High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Differential Begomovirus Species Diversity in Non-Cultivated Plants in Northern-Pacific Mexico
Abstract
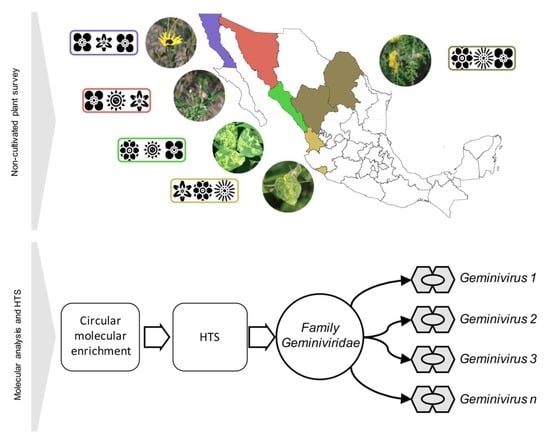
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Isolation, RCA, and Library Construction
2.3. Metagenomic Analysis of Geminivirus-Related Signatures
2.4. Begomovirus Full-Length Genome Amplification, Cloning, and Sequence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Non-Cultivated Plants from Northern-Pacific Mexico Region as a Reservoir of Begomoviruses
3.2. Metagenomics Study Reveals a Number of Geminviruses from Non-Cultivated Plants
3.3. Molecular Validation of the Predominant Begomoviruses Identified by HTS
3.4. Ecogenomic Analyis of Predominant Begomoviruses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garbach, K.; Milder, J.C.; Montenegro, M.; Karp, D.S.; DeClerck, F.A.J. Biodiversity and ecosystem services in agroecosystems. Encycl. Agric. Food Syst. 2014, 2, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Pacheco, I.; Garzón-Tiznado, J.A.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Rivera-Bustamente, R.F. Complete nucleotide sequence of pepper huasteco virus: Analysis and comparison with bipartite geminiviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 2225–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Ramirez, E.R.; Gilbertson, R.L. First report of tomato mottle geminivirus infecting tomatoes in Yucatan, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2007, 5, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Lozano, J.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; Perea-Araujo, L.L.; Ruelas-Ayala, R.D.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R. A Begomovirus isolated from chlorotic and stunted soybean plants in Mexico is a new strain of rhynchosia golden mosaic virus. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendrez-Bojorquez, N.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Magallanes-Tapia, M.A.; Camacho-Beltran, E.; Armenta-Anaya, C.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Mendez-Lozano, J. Pepper huasteco yellow vein virus associated to sweet pepper disease in Sinaloa, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2016, 9, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Durán, G.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Morales-Aguilar, J.J.; Camacho-Beltrán, E.; Romero-Romero, J.L.; Rivera-Acosta, M.A.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Arroyo-Becerra, A.; Méndez-Lozano, J. Molecular and biological characterization of Watermelon chlorotic stunt virus (WmCSV): An Eastern Hemisphere begomovirus introduced in the Western Hemisphere. Crop Prot. 2018, 103, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Peña, R.J.; Arguello-Astorga, G.R.; Brown, J.K.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. A new strain of tomato chino la paz virus associated with a leaf curl disease of tomato in Baja California Sur, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2007, 90, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffat, A.S. Geminiviruses emerge as serious crop threat. Science 1999, 286, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, G.W.; Martin, D.P.; Duffy, S.; Monjane, A.L.; Shepherd, D.N.; Windram, O.P.; Owor, B.E.; Donaldson, L.; van Antwerpen, T.; Sayed, R.A.; et al. Dating the origins of the maize-adapted strain of maize streak virus, MSV-A. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, B.L.; Fauquet, C.M. Cassava mosaic geminiviruses: Actual knowledge and perspectives. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.W.; Markham, P.G. Cotton leaf curl virus disease. Virus Res. 2000, 71, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accotto, G.P.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Noris, E.; Moriones, E.; Louro, D. Typing of tomato yellow leaf curl viruses in Europe. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2000, 106, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K. Transmission, host range, and virus-vector relationships of chino del tomate virus, a whitefly-transmitted geminivirus from Sinaloa, Mexico. Plant Dis. 1988, 72, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon-Tiznado, J.A. Inoculation of peppers with infectious clones of a new geminivirus by a biolistic procedure. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon-Tiznado, J.A.; Acosta-Garcia, G.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Gonzalez-Chavira, M.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F.; Maya-Hernandez, V.; Guevara-Gonzalez, R.G. Presence of geminivirus, pepper huasteco virus (PHV), texas pepper virus-variant Tamaulipas (TPV-T), and Chino del tomate virus (CdTV) in the states of Guanajuato, Jalisco and San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2002, 20, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Idris, A.M.; Carnevali, G.; Brown, J.K.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.A. Preliminary identification and coat protein gene phylogenetic relationships of begomoviruses associated with native flora and cultivated plants from the Yucatan peninsula of Mexico. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B.; Ambríz-Granados, S.; Velásquez-Valle, R.; Méndez-Lozano, J. A new strain of chino del tomate virus isolated from soybean plants (Glycine max L.) in Mexico. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2014, 5, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Ascencio-Ibáñez, J.T.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Méndez-Lozano, J.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. First report of rhynchosia golden mosaic virus (RhGMV) infecting tobacco in Chiapas, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio-Jorge, J.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Frías-Treviño, G.; Bernal-Alcocer, A.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.; Alpuche-Solís, Á.G.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B.; Hernández-Zepeda, C. Analysis of a new strain of Euphorbia mosaic virus with distinct replication specificity unveils a lineage of begomoviruses with short Rep sequences in the DNA-B intergenic region. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Varsani, A.; Brown, J.K. Intergeneric recombination between a new, spinach-infecting curtovirus and a new geminivirus belonging to the genus Becurtovirus: First New World exemplar. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefeuvre, P.; Moriones, E. Recombination as a motor of host switches and virus emergence: Geminiviruses as case studies. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 10, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Trenado, H.P.; Louro, D.; Navas-Castillo, J. Recurrent speciation of a tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus in Portugal by recombination. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monci, F.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E. A natural recombinant between the geminiviruses Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus and Tomato yellow leaf curl virus exhibits a novel pathogenic phenotype and is becoming prevalent in Spanish populations. Virology 2002, 303, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Pendón, J.A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Fortes, I.M.; Moriones, E. Tomato yellow leaf curl sardinia virus, a begomovirus species evolving by mutation and recombination: A challenge for virus control. Viruses 2019, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aregbesola, O.Z.; Legg, J.P.; Sigsgaard, L.; Lund, O.S.; Rapisarda, C. Potential impact of climate change on whiteflies and implications for the spread of vectored viruses. J. Pest Sci. (2004) 2018, 92, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anonymous. Scientific Opinion on the risks to plant health posed by Bemisia tabaci species complex and viruses it transmits for the EU territory. EFSA J. 2016, 11, 3162. [Google Scholar]
- Canto, T.; Aranda, M.A.; Fereres, A. Climate change effects on physiology and population processes of hosts and vectors that influence the spread of hemipteran-borne plant viruses. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffy, S.; Holmes, E.C. Phylogenetic evidence for rapid rates of molecular evolution in the single-stranded DNA begomovirus tomato yellow leaf curl virus. J. Virol. 2007, 82, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, P.; Martin, D.P.; Harkins, G.; Lemey, P.; Gray, A.J.; Meredith, S.; Lakay, F.; Monjane, A.; Lett, J.M.; Varsani, A.; et al. The spread of tomato yellow leaf curl virus from the Middle East to the world. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjane, A.L.; Harkins, G.W.; Martin, D.P.; Lemey, P.; Lefeuvre, P.; Shepherd, D.N.; Oluwafemi, S.; Simuyandi, M.; Zinga, I.; Komba, E.K.; et al. Reconstructing the history of maize streak virus strain a dispersal to reveal diversification hot spots and its origin in Southern Africa. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9623–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.; Golden, M.; Akram, M.; Naimuddin; Nadarajan, N.; Fernandez, E.; Granier, M.; Rebelo, A.G.; Peterschmitt, M.; Martin, D.P.; et al. Identification and characterisation of a highly divergent geminivirus: Evolutionary and taxonomic implications. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsani, A.; Roumagnac, P.; Fuchs, M.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E.; Idris, A.; Briddon, R.W.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.; Murilo Zerbini, F.; Martin, D.P. Capulavirus and Grablovirus: Two new genera in the family Geminiviridae. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybicki, E.P. A phylogenetic and evolutionary justification for three genera of Geminiviridae. Arch. Virol. 1994, 139, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, M.; Czosnek, H.; Hadidi, A. Historical perspective, development and applications of next-generation sequencing in plant virology. Viruses 2014, 6, 106–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massart, S.; Olmos, A.; Jijakli, H.; Candresse, T. Current impact and future directions of high-throughput sequencing in plant virus diagnostics. Virus Res. 2014, 188, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, S.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. Identification of viruses and viroids by next-generation sequencing and homology-dependent and homology-independent algorithms. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooggin, M.M. Small RNA-omics for plant virus identification, virome reconstruction, and antiviral defense characterization. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.J.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Cascardo, R.S.; Andrade, E.C.; Murilo Zerbini, F. Analysis of the full-length genome sequence of papaya lethal yellowing virus (PLYV), determined by deep sequencing, confirms its classification in the genus Sobemovirus. Arch. Virol. 2012, 10, 2009–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampelli, S.; Soverini, M.; Turroni, S.; Quercia, S.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Candela, M. ViromeScan: A new tool for metagenomic viral community profiling. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.; Charles-Dominique, T.; Barakat, M.; Ortet, P.; Fernandez, E.; Filloux, D.; Hartnady, P.; Rebelo, T.A.; Cousins, S.R.; Mesleard, F.; et al. Geometagenomics illuminates the impact of agriculture on the distribution and prevalence of plant viruses at the ecosystem scale. ISME J. 2017, 12, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llorente-Bousquets, J.; Ocegueda, S. Estado del conocimiento de la biota. in Capital natural de México: Conocimiento actual de la biodiversidad. Conabio Méx. 2008, 1, 283–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; Arguello-Astorga, G.R.; Ambriz-Granados, S.; Alpuche-Solís, A.G. First Report of Tomato golden mottle virus on Lycopersicon esculentum and Solanum rostratum in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2007, 11, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikov, A.S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Tesler, G.; Vyahhi, N.; Sirotkin, A.V.; Pham, S.; Dvorkin, M.; Pevzner, P.A.; Bankevich, A.; Nikolenko, S.I.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 5, 455–477. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Aligment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Albuquerque, L.C.; Rocha, W.B.; Nagata, T. A simple method for cloning the complete begomovirus genome using the bacteriophage 29 DNA polymerase. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 116, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellens, R.P.; Anne Edwards, E.; Leyland, N.R.; Bean, S.; Mullineaux, P.M. pGreen: A versatile and flexible binary Ti vector for agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 42, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, M.; Fischer, G.; Rosenzweig, C.; Parry, M.; Iglesias, A. Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Velásquez, A.C.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; He, S.Y. Plant–pathogen warfare under changing climate conditions. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, J.; Spackman, M.; Freeman, A.; TreBicki, P.; Griffiths, W.; Finlay, K.; Chakraborty, S. Climate change and diseases of food crops. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J. Plant Virus Metagenomics: Biodiversity and Ecology. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapat, R.; Marwal, A.; Gaur, R.K. Begomovirus associated with alternative host weeds: A critical appraisal. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2014, 2, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-García, J.A.; Hernández-Vizcarra, J.A.; Villaseñor, J.L.; Vega-Aviña, R.; Aguiar-Hernández, H.; Vega-López, I.F. Endemismo regional presente en la flora del municipio de Culiacán, Sinaloa, México. Acta Bot. Mex. 2017, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Pacheco, I.; Garzón Tiznado, J.A.; Brown, J.K.; Becerra-Flora, A.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. Detection and distribution of geminiviruses in Mexico and the Southern United States. Phytopathology 1996, 11, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Alpuche-Solís, A.G.; Monreal-Vargas, C.T.; Díaz-Gómez, O.; De La Torre-Almaraz, R. First report of tomato severe leaf curl virus in México. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, A.M.; Carnevali, G.; Brown, J.K.; Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.A.; Argüello-Astorga, G.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. Characterization of Rhynchosia yellow mosaic Yucatan virus, a new recombinant begomovirus associated with two fabaceous weeds in Yucatan, Mexico. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Reveles Torres, L.R.; Velásquez Valle, R.; Mauricio Castillo, J.A.; Salas Muñoz, S. Detection of mixed infections caused by begomovirus and curtovirus in chili pepper for drying plants in San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2012, 30, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gasperin-Bulbarela, J.; Hernández-Martínez, R.; Licea-Navarro, A.F.; Pino-Villar, C.; Carrillo-Tripp, J. First report of grapevine red blotch virus in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2018, 2, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Seah, Y.M.; Marr, C.; Varsani, A.; Kraberger, S.; Stainton, D.; Moriones, E.; Polston, J.E.; Duffy, S.; Breitbart, M. Vector-enabled metagenomic (VEM) surveys using whiteflies (Aleyrodidae) reveal novel begomovirus species in the new and old worlds. Viruses 2015, 7, 5553–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodelo-Urrego, M.; García-Arenal, F.; Pagá, I. The effect of ecosystem biodiversity on virus genetic diversity depends on virus species: A study of chiltepin-infecting begomoviruses in Mexico. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ascencio-Ibáñez, J.T.; Diaz-Plaza, R.; Méndez-Lozano, J.; Monsalve-Fonnegra, Z.I.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus in Yucatán, México. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Aguilar, J.J.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Camacho-Beltrán, E.; López-Luque, C.A.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Jiménez-Díaz, F.; Voloudakis, A.; Santos-Cervantes, M.E.; Méndez-Lozano, J. Identification of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus, Pepper huasteco yellow vein virus and Pepper golden mosaic virus associated with pepper diseases in northern Mexico. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Félix, M.L.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Camacho-Beltrán, E.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Meléndrez-Bojórquez, N.; Méndez-Lozano, J. A new isolate of Pepper huasteco yellow vein virus (PHYVV) breaks geminivirus tolerance in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) commercial lines. Acta Hortic. 2018, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudy, A.; Sufrin-Ringwald, T.; Dayan-Glick, C.; Guenoune-Gelbart, D.; Livneh, O.; Zaccai, M.; Lapidot, M. Watermelon chlorotic stunt and Squash leaf curl begomoviruses—New threats to cucurbit crops in the Middle East. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 58, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Idris, A.M.; Carnevali, G.; Brown, J.K.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.A. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic relationships of two new bipartite begomovirus infecting malvaceous plants in Yucatan, Mexico. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.R.; Albuquerque, L.C.; de Oliveira, C.L.; Cruz, A.R.R.; da Rocha, W.B.; Pereira, T.G.; Naito, F.Y.B.; De Dias, N.M.; Nagata, T.; Faria, J.C.; et al. Molecular and biological characterization of a new Brazilian begomovirus, euphorbia yellow mosaic virus (EuYMV), infecting Euphorbia heterophylla plants. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantú-Iris, M.; Pastor-Palacios, G.; Mauricio-Castillo, J.A.; Bañuelos-Hernández, B.; Avalos-Calleros, J.A.; Juárez-Reyes, A.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R. Analysis of a new begomovirus unveils a composite element conserved in the CP gene promoters of several Geminiviridae genera: Clues to comprehend the complex regulation of late genes. PLoS ONE 2019, 1, e0210485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ayala, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Cáceres, F.; Aragõn-Caballero, L.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E. Characterisation and genetic diversity of pepper leafroll virus, a new bipartite begomovirus infecting pepper, bean and tomato in Peru. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.C.; Manhani, G.G.; Alfenas, P.F.; Calegario, R.F.; Fontes, E.P.B.; Zerbini, F.M. Tomato yellow spot virus, a tomato-infecting begomovirus from Brazil with a closer relationship to viruses from Sida sp., forms pseudorecombinants with begomoviruses from tomato but not from Sida. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.L.; Tsai, W.S.; Green, S.K.; Khalid, S.; Ahmad, I.; Rezaian, M.A.; Smith, J. Molecular characterization of tomato and chili leaf curl begomoviruses from Pakistan. Plant Dis. 2007, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, C.M.; Melcher, U.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A. The expanding field of plant virus ecology: Historical foundations, knowledge gaps, and research directions. Virus Res. 2011, 159, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roossinck, M.J. Environmental viruses from biodiversity to ecology. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobbe, A.H.; Roossinck, M.J. Plant virus metagenomics: What we know and why we need to know more. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.W.S.; Alves, G.B.; Queiroz, A.P.; Nascimento, I.R.; Lima, M.F. Evaluation of Weeds as Virus Reservoirs in Watermelon Crops. Planta Daninha 2017, 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, J. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus: A serious threat to tomato plants world wide. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Carrasco, L.C.; Castillo-Urquiza, G.P.; Lima, A.T.M.; Xavier, C.A.D.; Vivas-Vivas, L.M.; Mizubuti, E.S.G.; Zerbini, F.M. Begomovirus diversity in tomato crops and weeds in Ecuador and the detection of a recombinant isolate of rhynchosia golden mosaic Yucatan virus infecting tomato. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, K.L.; McLane, H.; Thompson, J.R.; Fuchs, M. A novel grablovirus from non-cultivated grapevine (Vitis sp.) in North America. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, B.; Kumari, S.; Ahmed, S.; Fininsa, C.; Yusuf, A.; Abraham, A. Non-cultivated grass hosts of yellow dwarf viruses in Ethiopia and their epidemiological consequences on cultivated cereals. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 166, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, E.; Pietersen, G. Alternative hosts and seed transmissibility of soybean blotchy mosaic virus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Haider, M.; Tahir, M.; Briddon, R.; Amin, I. Ageratum enation virus—A begomovirus of weeds with the potential to infect crops. Viruses 2015, 7, 647–665. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.K.; Zerbini, F.M.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E.; Ramos-Sobrinho, R.; Silva, J.C.F.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Briddon, R.W.; Hernández-Zepeda, C.; Idris, A.; et al. Revision of begomovirus taxonomy based on pairwise sequence comparisons. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1593–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Ruan, M.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhou, G.Z.; Yao, Z.P.; Wang, R.Q.; Wan, H.J.; Ye, Q.J.; Li, Z.M. Assessment of the genetic diversity of tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 1, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kil, E.-J.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Byun, H.-S.; Park, J.; Seo, H.; Kim, C.-S.; Shim, J.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-K.; et al. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV-IL): A seed-transmissible geminivirus in tomatoes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriones, E.; Navas-Castillo, J. Review. Rapid evolution of the population of begomoviruses associated with the tomato yellow leaf curl disease after, invasion of a new ecological niche. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 6, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, R.; Nahkla, M.K.; Rojas, M.R.; Guzman, P.; Jaquez, J.; Maxwell, D.P.; Gilbertson, R.L. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus in the Dominican Republic: Characterization of an infectious clone, virus monitoring in whiteflies, and identification of reservoir hosts. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinones, M.; Fonseca, D.; Martinez, Y.; Accotto, G.P. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus infecting pepper plants in Cuba. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Conejo, Y.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Poghosyan, A.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, J.; Lebsky, V.; Holguin-Peña, J.; Medina-Hernandez, D.; Vega-Peña, S. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus co-infecting pepper with tomato chino La Paz virus in Baja California Sur, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Idris, A.M. Introduction of the exotic monopartite tomato yellow leaf curl virus into west coast Mexico. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamez-Jimenez, C.; Romero-Romero, J.L.; Santos-Cervantes, M.E.; Leyva-Lopez, N.E.; Mendez-Lozano, J. Tomatillo (Physalis ixocarpa) as a natural new host for tomato yellow leaf curl virus in Sinaloa, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, N.; Blanco-Meneses, M.; Hallwass, M.; Moriones, E.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus in tomato in Costa Rica. Plant Dis. 2013, 98, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.H.; Luo, Y.Q.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Z.K.; Yang, C.K. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus infecting vommon bean in China. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, I.D.; Kelly, A.; Banks, G.K.; Briddon, R.W.; Cenis, J.L.; Markham, P.G. Solanum nigrum: An indigenous weed reservoir for a tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus in southern Spain. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1998, 104, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Andrés, S.; Monci, F.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Moriones, E. Begomovirus genetic diversity in the native plant reservoir Solanum nigrum: Evidence for the presence of a new virus species of recombinant nature. Virology 2006, 350, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, E.J.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, S. Lamium amplexicaule (Lamiaceae): A weed reservoir for tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) in Korea. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashina, B.D.; Mabagala, R.B.; Mpunami, A.A. Reservoir weed hosts of tomato yellow leaf curl begomovirus from Tanzania. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2003, 35, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordá, C.; Font, I.; Martínez, P.; Juarez, M.; Ortega, A.; Lacasa, A. Current status and new natural hosts of tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) in Spain. Plant Dis. 2007, 85, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Díaz, L.; Zavaleta-Mejía, E.; Rojas-Martínez, R.I.; Alanís-Martínez, I.D.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.; Valadez-Moctezuma, E.; Grimaldo-Juárez, O. Detección de geminivirus asociados a la alstroemeria (Alstroemeria L.) en villa guerrero, estado de México. Interciencia 2009, 12, 903–908. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, J.L.; Roca de Doyle, M.M.; Nakhla, M.K.; Maxwell, D.P. First report and characterization of rhynchosia golden mosaic virus in Honduras. Plant Dis. 2007, 84, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.J.C.; Castillo-Urquiza, G.P.; Hora-Júnior, B.T.; Assunção, I.P.; Lima, G.S.A.; Pio-Ribeiro, G.; Mizubuti, E.S.G.; Zerbini, F.M. Species diversity, phylogeny and genetic variability of begomovirus populations infecting leguminous weeds in northeastern Brazil. Plant Pathol. 2012, 61, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Marr, C.; Varsani, A.; Kraberger, S.; Stainton, D.; Moriones, E.; Polston, J.E.; Breitbart, M. Begomovirus-associated satellite DNA diversity captured through vector-enabled metagenomic (VEM) surveys using whiteflies (Aleyrodidae). Viruses 2016, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondong, V.N.; Pita, J.S.; Rey, M.E.C.; De Kochko, A.; Beachy, R.N.; Fauquet, C.M. Evidence of synergism between African cassava mosaic virus and a new double-recombinant geminivirus infecting cassava in Cameroon. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pita, J.S.; Fondong, V.N.; Sangaré, A.; Kokora, R.N.N.; Fauquet, C.M. Genomic and biological diversity of the African cassava geminiviruses. Euphytica 2001, 120, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.G.; Ambrozevícius, L.P.; Ávila, A.C.; Bezerra, I.C.; Calegario, R.F.; Fernandes, J.J.; Lima, M.F.; De Mello, R.N.; Rocha, H.; Zerbini, F.M. Distribution and genetic diversity of tomato-infecting begomoviruses in Brazil. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pita, J.S.; Fondong, V.N.; Sangaré, A.; Otim-Nape, G.W.; Ogwal, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Recombination, pseudorecombination and synergism of geminiviruses are determinant keys to the epidemic of severe cassava mosaic disease in Uganda. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davino, S.; Napoli, C.; Dellacroce, C.; Miozzi, L.; Noris, E.; Davino, M.; Accotto, G.P. Two new natural begomovirus recombinants associated with the tomato yellow leaf curl disease co-exist with parental viruses in tomato epidemics in Italy. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J.; García-Arenal, F. Ecosystem simplification, biodiversity loss and plant virus emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 10, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.S.; El Siddig, M.A.; El Hussein, A.A.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Fiallo-Olivé, E. Complete genome sequence of datura leaf curl virus, a novel begomovirus infecting Datura innoxia in Sudan, related to begomoviruses causing tomato yellow leaf curl disease. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plant Family 1 | Sampling Region 2 Begomovirus PCR-Positive/Total Plants Collected | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | SO | SI | CN | CD | |
| Amaranthaceae | 4/5 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 5/6 | |
| Apiaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Asteraceae | 4/10 | 8/16 | 8/22 | 3/4 | 0/15 |
| Boraginaceae | 0/1 | 4/5 | |||
| Brassicaceae | 1/2 | 0/2 | 1/1 | ||
| Caesalpiniaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Capparaceae | 1/2 | ||||
| Chenopodiaceae | 4/4 | 6/10 | |||
| Convolvulaceae | 0/2 | 2/2 | 3/4 | 1/4 | |
| Cucurbitaceae | 0/1 | 2/6 | 1/3 | ||
| Euphorbiaceae | 2/3 | 5/15 | 0/2 | ||
| Fabaceae | 1/2 | 49/72 | 0/1 | ||
| Hydrophyllaceae | 1/1 | 0/1 | |||
| Malvaceae | 5/6 | 14/18 | 21/33 | 9/13 | 9/9 |
| Menispermaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Nyctaginaceae | 2/2 | 4/5 | 1/1 | ||
| Onagraceae | 1/2 | ||||
| Papaveraceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Pedaliaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Polygonaceae | 1/2 | 3/5 | |||
| Portulacaceae | 3/3 | 1/2 | |||
| Primulaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Rhamnaceae | 1/1 | 1/1 | |||
| Rubiaceae | 2/2 | ||||
| Sapindaceae | 1/1 | ||||
| Solanaceae | 1/2 | 11/14 | 18/22 | 0/2 | 14/14 |
| Sterculiaceae | 1/2 | ||||
| Verbenaceae | 1/2 | 2/2 | |||
| Vitaceae | 1/1 | 0/1 | |||
| Total positives | 17 | 60 | 122 | 24 | 29 |
| Library Name | Total Reads | Total Geminivirus-Related Reads | Number of Geminivirus-Related Contigs | Smallest/Largest Geminivirus-Related Contig 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baja California | 16,056,866 | 6156 | 92 | 78/2437 |
| Sonora | 30,440,802 | 23,546 | 195 | 78/2293 |
| Sinaloa | 215,007,456 | 4,685,423 | 15,465 | 78/2723 |
| Colima-Nayarit | 33,159,620 | 2,475,219 | 8368 | 78/2775 |
| Coahuila-Durango | 70,782,034 | 349,763 | 169 | 78/2858 |
| Total | 365,446,778 | 7,540,107 | 24,289 | 78/2858 |
| Host Adapted | Virus Acronym 2 | Plant Family of First Detection | Geminivirus-Signatures of DNA-A/DNA-B 1 per Region | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baja California | Sonora | Sinaloa | Colima-Nayarit | Coahuila-Durango | |||
| Crops | PHYVV | Solanaceae | ND 3 | 98.5/96.5 LN848858.1/LN848912.1 1462/2124 | 99.6/100 LN848873.1/KP890828.1 251/594 | 100/99.6 X70418.1/X70419.1 (583/1826) | 96.9/98.5 LN848872.1/LN848922.1 955/1742 |
| PepGMV | ND/98.4 ND/AY928515.1 ND/524 | ND | 98.1/95.9 U57457.1/AY928515.1 1115/2388 | 88.2/84.3 AY905553.1/LN848829.1 136/147 | 99.4/95.9 LN848772.1/LN848841.1 1120/1562 | ||
| PepLRV | ND | 88/ND KC769819.1/ND 458/ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| ChiLCV | ND | ND | 81.2/NA 4 JN555601.1/NA 559/NA | ND | ND | ||
| TYLCV | 98.4/NA JQ354991.1/NA 131/NA | 99.5/NA KU836749.1/NA 2540/NA | 99.5/NA FJ012359.1/NA 1247/NA | 99.7/NA EF523478.1/NA 1524/NA | 99.4/NA FJ012358.1/NA 2048/NA | ||
| ToChLPV | ND | 89.1/NA AY339618.1/NA 120/NA | ND | 81.9/NA HM459852.1/NA 337/NA | ND | ||
| ToSLCV | ND | 87.2/NA DQ347946.1/NA 359/NA | ND | 99.5/NA KC479066.1/NA 411/NA | ND | ||
| TPCTV | ND | ND | ND | 82.3/NA X84735.1/NA 385/NA | ND | ||
| ToYSV | ND | 84.2/ND DQ336350.1/ND 470/ND | 95.4/ND KJ742419.1/ND 155/ND | 84.9/ND KX348173.1/ND 192/ND | ND | ||
| PYMV | ND | ND | ND | 78.8/ND FR851299.1/ND 321/ND | ND | ||
| OYMMV | Malvaceae | ND/90.3 ND/GU972604.1 ND/2354 | ND | 93.6/96.4 GU990612.1/JX219471.1 174/226 | 98.9/94.9 GU990614.1/JX219471.1 1455/336 | ND/94.9 ND/JX219471.1 ND/236 | |
| CabLCV | Brassicaceae | ND | ND | 97.4/ND AJ228570.1/ND 119/ND | 84.2/82.8 MH359394.1/DQ178613.1 1645/157 | ND | |
| BCaMV | Fabaceae | ND | ND/95 ND/AF110190.1 ND/2576 | 97.2/96.7 AF110189.1/AF110190.1 2058/1296 | 92.3/88.9 AF110189.1/AF110190.1 353/135 | 97.9/82.9 AF110189.1/AF110190.1 1005/587 | |
| BYMMV | ND | 85.3/ND FJ944023.1/ND 677/ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| ViYMV | ND | ND | 86.6/86.7 KC430936.1/KC430937.1 758/369 | 89.6/86 KC430936.1/KC430937.1 242/115 | ND | ||
| WmCSV | Cucurbitaceae | ND | ND | ND | ND | 100/100 KY124280.1/KY124281.1 239/1025 | |
| SLCV | ND | 94.2/ND KM595165.1/ND 104/ND | ND | 80.6/83 KM595183.1/DQ285017.1 155/124 | 79.8/95.3 KM595165.1/M38182.1 188/1649 | ||
| SPLCV | Convolvulaceae | ND | ND | 92.4/NA KX611145.1/NA 1818/NA | 80/NA KJ013582.1/NA 261/NA | ND | |
| BCTV | Amaranthaceae | 99.8/NA JX487184.1/NA 508/NA | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Non-cultivated plants | SoMBoV | Solanaceae | ND | ND/84.7 ND/HM585436.1 ND/518 | ND | ND/82.3 ND/HM585436.1 ND/655 | ND |
| SiMSiV | Malvaceae | 96.3/ND DQ520944.1/ND 854/ND | 95.8/96.7 DQ520944.1/DQ356428.1 2581/1582 | 96.9/90.2 DQ520944.1/DQ356428.1 1003/2085 | 95.6/87.7 DQ520944.1/DQ356428.1 1584/245 | 94.2/98.9 DQ520944.1/DQ356428.1 572/289 | |
| SiGYSV | ND | 84.6/ND KX348185.1/ND 637/ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| MaBYMV | 96.9/ND KU058856.1/ND 1037/ND | ND | 97.2/84.9 KU058865.1/KU058860.1 403/153 | ND | 94.8/94.5 KU058853.1/KU058859.1 1822/1282 | ||
| RhGMV | Fabaceae | 95/90 EU339939.1/EU339937.1 1049/536 | 88.9/ND EU021216.1/ND 253/ND | 98.9/95.7 EU339939.1/EU339937.1 2086/675 | 92.2/85.4 EU339938.1/DQ356429.1 155/240 | 96.2/82.6 AF408199.1/EU339937.1 264/543 | |
| RhGMSV | ND | ND | 93.4/96.2 DQ406672.1/DQ406673.1 1754/1794 | 91.2/89.2 DQ406672.1/DQ406673.1 727/353 | ND | ||
| EuMV | Euphorbiaceae | ND | 86.8/ND JN368145.1/ND 678/ND | ND | 87.9/86.5 DQ318937.1/DQ520942.1 158/104 | ND/93.1 ND/HQ185235.1 ND/249 | |
| EuYMV | ND | ND | ND | 91.3/80.1 KY559516.1/KY559581.1 138/342 | ND | ||
| BleICV | Acanthaceae | ND | ND | ND/79 ND/JX827488.1 ND/783 | ND | ND | |
| Clon Code | Length (bp) | Accession No. | Virus Acronym 1 | Reference Genome | Complete Genome | Virus Gene 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP | V2 | Rep | TrAp | REn | C4 | ||||||||||||
| N 3 | n | a 4 | n | a | n | a | n | a | n | a | n | a | |||||
| LV15-Ng-04 | 2781 | MK643155 | TYLCV | EF523478.1 | 99.9 | 99.6 | 100 | 99.7 | 99.1 | 99.9 | 100 | 99.8 | 100 | 99.5 | 98.5 | 100 | 100 |
| LV15-Sa-03 | 2611 | MK636866 | SiMSiV | DQ520944.1 | 95.1 | 96.3 | 98.4 | NA 5 | NA | 94.9 | 95.8 | 96.5 | 93.7 | 95.6 | 93.2 | 94.8 | 98.4 |
| LV17-Rm-02 | 2605 | MK634355 | RhGMV | EU339939.1 | 98.6 | 98.8 | 100 | NA | NA | 98.5 | 98.9 | 98.5 | 97.1 | 98.9 | 97.7 | 99.2 | 97.7 |
| LV15-RM-02 | 2578 | MK618662 | RhGMSV | DQ406672.1 | 91.9 | 91 | 95.2 | NA | NA | 92.9 | 92.3 | 96.9 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 93.9 | 92 | 86.6 |
| Clon Code | Length (bp) | Accession No. | Virus Acronym 1 | Reference Genome | Complete Genome | MP 1 | NSP 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n 3 | n | a 4 | N | a | |||||
| LV15-Sa-02 | 2583 | MK643154 | SiMSiV | DQ356428.1 | 91.3 | 92.7 | 95.6 | 90.3 | 92.2 |
| LV17-Rm-06 | 2568 | MK634539 | RhGMV | DQ356429.1 | 91 | 94.8 | 99.3 | 91.7 | 91.6 |
| LV15-Rm-08 | 2525 | MK618663 | RhGMSV | DQ406673.1 | 85.9 | 90.4 | 98.3 | 83.3 | 86.7 |
| Sampling Area | Plant Family | Plant Species | Collection Year | Virus 1 Specific PCR-Positive Samples | Negative Samples | Total Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHYVV | TYLCV | SiMSiV | RhGMV/RhGMSV | ||||||
| BAJA CALIFORNIA | |||||||||
| Ensenada | Malvaceae | Malva parviflora | 2015 | ND 2 | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 |
| Solanaceae | Nicotiana glauca | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| San Quintin | Malvaceae | Malva parviflora | 2015 | ND | 3 | 1 | ND | 1 | 4 |
| SONORA | |||||||||
| Huatabampo | Malvaceae | Abutilon palmeri | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Abutilon trisulcatun | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | ||
| Anoda pedunculosa | 2015 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| Solanaceae | Datura stramonium | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Nicotiana glauca | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 1 | 2 | ||
| Nicotiana plumbanginifolia | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 2 | ||
| Solanum. spp | 2015 | 1 | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Solanum nigrescens | 2015 | ND | ND | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | ||
| Solanum. spp | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Solanum verbascifolium | 2015 | 1 | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 | ||
| Navojoa | Fabaceae | Meliotus indica | 2015 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Malvaceae | Malva parviflora | 2015 | ND | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
| Malvella leprosa | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | ||
| Obregón | Malvaceae | Abutilon palmeri | 2015 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 |
| Sida rombifolia | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Solanaceae | Nicotiana glauca | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Nicotina plumbanginifolia | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Río Colorado | Malvaceae | Malva parviflora | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 |
| SINALOA | |||||||||
| Agua caliente | Fabaceae | Rhynchosia minima | 2016 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| Concordia | Malvaceae | Anoda pentaschista | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 |
| Guasave | Fabaceae | Crotalaria juncea | 2016 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Lonchocarpus lanceolatus | 2012 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Melilotus indicus | 2015 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2016 | 1 | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Malvaceae | Abutilon palmeri | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Abutilon trisulcatun | 2014 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 2012 | 1 | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Herissantia crispa | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Kosteletzkya depressa | 2012 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Melochia piramydata | 2014 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Solanaceae | Datura reburra | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Datura stramonium | 2012 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2014 | 3 | 3 | ND | 3 | 1 | 4 | |||
| Nicotiana glauca | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Solanum americanum | 2012 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| Solanum nigrescens | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Mocorito | Malvaceae | Abutilon trisulcatun | 2012 | 1 | 1 | ND | ND | 1 | 2 |
| Sidastrum lodiegensis | 2012 | 1 | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Solanaceae | Datura discolor | 2012 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 2 | 2 | |
| Solanum tridynamum | 2012 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| Playa Ceuta | Fabaceae | Rhynchosia minima | 2016 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Rosario | Fabaceae | Macroptilium atropurpureum | 2016 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Rhynchosia precatoria | 2016 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Rhynchosia minima | 2016 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Senna uniflora | 2016 | 1 | ND | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 2014 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Malvaceae | Abutilon trisulcatun | 2014 | ND | 1 | ND | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Herissantia crispa | 2014 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Melochia piramydata | 2014 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | ||
| Sida acuta | 2014 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Solanaceae | Physalis acutifolia | 2014 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | |
| Sinaloa | Datura inoxia | 2012 | ND | 1 | ND | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Solanum tridynamum | 2012 | ND | 2 | ND | ND | 1 | 3 | ||
| COLIMA/NAYARIT | |||||||||
| Tecomán | Malvaceae | Herissantia crispa | 2014 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| Malvastrum coromandelianum | 2014 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Sida acuta | 2014 | ND | ND | + | ND | ||||
| COAHUILA/DURANGO | |||||||||
| La Goma | Malvaceae | Sida acuta | 2015 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1 |
| Sida rombifolia | 2015 | ND | 2 | 1 | ND | 0 | 2 | ||
| Solanaceae | Datura stramonium | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Poanas | Solanum elaeagnifolium | 2016 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 2 | 2 | |
| Solanum rostrarum | 2016 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Tlahualilo | Malvaceae | Sida rombifolia | 2015 | ND | ND | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Solanaceae | Solanum elaeagnifolium | 2015 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Torreón | Malvaceae | Sphaeralcea angustifolia | 2015 | ND | 2 | ND | ND | 1 | 3 |
| Solanaceae | Datura stramonium | 2015 | ND | 1 | 1 | ND | 0 | 1 | |
| Nicotiana glauca | 2015 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ND | 1 | 3 | ||
| Solanum elaeagnifolium | 2015 | ND | 3 | 3 | ND | 0 | 3 | ||
| Total | 46 | 89 | 63 | 62 | 30 | 126 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Morales-Aguilar, J.J.; Domínguez-Duran, G.; Torres-Devora, G.; Camacho-Beltrán, E.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Voloudakis, A.E.; Bejarano, E.R.; Méndez-Lozano, J. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Differential Begomovirus Species Diversity in Non-Cultivated Plants in Northern-Pacific Mexico. Viruses 2019, 11, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070594
Rodríguez-Negrete EA, Morales-Aguilar JJ, Domínguez-Duran G, Torres-Devora G, Camacho-Beltrán E, Leyva-López NE, Voloudakis AE, Bejarano ER, Méndez-Lozano J. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Differential Begomovirus Species Diversity in Non-Cultivated Plants in Northern-Pacific Mexico. Viruses. 2019; 11(7):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070594
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Negrete, Edgar Antonio, Juan José Morales-Aguilar, Gustavo Domínguez-Duran, Gadiela Torres-Devora, Erika Camacho-Beltrán, Norma Elena Leyva-López, Andreas E. Voloudakis, Eduardo R. Bejarano, and Jesús Méndez-Lozano. 2019. "High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Differential Begomovirus Species Diversity in Non-Cultivated Plants in Northern-Pacific Mexico" Viruses 11, no. 7: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070594
APA StyleRodríguez-Negrete, E. A., Morales-Aguilar, J. J., Domínguez-Duran, G., Torres-Devora, G., Camacho-Beltrán, E., Leyva-López, N. E., Voloudakis, A. E., Bejarano, E. R., & Méndez-Lozano, J. (2019). High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Differential Begomovirus Species Diversity in Non-Cultivated Plants in Northern-Pacific Mexico. Viruses, 11(7), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070594