Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Generation of Stable gB-Expressing Cell Lines
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Extracellular Vesicles Isolation
2.5. Immunoblotting and Immunoprecipitation
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Flow Cytometry, Internalization and Export Assays
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. gB ELISA
2.10. Sequence Alignment
3. Results
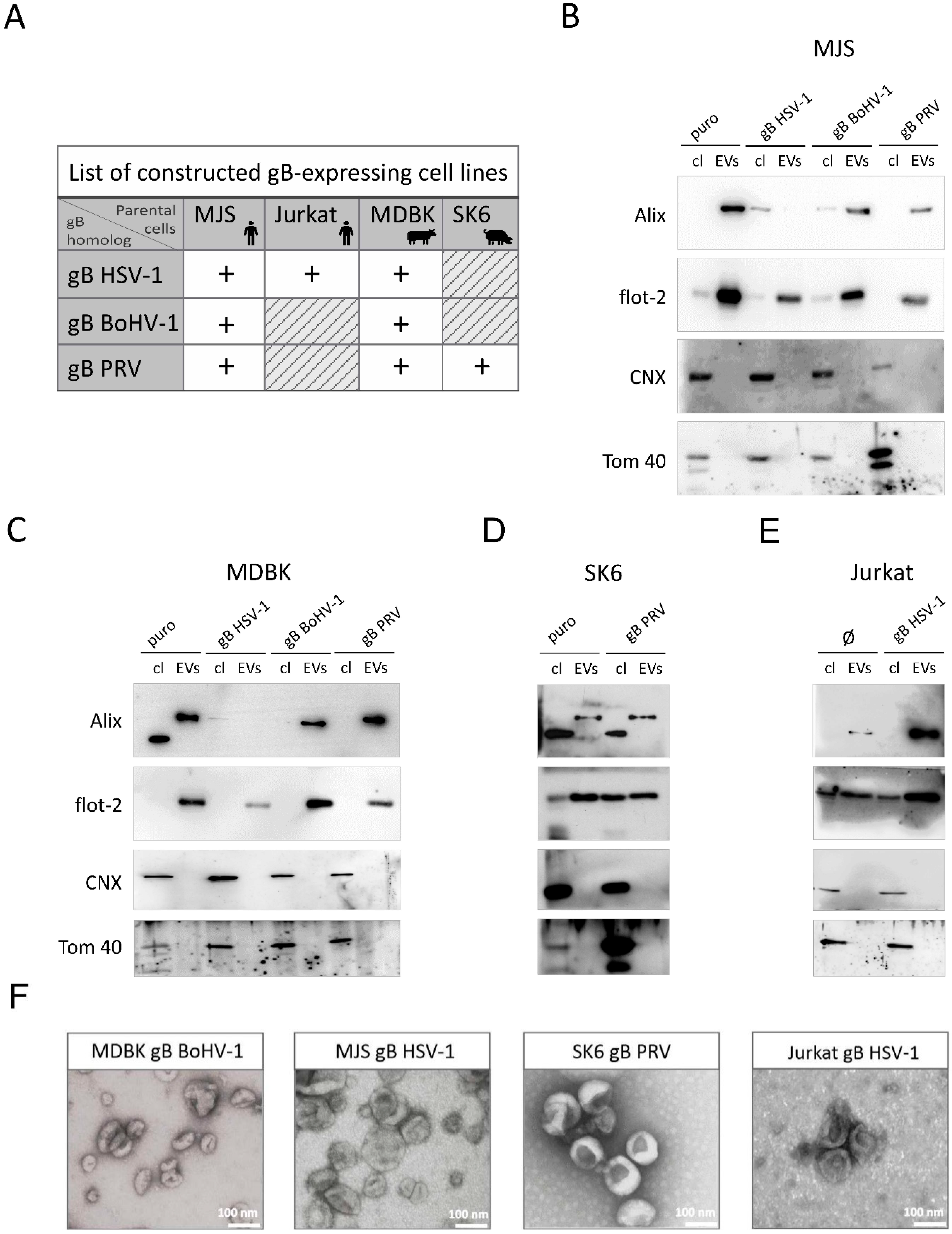
3.1. Localization of BoHV-1, PRV, and HSV-1 gB to EVs Is Conserved
3.1.1. Construction of Stable Cell Lines Expressing BoHV-1, PRV or HSV-1 gB, and Isolation of EVs by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
3.1.2. Mature HSV-1, BoHV-1 and PRV gB Localize to Extracellular Vesicles
3.2. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Affect MHC Class II-CD63 Trafficking
3.3. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Differentially Affect the Surface Expression of MHC II
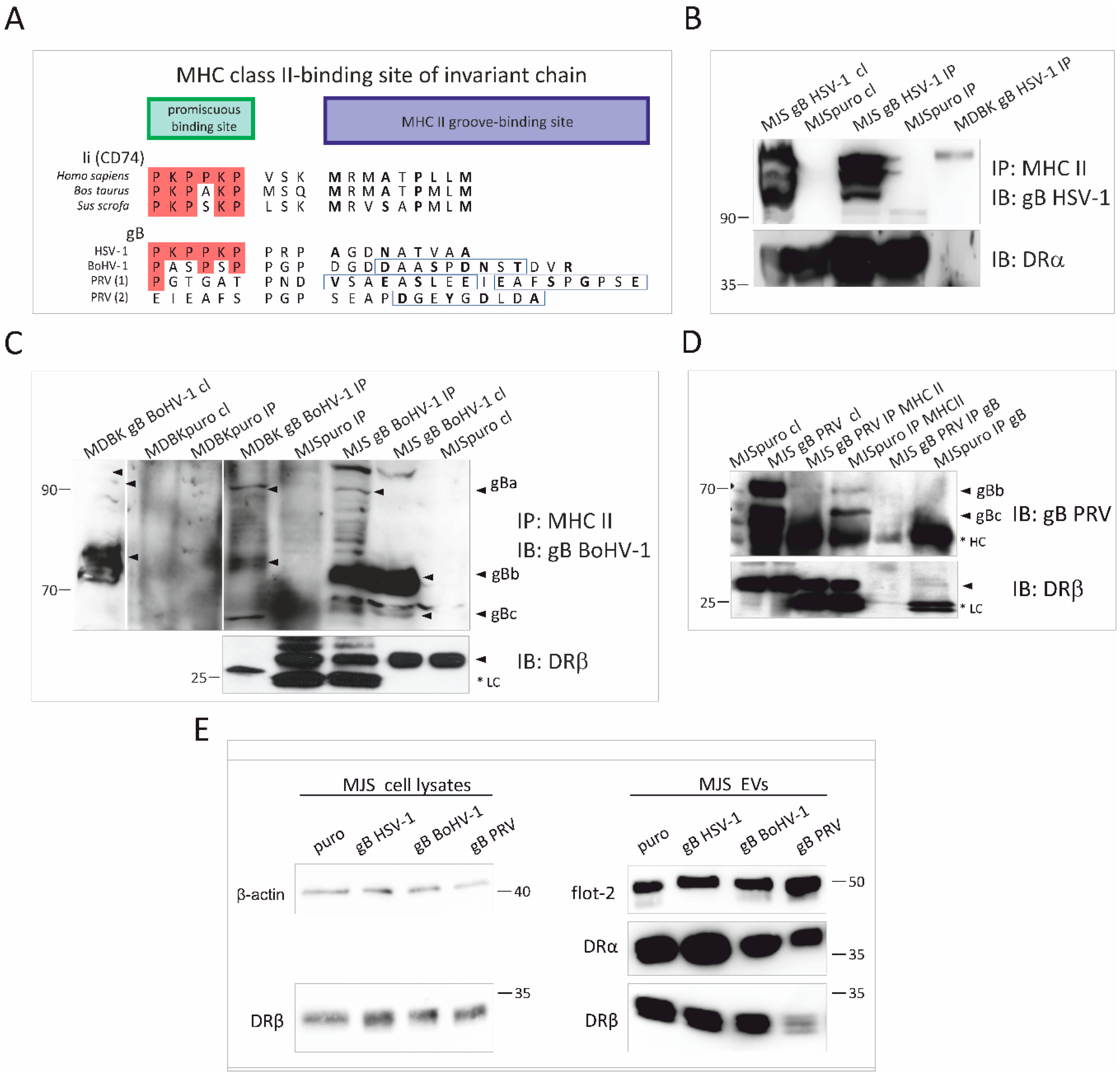
3.4. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Differentially Interact with MHC Class II Molecules and Affect the Incorporation of HLA-DR to EVs
3.5. HSV-1 gB and BoHV-1 gB Affect HLA-DR Export to the Plasma Membrane
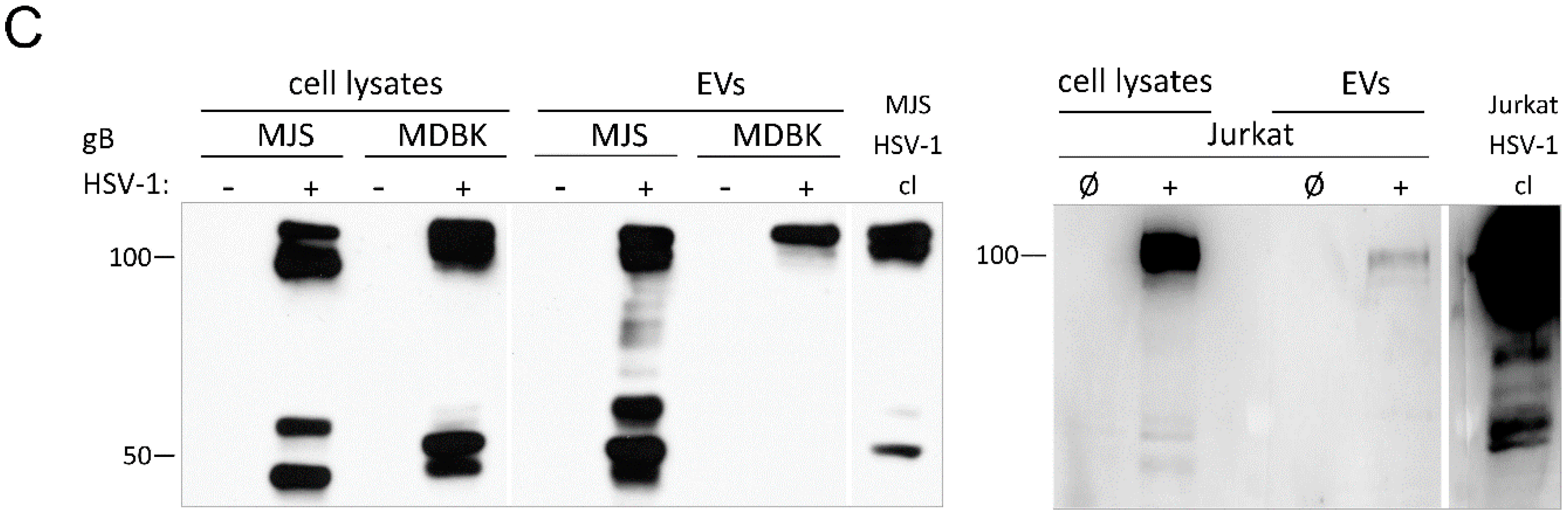
3.6. Alpherpesvirus gB Localizes to EVs Released during HSV-1, BoHV-1 and PRV Infection
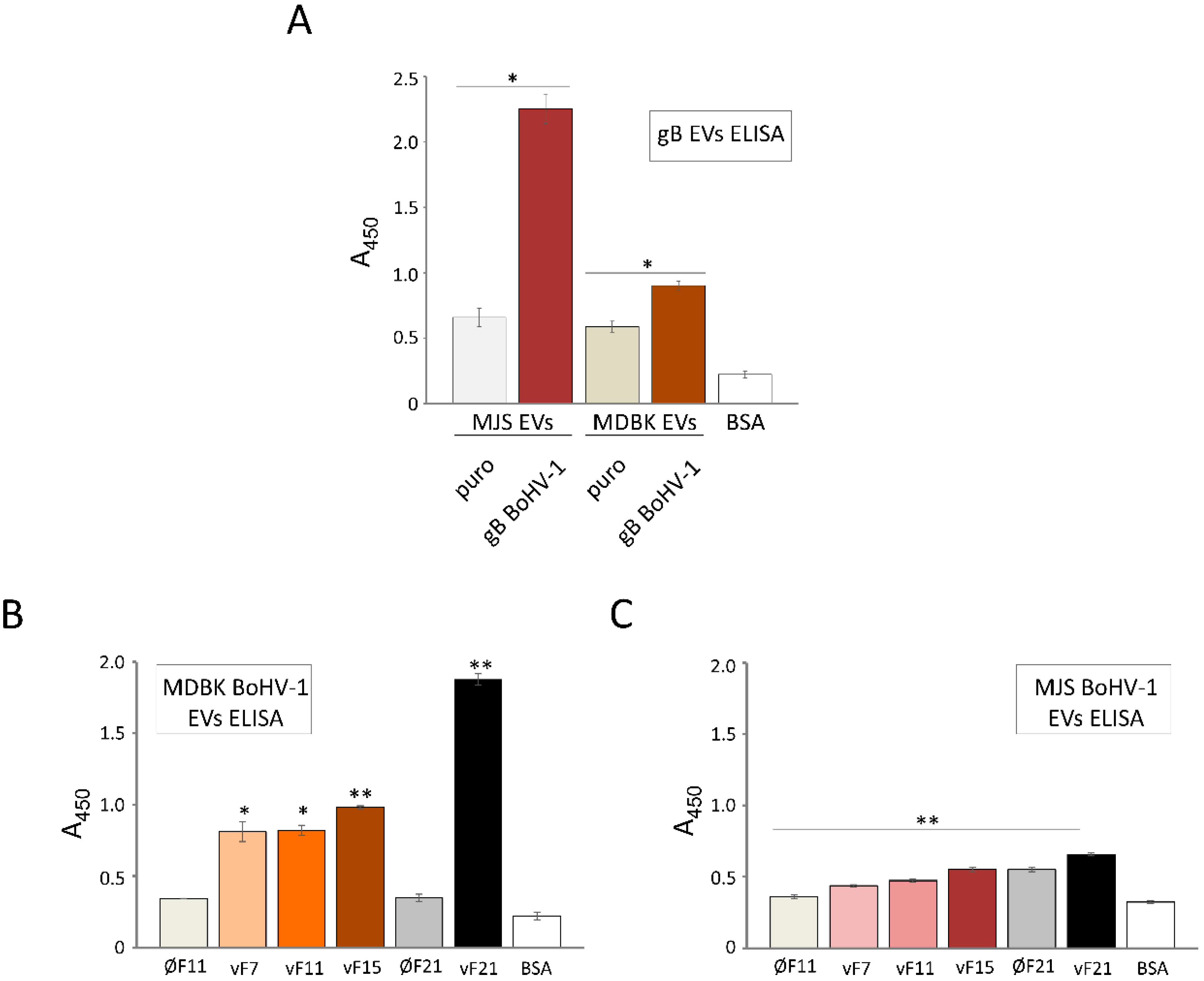
3.7. BoHV-1 gB Transferred by EVs can Bind Virus-Specific Antibodies from Animal Serum In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, J.D.; Maier, C.L.; Pober, J.S. Cytomegalovirus-infected human endothelial cells can stimulate allogeneic CD4+ memory T cells by releasing antigenic exosomes. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chugh, P.E.; Sin, S.H.; Ozgur, S.; Henry, D.H.; Menezes, P.; Griffith, J.; Eron, J.J.; Damania, B.; Dittmer, D.P. Systemically circulating viral and tumor-derived microRNAs in KSHV-associated malignancies. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yogev, O.; Henderson, S.; Hayes, M.J.; Marelli, S.S.; Ofir-Birin, Y.; Regev-Rudzki, N.; Herrero, J.; Enver, T. Herpesviruses shape tumour microenvironment through exosomal transfer of viral microRNAs. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, T.; Kalamvoki, M. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Infected Cells Block Virus Replication in Recipient Cells in a STING-Dependent Manner. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01102-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Nanbo, A.; Sun, L.; Lin, Z. Extracellular Vesicles in Epstein-Barr Virus’ Life Cycle and Pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageta, H.; Tsuchida, K. Post-translational modification and protein sorting to small extracellular vesicles including exosomes by ubiquitin and UBLs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4829–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defnes novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Understanding extracellular vesicle diversity—Current status. Expert. Rev. Proteomics 2018, 15, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Samuel, M.; Kumar, S.; Mathivanan, S. Ticket to a bubble ride: Cargo sorting into exosomes and extracellular vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 140203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanelli, L.; Buratta, S.; Tancini, B.; Sagini, K.; Delo, F.; Porcellati, S.; Emiliani, C. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infection and Transmission. Vaccines 2019, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heilingloh, C.S.; Kummer, M.; Mühl-Zürbes, P.; Drassner, C.; Daniel, C.; Klewer, M.; Steinkasserer, A.L. Particles Transmit Viral Proteins from Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Infected Mature Dendritic Cells to Uninfected Bystander Cells, Inducing CD83 Downmodulation. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11046–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mori, Y.; Koike, M.; Moriishi, E.; Kawabata, A.; Tang, H.; Oyaizu, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yamanishi, K. Human herpesvirus-6 induces MVB formation, and virus egress occurs by an exosomal release pathway. Traffic 2008, 9, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crump, C.M.; Yates, C.; Minson, T. Herpes simplex virus type 1 cytoplasmic envelopment requires functional Vps4. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7380–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharkwal, H.; Smith, C.G.; Wilson, D.W. Blocking ESCRT-mediated envelopment inhibits microtubule-dependent trafficking of alphaherpesviruses in vitro. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 14467–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zicari, S.; Arakelyan, A.; Alberto, R.; Palomino, Ñ.; Fitzgerald, W.; Vanpouille, C.; Lebedeva, A.; Schmitt, A.; Bomsel, M.; Britt, W.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus-infected cells release extracellular vesicles that carry viral surface proteins. Virology 2018, 524, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Oncogenic effects of exosomes in γ-herpesvirus-associated neoplasms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19167–19179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, S.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; McLellan, A.D.; Koch, N. The herpes simplex virus-1 encoded glycoprotein B diverts HLA-DR into the exosome pathway. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Speck, P.; Haan, K.M.; Longnecker, R. Epstein-Barr virus entry into cells. Virology 2000, 277, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanarsdall, A.L.; Ryckman, B.J.; Chase, M.C.; Johnson, D.C. Human cytomegalovirus glycoproteins gB and gH/gL mediate epithelial cell-cell fusion when expressed either in cis or in trans. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11837–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, R.J.; Atanasiu, D.; Cairns, T.M.; Gallagher, J.R.; Krummenacher, C.; Cohen, G.H. Herpes virus fusion and entry: A story with many characters. Viruses 2012, 4, 800–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazy, N.; Temme, S.; Bocuk, D.; Giesen, C.; König, A.; Temme, N.; Ziegfeld, A.; Gregers, T.F.; Bakke, O.; Lang, T.; et al. Misdirection of endosomal trafficking mediated by herpes simplex virus-encoded glycoprotein B. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heldwein, E.E.; Lou, H.; Bender, F.C.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal structure of glycoprotein B from herpes simplex virus 1. Science 2006, 313, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipińska, A.D.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Rychłowski, M.; Admiraal, P.; Rijsewijk, F.A.; Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Wiertz, E.J. Bovine herpesvirus 1 UL49.5 protein inhibits the transporter associated with antigen processing despite complex formation with glycoprotein M. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5822–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, A.K.; Lipińska, A.D.; Rohde, J.; Szewczyk, B.; Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Rziha, H.J. New baculovirus recombinants expressing Pseudorabies virus (PRV) glycoproteins protect mice against lethal challenge infection. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, J.P.; Land, H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: High titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleid Acid Res. 1990, 18, 3587–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graul, M.; Kisielnicka, E.; Rychłowski, M.; Verweij, M.C.; Tobler, K.; Ackermann, M.; Wiertz, E.J.H.J.; Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Lipińska, A.D. Transmembrane regions of bovine herpesvirus 1-encoded UL49.5 and glycoprotein M regulate complex maturation and ER-Golgi trafficking. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, E.J.K.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Regev, A.; Church, G.M. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Analysis by Western Blotting. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, L.L.; Williams, L.R.; White, C.; Forrest, C.; Zuo, J.; Rowe, M. Missing Link in Epstein-Barr Virus Immune Evasion: The BDLF3 Gene Induces Ubiquitination and Downregulation of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I (MHC-I) and MHC-II. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wubbolts, R.; Neefjes, J. Intracellular transport and peptide loading of MHC class II molecules: Regulation by chaperones and motors. Immunol. Rev. 1999, 172, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwart, W.; Peperzak, V.; de Vries, E.; Keller, A.M.; van der Horst, G.; Veraar, E.A.; Geumann, U.; Janssen, H.; Janssen, L.; Naik, S.H.; et al. The invariant chain transports TNF family member CD70 to MHC class II compartments in dendritic cells. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3817–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Lith, M.; van Ham, M.; Griekspoor, A.; Tjin, E.; Verwoerd, D.; Calafat, J.; Janssen, H.; Reits, E.; Pastoors, L.; Neefjes, J. Regulation of MHC Class II Antigen Presentation by Sorting of Recycling HLA-DM/DO and Class II within the Multivesicular Body. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Rychlowski, M.; van Leeuwen, D.; Rijsewijk, F.A.; Ressing, M.E.; Neefjes, J.J.; Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Wiertz, E.J. Bovine herpesvirus 1 interferes with TAP-dependent peptide transport and intracellular trafficking of MHC class I molecules in human cells. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 2023–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraj, C.; Eidmann, S.; Hariharan, M.J.; Sur, J.H.; Perry, G.A.; Srikumaran, S. Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Downregulates the Expression of Bovine MHC Class I Molecules. Viral Immunol. 1997, 10, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Whiteside, T.L.; Reichert, T.E. Challenges in Exosome Isolation and Analysis in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Gálvez-Montón, C.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Roura, S.; Borràs, F.E. Extracellular vesicle isolation methods: Rising impact of size-exclusion chromatography. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2369–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calistri, A.; Sette, P.; Salata, C.; Cancellotti, E.; Forghieri, C.; Comin, A.; Göttlinger, H.; Campadelli-Fiume, G.; Palù, G.; Parolin, C. Intracellular Trafficking and Maturation of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 gB and Virus Egress Require Functional Biogenesis of Multivesicular Bodies. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11468–11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babiuk, L.A. Synthesis and processing of bovine herpesvirus I glycoproteins. J. Virol. 1986, 59, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, D.R.; Zamb, T.; Parker, M.D.; Babiuk, L.A.; Lawman, M.J. Expression of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins gI and glll in transfected murine cells. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4239–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfer, U.; Kruft, V.; Sawitzky, D.; Hampl, H.; Wittmann-Liebold, B.; Habermehl, K.O. Processing of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gII. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3122–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagdonaite, I.; Nordén, R.; Joshi, H.J.; Dabelsteen, S.; Nyström, K.; Vakhrushev, S.Y.; Olofsson, S.; Wandall, H.H. A Strategy for O-Glycoproteomics of Enveloped Viruses—The O-Glycoproteome of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenske, E.A.; Bratton, M.W.; Courtney, R.J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J. Virol. 1982, 44, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atanasiu, D.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Cairns, T.M.; Reilly, B.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Bimolecular complementation reveals that glycoproteins gB and gH/gL of herpes simplex virus interact with each other during cell fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18718–18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoorn, T.; Paul, P.; Janssen, L.; Janssen, H.; Neefjes, J. Dynamics within tetraspanin pairs affect MHC class II expression. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weingartl, H.M.; Sabara, M.; Pasick, J.; Van Moorlehem, E.; Babiuk, L. Continuous porcine cell lines developed from alveolar macrophages: Partial characterization and virus susceptibility. J. Virol. Methods 2002, 104, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chanh Le, Q.; Le, T.M.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, W.I.; Hong, K.; Song, H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, C. Analysis of peptide-SLA binding by establishing immortalized porcine alveolar macrophage cells with different SLA class II haplotypes. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Deschamps, T. Extracellular vesicles during herpes simplex virus type 1 infection: An inquire. Virol. J. 2013, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, K.; Lipińska, A.D.; (Department of Virus Molecular Biology, University of Gdańsk, Gdańsk, Poland). Pseudorabies virus, strain NIA-3, replicates in human melanoma MJS cells with the kinetics similar to BoHV-1 [35], producing progeny 4 log-lower than in swine kidney cells. Personal communication, unpublished obvervation. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.Y.; Park, K.S.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Moon, H.G.; Jang, S.C.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S. Therapeutic effects of autologous tumor-derived nanovesicles on melanoma growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.H.; Gu, B.; Person, S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rauh, I.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Pseudorabies virus glycoproteins gII and gp50 are essential for virus penetration. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 5348–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miethke, A.; Keil, G.M.; Weiland, F.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Unidirectional complementation between glycoprotein B homologues ofpse udorabies virus and bovine herpesvirus 1 is determined by the carboxyterminal part of the molecule. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, S.; Vitiello, M.; D’Isanto, M.; Falanga, A.; Cantisani, M.; Browne, H.; Pedone, C.; Galdiero, M. The identification and characterization of fusogenic domains in herpes virus glycoprotein B molecules. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallbracht, M.; Brun, D.; Tassinari, M.; Vaney, M.C.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Haouz, A.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Rey, F.A.; et al. Structure-Function Dissection of Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein B Fusion Loops. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01203-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, G.V.; Letchworth, G.J. Temporal control of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein synthesis. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3292–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, S.N.; Jones, C.M.; Chen, W.; Kawaoka, Y.; Castrucci, M.R.; Heath, W.R.; Carbone, F.R. The early expression of glycoprotein B from herpes simplex virus can be detected by antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clase, A.C.; Lyman, M.G.; del Rio, T.; Randall, J.A.; Calton, C.M.; Enquist, L.W.; Banfield, B.W. The pseudorabies virus Us2 protein, a virion tegument component, is prenylated in infected cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12285–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, T.; Arii, J.; Suenaga, T.; Wang, J.; Kogure, A.; Uehori, J.; Arase, N.; Shiratori, I.; Tanaka, S.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. PILRalpha is a herpes simplex virus-1 entry coreceptor that associates with glycoprotein B. Cell 2008, 132, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; Dierick, E.; Klupp, B.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, M.; Favoreel, H.W. Expression of the pseudorabies virus gB glycoprotein triggers NK cell cytotoxicity and increases binding of the activating NK cell receptor PILRβ. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02107-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heineman, T.C.; Connolly, P.; Hall, S.L.; Assefa, D. Conserved cytoplasmic domain sequences mediate the ER export of VZV, HSV-1, and HCMV gB. Virology 2004, 328, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beitia Ortiz de Zarate, I.; Kaelin, K.; Rozenberg, F. Effects of mutations in the mytoplasmic momain of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein B on intracellular transport and infectivity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verweij, F.J.; de Heus, C.; Kroeze, S.; Cai, H.; Kieff, E.; Piersma, S.R.; Jimenez, C.R.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Pegtel, D.M. Exosomal sorting of the viral oncoprotein LMP1 is restrained by TRAF2 association at signalling endosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Nkosi, D.; Conlon, M.M.; York, S.B.; Liu, X.; Tremblay, D.C.; Meckes, D.G., Jr. CD63 regulates Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 exosomal packaging, enhancement of vesicle production, and noncanonical NF-κB signaling. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02251-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Conlon, M.M.; Rider, M.A.; Brownstein, N.C.; Meckes, D.G., Jr. Nanoparticle analysis sheds budding insights into genetic drivers of extracellular vesicle biogenesis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baietti, M.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mortier, E.; Melchior, A.; Degeest, G.; Geeraerts, A.; Ivarsson, Y.; Depoortere, F.; Coomans, C.; Vermeiren, E.; et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Madara, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Ruthel, G.; Freedman, B.D.; Harty, R.N. ALIX rescues budding of a double PTAP/PPEY L-domain deletion mutant of Ebola VP40: A role for ALIX in Ebola virus egress. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S138–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogrammatzis, C.; Deschamps, T.; Kalamvoki, M. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles during herpes simplex virus 1 infection: Role of the CD63 tetraspanin. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01850-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchings, D.L.; Babiuk, L.A. Lymphocyte proliferative responses to separated bovine herpesvirus 1 proteins in immune cattle. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 5114–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mettenleiter, T. Molecular biology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky’s disease) virus. Comp. Immunol. Microb. Infect. Dis. 1991, 14, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacklaws, B.A.; Krishna, S.; Minson, A.C.; Nash, A.A. Immunogenicity of herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoproteins expressed in vaccinia virus recombinants. Virology 1990, 177, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte’t Hoen, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Raab-Traub, N. Microvesicles and Viral Infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12844–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nehls, J.; Businger, R.; Hoffmann, M.; Brinkmann, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Maurer, B.; Schönfeld, C.; Kramer, D.; Hailfinger, S.; et al. Release of immunomodulatory Ebola virus glycoprotein-containing microvesicles is suppressed by tetherin in a species-specific manner. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1841–1853.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battke, C.; Ruiss, R.; Welsch, U.; Wimberger, P.; Lang, S.; Jochum, S.; Zeidler, R. Tumour exosomes inhibit binding of tumour-reactive antibodies to tumour cells and reduce ADCC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiu, I.; Narayanasamy, P.; Dash, P.K.; Zhang, W.; Gendelman, H.E. Biochemical and biologic characterization of exosomes and microvesicles as facilitators of HIV-1 infection in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, G.; Roizman, B. Herpes simplex virus 1 microRNA miR-H28 exported to uninfected cells in exosomes restricts cell-to-cell virus spread by inducing gamma interferon mRNA. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01005-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievers, E.; Neumann, J.; Raftery, M.; Schönrich, G. Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Koch, N. Glycoprotein B from strain 17 of herpes simplex virus type I contains an invariant chain homologous sequence that binds to MHC class II molecules. Immunology. 2002, 107, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Koch, N. Herpes simplex virus type 1 targets the MHC class II processing pathway for immune evasion. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3075–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, F.; Hu, X.; Tan, F.; Qi, J.; Peng, R.; Wang, M.; Chai, Y.; Hao, L.; Deng, J.; et al. Two classes of protective antibodies against Pseudorabies virus variant glycoprotein B: Implications for vaccine design. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trgovcich, J.; Johnson, D.; Roizman, B. Cell surface major histocompatibility complex class II proteins are regulated by the products of the γ134.5 and UL41 genes of herpes simplex virus 1. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6974–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barcy, S.; Lawrence, C.J. Herpes simplex inhibits the capacity of lymphoblastoid B cell lines to stimulate CD4+ T cells. Immunology 2001, 166, 6242–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinkley, S.; Ambagala, A.P.; Jones, C.J.; Srikumaran, S. A vhs-like activity of bovine herpesvirus-1. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 2027–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgadi, M.M.; Hayes, C.E.; Smiley, J.R. The herpes simplexvirus vhs protein induces endoribonucleolytic cleavage of targetRNAs in cell extracts. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7153–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Cell Line | Compared Channels | Pearson’s Correlation ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| MJSpuro | gB-CD63 | nd |
| gB-DRα | nd | |
| CD63-DRα | 0.64 ± 0.02 | |
| MJS gB HSV-1 | gB-CD63 | 0.84 ± 0.02 |
| gB-DRα | 0.64 ± 0.04 | |
| CD63-DRα | 0.71 ± 0.07 | |
| MJS gB BoHV-1 | gB-CD63 | 0.92 ± 0.01 |
| gB-DRα | 0.68 ± 0.08 | |
| CD63-DRα | 0.76 ± 0.07 | |
| MJS gB PRV | gB-CD63 | 0.94 ± 0.01 |
| gB-DRα | 0.70 ± 0.02 | |
| CD63-DRα | 0.74 ± 0.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grabowska, K.; Wąchalska, M.; Graul, M.; Rychłowski, M.; Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Lipińska, A.D. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules. Viruses 2020, 12, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040429
Grabowska K, Wąchalska M, Graul M, Rychłowski M, Bieńkowska-Szewczyk K, Lipińska AD. Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040429
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrabowska, Kinga, Magda Wąchalska, Małgorzata Graul, Michał Rychłowski, Krystyna Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, and Andrea D. Lipińska. 2020. "Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules" Viruses 12, no. 4: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040429
APA StyleGrabowska, K., Wąchalska, M., Graul, M., Rychłowski, M., Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K., & Lipińska, A. D. (2020). Alphaherpesvirus gB Homologs Are Targeted to Extracellular Vesicles, but They Differentially Affect MHC Class II Molecules. Viruses, 12(4), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040429






