Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and PCR Detection
2.2. Whole Genome Amplification of OsPV
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Homology Comparisons with Other Avian Parvoviruses
3.2. Sequence Analysis among OsPV, GPV, and NGPV
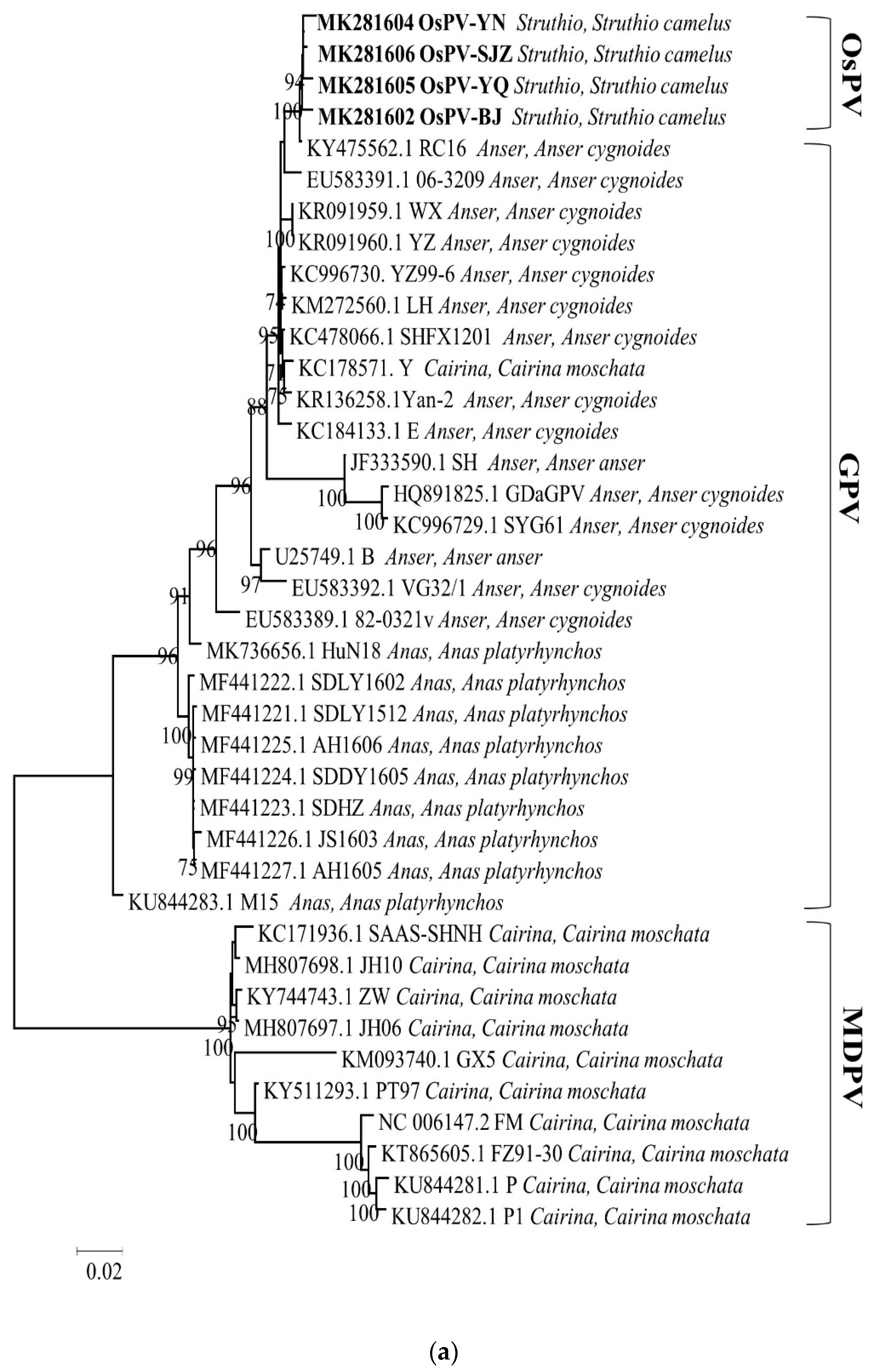
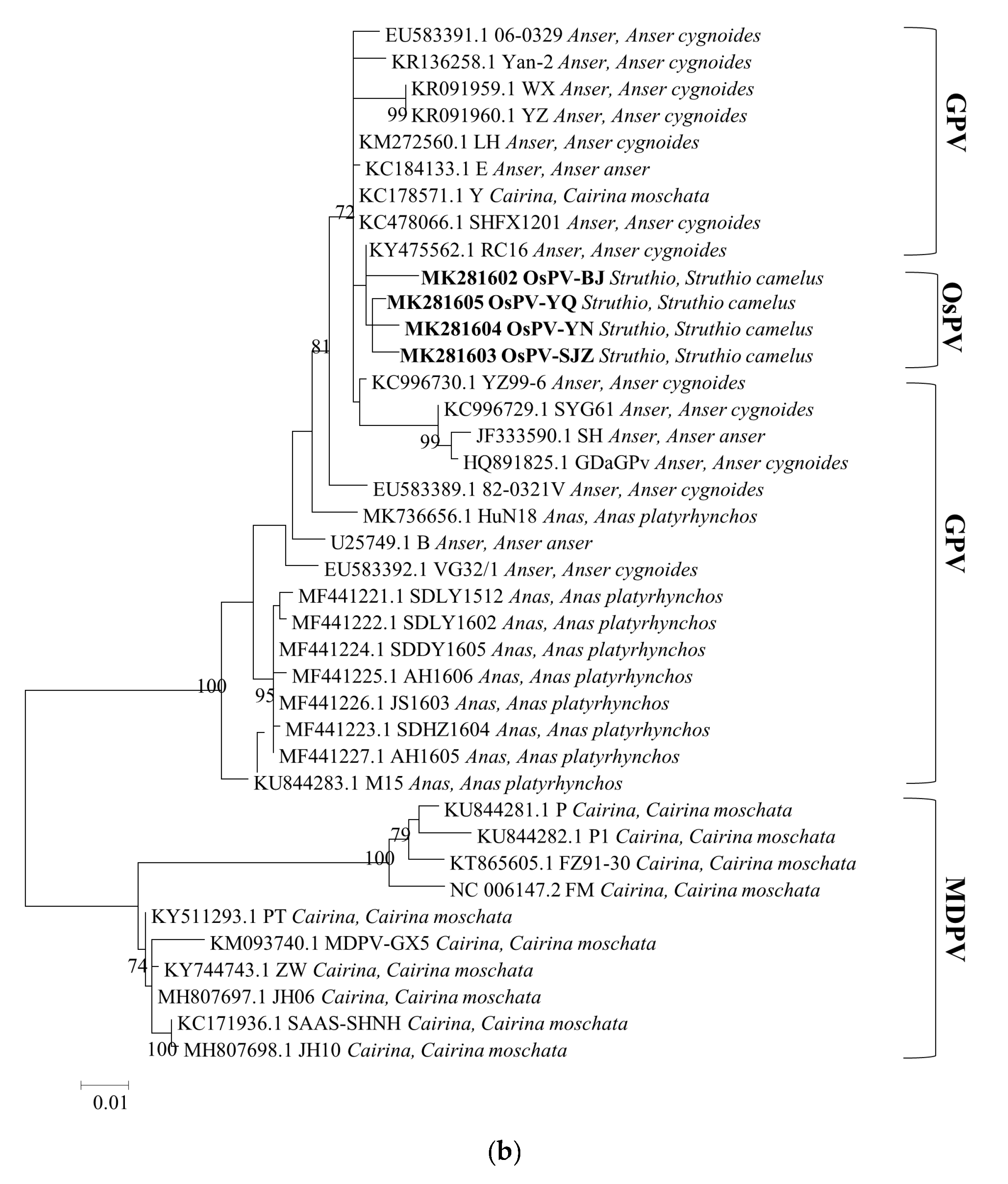
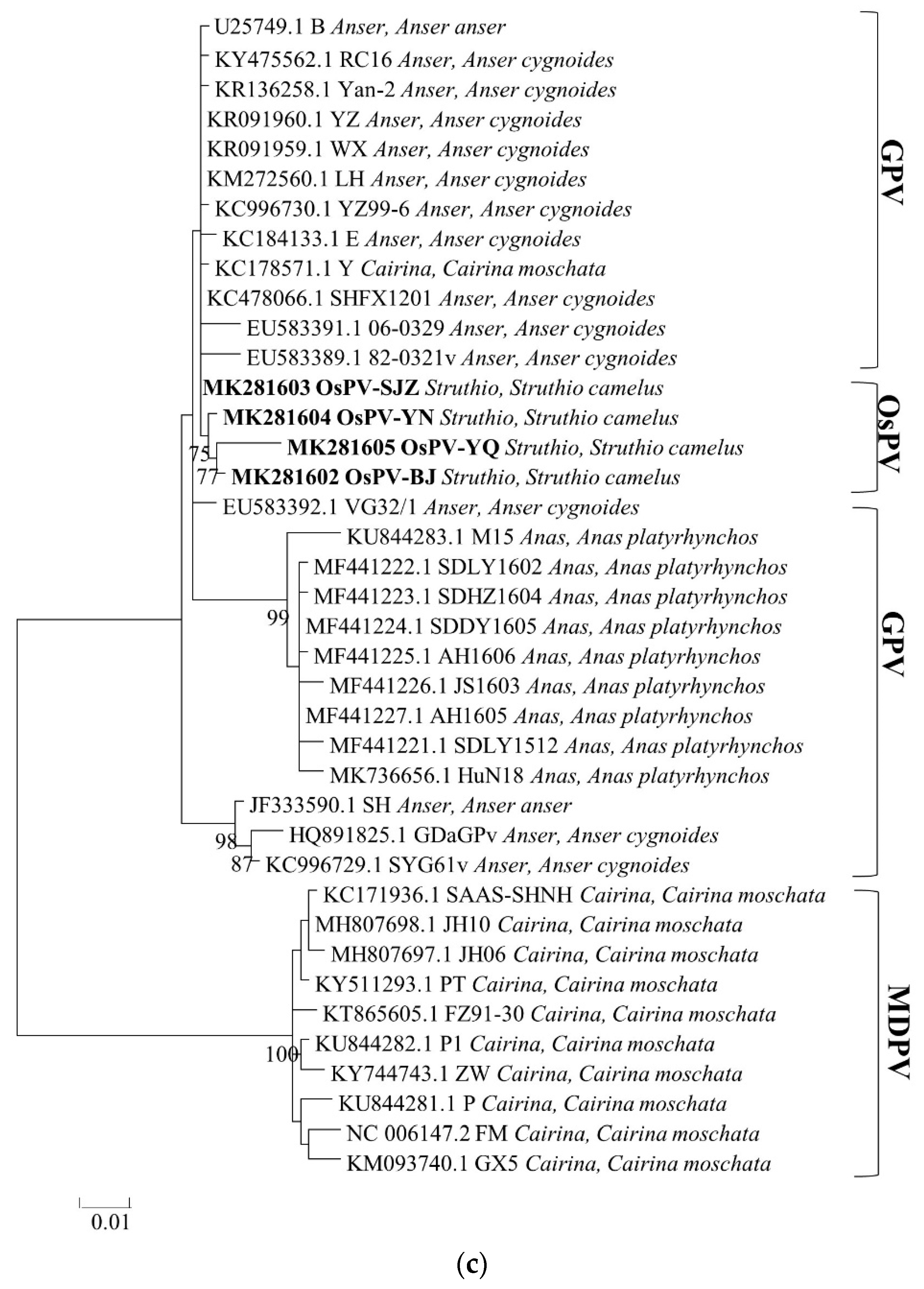
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, W.M.; Dennis, T.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Araujo, J.; Sabino-Santos, G.; Maia, F.G.M.; Acrani, G.O.; De Oliveira Torres Carrasco, A.; Romeiro, M.F.; Vieira, L.C.; et al. Novel Parvoviruses from Wild and Domestic Animals in Brazil Provide New Insights into Parvovirus Distribution and Diversity. Viruses 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapgate, S.S.; Kumanan, K.; Vijayarani, K.; Barbuddhe, S.B. Avian parvovirus: Classification, phylogeny, pathogenesis and diagnosis. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pénzes, J.J.; de Souza, W.M.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Gifford, R.J. An Ancient Lineage of Highly Divergent Parvoviruses Infects both Vertebrate and Invertebrate Hosts. Viruses 2019, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, S.; Filloux, D.; Roumagnac, P.; Bigot, D.; Gayral, P.; Martin, D.P.; Froissart, R.; Ogliastro, M. Discovery of parvovirus-related sequences in an unexpected broad range of animals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar-Kis, T.; Mato, T.; Markos, B.; Palya, V. Phylogenetic analysis of Hungarian goose parvovirus isolates and vaccine strains. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadori, Z.; Stefancsik, R.; Rauch, T.; Kisary, J. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequences of goose and muscovy duck parvoviruses indicates common ancestral origin with adeno-associated virus 2. Virology 1995, 212, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lin, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, D.; Lan, J.; Song, S.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, S. Isolation and characterization of novel goose parvovirus-related virus reveal the evolution of waterfowl parvovirus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e284–e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Genome Sequence of a Goose Parvovirus Strain Isolated from an Ill Goose in China. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Liu, P.; Chen, C.; Cheng, L.; Shi, S.; Fu, G.; Chen, H.; Fu, Q.; Huang, Y. Novel goose parvovirus in domestic Linwu sheldrakes with short beak and dwarfism syndrome, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. Molecular evidence of goose-parvovirus-related abnormal molting in Pekin ducks. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2837–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, J.; Ling, J.; Mi, Q.; Zhu, G. Retrospective investigation and molecular characteristics of the recombinant Muscovy duck parvovirus circulating in Muscovy duck flocks in China. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, S.; Cheng, X.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X.; Lin, F.; Chen, S. Recovery of Muscovy duck-origin goose parvovirus from an infectious clone containing an E-box motif (CACATG) deletion within the left terminal region. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 46, 101410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasan, S.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Parrish, C.R. Parvovirus Family Conundrum: What Makes a Killer? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2015, 2, 425–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.E.; Green, S.W.; Young, N.S. Goose parvovirus–an autonomous member of the dependovirus genus? Virology 1995, 210, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corre, S.; Galibert, M.D. Upstream stimulating factors: Highly versatile stress-responsive transcription factors. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, G. Analysis of the genome sequence of the pathogenic Muscovy duck parvovirus strain YY reveals a 14-nucleotide-pair deletion in the inverted terminal repeats. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavits, R.; Zolnai, A.; Szabo, E.; Ivanics, E.; Zarka, P.; Mato, T.; Palya, V. Comparative pathological studies on domestic geese (Anser anser domestica) and Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata) experimentally infected with parvovirus strains of goose and Muscovy duck origin. Acta Vet. Hung. 2005, 53, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Genomic and transcriptional analyses of novel parvoviruses identified from dead peafowl. Virology 2020, 539, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Place of Origin | Date | Number of Samples | Positive Rate | Total of Samples per City | Total Positive Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 2018.6 | 4 | 4/4 | 25 | 25/25 |
| 2019.6 | 15 | 15/15 | |||
| 2019.7 | 6 | 6/6 | |||
| Yunnan | 2018.6 | 2 | 2/2 | 2 | 2/2 |
| Hebei | 2018.7 | 2 | 2/2 | 30 | 29/30 |
| 2018.8 | 12 | 12/12 | |||
| 2018.8 | 9 | 9/9 | |||
| 2019.7 | 6 | 6/6 | |||
| 2019.8 | 1 | 0/1 | |||
| Shanxi | 2018.8 | 11 | 11/11 | 11 | 11/11 |
| MDPV a (FM Strain) | GPV b (SYG61v Strain) | NGPV c (SDLY1602 Strain) | GPV d (B Strain) | GPV e (RC16 Strain) | NGPV f (HuN18 Strain) | MDPV g (JH10 Strain) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| whole genome | 80.8–81.3% | 94.1–94.4% | 94.4–94.7% | 97.7–97.9% | 99.2–99.6% | 95.5–95.9% | 86.0–86.3% |
| Rep sequence | 82.3–82.9% | 93.7–94.4% | 95.9–96.4% | 98.6–99.3% | 99.0–99.9% | 95.9–96.3% | 82.6–83.2% |
| Cap sequence | 80.3–80.4% | 95.3–95.5% | 94.5–94.8% | 96.2–96.6% | 99.3–99.6% | 96.0–96.3% | 89.6–89.8% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, K.; Wang, D.; Luan, Q.; Sun, J.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Qu, X.; Cui, Y.; et al. Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus. Viruses 2020, 12, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030334
Yuan K, Wang D, Luan Q, Sun J, Gao Q, Jiang Z, Wang S, Han Y, Qu X, Cui Y, et al. Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus. Viruses. 2020; 12(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Kunpeng, Dongdong Wang, Qingdong Luan, Ju Sun, Qianwen Gao, Zhiyao Jiang, Shouchun Wang, Yijun Han, Xueting Qu, Yueying Cui, and et al. 2020. "Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus" Viruses 12, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030334
APA StyleYuan, K., Wang, D., Luan, Q., Sun, J., Gao, Q., Jiang, Z., Wang, S., Han, Y., Qu, X., Cui, Y., Qiu, S., Di, Y., Wang, X., Song, S., Wang, P., Xia, S., Yu, Y., Liu, W., & Yin, Y. (2020). Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus. Viruses, 12(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030334




