The Potyviruses: An Evolutionary Synthesis Is Emerging
Abstract
:1. Historical Origins
2. The Origins of the Potyviridae
3. The Potyvirus: Rymovirus Divergence
4. Potyvirus Diversity
4.1. Phylogenetics
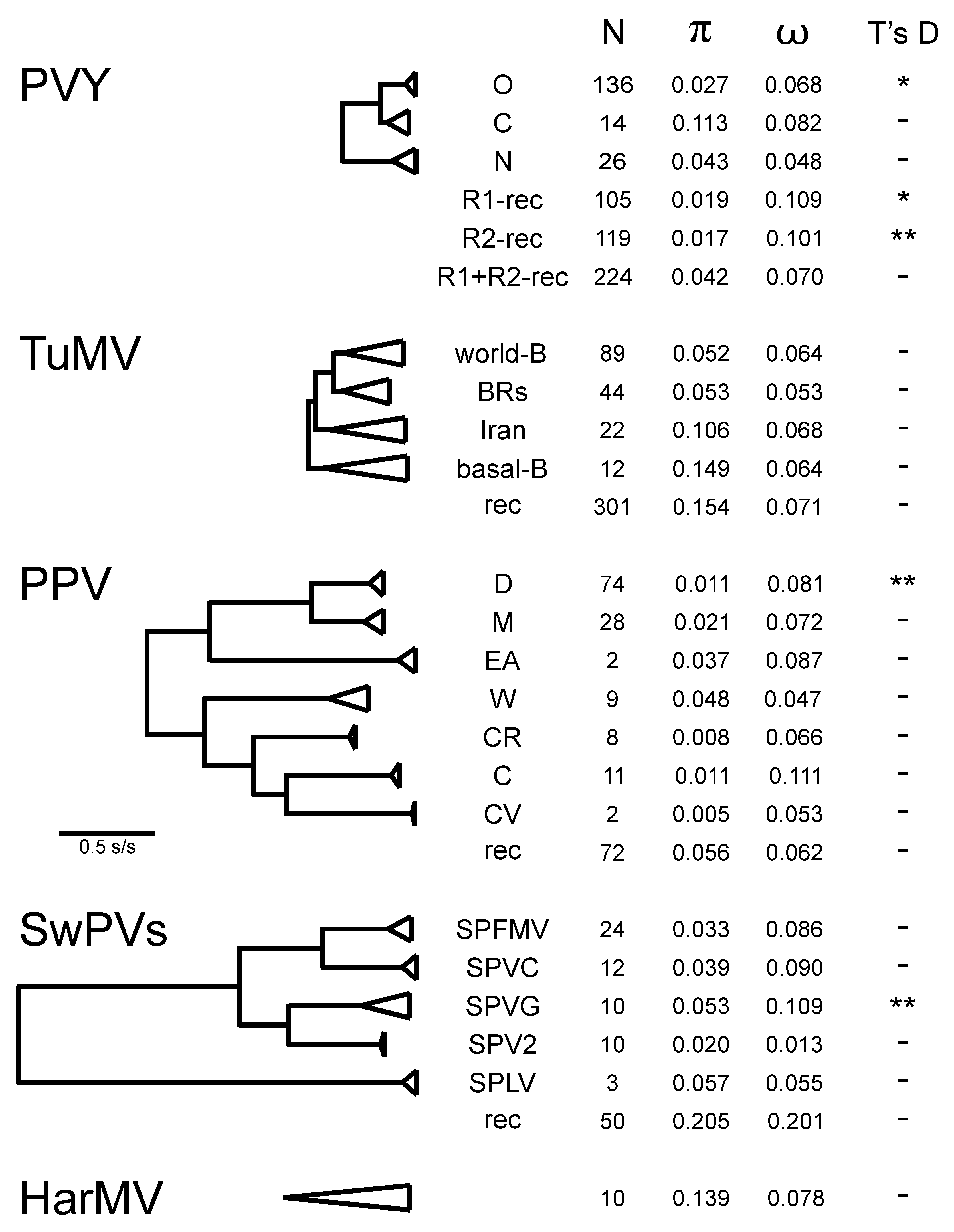
4.2. Population Genetics
4.2.1. Potato Virus Y
4.2.2. Turnip Mosaic Virus
4.2.3. Plum Pox Virus
4.2.4. Sweet Potato Potyviruses
4.2.5. Hardenbergia Mosaic Virus
5. Potyviruses in Space and Time
6. Evolutionary Vignettes from Potyvirus Studies
6.1. Super-Adapters
6.2. Australian Potyviruses
6.3. Papaya Ringspot Virus
6.4. The Columbian Exchange
6.5. The Major Lineages: BCMV and PVY
6.6. Genetic Connectivity
6.7. Seed Transmission
6.8. Potyvirus Emergence from Natural Ecosystems
6.9. Historical Potyvirus Specimens
6.10. Metagenomes, A New Frontier?
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salaman, R.N. Degeneration of the potato. An urgent problem. J. Nat. Inst. Agric. Bot. 1925, 1, 30–51. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.M. On the composite nature of certain potato virus diseases of the mosaic group as revealed by the use of plant indicators and selective methods of transmission. Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. B. 1931, 109, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, M.A. On three new viruses diseases in Hyoscyamus niger. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1932, 19, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.D.; Finch, J.T.; Gibbs, A.J.; Hollings, M.; Shepherd, R.J.; Valenta, V.; Wetter, C. Sixteen groups of plant viruses. Virology 1971, 45, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, O.W. A summary of potyvirus taxonomy and definitions. In Potyvirus Taxonomy; Barnett, O.W., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, J.; Wetter, C. Classification of elongated plant viruses on the basis of particle morphology. Virology 1959, 8, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, R. Plant Virology, 5th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Min Jou, W.; Haegeman, G.; Ysebaert, M.; Fiers, W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the bacteriophage MS2 coat protein. Nature 1972, 237, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pagán, I. The diversity, evolution and epidemiology of plant viruses: A phylogenetic view. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, A.A. The general properties of potyviruses. In Potyvirus Taxonomy; Barnett, O.W., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, A.; Mackenzie, A.A. Primer pair for amplifying part of the genome of all potyvirids by RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 1997, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Rodoni, B.C.; Gibbs, M.J.; Gibbs, A.J. A novel pair of universal primers for the detection of potyviruses. Plant Pathol. 2009, 59, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.J.; Adams, M.; Chalam, C.; Kreuze, J.; López-Moya, J.J.; Ohshima, K.; Praveen, S.; Rabenstein, F.; Stenger, D.; Wang, A.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Potyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C.; Naidu, R.A. Global dimensions of plant virus diseases: Current status and future perspectives. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revers, F.; García, J.A. Molecular biology of potyviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2015, 92, 101–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sastry, K.S. Seed-Borne Plant Virus Diseases; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- Illergard, K.; Ardell, D.H.; Elofsson, A. Structure is three to ten times more conserved than sequence—A study of structural response in protein cores. Proteins 2009, 77, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pál, C.; Papp, B.; Lercher, M.J. An integrated view of protein evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M. Origins and evolution of viruses of eukaryotes: The ultimate modularity. Virology 2015, 479–480, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valle, M. Structural shomology between nucleoproteins of ssRNA viruses. Subcell. Biochem. 2018, 88, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, M.; Méndez-López, E.; Agirrezabala, X.; Cuesta, R.; Lavín, J.L.; Sánchez-Pina, M.A.; Aranda, M.A.; Valle, M. Potyvirus virion structure shows conserved protein fold and RNA binding site in ssRNA viruses. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kežar, A.L.; Kavčič, M.; Polak, J.; Novaček, I.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, M.T.; Žnidarič, A.; Coll, K.; Stare, K.; Gruden, M.; Ravnikar, D.; et al. Structural basis for the multitasking nature of the potato virus Y coat protein. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigam, D.; LaTourrette, K.; Souza, P.F.N.; Garcia-Ruiz, H. Genome—wide variation in potyviruses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Kazlauskas, D.; Iranzo, J.; Lucía-Sanz, A.; Kuhn, J.H.; Krupovic, M.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, E.V. Origins and evolution of the global RNA virome. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, G.; Myers, K.; Hillman, B.I.; Fry, W.E. A novel virus of the late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans, with two RNA segments and a supergroup 1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Virology 2009, 392, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Vasilakis, N.; Tian, J.-H.; Li, C.-X.; Chen, L.-J.; Eastwood, G.; Diao, X.-N.; Chen, M.-H.; Chen, X.; et al. Divergent viruses discovered in arthropods and vertebrates revise the evolutionary history of the Flaviviridae and related viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, M.J.; Antoniw, J.F.; Beaudoin, F. Overview and analysis of the polyprotein cleavage sites in the family Potyviridae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingot, A.; Valli, A.; Rodamilans, B.; San León, D.; Baulcombe, D.C.; García, J.A.; López-Moya, J.J. The P1N-PISPO trans-frame gene of sweet potato feathery mottle potyvirus is produced during virus infection and functions as an RNA silencing suppressor. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3543–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, S.; Jones, R.A.C.; Matsuoka, H.; Ohshima, K.; Kreuze, J.; Gibbs, A.J. Potato virus Y, the Andean connection. Virus Evol. 2019, 5, vez037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K.; Yasaka, R.; Mohammad, M.; Gibbs, M.J.; Jones, R.A.C. The phylogenetics of the global population of potato virus Y and its necrogenic recombinants. Virus Evol. 2017, 3, vex002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hajizadeh, M.; Gibbs, A.J.; Amirnia, F.; Glasa, M. The global phylogeny of Plum pox virus is emerging. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, L.; Diaz-Ruiz, J.R.; Maat, D.Z. Further characterization of celery latent virus. Neth. J. Plant Path. 1978, 84, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisoni, E. Celery latent virus. In Viruses of Plants; Brunt, A.A., Crabtree, K., Dallwitz, M., Gibbs, A., Watson, L., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, H.; Döring, I.; Vetten, H.J.; Menzel, W.; Richert-Pöggeler, K.R.; Maiss, E. Complete genome sequence and construction of an infectious full-length cDNA clone of celery latent virus—An unusual member of a putative new genus within the Potyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; Garcıa, J.A. Mechanistic divergence between P1 proteases of the family Potyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keese, P.; Gibbs, A. Origins of genes: Big bang or continuous creation? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9489–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavesi, A.; Vianelli, A.; Chirico, N.; Bao, Y.; Blinkova, O.; Belshaw, R.; Firth, A.; Karlin, D. Overlapping genes and the proteins they encode differ significantly in their sequence composition from non-overlapping genes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabath, N.; Wagner, A.; Karlin, D. Evolution of viral proteins originated de novo by overprinting. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 3767–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Govier, D.A.; Kassanis, B. A virus-induced component of plant sap needed when aphids acquire potato virus Y from purified preparations. Virology 1974, 61, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govier, D.A.; Kassanis, B. Evidence that a component other than the virus particle is needed for aphid transmission of potato virus Y. Virology 1974, 57, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Calvino, L.; Goytia, E.; Dionisio Lo’pez-Abella, D.; Ana Giner, A.; Urizarna, M.; Vilaplana, L.; Lo’pez-Moya, J.J. The helper-component protease transmission factor of tobacco etch potyvirus binds specifically to an aphid ribosomal protein homologous to the laminin receptor precursor. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2862–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, D.C.; Hein, G.L.; Gildow, F.E.; Horken, K.M.; French, R. Plant virus HC-Pro is a determinant of eriophyid mite transmission. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9054–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K. Potyviruses in the Digital Age. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, H. Generelle Morphologie der Organismen; G. Reimer: Berlin, Germany, 1866; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mindell, D.P. The tree of life: Metaphor, model, and heuristic device. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bald, J.G.; Tinsley, T.W. Virus reactions and taxonomy. Nature 1967, 214, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.; Gibbs, A.J. Taxonomic patterns in the host ranges of viruses among grasses, and suggestions on generic sampling for host range studies. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1974, 77, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, P.L.; Dale, J.L.; Adena, M.A.; Gibbs, A.J. A taxonomic study of the host ranges of tymoviruses. Plant Path. 1984, 33, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Armstrong, J.; Weiller, G.F.; Gibbs, A.J. Virus evolution; the past, a window on the future? In Virus-Resistant Transgenic Plants: Potential Ecological Impact; Tepfer, M., Balazs, E., Eds.; INRA: Versailles, France; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Wood, J.; Garcia-Arenal, F.; Ohshima, K.; Armstrong, J.S. Tobamoviruses have probably co-diverged with their eudicotyledonous hosts for at least 110 million years. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leebens-Mack, J.H.; Barker, M.S.; Carpenter, E.J.; Deyholos, M.K.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Graham, S.W.; Grosse, I.; Li, Z.; Melkonian, M.; Mirarab, S.; et al. One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 2019, 574, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, S.H.; Li, H.; Admiraal, R.; Jones, M.G.K.; Wylie, S.J. Catharanthus mosaic virus: A potyvirus from a gymnosperm, Welwitschia mirabilis. Virus Res. 2015, 203, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eastop, V.F. Worldwide importance of aphids as virus vectors. In Aphids as Virus Vectors; Harris, K.F., Maramorosch, C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 3–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Wada, Y.; Chen, J.; Ohshima, K. Inter- and intralineage recombinants are common in natural populations of Turnip mosaic virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2683–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromas, N.; Zwart, M.P.; Poulain, M.; Elena, S.F. Estimation of the in vivo recombination rate for a plant RNA virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bujarski, J.J. Genetic recombination in plant-infecting messenger-sense RNA viruses: Overview and research perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbiez, C.; Lecoq, H. The nucleotide sequence of Watermelon mosaic virus (WMV, Potyvirus) reveals interspecific recombination between two related potyviruses in the 5′ part of the genome. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbiez, C.; Wipf-Scheibel, C.; Millot, P.; Verdin, E.; Dafalla, G.; Lecoq, H. New species in the papaya ringspot virus cluster: Insights into the evolution of the PRSV lineage. Virus Res. 2017, 241, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchêne, S.; Holmes, E.C.; Ho, S.Y. Analyses of evolutionary dynamics in viruses are hindered by a time-dependent bias in rate estimates. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Cooper, A.; Drummond, A.J. Time dependency of molecular rate estimates and systematic overestimation of recent divergence times. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.A. The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S. Evolution in Mendelian populations. Genetics 1931, 16, 97–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dobzhansky, T. Genetics and the Origin of Species, Reprint ed. No. 11; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Achon, M.A.; Larrañaga, A.; Alonso-Dueñas, N. The population genetics of maize dwarf mosaic virus in Spain. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2377–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of Sugarcane mosaic virus. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, L.F.; Cooper, J.I. Analyses on mutation patterns, detection of population bottlenecks, and suggestion of deleterious-compensatory evolution among members of the genus Potyvirus. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, M.; Bahrampour, H.; Abdollahzadeh, J. Genetic diversity and population structure of Watermelon mosaic virus. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2017, 124, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.M.; Willemsen, A.; Hillung, J.; Zwart, M.P.; Elena, S.F. Temporal dynamics of intrahost molecular evolution for a plant RNA virus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domingo, E.; Perales, C. Viral quasispecies. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunham, J.P.; Simmons, H.E.; Holmes, E.C.; Stephenson, A.G. Analysis of viral (Zucchini yellow mosaic virus) genetic diversity during systemic movement through a Cucurbita pepo vine. Virus Res. 2014, 191, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutnjak, D.; Rupar, M.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Curk, T.; Kreuze, J.F.; Ravnikar, M. Deep sequencing of virus-derived small interfering RNAs and RNA from viral particles shows highly similar mutational landscapes of a plant virus population. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4760–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rousseau, E.; Moury, B.; Mailleret, L.; Senoussi, R.; Palloix, A.; Simon, V.; Valière, S.; Grognard, F.; Fabre, F. Estimating virus effective population size and selection without neutral markers. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, J.K.; Ohshima, K.; Lee, H.G.; Son, M.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Sohn, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Molecular variability and genetic structure of the population of Soybean mosaic virus based on the analysis of complete genome sequences. Virology 2009, 393, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.L. Small effective population sizes and rare nonsynonymous variants in potyviruses. Virology 2009, 393, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcıa-Arenal, F.; Fraile, A.; Malpica, J.M. Variability and genetic structure of plant virus populations. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2001, 39, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fribourg, C.E.; Gibbs, A.J.; Adams, I.P.; Boonham, I.; Jones, R.A.C. Biological and molecular properties of Wild potato mosaic virus isolates from pepino (Solanum muricatum). Plant Dis. 2019. 103, 1746–1756. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Bowers, J.E.; McKain, M.R.; McNeal, J.; Rolf, M.; Ruzicka, D.R.; Wafula, E.; Wickett, N.J.; et al. A genome triplication associated with early diversification of the core eudicots. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Tomitaka, Y.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Duchene, S.; Vetten, H.J.; Lesemann, D.; Walsh, J.A.; Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K. Turnip mosaic potyvirus probably first spread to eurasian brassica crops from wild orchids about 1000 years ago. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provvidenti, R. Turnip mosaic virus. In Viruses of Plants; Brunt., A.A., Crabtree, K., Dallwitz, M.J., Gibbs, a.J., Watson, L., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1996; pp. 1340–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, J.A.; Walker, V.M. Further studies on seed transmission in the ecology of some aphid-transmitted viruses. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1973, 73, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubareva, I.A.; Vinogradova, S.V.; Gribova, T.N.; Monakhos, S.G.; Skryabin, K.G.; Ignatov, A.N. Genetic diversity of Turnip mosaic virus and the mechanism of its transmission by Brassica seeds. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 450, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, B.A.; Kehoe, M.A.; Webster, G.C.; Wylie, S.J.; Jones, R.A.C. Indigenous and introduced potyviruses of legumes and Passiflora spp. from Australia: Biological properties and comparison of coat protein nucleotide sequences. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1757–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Trueman, J.W.H.; Gibbs, M.J. The bean common mosaic virus lineage of potyviruses: Where did it arise and when? Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryazhimskiy, S.; Plotkin, J.B. The population genetics of dN/dS. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudson, R.R.; Boos, D.D.; Kaplan, N.L. A statistical test for detecting geographic subdivision. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsompana, M.; Abad, J.; Purugganan, M.; Moyer, J.W. The molecular population genetics of the Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) genome. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Nevado, C.; Montes, N.; Pagán, I. Ecological factors affecting infection risk and population genetic diversity of a novel Potyvirus in its native wild ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, M.J.; Antoniw, J.F.; Fauquet, C.M. Molecular criteria for genus and species discrimination within the family Potyviridae. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Mitoma, S.; Gibbs, A.J. The genetic diversity of narcissus viruses related to turnip mosaic virus blur arbitrary boundaries used to discriminate potyvirus species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyambari, M.; Warner, S.; Stoler, N.; Rainer, D.; Roossinck, M.J. A 1,000-year-old RNA virus. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- To, T.H.; Jung, M.; Lycett, S.; Gascuel, O. Fast dating using least-squares criteria and algorithms. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielejec, F.; Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P. SPREAD: Spatial phylogenetic reconstruction of evolutionary dynamics. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2910–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harkins, G.W.; Martin, D.P.; Duffy, S.; Monjane, A.L.; Shepherd, D.N.; Windram, O.P.; Betty, E.; Owor, B.E.; Donaldson, L.; Antwerpen, T.V.; et al. Dating the origins of the maize-adapted strain of maize streak virus, MSV-A. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefeuvre, D.P.; Martin, G.; Harkins, P.; Lemey, A.J.; Gray, S.; Meredith, F.; Lakay, A.; Monjane, J.M.; Lett, A.; Varsani, J. Heydarnejad The spread of tomato yellow leaf curl virus from the Middle East to the world. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mabvakure, B.; Martin, D.P.; Kraberger, S.; Cloete, L.; Van Brunschot, S.; Geering, A.D.W.; Thomas, J.E.; Bananej, K.; Lett, J.M.; Lefeuvre, P.; et al. Ongoing geographical spread of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Virology 2016, 498, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel-Galzi, A.; Traoré, O.; Séré, Y.; Hébrard, E.; Fargette, D. The biogeography of viral emergence: Rice yellow mottle virus as a case study. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovão, N.S.; Baele, G.; Vrancken, B.; Bielejec, F.; Suchard, M.A.; Fargette, D.; Lemey, P. Host ecology determines the dispersal patterns of a plant virus. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasaka, R.; Ohba, K.; Schwinghamer, M.W.; Fletcher, J.; Ochoa-Corona, F.M.; Thomas, J.E.; Ho, S.Y.; Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K. Phylodynamic evidence of the migration of turnip mosaic potyvirus from Europe to Australia and New Zealand. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasaka, R.; Fukagawa, H.; Ikematsu, M.; Soda, H.; Korkmaz, S.; Golnaraghi, A.; Katis, N.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K. The time of emergence and spread of turnip mosaic potyvirus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmons, H.E.; Holmes, E.C.; Stephenson, A.G. Rapid evolutionary dynamics of zucchini yellow mosaic virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarte-Castillo, X.A.; Fermin, G.; Tabima, J.; Rojas, Y.; Tennant, P.F.; Fuchs, M.; Sierra, R.; Bernal, A.J.; Restrepo, S. Phylogeography and molecular epidemiology of Papaya ringspot virus. Virus Res. 2011, 159, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Ohshima, K.; Phillips, M.J.; Gibbs, M.J. The prehistory of potyviruses: Their initial radiation was during the dawn of agriculture. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohshima, K.; Nomiyama, R.; Mitoma, S.; Honda, Y.; Yasaka, R.; Tomimura, K. Evolutionary rates and genetic diversities of mixed potyviruses in Narcissus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 45, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.C.; Bellstedt, D.U.; Pirie, M.D. The recent recombinant evolution of a major crop pathogen, Potato virus Y. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Y.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Gao, F.; Qiu, G.; Wang, T.; Nie, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Bai, Y. Molecular evolutionary analysis of potato virus Y infecting potato based on the VPg gene. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, M.; Gibbs, A.J.; Hosseini, A.; Hosseini, S. An Iranian genomic sequence of Beet mosaic virus provides insights into diversity and evolution of the world population. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, K.; Janick, J.; Scofield, S.; Goldschmidt, E.E. A history of grafting. Hortic. Rev. 2009, 35, 437–493. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, C.; Jacobs, Z.; Marwick, B.; Fullagar, R.; Wallis, L.; Smith, M.; Roberts, R.G.; Hayes, E.; Lowe, K.; Carah, X.; et al. Human occupation of northern Australia by 65,000 years ago. Nature 2017, 547, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, R.; Kemp, E. Late Cainozoic environments in Australia. In Vertebrate Zoogeography and Evolution in Australasia; Archer, M., Clayton, G., Eds.; Hesperian Press: Carlisle, AZ, USA, 1984; pp. 82–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Jang, Y. Macroevolutionary patterns in the Aphidini aphids: Diversification, host association, and biogeographic origins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.D.; Yeates, D.K.; Cassis, G.; Fletcher, M.J.; La Salle, J.; Lawrence, J.F.; PeterMcQuillan, P.B.; Mound, L.A.; Bickel, D.J.; Gullan, P.J.; et al. Insects down under—Diversity, endemism and evolution of the Australian insect fauna: Examples from select orders. Aust. J. Entomol. 2004, 43, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, M. Super family Aphidoidea. In The Insects of Australia, 2nd ed.; Naumann, I.D., Ed.; Melbourne University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 452–457. [Google Scholar]
- Eastop, V.F. A taxonomic study of Australian Aphidoidea (Homoptera). Aust. J. Zool. 1966, 14, 399–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heie, O.E. Why are there so few aphid species in the temperate areas of the southern hemisphere? Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, J.; Gardiner, J.E.; Gibbs, A.J. Viruses in Kennedia rubicunda. Aust. Plant Path. Soc. Newsl. 1975, 4, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.; Mackenzie, A.; Blanchfield, A.L.; Cross, P.; Wilson, C.R.; Kitajima, E.; Nightingale, M.; Clements, M. Viruses of orchids in Australia: Their identification, biology and control. Aust. Orchid Rev. 2000, 65, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Mackenzie, A.M.; Wei, K.-G.; Gibbs, M.J. The potyviruses of Australia. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, A.M.; Nolan, M.; Wei, K.J.; Clements, M.A.; Gowanlock, D.; Wallace, B.J.; Gibbs, A.J. Ceratobium mosaic potyvirus: Another virus from orchids. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, J.N.; Davis, R.I.; Thomas, J.E. Passiflora virus Y, a novel virus infecting Passiflora spp. in Australia and the Indonesian province of Papua. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2004, 33, 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Sokhandan Bashir, N.; Gillings, M.R.; Bowyer, J.W. Polymerase chain reaction detection and assessment of genetic variation in New South Wales isolates of passionfruit woodiness potyvirus. Australas. Plant Pathol. 1997, 26, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, C.G.; Coutts, B.A.; Jones, R.A.C.; Jones, M.G.K.; Wylie, S.J. Virus impact at the interface of an ancient ecosystem and a recent agroecosystem: Studies on three legume-infecting potyviruses in the southwest Australian floristic region. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wylie, S.J.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Jones, M.G.K. Multiple polyadenylated RNAviruses detected in pooled cultivated and wild plant samples. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.J.; Tan, A.; Li, H.; Dixon, K.W.; Jones, M.G.K. Caladenia virus A, an unusual new member of the Potyviridae from terrestrial orchids in Western Australia. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2447–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, S.J.; Li, H.; Dixon, K.W.; Richards, H.; Jones, M.G. 2013. Exotic and indigenous viruses infect wild populations and captive collections of temperate terrestrial orchids (Diuris species) in Australia. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, D.D. Papaya virus diseases with special reference to papaya ringspot. Phytopathology 1949, 39, 191–211. [Google Scholar]
- Purcifull, D.; Edwardson, J.; Hiebert, E.; Gonsalves, D. Papaya ringspot virus. In CMI/AAB Descriptions of Plant Viruses No. 292; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bayot, R.G.; Villegas, V.N.; Magdalita, P.M.; Jovellana, M.D.; Espino, T.M.; Exconde, S.B. Seed transmissibility of papaya ringspot virus. Philipp. J. Crop Sci. 1990, 15, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Laney, A.; Avanzato, M.V.; Tzanetakis, I.E. High incidence of seed transmission of Papaya ringspot virus and Watermelon mosaic virus, two viruses newly identified in Robinia pseudoacacia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 134, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitter, T.A.; Hopkins, D.L.; Claude, E.; Thomas, C.E. Compendium of Cucurbit Diseases and Pests; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, M.; Ahmad, M.H.; Tennant, P. Momordica charantia is a weed host reservoir for Papaya ringspot virus type P in Jamaica. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocha, Y.; Vigheri, N.; Nkoy-Florent, B.; Bakwanamaha, K.; Bolomphety, B.; Kasongo, M.; Betts, P.; Monger, V.; Harju, W.A.; Mumford, R.A.; et al. First report of the identification of Moroccan watermelon mosaic virus in papaya in Democratic Republic of Congo. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, M.F.; Henderson, J.; Chaleeprom, W.; Gibbs, A.J.; Dale, J.L. Papaya ringspot potyvirus: Isolate variability and the origin of PRSV type P (Australia). J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 3547–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, M.F.; Lines, R.E.; Revill, P.; Chaleeprom, W.; Ha, C.V.; Gibbs, A.J.; Dale, J.L. On the evolution and molecular epidemiology of the potyvirus Papaya ringspot virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, W.P. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis; 2007. Version 2.0. 2010. Available online: http://mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 22 January 2020).
- Davis, R.I.; Ruabete, T. Records of plant pathogenic virus and virus-like agents from 22 Pacific island countries and territories: A review and an update. Australas. Plant Path. 2010, 39, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, S.; Barbetti, M.J.; Edwards, O.R.; Minemba, D.; Areke, M.W.; Jones, R.A.C. Genetic connectivity between Papaya ringspot virus genomes from Papua New Guinea and Northern Australia, and new recombination insights. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.C.; Chiang, C.H.; Raja, J.A.J.; Liu, F.L.; Tai, C.H.; Yeh, S.D. A single amino acid of NIaPro of Papaya ringspot virus determines host specificity for infection of papaya. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morton, J. Papaya. In Fruits of Warm Climates; Creative Resource Systems, Inc.: Miami, FL, USA, 1987; pp. 336–346. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.A.C. Plant virus emergence and evolution: Origins, new encounter scenarios, factors driving emergence, effects of changing world conditions, and prospects for control. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rodríguez, P.; Carruthers, T.; Wood, J.R.I.; Williams, B.R.M.; Weitemier, K.; Kronmiller, B.; Ellis, D.; Anglin, N.L.; Longway, L.; Harris, S.A.1.; et al. Reconciling conflicting phylogenies in the origin of sweet potato and dispersal to Polynesia. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Meiri, M.; Lister, A.M.; Collins, M.J.; Tuross, N.; Geobel, T.; Blockley, S.; Zazula, G.D.; Guthrie, R.D.; Boeskorov, G.G.; Baryshnikov, G.F.; et al. Faunal record identifies Bering isthmus conditions as constraint to end-Pleistocene migration to the New World. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B 2014, 281, 2013–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willerslev, E.; Davison, J.; Moora, M.; Zobel, M.; Coissac, E.; Edwards, M.E.; Lorenzen, E.D.; Vestergård, M.; Gussarova, G.; Haile, J.; et al. Fifty thousand years of Arctic vegetation and megafaunal diet. Nature 2014, 506, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zazula, G.D.; Froese, D.G.; Schweger, C.E.; Mathewes, R.W.; Beaudoin, A.B.; Telka, M.A.; Harington, C.R.; Westgate, J.A. Ice-age steppe vegetation in east Beringia. Nature 2003, 423, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, S.; Coutts, B.A.; Edwards, O.R.; De Almeida, L.; Kehoe, M.A.; Ximenes, A.; Jones, R.A.C. Zucchini yellow mosaic virus populations from East Timorese and northern Australian cucurbit crops: Molecular properties, genetic connectivity and biosecurity implications. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maina, S.; Barbetti, M.J.; Martin, D.P.; Edwards, O.R.; Jones, R.A.C. New isolates of Sweet potato feathery mottle virus and Sweet potato virus C: Biological and molecular properties, and recombination analysis based on complete genomes. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmons, H.E.; Munkvold, G.P. Seed transmission in the Potyviridae. In Global Perspectives on the Health of Seeds and Plant Propagation Material; Gullino, M.L., Munkvold, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, D.; Penrose, L.; Daly, A.; Constable, F.; Gibbs, M. Prevalences of Pospiviroid contamination in large seed lots of tomato and capsicum, and related seed testing considerations. Viruses 2019, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.A.C. Determining ‘threshold’ levels for seed-borne virus infection in seed stocks. Virus Res. 2000, 71, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C. Developing integrated disease management strategies against non-persistently aphid-borne viruses: A model program. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 2001, 6, 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C. Using epidemiological information to develop effective integrated virus disease management strategies. Virus Res. 2004, 100, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoe, B. Dark Emu Black Seeds: Agriculture or Accident? Magabala Books: Broome, Australia, 2014; pp. 1–177. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Wylie, S.J.; Coutts, B.; Jones, R.A.C.; Jones, M.G.K. A virus of an isolated indigenous flora spreads naturally to an introduced crop species. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2011, 159, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, M.A.; Coutts, B.A.; Buirchell, B.; Jones, R.A.C. Hardenbergia mosaic virus: Crossing the barrier between native and introduced plant species. Virus Res. 2014, 184, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchen-Osmond, C.; Crabtree, K.; Gibbs, A.; McLean, G. Viruses of Plants in Australia; Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Spetz, C.; Taboada, A.M.; Darwich, S.; Ramsell, J.; Salazar, L.F.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Molecular resolution of a complex of potyviruses infecting solanaceous crops at the centre of origin in Peru. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2565–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.J.; Coutts, B.A.; Jones, R.A. Effects of introduced and indigenous viruses on native plants: Exploring their disease causing potential at the agro-ecological interface. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, M.A.; Jones, R.A.C. Improving Potato virus Y strain nomenclature: Lessons from comparing isolates obtained over a 73-year period. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, I.P.; Boonham, N.; Jones, R.A.C. Full-genome sequencing of a virus from a 33-year-old sample demonstrates that Arracacha mottle virus is synonymous with Arracacha virus Y. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, I.P.; Fox, A.; Boonham, N.; Jones, R.A.C. Complete genomic sequence of the potyvirus Mashua virus Y, obtained from a 33-year-old mashua (Tropaeaolum tuberosum) sample. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.A.C.; Fribourg, C.E. Host plant reactions, some properties and serology of wild potato mosaic virus. Phytopatholgy 1979, 69, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.; Seifert, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Seitz, S. Discovery of highly divergent lineages of plant-associated astro-like viruses sheds light on the emergence of potyviruses. Virus Res. 2019, 260, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuze, J.F.; Souza-Dias, J.A.C.; Jeevalatha, A.; Figueira, A.R.; Valkonen, J.P.T.; Jones, R.A.C. Viral Diseases in Potato. In The Potato Crop; Campos, H., Ortiz, O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 389–430. [Google Scholar]







| Parameter | PVY | TuMV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [105] | [29] and this study | [106] | [100] | ||||
| Method | BEAST 1.7.2 | BEAST 1.8.2 | BEAST 1.8.4 | BEAST 1.8.2 | |||
| Number of sequences; | 28 | 162 | 177 | 106 | 329 | 369 | 369 |
| Sequence length (nucleotides) | 9723 | 8913 | 564 | 9432 | 927 | 873 | 855 |
| Region | Polyprotein | Polyprotein | VPg | Polyprotein | Partial HC-Pro | Partial P3 | Partial NIb |
| Sampling date range | 1982–2010 | 1943–2016 | 1983–2015 | 1968–2012 | 1968–2012 | 1968–2012 | 1968–2012 |
| Best-fit substitution model | GTR+I+G | GTR+I+Γ4 | HKY+G4 | GTR+I+G | GTR+I+G | GTR+I+G | GTR+I+G |
| Best-fit clock model | UCLD, UCED, SC | UCLD | UCLD | UCED | UCED | UCED | UCED |
| Best-fit demographic model | ND | EG, BSP | BSP | CZ | CZ | CZ | CZ |
| TMRCA (95% CI) Year before present (YBP) | 161–619 (UCLD), 123–436 (UCED), 525–970 (SC) | 1841 (1157–2622) (EG), 1879 (1192–2659) (BSP) | 158 (71–269) | 1201 (468–2150) | 951 (326–1291) | 758 (274–1548) | 758 (274–1548) |
| TMRCA effective sample size | ND | 238 (EG), 261 (BSP) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Substitution rate (nt/site/year) | Unknown | 9.30 × 10−5 (6.79 × 10−5–1.18 × 10-4) (EG), 9.16 × 10−5 (6.90 × 10−5–1.15 × 10−4) (BSP) | 5.6 × 10−4 (3.35 × 10−4–8.17 × 10-4) | 8.89 × 10−4 (6.87 × 10−4–1.30 × 10−3) | 1.41 × 10−3 (1.09 × 10−3–1.78 × 10−3) | 1.46 × 10−3 (1.25 × 10−3–1.87 × 10−3) | 1.37 × 10−3 (1.04 × 10−3–1.73 × 10−3) |
| Substitution rates effective sample size | ND | >200 | >200 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Date (DRT) or cluster-based date (CDRT) randomization test | Not passed | DRT passed | CDRT passed | DRT passed | DRT passed | DRT passed | DRT passed |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibbs, A.J.; Hajizadeh, M.; Ohshima, K.; Jones, R.A.C. The Potyviruses: An Evolutionary Synthesis Is Emerging. Viruses 2020, 12, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020132
Gibbs AJ, Hajizadeh M, Ohshima K, Jones RAC. The Potyviruses: An Evolutionary Synthesis Is Emerging. Viruses. 2020; 12(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibbs, Adrian J., Mohammad Hajizadeh, Kazusato Ohshima, and Roger A.C. Jones. 2020. "The Potyviruses: An Evolutionary Synthesis Is Emerging" Viruses 12, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020132
APA StyleGibbs, A. J., Hajizadeh, M., Ohshima, K., & Jones, R. A. C. (2020). The Potyviruses: An Evolutionary Synthesis Is Emerging. Viruses, 12(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020132






