Flow Virometry Quantification of Host Proteins on the Surface of HIV-1 Pseudovirus Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Virus Production
2.2. Cellular Flow Cytometry
2.3. Flow Virometry
2.4. Virion Capture Assay
2.5. p24 ELISA
2.6. Electron Microscopy
3. Results
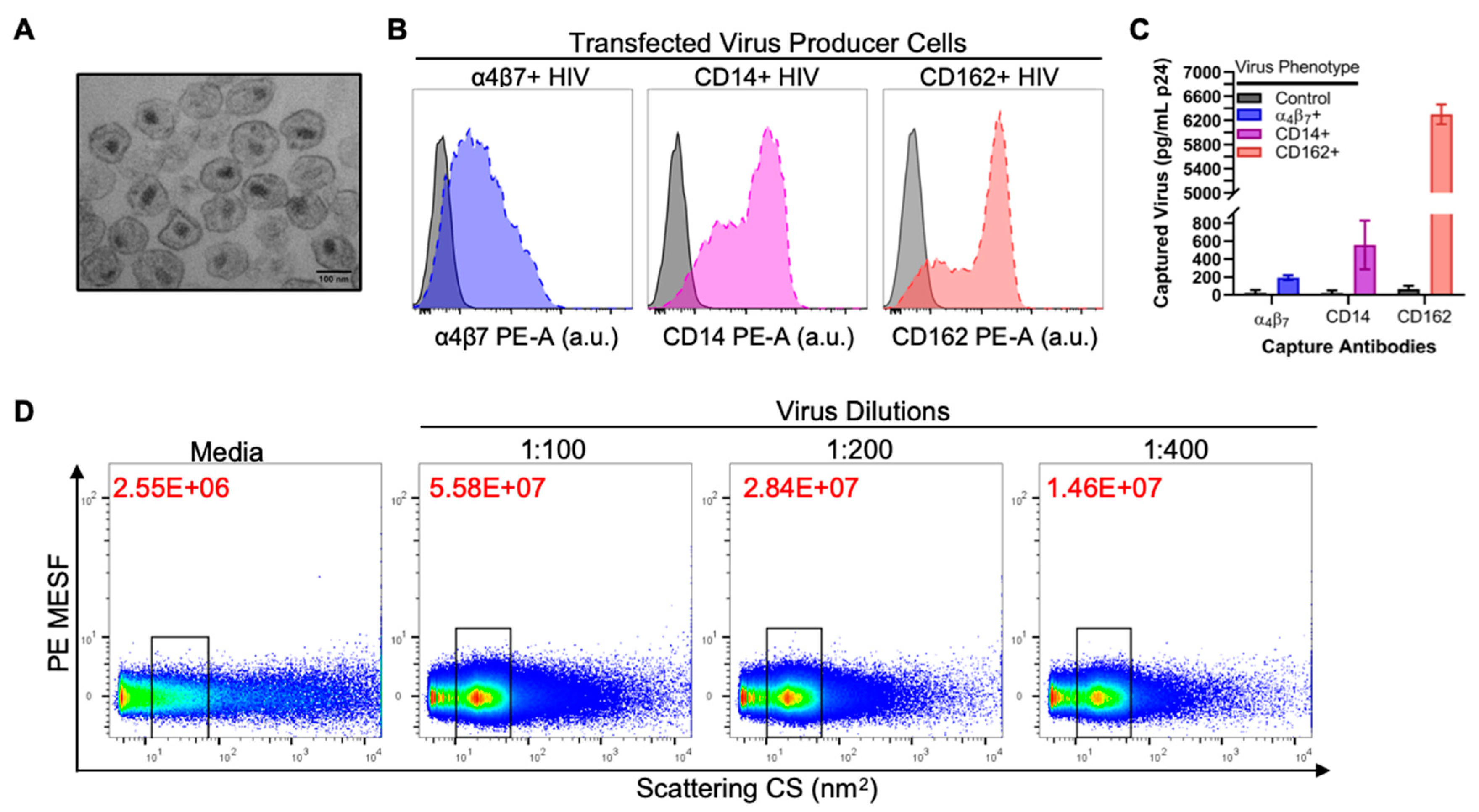
3.1. Validation of Virus Stocks for Flow Virometry
3.2. Flow Virometry Data Calibration
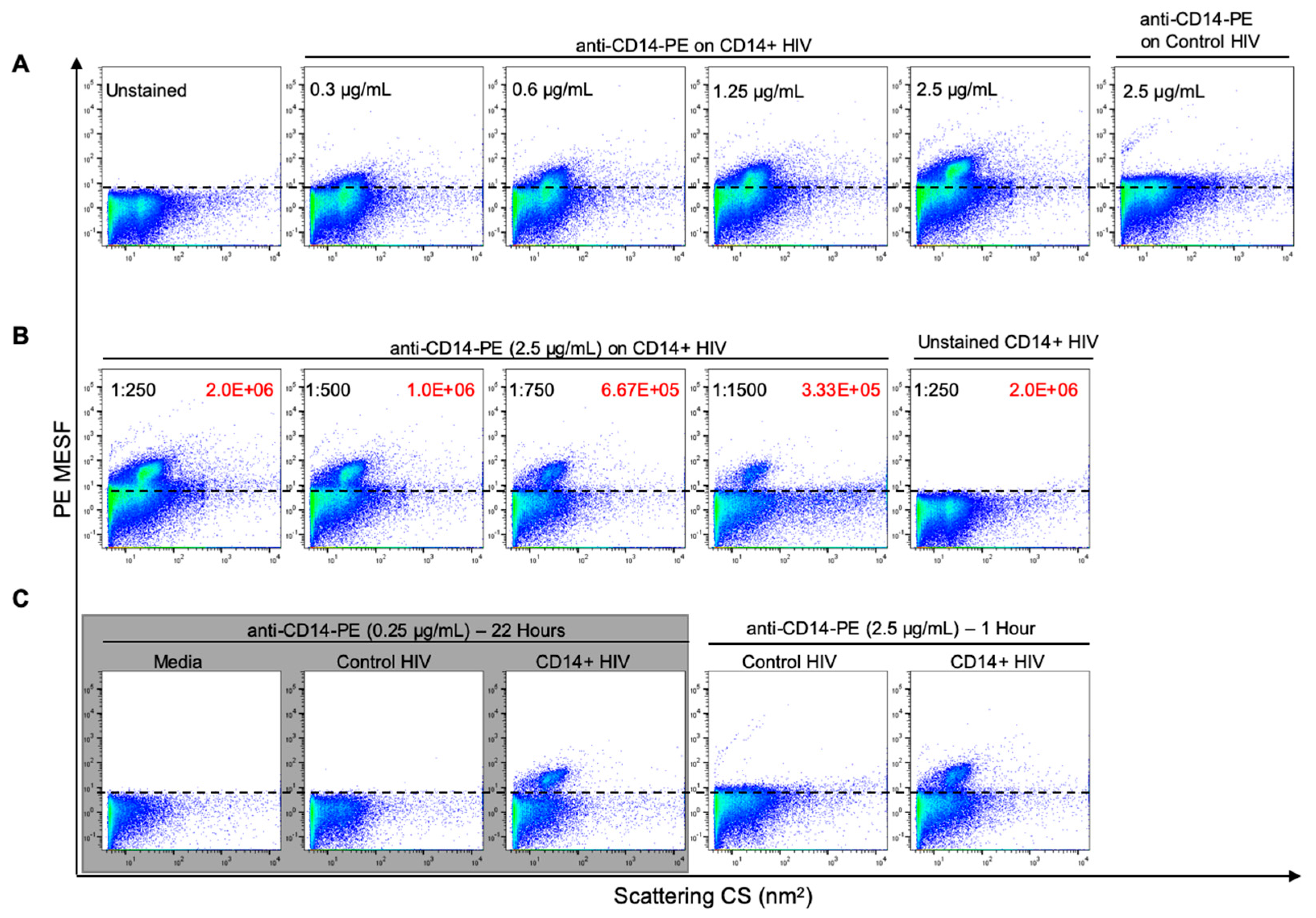
3.3. Optimization of Antibody Labeling and Staining Parameters for Flow Virometry
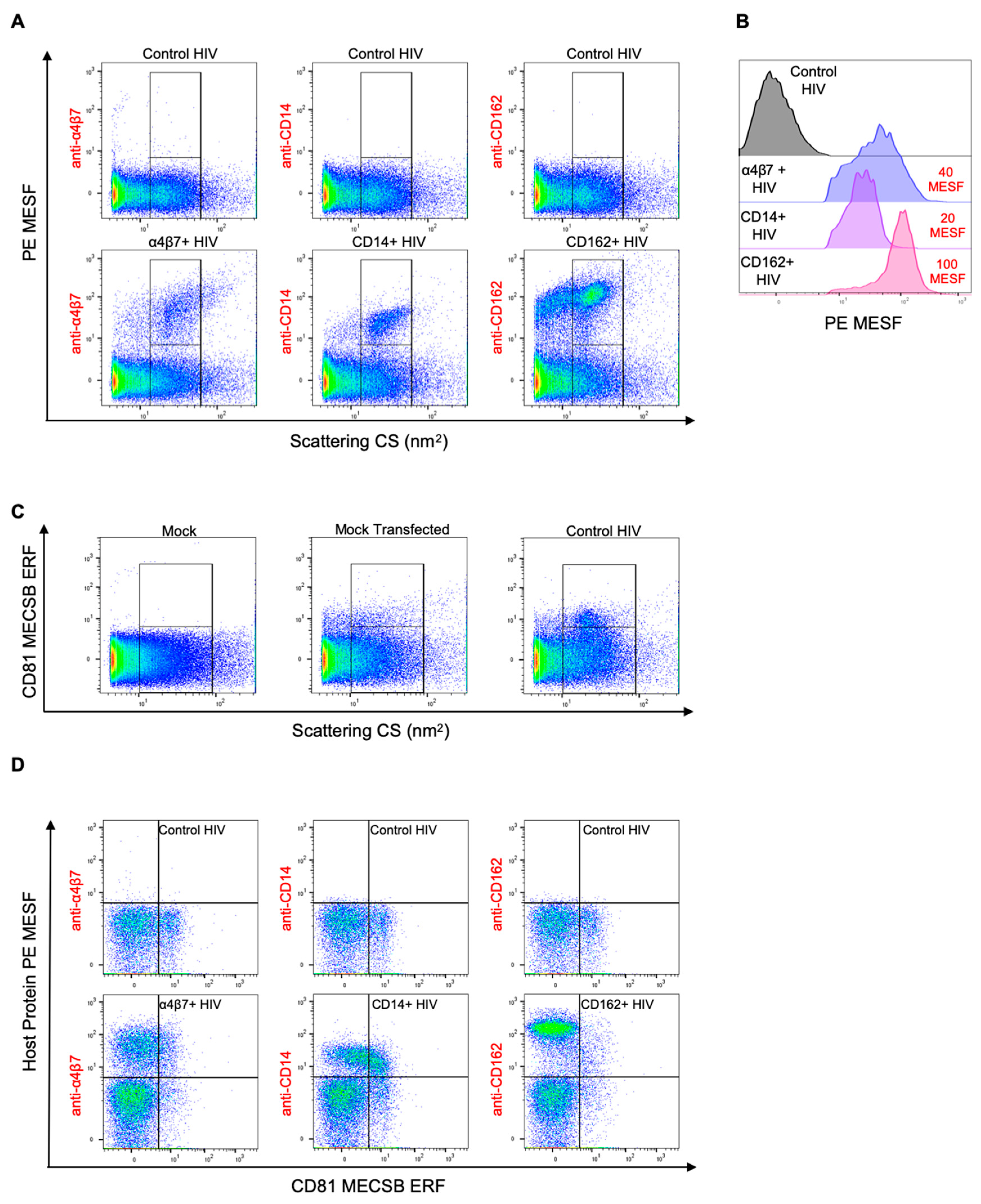
3.4. Double Labeling of Cellular Antigens on HIV-1 Pseudoviruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—2020 Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Guzzo, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Kwon, A.L.; Uddin, F.; Wells, A.I.; Schmeisser, H.; Cimbro, R.; Huang, J.; Doria-Rose, N.; et al. Structural Constraints at the Trimer Apex Stabilize the HIV-1 Envelope in a Closed, Antibody-Protected Conformation. mBio 2018, 9, e00955-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardetzky, T. HIV: Conformational camouflage. Nature 2002, 420, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejchal, R.; Wilson, I.A. Structure-based vaccine design in HIV: Blind men and the elephant? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3744–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Doyle, M.L.; Casper, D.J.; Cicala, C.; Leavitt, S.A.; Majeed, S.; Steenbeke, T.D.; Venturi, M.; Chaiken, I.; Fung, M.; et al. HIV-1 evades antibody-mediated neutralization through conformational masking of receptor-binding sites. Nature 2002, 420, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.M.; Geller, R.; Garijo, R.; López-Aldeguer, J.; Sanjuán, R. Extremely High Mutation Rate of HIV-1 in Vivo. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.J.; Fortin, J.-F.; Cantin, R. The acquisition of host-encoded proteins by nascent HIV-1. Immunol. Today 1998, 19, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantin, R.; Methot, S.; Tremblay, M.J. Plunder and Stowaways: Incorporation of Cellular Proteins by Enveloped Viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6577–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifuddin, M. Role of virion-associated glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked proteins CD55 and CD59 in complement resistance of cell line-derived and primary isolates of HIV-1. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, C.D.; Sodroski, J.G. Contribution of virion ICAM-1 to human immunodeficiency virus infectivity and sensitivity to neutralization. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4847–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantin, R.; Fortin, J.-F.; Lamontagne, G.; Tremblay, M. The presence of host-derived HLA-DR1 on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 increases viral infectivity. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.-F.; Cantin, R.; Bergeron, M.G.; Tremblay, M.J. Interaction between Virion-Bound Host Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 and the High-Affinity State of Lymphocyte Function-Associated Antigen-1 on Target Cells Renders R5 and X4 Isolates of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 More Refractory to Neutralization. Virology 2000, 268, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnie, J.; Guzzo, C. The Incorporation of Host Proteins into the External HIV-1 Envelope. Viruses 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertova, E.; Chertov, O.; Coren, L.V.; Roser, J.D.; Trubey, C.M.; Bess, J.W.; Sowder, R.C.; Barsov, E.; Hood, B.L.; Fisher, R.J. Proteomic and biochemical analysis of purified human immunodeficiency virus type 1 produced from infected monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9039–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, I.; Stoiber, H.; Godar, S.; Stockinger, H.; Steindl, F.; Katinger, H.W.D.; Dierich, M.P. Acquisition of host cell-surface-derived molecules by HIV-1. AIDS 1996, 10, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerloo, T.; Sheikh, M.A.; Bloem, A.C.; de Ronde, A.; Schutten, M.; van Els, C.A.C.; Roholl, P.J.M.; Joling, P.; Goudsmit, J.; Schuurman, H.-J. Host cell membrane proteins on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 after in vitro infection of H9 cells and blood mononuclear cells. An immuno-electron microscopic study. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxie, J.A.; Fitzharris, T.P.; Youngbar, P.R.; Matthews, D.M.; Rackowski, J.L.; Radka, S.F. Nonrandom association of cellular antigens with HTLV-III virions. Hum. Immunol. 1987, 18, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, C.; Ichikawa, D.; Park, C.; Phillips, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Kwon, A.; Miao, H.; Lu, J.; Rehm, C.; et al. Virion incorporation of integrin α4β7 facilitates HIV-1 infection and intestinal homing. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaam7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Carmona, N.; Ono, A. Virion-incorporated PSGL-1 and CD43 inhibit both cell-free infection and transinfection of HIV-1 by preventing virus–cell binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8055–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; He, S.; Waheed, A.A.; Dabbagh, D.; Zhou, Z.; Trinité, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; et al. PSGL-1 restricts HIV-1 infectivity by blocking virus particle attachment to target cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9537–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Dabbagh, D.; Fu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; et al. Proteomic profiling of HIV-1 infection of human CD4+ T cells identifies PSGL-1 as an HIV restriction factor. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, L.O.; Bess, J.W.; Sowder, R.C.; Benveniste, R.E.; Mann, D.L.; Chermann, J.-C.; Henderson, L.E. Cellular proteins bound to immunodeficiency viruses: Implications for pathogenesis and vaccines. Science 1992, 258, 1935–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.A.; Reimann, K.A.; Mayne, A.E.; Takahashi, Y.; Stephenson, S.T.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Price, A.A.; Little, D.M.; et al. Blocking of α4β7 Gut-Homing Integrin during Acute Infection Leads to Decreased Plasma and Gastrointestinal Tissue Viral Loads in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrareddy, S.N.; Kallam, B.; Arthos, J.; Cicala, C.; Nawaz, F.; Hiatt, J.; Kersh, E.N.; McNicholl, J.M.; Hanson, D.; Reimann, K.A.; et al. Targeting α4β7 integrin reduces mucosal transmission of SIV and protects GALT from infection. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrareddy, S.N.; Arthos, J.; Cicala, C.; Villinger, F.; Ortiz, K.T.; Little, D.; Sidell, N.; Kane, M.A.; Yu, J.; Jones, J.W.; et al. Sustained virologic control in SIV+ macaques after antiretroviral and α4β7 antibody therapy. Science 2016, 354, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzzan, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Rosenstein, A.K.; Tomescu, C.; SahBandar, I.N.; Ko, H.M.; Leyre, L.; Chokola, A.; Kaplan-Lewis, E.; Rodriguez, G.; et al. Anti-α4β7 therapy targets lymphoid aggregates in the gastrointestinal tract of HIV-1–infected individuals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orentas, R.J.; Hildreth, J.E.K. Association of Host Cell Surface Adhesion Receptors and Other Membrane Proteins with HIV and SIV. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1993, 9, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerloo, T.; Parmentier, H.K.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Goudsmit, J.; Schuurman, H.-J. Modulation of cell surface molecules during HIV-1 infection of H9 cells. An immunoelectron microscopic study. AIDS 1992, 6, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, M.; Kiyotaki, M.; King, N.W.; Lord, C.I.; Letvin, N.L. Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Induces Expression of Class II Major Histocompatibility Complex Structures on Infected Target Cells In Vitro. J Virol. 1987, 61, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.D.; Neumann, A.U.; Perelson, A.S.; Chen, W.; Leonard, J.M.; Markowitz, M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 1995, 373, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashov, V.V.; Goudsmit, J. HIV heterogeneity and disease progression in AIDS: A model of continuous virus adaptation. AIDS 1998, 12, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Poss, M.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Gosink, J.J.; Learn, G.H.; de Vange Panteleeff, D.; Martin, H.L.; Bwayo, J.; Kreiss, J.K.; Overbaugh, J. Evolution of Envelope Sequences from the Genital Tract and Peripheral Blood of Women Infected with Clade A Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8240–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Ghosh, S.K.; Taylor, M.E.; Johnson, V.A.; Emini, E.A.; Deutsch, P.; Lifson, J.D.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Nowak, M.A.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 1995, 373, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Leroux, C.; Patterson, B.K.; Kingsley, L.; Rinaldo, C.; Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Kulka, K.; Buchanan, W.; McKeon, B.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Shedding Pattern in Semen Correlates with the Compartmentalization of Viral Quasi Species between Blood and Semen. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, R.; Tremblay, M. Homologous interference resulting from the presence of defective particles of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamichi, H.; Smith, M.; Adelsberger, J.W.; Izumi, T.; Scrimieri, F.; Sherman, B.T.; Rehm, C.A.; Imamichi, T.; Pau, A.; Catalfamo, M.; et al. Defective HIV-1 proviruses produce viral proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, D.; Plaeger, S.F.; Dieffenbach, C.W. Defective Virus Drives Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection, Persistence, and Pathogenesis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourinbaiar, A.S. The ratio of defective HIV-1 particles to replication-competent infectious virions. Acta Virol. 1994, 38, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, T.K.; Klinkner, A.M.; Ventre, J.; Bugelski, P.J. Morphometric analysis of envelope glycoprotein gp120 distribution on HIV-1 virions. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 1993, 41, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippé, R. Flow virometry: A powerful tool to functionally characterize viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01765-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakelyan, A.; Fitzgerald, W.; Margolis, L.; Grivel, J.-C. Nanoparticle-based flow virometry for the analysis of individual virions. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3716–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.A.; Renner, T.M.; Fritzsche, A.K.; Burger, D.; Langlois, M.-A. Single-Particle Discrimination of Retroviruses from Extracellular Vesicles by Nanoscale Flow Cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Kastresana, A.; Telford, B.; Musich, T.A.; McKinnon, K.; Clayborne, C.; Braig, Z.; Rosner, A.; Demberg, T.; Watson, D.C.; Karpova, T.S. Labeling extracellular vesicles for nanoscale flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loret, S.; Bilali, N.E.; Lippé, R. Analysis of herpes simplex virus type I nuclear particles by flow cytometry. Cytom. A 2012, 81A, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilali, N.E.; Duron, J.; Gingras, D.; Lippé, R. Quantitative Evaluation of Protein Heterogeneity within Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Particles. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.A.; Kearney, B.J.; Olschner, S.P.; Williams, P.L.; Robinson, C.G.; Heinrich, M.L.; Zovanyi, A.M.; Ingram, M.F.; Norwood, D.A.; Schoepp, R.J. Evaluation of ViroCyt® Virus Counter for Rapid Filovirus Quantitation. Viruses 2015, 7, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, J.Y.B.; Langlois, T.; Andreani, J.; Sorraing, J.-M.; Raoult, D.; Camoin, L.; La Scola, B. Flow Cytometry Sorting to Separate Viable Giant Viruses from Amoeba Co-culture Supernatants. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Sevvana, M.; Benamar, S.; Pinto, F.D.; Bitam, I.; Colson, P.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.G.; Raoult, D.; et al. Pacmanvirus, a New Giant Icosahedral Virus at the Crossroads between Asfarviridae and Faustoviruses. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.A.; Fritzsche, A.K.; Renner, T.M.; Burger, D.; van der Pol, E.; Lannigan, J.A.; Brittain, G.C.; Welsh, J.A.; Jones, J.C.; Langlois, M.-A. Engineered Retroviruses as Fluorescent Biological Reference Particles for Small Particle Flow Cytometry. bioRxiv 2019, 614461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, M.M.; Tilton, J.C. High sensitivity detection and sorting of infectious human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) particles by flow virometry. Virology 2017, 505, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, G.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Martinez, E.; Tang, V.A.; Renner, T.M.; Langlois, M.-A.; Gulnik, S. A Novel Semiconductor-Based Flow Cytometer with Enhanced Light-Scatter Sensitivity for the Analysis of Biological Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musich, T.; Jones, J.C.; Keele, B.F.; Jenkins, L.M.M.; Demberg, T.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Robert-Guroff, M. Flow virometric sorting and analysis of HIV quasispecies from plasma. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e90626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakelyan, A.; Petersen, J.D.; Blazkova, J.; Margolis, L. Macrophage-derived HIV-1 carries bioactive TGF-beta. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staropoli, I.; Dufloo, J.; Ducher, A.; Commere, P.-H.; Sartori-Rupp, A.; Novault, S.; Bruel, T.; Lorin, V.; Mouquet, H.; Schwartz, O.; et al. Flow Cytometry Analysis of HIV-1 Env Conformations at the Surface of Infected Cells and Virions: Role of Nef, CD4, and SERINC5. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zicari, S.; Arakelyan, A.; Fitzgerald, W.; Zaitseva, E.; Chernomordik, L.V.; Margolis, L.; Grivel, J.-C. Evaluation of the maturation of individual Dengue virions with flow virometry. Virology 2016, 488, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowski, M.; Dabundo, J.; Liu, Q.; Nicola, A.V.; Aguilar, H.C. Nipah Virion Entry Kinetics, Composition, and Conformational Changes Determined by Enzymatic Virus-Like Particles and New Flow Virometry Tools. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 14197–14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasak, J.; Hoang, V.M.; Christanti, S.; Peluso, R.; Li, F.; Culp, T.D. Use of flow cytometry for characterization of human cytomegalovirus vaccine particles. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Jones, J.C.; Tang, V.A. Fluorescence and Light Scatter Calibration Allow Comparisons of Small Particle Data in Standard Units across Different Flow Cytometry Platforms and Detector Settings. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornilov, R.; Puhka, M.; Mannerström, B.; Hiidenmaa, H.; Peltoniemi, H.; Siljander, P.; Seppänen-Kaijansinkko, R.; Kaur, S. Efficient ultrafiltration-based protocol to deplete extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarovits, A.I.; Moscicki, R.A.; Kurnick, J.T.; Camerini, D.; Baird, L.G.; Erikson, M.; Colvin, R.B. Lymphocyte activation antigens. I. A monoclonal antibody, anti-Act I, defines a new late lymphocyte activation antigen. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, J.A.; Jones, J.C. Small Particle Fluorescence and Light Scatter Calibration Using FCMPASS Software. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2020, 94, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Pol, E.V.D.; Arkesteijn, G.J.A.; Bremer, M.; Brisson, A.; Coumans, F.; Dignat-George, F.; Duggan, E.; Ghiran, I.; Giebel, B.; et al. MIFlowCyt-EV: A framework for standardized reporting of extracellular vesicle flow cytometry experiments. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1713526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzo, C.; Fox, J.; Lin, Y.; Miao, H.; Cimbro, R.; Volkman, B.F.; Fauci, A.S.; Lusso, P. The CD8-Derived Chemokine XCL1/Lymphotactin Is a Conformation-Dependent, Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of HIV-1. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Decker, J.M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Arani, R.B.; Kilby, J.M.; Saag, M.S.; Wu, X.; Shaw, G.M.; Kappes, J.C. Emergence of Resistant Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 in Patients Receiving Fusion Inhibitor (T-20) Monotherapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawn, S.D.; Pisell, T.L.; Hirsch, C.S.; Wu, M.; Butera, S.T.; Toossi, Z. Anatomically Compartmentalized Human Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in HLA-DR+ Cells and CD14+ Macrophages at the Site of Pleural Tuberculosis Coinfection. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisell, T.L.; Hoffman, I.F.; Jere, C.S.; Ballard, S.B.; Molyneux, M.E.; Butera, S.T.; Lawn, S.D. Immune activation and induction of HIV-1 replication within CD14 macrophages during acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria coinfection. AIDS 2002, 16, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Davis, K.A.; Abrams, B.; Iyer, S.B.; Hoffman, R.A.; Bishop, J.E. Determination of CD4 antigen density on cells: Role of antibody valency, avidity, clones, and conjugation. Cytometry 1998, 33, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, F.F.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Sennikov, S.V. Optimized flow cytometry protocol for analysis of surface expression of interleukin-1 receptor types I and II. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, K.K.; Joe, E.T.; Iyer, S.B. Performance evaluation of quantiBRITE phycoerythrin beads. Cytometry 2001, 45, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratama, J.W.; D’hautcourt, J.-L.; Mandy, F.; Rothe, G.; Barnett, D.; Janossy, G.; Papa, S.; Schmitz, G.; Lenkei, R.; The European Working Group on Clinical Cell Analysis. Flow cytometric quantitation of immunofluorescence intensity: Problems and perspectives. Cytometry 1998, 33, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becton, Dickinson and Company. BD QuantibriteTM Beads PE Fluorescence Quantitation Kit Data Sheet. 2014. Available online: https://www.bdbiosciences.com/ds/is/tds/23-3337.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Welsh, J.A.; Horak, P.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Ford, V.J.; Jones, J.C.; Smith, D.; Holloway, J.A.; Englyst, N.A. FCMPASS Software Aids Extracellular Vesicle Light Scatter Standardization. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gaigalas, A.K.; Abbasi, F.; Marti, G.E.; Vogt, R.F.; Schwartz, A. Quantitating Fluorescence Intensity from Fluorophores: Practical Use of MESF Values. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2002, 107, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.; Wang, L.; Early, E.; Gaigalas, A.; Zhang, Y.; Marti, G.E.; Vogt, R.F. Quantitating Fluorescence Intensity from Fluorophore: The Definition of MESF Assignment. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2002, 107, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-S.; Won, J.-H.; Lim, G.J.; Han, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, K.-O.; Bae, Y.-K. A novel population of extracellular vesicles smaller than exosomes promotes cell proliferation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escola, J.-M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Stoorvogel, W.; Griffith, J.M.; Yoshie, O.; Geuze, H.J. Selective Enrichment of Tetraspan Proteins on the Internal Vesicles of Multivesicular Endosomes and on Exosomes Secreted by Human B-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20121–20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Szabó, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzás, E.I.; Lötvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Cabañas, C.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lim, K. Stability of Retroviral Vectors against Ultracentrifugation Is Determined by the Viral Internal Core and Envelope Proteins Used for Pseudotyping. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Hua, R.; Wei, M.; Li, C.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C. An optimized method for high-titer lentivirus preparations without ultracentrifugation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.C.; Friedmann, T.; Driever, W.; Burrascano, M.; Yee, J.K. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: Concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8033–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.A.; Renner, T.M.; Varette, O.; Le Boeuf, F.; Wang, J.; Diallo, J.-S.; Bell, J.C.; Langlois, M.-A. Single-particle characterization of oncolytic vaccinia virus by flow virometry. Vaccine 2016, 34, 5082–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, A.; Ringe, R.; Derking, R.; Cupo, A.; Julien, J.-P.; Burton, D.R.; Ward, A.B.; Wilson, I.A.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; et al. Differential binding of neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies to native-like soluble HIV-1 Env trimers, uncleaved Env proteins, and monomeric subunits. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.D.; Azadnia, P.; de Val, N.; Vora, N.; Honda, A.; Giang, E.; Saye-Francisco, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, X.; Mann, C.J.; et al. Differential Antibody Responses to Conserved HIV-1 Neutralizing Epitopes in the Context of Multivalent Scaffolds and Native-Like gp140 Trimers. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyster, J.G.; Shotton, D.M.; Williams, A.F. The dimensions of the T lymphocyte glycoprotein leukosialin and identification of linear protein epitopes that can be modified by glycosylation. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEver, R.P.; Moore, K.L.; Cummings, R.D. Leukocyte trafficking mediated by selectin-carbohydrate interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11025–11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, C.; Sattentau, Q.J. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Assembly, Budding, and Cell-Cell Spread in T Cells Take Place in Tetraspanin-Enriched Plasma Membrane Domains. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7873–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.G.; Booth, A.; Gould, S.J.; Hildreth, J.E.K. Evidence That HIV Budding in Primary Macrophages Occurs through the Exosome Release Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52347–52354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Hildreth, J.E.K. Evidence for Budding of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Selectively from Glycolipid-Enriched Membrane Lipid Rafts. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burnie, J.; Tang, V.A.; Welsh, J.A.; Persaud, A.T.; Thaya, L.; Jones, J.C.; Guzzo, C. Flow Virometry Quantification of Host Proteins on the Surface of HIV-1 Pseudovirus Particles. Viruses 2020, 12, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111296
Burnie J, Tang VA, Welsh JA, Persaud AT, Thaya L, Jones JC, Guzzo C. Flow Virometry Quantification of Host Proteins on the Surface of HIV-1 Pseudovirus Particles. Viruses. 2020; 12(11):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111296
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurnie, Jonathan, Vera A. Tang, Joshua A. Welsh, Arvin T. Persaud, Laxshaginee Thaya, Jennifer C. Jones, and Christina Guzzo. 2020. "Flow Virometry Quantification of Host Proteins on the Surface of HIV-1 Pseudovirus Particles" Viruses 12, no. 11: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111296
APA StyleBurnie, J., Tang, V. A., Welsh, J. A., Persaud, A. T., Thaya, L., Jones, J. C., & Guzzo, C. (2020). Flow Virometry Quantification of Host Proteins on the Surface of HIV-1 Pseudovirus Particles. Viruses, 12(11), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111296








