Synthesis Pathways with Cellular Immunity in Constraining Hepatitis E Virus Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2834–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Woodard, J.L.; Lucas, D.M.; Fuchs, J.R.; Kinghorn, A.D. Rocaglamide, silvestrol and structurally related bioactive compounds from Aglaia species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bordeleau, M.-E.; Robert, F.; Gerard, B.; Lindqvist, L.; Chen, S.M.H.; Wendel, H.-G.; Brem, B.; Greger, H.; Lowe, S.W.; Porco, J.A.; et al. Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation modulates chemosensitivity in a mouse lymphoma model. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henss, L.; Scholz, T.; Grünweller, A.; Schnierle, B.S. Silvestrol Inhibits Chikungunya Virus Replication. Viruses 2018, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Schulte, F.W.; Lange-Grünweller, K.; Obermann, W.; Madhugiri, R.; Pleschka, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grünweller, A. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of the eIF4A inhibitor silvestrol against corona- and picornaviruses. Antiviral Res. 2018, 150, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenkopf, N.; Lange-Grünweller, K.; Schulte, F.W.; Weißer, A.; Müller, C.; Becker, D.; Becker, S.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grünweller, A. The natural compound silvestrol is a potent inhibitor of Ebola virus replication. Antiviral Res. 2017, 137, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitscher, M.; Himmelsbach, K.; Woytinek, K.; Johne, R.; Reuter, A.; Spiric, J.; Schwaben, L.; Grünweller, A.; Hildt, E. Inhibition of Hepatitis E Virus Spread by the Natural Compound Silvestrol. Viruses 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, D.; Moeller, N.; Praditya, D.; Kinast, V.; Friesland, M.; Engelmann, M.; Verhoye, L.; Sayed, I.M.; Behrendt, P.; Dao Thi, V.L.; et al. The natural compound silvestrol inhibits hepatitis E virus (HEV) replication in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 2018, 157, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Gisa, A.; Dallmeier, K.; Pischke, S.; Bremer, B.; Manns, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Suneetha, P.V.; Neyts, J. A mutation in the hepatitis E virus RNA polymerase promotes its replication and associates with ribavirin treatment failure in organ transplant recipients. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1008–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, D.; Gisa, A.; Radonic, A.; Nitsche, A.; Behrendt, P.; Suneetha, P.V.; Pischke, S.; Bremer, B.; Brown, R.J.P.; Manns, M.P.; et al. In vivo evidence for ribavirin-induced mutagenesis of the hepatitis E virus genome. Gut 2016, 65, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.M.; Ou, S.H.; Huang, G.Y.; He, Z.Q.; Ge, S.X.; Xian, Y.L.; Pang, S.Q.; Ng, M.H.; et al. A bacterially expressed particulate hepatitis E vaccine: Antigenicity, immunogenicity and protectivity on primates. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2893–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Huang, S.-J.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.-L.; Jiang, H.-M.; Cai, J.-P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine in healthy adults: A large-scale, randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet 2010, 376, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Huang, S.-J.; Wu, T.; Hu, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.-M.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yan, Q.; et al. Long-term efficacy of a hepatitis E vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, F.-C.; Huang, S.-J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.-S. Safety of the hepatitis E vaccine for pregnant women: A preliminary analysis. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Mansuy, J.-M.; Muscari, F.; Sallusto, F.; Rostaing, L.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E virus reinfections in solid-organ-transplant recipients can evolve into chronic infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1900–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, I.H.; Nanda, S.K.; Durgapal, H.; Agrawal, S.; Mohanty, S.K.; Gupta, D.; Jameel, S.; Panda, S.K. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) nonstructural open reading frame 1 (ORF1). J. Med. Virol. 2000, 60, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropp, S.L.; Tam, A.W.; Beames, B.; Purdy, M.; Frey, T.K. Expression of the hepatitis E virus ORF1. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppiah, S.; Zhou, Y.; Frey, T.K. Lack of Processing of the Expressed ORF1 Gene Product of Hepatitis E Virus. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perttilä, J.; Spuul, P.; Ahola, T. Early secretory pathway localization and lack of processing for hepatitis E virus replication protein pORF1. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Ansari, I.H.; Durgapal, H.; Agrawal, S.; Jameel, S. The In Vitro-Synthesized RNA from a cDNA Clone of Hepatitis E Virus Is Infectious. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, D.; Thomas, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Jameel, S. Expression and processing of the Hepatitis E virus ORF1 nonstructural polyprotein. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanade, G.D.; Pingale, K.D.; Karpe, Y.A. Activities of Thrombin and Factor Xa Are Essential for Replication of Hepatitis E Virus and Are Possibly Implicated in ORF1 Polyprotein Processing. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magden, J.; Takeda, N.; Li, T.; Auvinen, P.; Ahola, T.; Miyamura, T.; Merits, A.; Kääriäinen, L. Virus-specific mRNA capping enzyme encoded by hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, D.; Panda, S.K.; Kapur, N.; Varma, S.P.K.; Durgapal, H. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: A chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, Y.A.; Lole, K.S. NTPase and 5’ to 3’ RNA duplex-unwinding activities of the hepatitis E virus helicase domain. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Gupta, D.; Panda, S.K. The 3’ end of hepatitis E virus (HEV) genome binds specifically to the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Virology 2001, 282, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinast, V.; Burkard, T.L.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E. Hepatitis E Virus Drug Development. Viruses 2019, 11, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060485
Kinast V, Burkard TL, Todt D, Steinmann E. Hepatitis E Virus Drug Development. Viruses. 2019; 11(6):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060485
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinast, Volker, Thomas L Burkard, Daniel Todt, and Eike Steinmann. 2019. "Hepatitis E Virus Drug Development" Viruses 11, no. 6: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060485
APA StyleKinast, V., Burkard, T. L., Todt, D., & Steinmann, E. (2019). Hepatitis E Virus Drug Development. Viruses, 11(6), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060485





