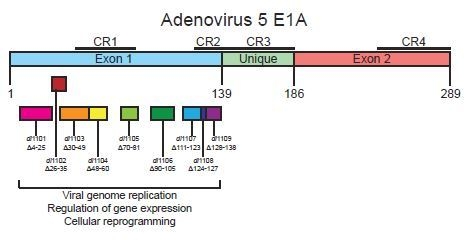
Characterization of Adenovirus 5 E1A Exon 1 Deletion Mutants in the Viral Replicative Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
2.2. Cell and Virus Culture
2.3. EdU Incorporation Assay
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. PCR Primers
2.6. Real-Time Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Viral Genome Quantification
2.9. Virus Growth Assay
3. Results
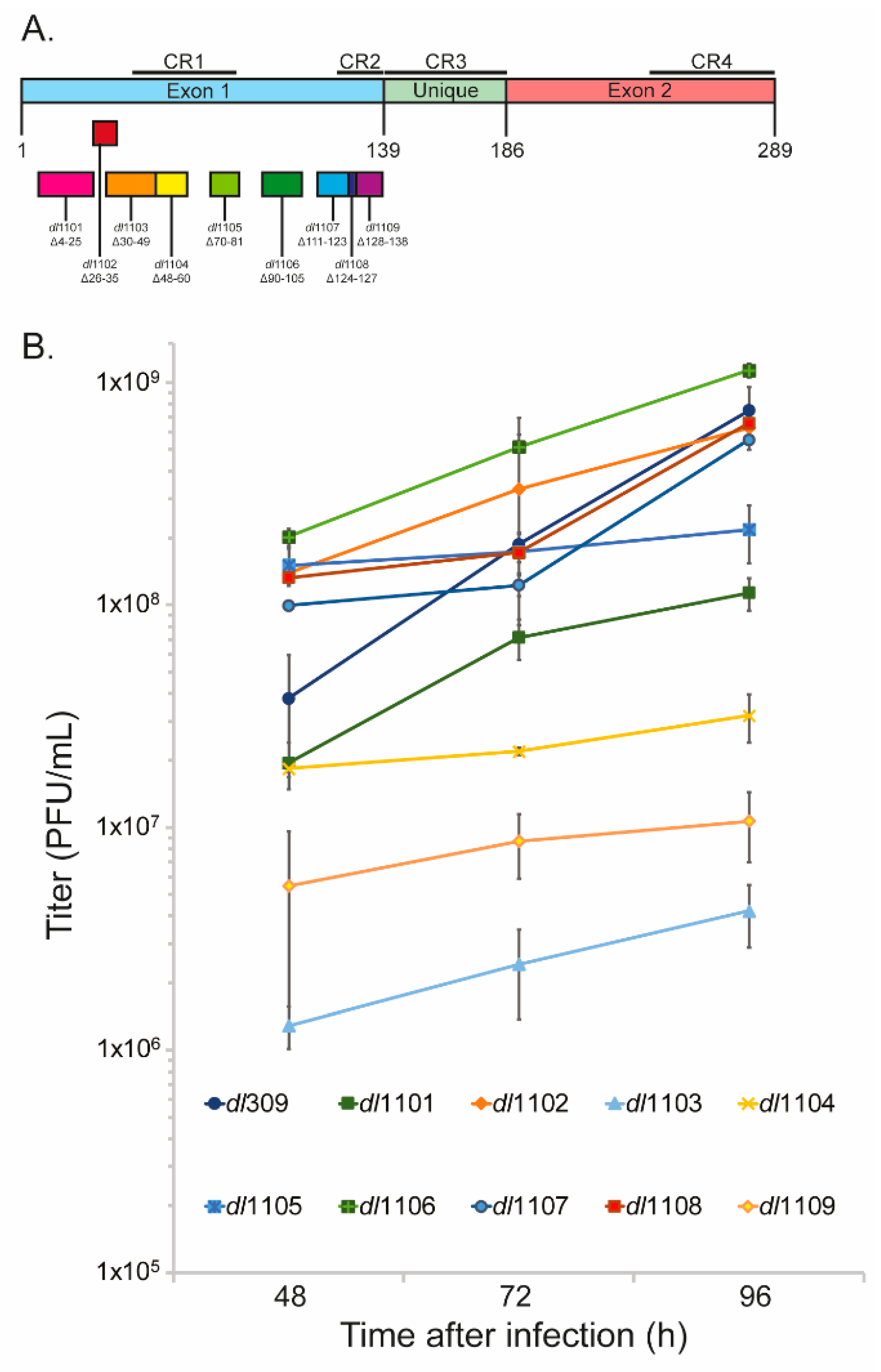
3.1. Deletions in the First Exon of E1A Affect Virus Growth
3.2. Deletions within Exon 1 of E1A Do Not Affect Its Sub-Cellular Localization
3.3. Viral Genome Replication in Viruses Expressing E1A Deletion Mutants
3.4. E1A Exon 1 Mutants Affect Viral Gene and Protein Expression
3.5. Induction of S-Phase and Expression of Cellular S-Phase Specific Genes by Exon 1 E1A Mutants
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berk, A.J. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, E.; Everitt, E. Adenovirus uncoating and nuclear establishment are not affected by weak base amines. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3470–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saphire, A.C.; Guan, T.; Schirmer, E.C.; Nemerow, G.R.; Gerace, L. Nuclear import of adenovirus DNA in vitro involves the nuclear protein import pathway and hsc70. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4298–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisostomo, L.; Soriano, A.M.; Mendez, M.; Graves, D.; Pelka, P. Temporal dynamics of adenovirus 5 gene expression in normal human cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, P.; Ablack, J.N.; Fonseca, G.J.; Yousef, A.F.; Mymryk, J.S. Intrinsic structural disorder in adenovirus e1a: A viral molecular hub linking multiple diverse processes. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7252–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, C.R.; Zhang, A.; Tessier, T.M.; Gameiro, S.F.; Mymryk, J.S. Hacking the cell: Network intrusion and exploitation by adenovirus e1a. MBio 2018, 9, e00390-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano, A.M.; Crisostomo, L.; Mendez, M.; Graves, D.; Frost, J.R.; Olanubi, O.; Whyte, P.F.; Hearing, P.; Pelka, P. Adenovirus 5 e1a interacts with e4orf3 to regulate viral chromatin organization. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00157-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dallaire, F.; Schreiner, S.; Blair, G.E.; Dobner, T.; Branton, P.E.; Blanchette, P. The human adenovirus type 5 e4orf6/e1b55k e3 ubiquitin ligase complex enhances e1a functional activity. MSphere 2016, 1, e00015-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radko, S.; Jung, R.; Olanubi, O.; Pelka, P. Effects of adenovirus type 5 e1a isoforms on viral replication in arrested human cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crisostomo, L.; Soriano, A.M.; Frost, J.R.; Olanubi, O.; Mendez, M.; Pelka, P. The influence of e1a c-terminus on adenovirus replicative cycle. Viruses 2017, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harlow, E.; Franza, B.R., Jr.; Schley, C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1a proteins: Extensive heterogeneity in early region 1a products. J. Virol. 1985, 55, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephens, C.; Harlow, E. Differential splicing yields novel adenovirus 5 e1a mrnas that encode 30 kd and 35 kd proteins. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, N.C.; Sarnow, P.; Duprey, E.; Levine, A.J. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize native and denatured forms of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. Virology 1983, 128, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Shenk, T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell 1979, 17, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsma, T.N.; Howe, J.A.; Evelegh, C.M.; Cunniff, N.F.; Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Floroff, M.R.; Denman, J.E.; Bayley, S.T. Use of deletion and point mutants spanning the coding region of the adenovirus 5 e1a gene to define a domain that is essential for transcriptional activation. Virology 1988, 163, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.R.; Olanubi, O.; Cheng, S.K.; Soriano, A.; Crisostomo, L.; Lopez, A.; Pelka, P. The interaction of adenovirus e1a with the mammalian protein ku70/xrcc6. Virology 2016, 500, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time rt-pcr. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Etemadi, M.; Ling, K.H.; Zainal Abidin, S.; Chee, H.Y.; Sekawi, Z. Gene expression patterns induced at different stages of rhinovirus infection in human alveolar epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bett, A.J.; Krougliak, V.; Graham, F.L. DNA sequence of the deletion/insertion in early region 3 of ad5 dl309. Virus Res. 1995, 39, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappaya, B.; Jones, N.; Shenk, T. A mutation which alters initiation of transcription by rna polymerase iii on the ad5 chromosome. Cell 1979, 18, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Shenk, T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 3665–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, C.; Jelsma, T.N.; Howe, J.A.; Bayley, S.T.; Ferguson, B.; Branton, P.E. Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1a of human adenovirus type 5. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 3955–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporossi, D.; Bacchetti, S. Definition of adenovirus type 5 functions involved in the induction of chromosomal aberrations in human cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedrich, R.W.; Bayley, S.T.; Engel, D.A. Induction of ap-1 DNA-binding activity and c-fos mrna by the adenovirus 243r e1a protein and cyclic amp requires domains necessary for transformation. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 5849–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.E.; Engel, D.A.; Smith, M.M. Cyclic amp signaling is required for function of the n-terminal and cr1 domains of adenovirus e1a in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Oncogene 1995, 11, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Slack, R.S.; Craig, J.; Costa, S.; McBurney, M.W. Adenovirus 5 e1a induced differentiation of p19 embryonal carcinoma cells requires binding to p300. Oncogene 1995, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mymryk, J.S.; Lee, R.W.; Bayley, S.T. Ability of adenovirus 5 e1a proteins to suppress differentiation of bc3h1 myoblasts correlates with their binding to a 300 kda cellular protein. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1992, 3, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayflick, L.; Plotkin, S.A.; Norton, T.W.; Koprowski, H. Preparation of poliovirus vaccines in a human fetal diploid cell strain. Am. J. Hyg. 1962, 75, 240–258. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, K.S.; Cohen, M.J.; Fonseca, G.J.; Todorovic, B.; King, C.R.; Yousef, A.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mymryk, J.S. Identification and characterization of multiple conserved nuclear localization signals within adenovirus e1a. Virology 2014, 454–455, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radko, S.; Koleva, M.; James, K.M.; Jung, R.; Mymryk, J.S.; Pelka, P. Adenovirus e1a targets the dref nuclear factor to regulate virus gene expression, DNA replication, and growth. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13469–13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, R.; Radko, S.; Pelka, P. The dual nature of nek9 in adenovirus replication. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, J.M.; Subramanian, T.; Schaeper, U.; La Regina, M.; Bayley, S.; Chinnadurai, G. A region in the c-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 e1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of t24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelsma, T.N.; Howe, J.A.; Mymryk, J.S.; Evelegh, C.M.; Cunniff, N.F.; Bayley, S.T. Sequences in e1a proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology 1989, 171, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, T.; Zhao, L.J.; Chinnadurai, G. Interaction of ctbp with adenovirus e1a suppresses immortalization of primary epithelial cells and enhances virus replication during productive infection. Virology 2013, 443, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egan, C.; Yee, S.P.; Ferguson, B.; Rosenberg, M.; Branton, P.E. Binding of cellular polypeptides to human adenovirus type 5 e1a proteins produced in escherichia coli. Virology 1987, 160, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, P.; Miller, M.S.; Cecchini, M.; Yousef, A.F.; Bowdish, D.M.; Dick, F.; Whyte, P.; Mymryk, J.S. Adenovirus e1a directly targets the e2f/dp-1 complex. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8841–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dyson, N.; Guida, P.; McCall, C.; Harlow, E. Adenovirus e1a makes two distinct contacts with the retinoblastoma protein. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4606–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howe, J.A.; Pelka, P.; Antelman, D.; Wilson, C.; Cornell, D.; Hancock, W.; Ramachandra, M.; Avanzini, J.; Horn, M.; Wills, K.; et al. Matching complementing functions of transformed cells with stable expression of selected viral genes for production of e1-deleted adenovirus vectors. Virology 2006, 345, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazzerini Denchi, E.; Helin, K. E2f1 is crucial for e2f-dependent apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iaquinta, P.J.; Lees, J.A. Life and death decisions by the e2f transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2007, 19, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farley, D.C.; Brown, J.L.; Leppard, K.N. Activation of the early-late switch in adenovirus type 5 major late transcription unit expression by l4 gene products. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babiss, L.E.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Adenovirus e1b proteins are required for accumulation of late viral mrna and for effects on cellular mrna translation and transport. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leppard, K.N. E4 gene function in adenovirus, adenovirus vector and adeno-associated virus infections. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, J.N.; Berk, A.J. P53-independent and -dependent requirements for e1b-55k in adenovirus type 5 replication. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5333–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, J.A.; Bayley, S.T. Effects of ad5 e1a mutant viruses on the cell cycle in relation to the binding of cellular proteins including the retinoblastoma protein and cyclin a. Virology 1992, 186, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Strain | Viral Growth | CPE | Subcellular Localization | Viral Genome Replication | Viral Gene Expression | Induction of S-phase | S-phase Gene Expression | Transformation with Ras b | pRb b Binding | p300 b Binding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dl309 | +++ | ++++ | N | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ |
| dl311 a | + | +/− | N, C | + | + | + | +/− | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1101 | ++ | + | N | + | + | + | + | +/− | ++ | − |
| dl1102 | +++ | ++++ | N | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| dl1103 | + | + | N | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| dl1104 | ++ | + | N | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | − |
| dl1105 | ++ | ++ | N | ++++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| dl1106 | ++++ | +++ | N | ++++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ |
| dl1107 | +++ | ++ | N | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | − | ++++ |
| dl1108 | +++ | ++ | N | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | − | +++ |
| dl1109 | + | + | N | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++++ |
| dl1116 a | +++ | ++ | N | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1132 a | +++ | + | N | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1133 a | +++ | +++ | N | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1134 a | ++ | +++ | N, C | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1135 a | +++ | +++ | N, C | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ |
| dl1136 a | + | + | N, C | ++ | ++ | ++ | +/− | +++ | ++ | +++ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, R.; Akkerman, N.; Graves, D.; Crisostomo, L.; Bachus, S.; Pelka, P. Characterization of Adenovirus 5 E1A Exon 1 Deletion Mutants in the Viral Replicative Cycle. Viruses 2020, 12, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020213
Costa R, Akkerman N, Graves D, Crisostomo L, Bachus S, Pelka P. Characterization of Adenovirus 5 E1A Exon 1 Deletion Mutants in the Viral Replicative Cycle. Viruses. 2020; 12(2):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Rita, Nikolas Akkerman, Drayson Graves, Leandro Crisostomo, Scott Bachus, and Peter Pelka. 2020. "Characterization of Adenovirus 5 E1A Exon 1 Deletion Mutants in the Viral Replicative Cycle" Viruses 12, no. 2: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020213
APA StyleCosta, R., Akkerman, N., Graves, D., Crisostomo, L., Bachus, S., & Pelka, P. (2020). Characterization of Adenovirus 5 E1A Exon 1 Deletion Mutants in the Viral Replicative Cycle. Viruses, 12(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020213