Maize AKINβγ Proteins Interact with P8 of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Inhibit Viral Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Plant Growth and Virus Inoculation
2.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
2.4. Confocal Microscopy
2.5. BMV-Induced Target Gene Silencing Coupled with RBSDV Inoculation in Maize
2.6. Maize Protoplasts Preparation and Transformation
2.7. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis of Gene Expression
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Analyses of Nonstructural Soluble Carbohydrates and Starch
3. Results
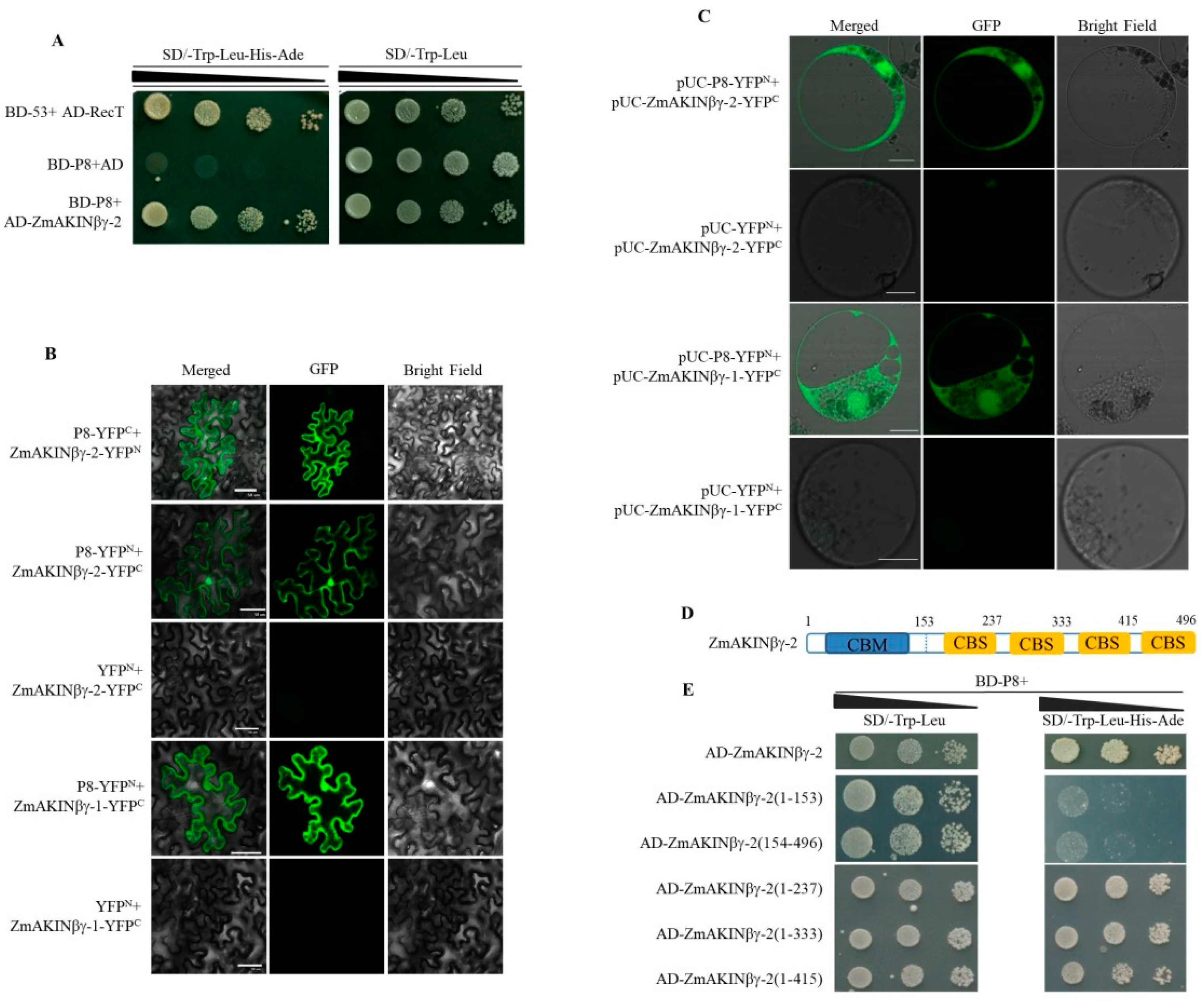
3.1. RBSDV P8 Interacts with ZmAKINβγs
3.2. RBSDV Infection Regulated the Expression of ZmAKINβγ Genes
3.3. The Subcellular Localization of ZmAKINβγ Proteins
3.4. Silencing of ZmAKINβγs Affects Primary Carbohydrate Metabolism of Maize
3.5. Knockdown of ZmAKINβγs Expressions Facilitated RBSDV Accumulation in Maize
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RBSDV | Rice black streaked dwarf virus |
| AKINβγ | βγ subunit of Arabidopsis SNF1 kinase homolog |
| BMV | Brome mosaic virus |
| SCMVMCMV | sugarcane mosaic virusmaize chlorotic mottle virus |
| Sus | sucrose synthase |
| SPS | sucrose-phosphate synthase |
| AGPaseLS | ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit |
| SSIIIb-2 | starch synthase IIIb-2 |
| SSIV | starch synthase IV |
| Phos | phosphoglucomutase |
| SBEIII | starch branching enzyme III |
| GFP | green fluorescence protein |
| YFP | yellow fluorescence protein |
References
- Zuo, W.; Chao, Q.; Zhang, N.; Ye, J.; Tan, G.; Li, B.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Fengler, K.A.; et al. A maize wall-associated kinase confers quantitative resistance to head smut. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, S.; Liu, B.; Tao, Y.; Ai, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M. A helitron-induced RabGDIα variant causes quantitative recessive resistance to maize rough dwarf disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achon, M.A.; Serrano, L.; Sabate, J.; Porta, C. Understanding the epidemiological factors that intensify the incidence of maize rough dwarf disease in Spain. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 166, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Yu, J.; Feng, J.; Han, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Identification of rice black-streaked dwarf fijivirus in maize with rough dwarf disease in China. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Chen, J.P.; Lei, J.L.; Adams, M.J. Sequence analysis shows that a dwarfing disease on rice, wheat and maize in China is caused by rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Xu, F.F.; Zheng, F.Q.; Li, X.D.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, C.Q. Molecular characterization of segments S7 to S10 of a southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus isolate from maize in northern China. Virol. Sin. 2011, 26, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, A. Studies on insect transmission of rice virus diseases in Japan. Bull. Nat. Inst. Agric. Sci. Ser. C 1962, 14, 1–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Yoshimura, S. Epidemiological studies on the rice black-streaked dwarf virus in Kanto-Tosan district, Japan. Konosu Cent. Agric. Exp. Stn. J. 1973, 17, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Gerola, F.M.; Bassi, M. An electron microscopy study of leaf vein tumours from maize plants experimentally infected with Maize rough dwarf virus. Caryol. Firenze 2014, 19, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, L. A phloem-limited fijivirus induces the formation of neoplastic phloem tissues that house virus multiplication in the host plant. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Chen, J.P.; Adams, M.J. Molecular characterisation of segments 1 to 6 of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus from China provides the complete genome. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, M.; Uyeda, I.; Lee, B.C. Detection and assignment of proteins encoded by rice black streaked dwarf fijivirus S7, S8, S9 and S10. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; He, Y.; Xie, K.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Hong, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Taliansky, M.; et al. Rice black-streaked dwarf virus P10 acts as either a synergistic or antagonistic determinant during superinfection with related or unrelated virus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Wei, C.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y. Rice black-streaked dwarf virus minor core protein P8 is a nuclear dimeric protein and represses transcription in tobacco protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Qin, Q.; Chen, C.; Wei, Z.; Tan, X.; Xie, K.; Zhang, R.; Hong, G.; et al. Distinct modes of manipulation of rice auxin response factor OsARF17 by different plant RNA viruses for infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9112–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepin, N.; Rolland, F. SnRK1 activation, signaling, and networking for energy homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2019, 51, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polge, C.; Thomas, M. SNF1/AMPK/SnRK1 kinases, global regulators at the heart of energy control? Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckx, T.; Hulsmans, S.; Rolland, F. The plant energy sensor: Evolutionary conservation and divergence of SnRK1 structure, regulation, and function. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 6215–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozet, P.; Margalha, L.; Confraria, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Martinho, C.; Adamo, M.; Elias, C.A.; Baena-Gonzalez, E. Mechanisms of regulation of SNF1/AMPK/SnRK1 protein kinases. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbreras, V.; Alba, M.M.; Kleinow, T.; Koncz, C.; Pages, M. Domain fusion between SNF1-related kinase subunits during plant evolution. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gissot, L.; Polge, C.; Jossier, M.; Girin, T.; Bouly, J.P.; Kreis, M.; Thomas, M. AKINβγ contributes to SnRK1 heterotrimeric complexes and interacts with two proteins implicated in plant pathogen resistance through its KIS/GBD sequence. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramon, M.; Ruelens, P.; Li, Y.; Sheen, J.; Geuten, K.; Rolland, F. The hybrid four-CBS-domain KINβγ subunit functions as the canonical gamma subunit of the plant energy sensor SnRK1. Plant J. 2013, 75, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.A.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, K.W.; Chen, J.L.; Huang, L.F.; Ho, S.L.; Liu, H.J.; Hsing, Y.I.; Yu, S.M. The SnRK1A protein kinase plays a key role in sugar signaling during germination and seedling growth of rice. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2484–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, L.; Wang, H.; Sunter, G.; Bisaro, D.M. Geminivirus AL2 and L2 proteins interact with and inactivate SNF1 kinase. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.Y.; Gazzarrini, S. AKIN10 and FUSCA3 interact to control lateral organ development and phase transitions in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Dallas, M.B.; Goshe, M.B.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L. SnRK1 phosphorylation of AL2 delays Cabbage leaf curl virus infection in Arabidopsis. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10598–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Song, F.; Xie, Q.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L.; Zhou, X. Tomato SlSnRK1 protein interacts with and phosphorylates βC1, a pathogenesis protein encoded by a geminivirus beta-satellite. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1394–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avila-Castaneda, A.; Gutierrez-Granados, N.; Ruiz-Gayosso, A.; Sosa-Peinado, A.; Martinez-Barajas, E.; Coello, P. Structural and functional basis for starch binding in the SnRK1 subunits AKINβ2 and AKINβγ. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 199. [Google Scholar]
- López-Paz, C.; Vilela, B.; Riera, M.; Pagès, M.; Lumbreras, V. Maize AKINβγ dimerizes through the KIS/CBM domain and assembles into SnRK1 complexes. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.S.; Rao, C.S.; Nelson, R.S. Analysis of gene function in rice through virus-induced gene silencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 354, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.S.; Schneider, W.L.; Chaluvadi, S.R.; Mian, M.A.; Nelson, R.S. Characterization of a Brome mosaic virus strain and its use as a vector for gene silencing in monocotyledonous hosts. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z.; Di, D.; Zhang, A.; Miao, H.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Characterization of small interfering RNAs derived from Rice black streaked dwarf virus in infected maize plants by deep sequencing. Virus Res. 2016, 228, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.A.; Li, Y.; Lei, L.; Di, D.; Miao, H.; Fan, Z. Alteration of gene expression profile in maize infected with a double-stranded RNA fijivirus associated with symptom development. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Z. HC-Pro protein of sugar cane mosaic virus interacts specifically with maize ferredoxin-5 in vitro and in planta. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, Y.; Ding, X.S.; Webb, S.L.; Zhou, T.; Nelson, R.S.; Fan, Z. Maize Elongin C interacts with the viral genome-linked protein, VPg, of Sugarcane mosaic virus and facilitates virus infection. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheen, J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the differential expression of maize pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase genes. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z.; Xie, J.; Carr, J.P.; Wu, B.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, T. Identification of differentially regulated maize proteins conditioning Sugarcane mosaic virus systemic infection. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 1156–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆ CT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Possible involvement of maize Rop1 in the defence responses of plants to viral infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Fritschi, F.B. Apoplastic infusion of sucrose into stem internodes during female flowering does not increase grain yield in maize plants grown under nitrogen-limiting conditions. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 148, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Mackown, C.T.; Starks, P.J.; Kindiger, B.K. Rapid analysis of nonstructural carbohydrate components in grass forage using microplate enzymatic assays. Crop. Sci. 2010, 50, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Nelson, R.S.; Li, W.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, T. An efficient virus-induced gene silencing vector for maize functional genomics research. Plant J. 2016, 86, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Gonzalez, E.; Rolland, F.; Thevelein, J.M.; Sheen, J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghillebert, R.; Swinnen, E.; Wen, J.; Vandesteene, L.; Ramon, M.; Norga, K.; Rolland, F.; Winderickx, J. The AMPK/SNF1/SnRK1 fuel gauge and energy regulator: Structure, function and regulation. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3978–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsmans, S.; Rodriguez, M.; De Coninck, B.; Rolland, F. The SnRK1 energy sensor in plant biotic interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.L. Sucrose metabolism: Gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri Moghaddam, M.R.; Van den Ende, W. Sugars and plant innate immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolton, M.D. Primary metabolism and plant defense--fuel for the fire. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filipe, O.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Haeck, A.; Demeestere, K.; Hofte, M. The energy sensor OsSnRK1a confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Sun, X.; Di, D.; Zhang, A.; Qing, L.; Zhou, T.; Miao, H.; Fan, Z. Maize AKINβγ Proteins Interact with P8 of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Inhibit Viral Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121387
Li M, Sun X, Di D, Zhang A, Qing L, Zhou T, Miao H, Fan Z. Maize AKINβγ Proteins Interact with P8 of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Inhibit Viral Infection. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mingjun, Xi Sun, Dianping Di, Aihong Zhang, Ling Qing, Tao Zhou, Hongqin Miao, and Zaifeng Fan. 2020. "Maize AKINβγ Proteins Interact with P8 of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Inhibit Viral Infection" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121387
APA StyleLi, M., Sun, X., Di, D., Zhang, A., Qing, L., Zhou, T., Miao, H., & Fan, Z. (2020). Maize AKINβγ Proteins Interact with P8 of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Inhibit Viral Infection. Viruses, 12(12), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121387





