The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tick Viruses That Infect Humans and Animals
2.1. Powassan and Deer Tick Virus
2.2. Crimean–Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus
2.3. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus
2.4. Colorado Tick Fever Virus
2.5. Hearthland Virus
3. Composition of the Tick Virome
3.1. A Comparison of Tick Viromes from Different Countries
3.2. Newly Identified Tick Viruses
3.2.1. Tick Nairoviruses
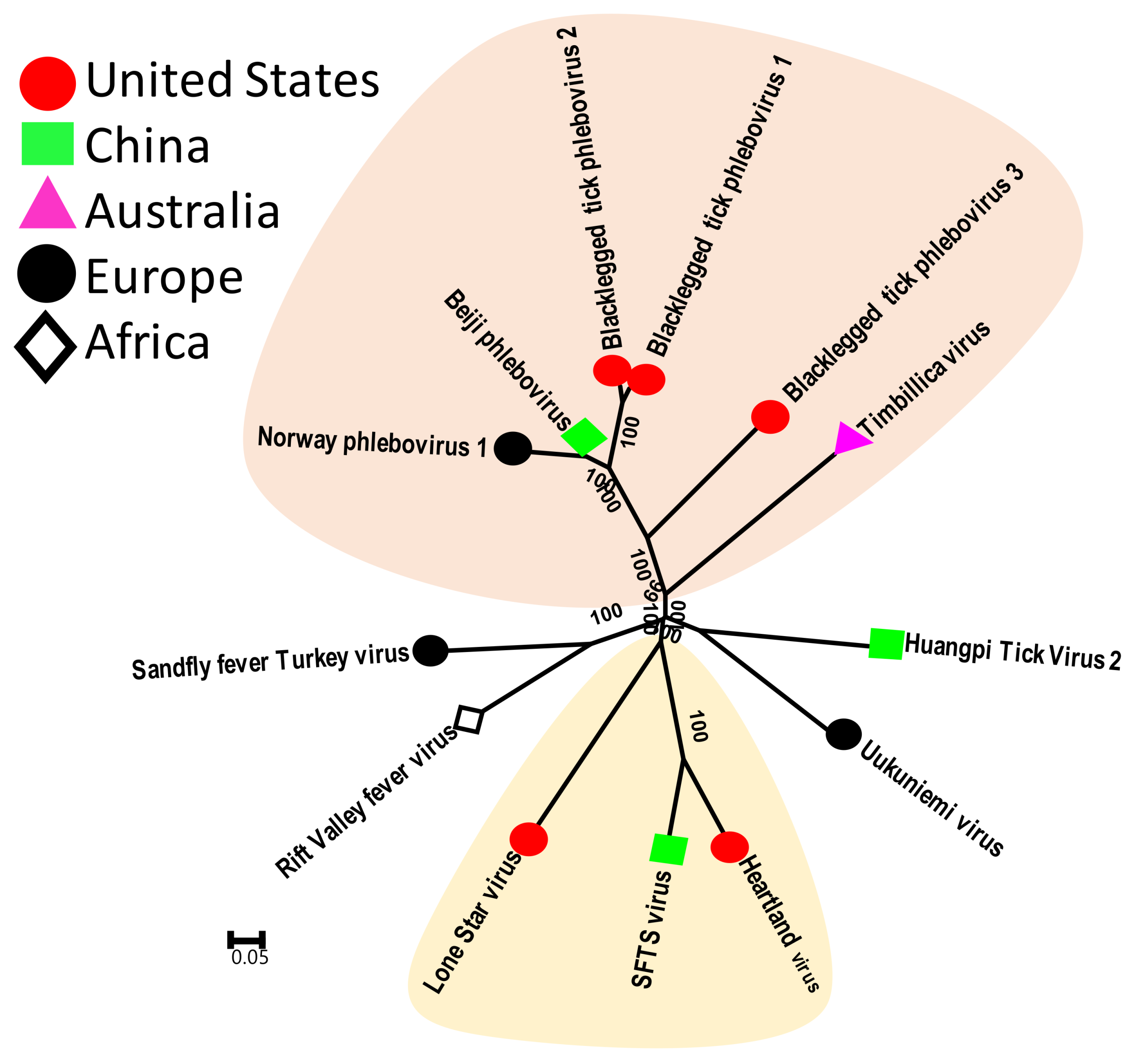
3.2.2. Tick Phleboviruses
3.2.3. Tick Chuviruses
3.2.4. Tick Flaviviruses
4. Summary and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A. Biology of ticks. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 22, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brites-Neto, J.; Duarte, K.M.; Martins, T.F. Tick-borne infections in human and animal population worldwide. Vet. World 2015, 8, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgdorfer, W.; Barbour, A.G.; Hayes, S.F.; Benach, J.L.; Grunwaldt, E.; Davis, J.P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 1982, 216, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steere, A.C. Lyme borreliosis in 2005, 30 years after initial observations in lyme connecticut. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2006, 118, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, O. Illnesses caused by us ticks and mosquitoes tripled in recent years. BMJ 2018, 361, k1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoGiudice, K.; Duerr, S.T.; Newhouse, M.J.; Schmidt, K.A.; Killilea, M.E.; Ostfeld, R.S. Impact of host community composition on lyme disease risk. Ecology 2008, 89, 2841–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Brunner, J.L. Climate change and ixodes tick-borne diseases of humans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.S. Factors in the emergence of infectious diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1995, 1, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergonul, O. Crimean-congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karti, S.S.; Odabasi, Z.; Korten, V.; Yilmaz, M.; Sonmez, M.; Caylan, R.; Akdogan, E.; Eren, N.; Koksal, I.; Ovali, E.; et al. Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever in Turkey. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimirova, M.; Thangamani, S.; Bartikova, P.; Hermance, M.; Holikova, V.; Stibraniova, I.; Nuttall, P.A. Tick-borne viruses and biological processes at the tick-host-virus interface. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermance, M.E.; Thangamani, S. Powassan virus: An emerging arbovirus of public health concern in North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.A.; Solomon, T. Pathogenic flaviviruses. Lancet 2008, 371, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, D.J.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X.P.; He, Y.W.; Sun, Q.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.A.; Tian, J.H.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel tick-borne bunyavirus in huaiyangshan, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2011, 32, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; He, Y.W.; Dai, Y.A.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, D.J.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Luo, X.L.; Cheng, Y.L.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel bunyavirus in China: Pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullan, L.K.; Folk, S.M.; Kelly, A.J.; MacNeil, A.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Batten, B.C.; Albarino, C.G.; Zaki, S.R.; Rollin, P.E.; et al. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Williams, S.H.; Sameroff, S.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Virome analysis of amblyomma americanum, dermacentor variabilis, and ixodes scapularis ticks reveals novel highly divergent vertebrate and invertebrate viruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11480–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Sameroff, S.; Leon, M.S.; Jain, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Genome characterization of long island tick rhabdovirus, a new virus identified in amblyomma americanum ticks. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, W.G. The rockefeller foundation virus program: 1951–1971 with update to 1981. Annu. Rev. Med. 1982, 33, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc, L.D.; Donohue, W.L. Powassan virus: Isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1959, 80, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, S.R., 3rd; Armstrong, P.M.; Katavolos, P.; Foppa, I.; Garcia, A.S.; Wilson, M.L.; Spielman, A. A new tick-borne encephalitis-like virus infecting New England deer ticks, ixodes dammini. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesko, K.N.; Torres-Perez, F.; Hjelle, B.L.; Ebel, G.D. Molecular epidemiology of powassan virus in North America. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemenesi, G.; Banyai, K. Tick-borne flaviviruses, with a focus on powassan virus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanaugh, C.E.; Muscat, P.L.; Telford, S.R., 3rd; Goethert, H.; Pendlebury, W.; Elias, S.P.; Robich, R.; Welch, M.; Lubelczyk, C.B.; Smith, R.P. Fatal deer tick virus infection in Maine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, N.P.; Wang, H.; Dupuis, M.; Hull, R.; Ebel, G.D.; Gilmore, E.J.; Faust, P.L. Fatal case of deer tick virus encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, S.; Bokaean, M.; Shahrivar, M.R.; Chinikar, S. Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever. Lab. Med. 2015, 46, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, B.; Gruber, C.E.; Koopmans, M.; Avsic, T.; Bino, S.; Christova, I.; Grunow, R.; Hewson, R.; Korukluoglu, G.; Lemos, C.M.; et al. Laboratory management of crimean-congo haemorrhagic fever virus infections: Perspectives from two European networks. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, N.J.C.; Han, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Choi, Y.K. Epidemiology of severe fever and thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection and the need for therapeutics for the prevention. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2018, 7, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.Y.; Feng, Z.J.; Matsui, T.; Foxwell, A.R. Risk assessment of human infection with a novel bunyavirus in China. West. Pac. Surveill. Response J. 2012, 3, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.Y.; Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Wang, E.; Park, S.W.; Lee, W.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Uh, Y.; Kim, Y.K. Nosocomial person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yendell, S.J.; Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E. Colorado tick fever in the United States, 2002–2012. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, H.M.; Godsey, M.S., Jr.; Lambert, A.; Panella, N.A.; Burkhalter, K.L.; Harmon, J.R.; Lash, R.R.; Ashley, D.C.; Nicholson, W.L. First detection of heartland virus (bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) from field collected arthropods. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, H.M.; Godsey, M.S., Jr.; Panella, N.A.; Burkhalter, K.L.; Ashley, D.C.; Lash, R.R.; Ramsay, B.; Patterson, T.; Nicholson, W.L. Surveillance for heartland virus (bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus) in Missouri during 2013: First detection of virus in adults of amblyomma americanum (acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, N.P.; Menitove, J.E.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Turabelidze, G.; Parton, P.; Peck, K.; Basile, A.J.; Kosoy, O.I.; Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E. Seroprevalence of heartland virus antibodies in blood donors, Northwestern Missouri, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Ding, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; He, B.; Tu, C. Virome analysis of tick-borne viruses in heilongjiang province, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, E.; Rose, K.; Eden, J.S.; Lo, N.; Abeyasuriya, T.; Shi, M.; Doggett, S.L.; Holmes, E.C. Extensive diversity of RNA viruses in Australian ticks. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.H.; Shi, M.; Bohlin, J.; Eldholm, V.; Brynildsrud, O.B.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, A.; Holmes, E.C. Characterizing the virome of ixodes ricinus ticks from Northern Europe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, R.; Sameroff, S.; Tagliafierro, T.; Jain, K.; Williams, S.H.; Cucura, D.M.; Rochlin, I.; Monzon, J.; Carpi, G.; Tufts, D.; et al. Identification of novel viruses in amblyomma americanum, dermacentor variabilis, and ixodes scapularis ticks. mSphere 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutailler, S.; Popovici, I.; Devillers, E.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Eloit, M. Diversity of viruses in ixodes ricinus, and characterization of a neurotropic strain of eyach virus. New Microbes New Infect. 2016, 11, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kou, Z.; Fan, Z.; Bente, D.; Zeng, C.; Li, T. Metagenomic profile of the viral communities in rhipicephalus spp. Ticks from Yunnan, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Murthy, S.; Kapoor, A. Evolution of selective-sequencing approaches for virus discovery and virome analysis. Virus Res. 2017, 239, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Gao, D.Y.; He, J.R.; Wang, J.B.; Li, C.X.; Kang, Y.J.; Yu, B.; et al. A tick-borne segmented rna virus contains genome segments derived from unsegmented viral ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. eLife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Ayllon, M.A.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Brown, P.A.; Bukreyev, A.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order mononegavirales: Second update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Adkins, S.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avsic-Zupanc, T.; Ballinger, M.J.; Bente, D.A.; Beer, M.; Bergeron, E.; Blair, C.D.; Briese, T.; et al. Taxonomy of the order bunyavirales: Second update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. Mega7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.C.; Maruyama, S.R.; de Miranda-Santos, I.K.F.; Palacios, G.; Ladner, J.T. Complete coding genome sequence for mogiana tick virus, a jingmenvirus isolated from ticks in Brazil. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00232-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Beitzel, B.; Auguste, A.J.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Lindquist, M.E.; Sibley, S.D.; Kota, K.P.; Fetterer, D.; Eastwood, G.; et al. A multicomponent animal virus isolated from mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Liu, H.B.; Ni, X.B.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zheng, Y.C.; Song, J.L.; Li, J.; Jiang, B.G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Emergence of human infection with jingmen tick virus in China: A retrospective study. EBioMedicine 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandegrift, K.J.; Wale, N.; Epstein, J.H. An ecological and conservation perspective on advances in the applied virology of zoonoses. Viruses 2011, 3, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Virome | Tick Species | Virus Names | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Ixodes scapularis | South Bay virus, Suffolk virus, Phleboviruses, Rhabdoviruses, Powassan virus | [17,18,39] |
| Dermacentor variabilis | Phlebovirus, Rhabdoviruses, Noda or Tetravirus-like virus | ||
| Amblyomma americanum | Rhabdovirus | ||
| Norway (Europe) | Ixodes ricinus | Phleboviruses, Nairovirus, Churivirus, Luteovirus | [38] |
| France (Europe) | Ixodes ricinus | Nairovirus, Phlebovirus, Coltivirus (Eyach virus), Rhabdoviridae | [40] |
| Australia | Amblyomma moreliae, Ixodes trichosuri and Ixodes holocyclus | Chuviridae, Flaviviridae, Luteoviridae, Narnaviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, Partitiviridae, Phenuiviridae,, Picornaviridae, Reoviridae, Rhabdoviridae, Unclassified−Mononegavirales, Virgaviridae | [37] |
| China | Ixodes persulcatus, Dermacentor nuttalli, Dermacentor silvarum, Haemaphysalis longicornis, and Haemaphysalis concinna. | Phleboviruses, Nairovirus, Churivirus and Jingmen tick virus | [36] |
| Rhipicephalus spp. | Nairovirus, Rhabdovirus | [41] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vandegrift, K.J.; Kapoor, A. The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health. Viruses 2019, 11, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060529
Vandegrift KJ, Kapoor A. The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health. Viruses. 2019; 11(6):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060529
Chicago/Turabian StyleVandegrift, Kurt J., and Amit Kapoor. 2019. "The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health" Viruses 11, no. 6: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060529
APA StyleVandegrift, K. J., & Kapoor, A. (2019). The Ecology of New Constituents of the Tick Virome and Their Relevance to Public Health. Viruses, 11(6), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060529





