West Nile Virus Epidemic in Germany Triggered by Epizootic Emergence, 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WNV Screening of Birds, Horses and Mosquitoes
2.2. Risk of WNV Transmission
2.3. Data Sets and Genome Characterization of WNV
2.4. Evolutionary Dynamics and Phylogeography of German WNV
3. Results
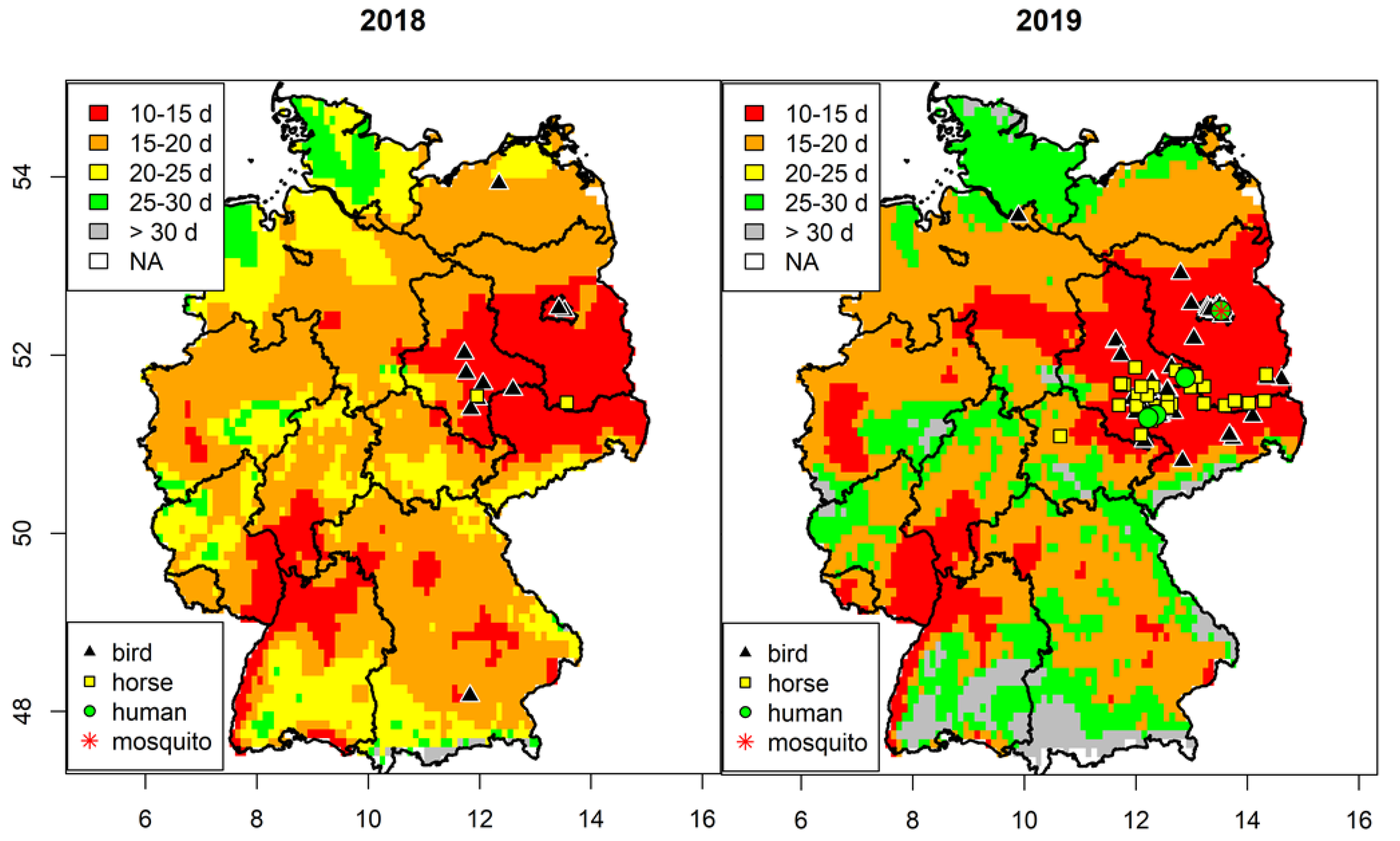
3.1. Spatial Analysis of West Nile Virus Circulation
3.2. Autochthonous Human WNV Cases
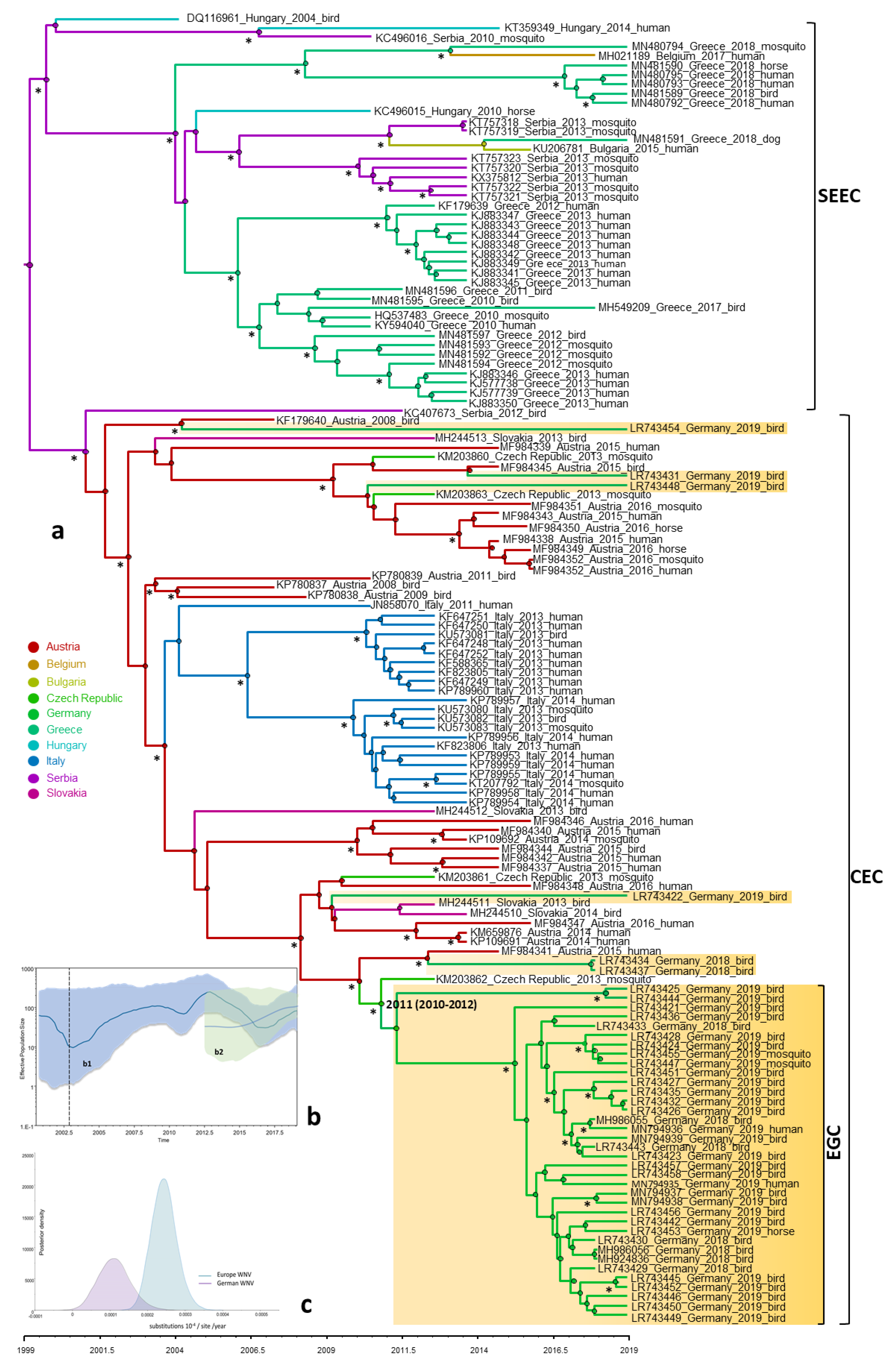
3.3. Genetic Characterization of German WNV
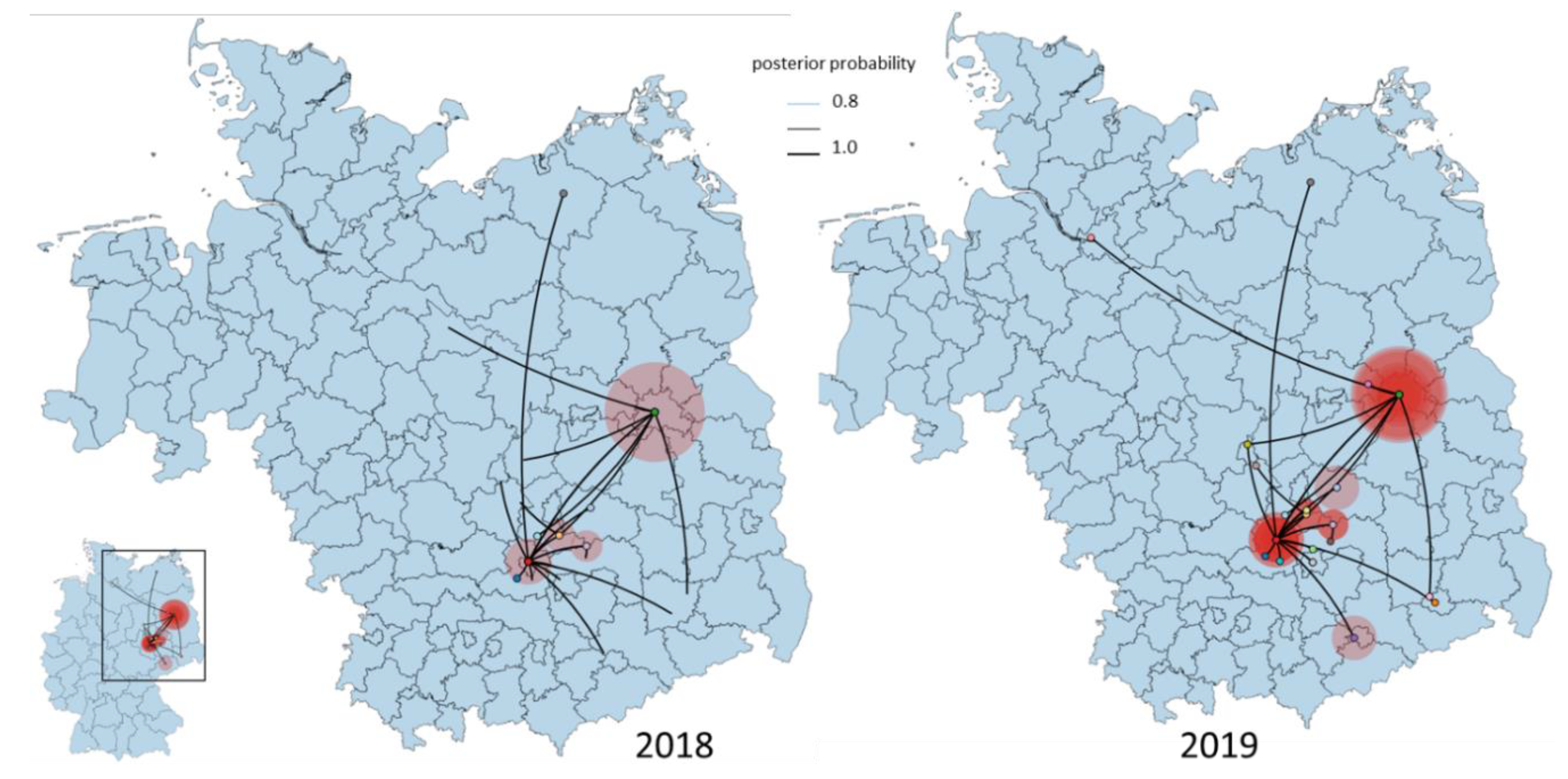
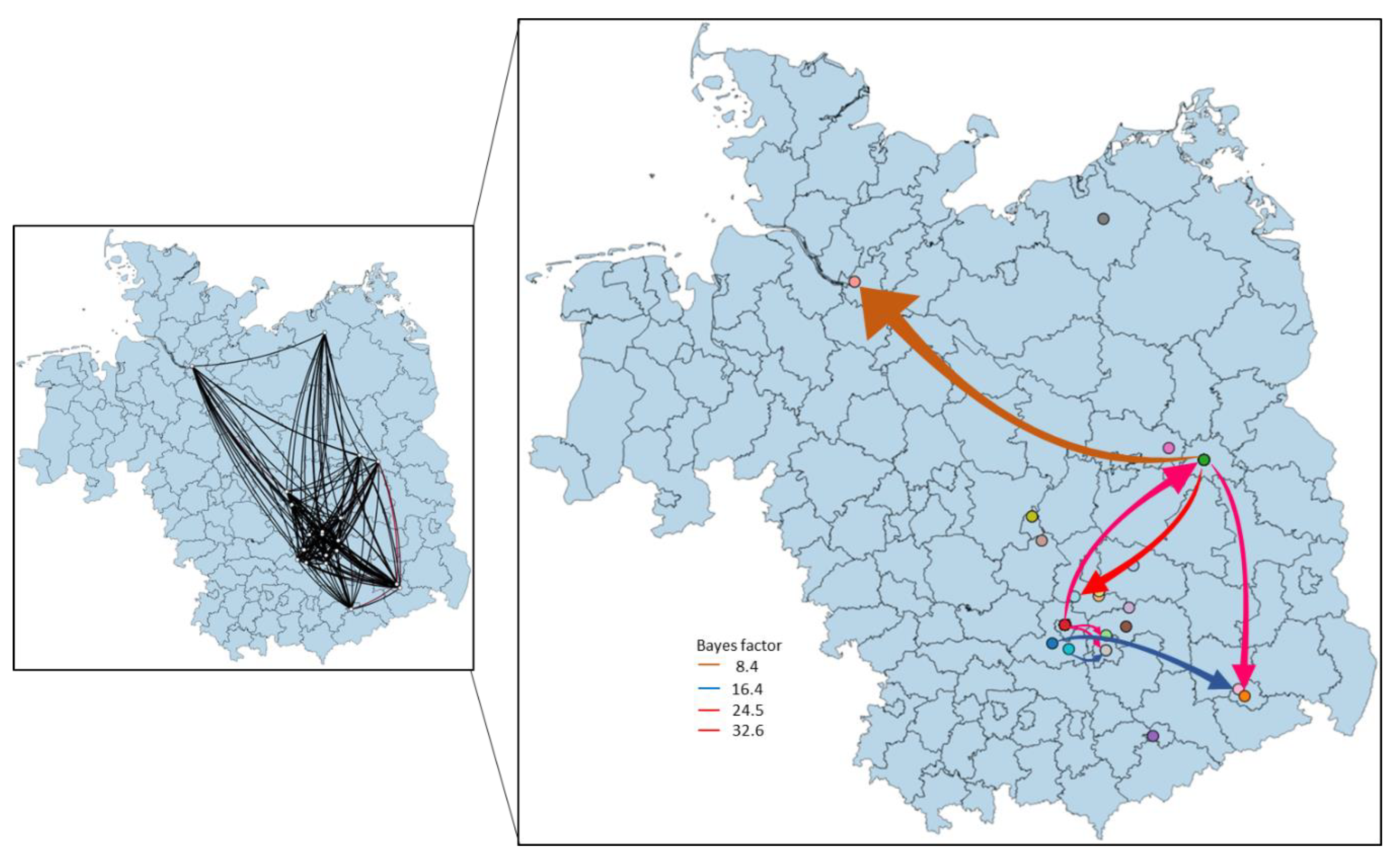
3.4. Phylogeny, Phylogeography and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of WNV
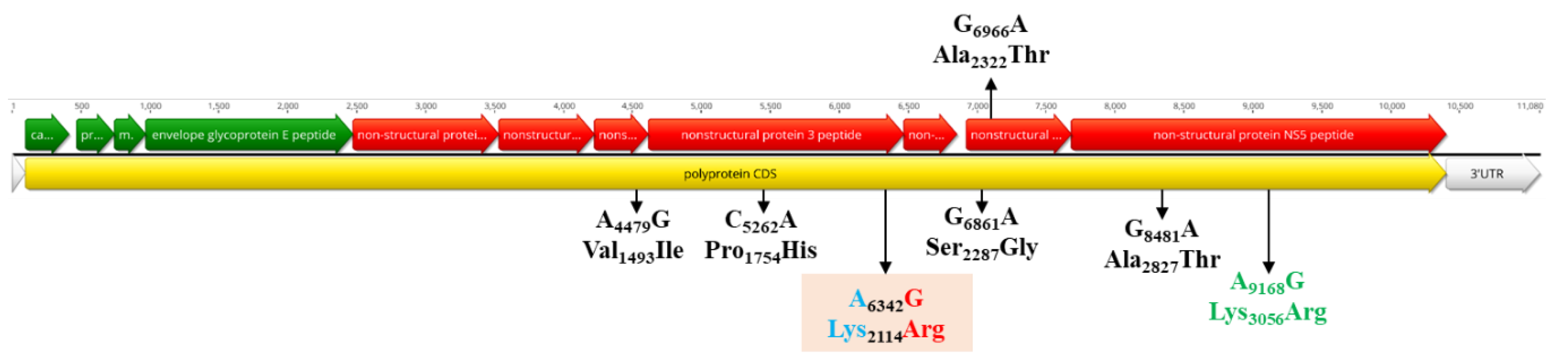
3.5. Population Dynamics, Protein Changes and Analysis of Selection Pressure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kramer, L.D.; Styer, L.M.; Ebel, G.D. A global perspective on the epidemiology of West Nile virus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.W.; Shing, E.; Nelder, M.; Sander, B. Epidemiologic and clinical parameters of West Nile virus infections in humans: A scoping review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Foster, G.A.; Dodd, R.Y.; Petersen, L.R.; Stramer, S.L. West Nile fever characteristics among viremic persons identified through blood donor screening. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostashari, F.; Bunning, M.L.; Kitsutani, P.T.; Singer, D.A.; Nash, D.; Cooper, M.J.; Katz, N.; Liljebjelke, K.A.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Fine, A.D.; et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: Results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet 2001, 358, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile Virus Disease Cases and Deaths Reported to CDC by Year and Clinical Presentation, 1999–2018. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/statsmaps/cumMapsData.html (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Petersen, L.R. Epidemiology of West Nile virus in the United States: Implications for arbovirology and public health. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Historical Data by Year—West Nile Fever Seasonal Surveillance. 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/west-nile-fever/surveillance-and-disease-data/historical (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Börstler, J.; Engel, D.; Petersen, M.; Poggensee, C.; Jansen, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Lühken, R. Surveillance of maternal antibodies against West Nile virus in chicken eggs in South-West Germany. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2016, 21, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Sieg, M.; Fischer, D.; Keller, M.; Eiden, M.; Reuschel, M.; Schmidt, V.; Schwehn, R.; Rinder, M.; Urbaniak, S.; et al. Evidence for West Nile virus and Usutu virus infections in wild and resident birds in Germany, 2017 and 2018. Viruses 2019, 11, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuch, D.; Schäfer, M.; Eiden, M.; Heym, E.; Ziegler, U.; Walther, D.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Keller, M.; Groschup, M.; Kampen, H. Detection of Usutu, Sindbis, and Batai Viruses in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) collected in Germany, 2011–2016. Viruses 2018, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Fischer, D.; Eiden, M.; Fast, C.; Reuschel, M.; Müller, K.; Rinder, M.; Urbaniak, S.; Brandes, F.; Schwehn, R.; et al. West Nile virus and Usutu virus monitoring of wild birds in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, U.; Angenvoort, J.; Klaus, C.; Nagel-Kohl, U.; Sauerwald, C.; Thalheim, S.; Horner, S.; Braun, B.; Kenklies, S.; Tyczka, J.; et al. Use of competition ELISA for monitoring of West Nile virus infections in horses in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2013, 10, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, U.; Lühken, R.; Keller, M.; Cadar, D.; van der Grinten, E.; Michel, F.; Albrecht, K.; Eiden, M.; Rinder, M.; Lachmann, L.; et al. West Nile virus epizootic in Germany, 2018. Antiviral Res. 2019, 162, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, S.; Heitmann, A.; Lühken, R.; Leggewie, M.; Helms, M.; Badusche, M.; Rossini, G.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tannich, E. Culex torrentium: A potent vector for the transmission of West Nile virus in Central Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Jöst, H.; Ziegler, U.; Eiden, M.; Höper, D.; Emmerich, P.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Ehichioya, D.U.; Czajka, C.; Gabriel, M.; et al. Epizootic emergence of Usutu virus in wild and captive birds in Germany. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden, M.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Ziegler, U.; Groschup, M.H. Two new real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays with unique target sites for the specific and sensitive detection of lineages 1 and 2 West Nile Virus Strains. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöst, H.; Bialonski, A.; Maus, D.; Sambri, V.; Eiden, M.; Groschup, M.H.; Günther, S.; Becker, N.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Isolation of Usutu virus in Germany. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kampen, H.; Holicki, C.M.; Ziegler, U.; Groschup, M.; Tews, B.A.; Werner, D. West Nile virus mosquito vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) in Germany. Viruses 2020. (in review). [Google Scholar]
- Reisen, W.K.; Niu, T.; Gaff, H.D.; Barker, C.M.; Le Menach, A.; Hartley, D.M. Effects of temperature on emergence and seasonality of West Nile virus in California. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 884–894. [Google Scholar]
- Cornes, R.C.; van der Schrier, G.; van den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Jones, P.D. An ensemble version of the E-OBS temperature and precipitation data sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019.
- Grolemund, G.; Wickham, H. Dates and times made easy with lubridate. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 40, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling, R Package Version 2.9-5; 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Wylezich, C.; Papa, A.; Beer, M.; Höper, D. A Versatile sample processing workflow for metagenomic pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. popart: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koraka, P.; Barzon, L.; Martina, B.E. West Nile Virus Infections in (European) Birds. J Neuroinfect Dis 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, T.; Ferenczi, E.; Erdélyi, K.; Kutasi, O.; Csörgő, T.; Seidel, B.; Weissenböck, H.; Brugger, K.; Bán, E.; Nowotny, N. Explosive spread of a neuroinvasive lineage 2 West Nile virus in Central Europe, 2008/2009. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf, I.; Betášová, L.; Blažejová, H.; Venclíková, K.; Straková, P.; Šebesta, O.; Mendel, J.; Bakonyi, T.; Schaffner, F.; Nowotny, N.; et al. West Nile virus in overwintering mosquitoes, central Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heym, E.C.; Kampen, H.; Krone, O.; Schäfer, M.; Werner, D. Molecular detection of vector-borne pathogens from mosquitoes collected in two zoological gardens in Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, U.; Fischer, D.; Eiden, M.; Reuschel, M.; Rinder, M.; Müller, K.; Schwehn, R.; Schmidt, V.; Groschup, M.H.; Keller, M. Sindbis virus—A wild bird associated zoonotic arbovirus circulates in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Añez, G.; Grinev, A.; Chancey, C.; Ball, C.; Akolkar, N.; Land, K.J.; Winkelman, V.; Stramer, S.L.; Kramer, L.D.; Rios, M. Evolutionary dynamics of West Nile virus in the United States, 1999–2011: Phylogeny, selection pressure and evolutionary time-scale analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Docherty, D.E.; McLean, R.G.; Zody, M.C.; Qu, J.; Yang, X.; Birren, B.W.; Malboeuf, C.M.; Newman, R.M.; et al. Fluid spatial dynamics of West Nile virus in the United States: Rapid spread in a permissive host environment. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, D.; Jöst, H.; Wink, M.; Börstler, J.; Bosch, S.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Jöst, A.; Czajka, C.; Lühken, R.; Ziegler, U.; et al. Reconstruction of the evolutionary history and dispersal of Usutu virus, a neglected emerging arbovirus in Europe and Africa. mBio 2016, 7, e01938-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. Patterns of intra- and interhost nonsynonymous variation reveal strong purifying selection in dengue virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11296–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.M.; Vossbrinck, C.R.; Andreadis, T.G.; Anderson, J.F.; Pesko, K.N.; Newman, R.M.; Lennon, N.J.; Birren, B.W.; Ebel, G.D.; Henn, M.R. Molecular evolution of West Nile virus in a northern temperate region: Connecticut, USA 1999–2008. Virology 2011, 417, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, A.C.; Huang, C.Y.-H.; Langevin, S.A.; Kinney, R.M.; Bowen, R.A.; Ramey, W.N.; Panella, N.A.; Holmes, E.C.; Powers, A.M.; Miller, B.R. A single positively selected West Nile viral mutation confers increased virogenesis in American crows. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Federal State | Birds (2018) | Horses (2018) | Birds (2019) | Horses (2019) | Humans (2019) | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bavaria (BY) | 2 (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (2) |
| Berlin (BE) | 3 (1) | 0 | 33 (6) | 0 | 1 (1) | 37 (8) |
| Brandenburg (BB) | 0 | 1 | 6 (3) | 7 | 0 | 14 (3) |
| Hamburg (HH) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) |
| Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (MV) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Saxony (SN) | 1 (1) | 0 | 21 (8) | 9 (1) | 3 | 34 (10) |
| Saxony-Anhalt (ST) | 5 (2) | 1 | 15 (10) | 19 | 1 (1) | 41 (13) |
| Thuringia (TH) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Sum | 12 (6) | 2 | 76 (28) | 36 (1) | 5 (2) | 131 (37) |
| Bird Species | Scientific Name | Housing | Number of WNV-Infected Birds | Affected Federal States * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian Blackbird | Turdus merula | wild | 3 | ST, MV |
| Andean Flamingo | Phoenicoparrus andinus | captive | 1 | BE |
| Great Grey Owl | Strix nebulosa | captive | 6 | SN, ST, BY |
| Unspecified buzzard | Buteo sp. | wild | 1 | ST |
| Blue Tit | Parus caeruleus | wild | 3 | SN, ST |
| Chilean Flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | captive | 6 | BE, SN |
| Eurasian Jay | Garrulus glandarius | wild | 1 | BB |
| Coconut Lorikeet | Trichoglossus haematodus | captive | 1 | ST |
| Scarlet-chested Parrot | Neophema splendida | captive | 1 | SN |
| Eurasian Golden Plover | Pluvialis apricaria | wild | 1 | SN |
| Northern Goshawk | Accipiter gentilis | wild/captive | 19 | BB, BE, SN, ST |
| House Sparrow | Passer domesticus | wild | 4 | SN, ST |
| Dunnock | Prunella modularis | wild | 1 | HH |
| Humboldt-Penguin | Spheniscus humboldti | captive | 1 | BB |
| Inka-Tern | Larosterna inca | captive | 1 | BE |
| Black-tailed Gull | Larus crassirostris | captive | 8 | BE |
| Kagu | Rhynochetos jubatus | captive | 1 | BE |
| Domestic Canary | Serinus canaria forma domestica | captive | 2 | SN |
| Great Tit | Parus major | wild | 3 | SN |
| American Flamingo | Phoenicopterus ruber | captive | 3 | BE |
| Hooded Crow | Corvus corone cornix | wild | 1 | BE |
| Unspecified pelican | Pelecanus sp. | captive | 1 | ST |
| Javan Pond Heron | Ardeola speciosa | captive | 1 | BE |
| Common Wood Pigeon | Columba palumbus | wild | 1 | BE |
| Snowy Owl | Bubo scandiacus | captive | 8 | BE, ST |
| Chinese Merganser | Mergus squamatus | captive | 1 | BE |
| Swift Parrot | Lathamus discolor | captive | 1 | SN |
| Little Owl | Athene noctua | wild | 2 | BB |
| European Goldfinch | Carduelis carduelis | captive | 1 | SN |
| Eurasian Eagle-Owl | Bubo bubo | wild | 1 | SN |
| Tawny Owl | Strix aluco | wild | 1 | ST |
| White Eared Pheasant | Crossoptilon crossoptilon | captive | 2 | BE |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziegler, U.; Santos, P.D.; Groschup, M.H.; Hattendorf, C.; Eiden, M.; Höper, D.; Eisermann, P.; Keller, M.; Michel, F.; Klopfleisch, R.; et al. West Nile Virus Epidemic in Germany Triggered by Epizootic Emergence, 2019. Viruses 2020, 12, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040448
Ziegler U, Santos PD, Groschup MH, Hattendorf C, Eiden M, Höper D, Eisermann P, Keller M, Michel F, Klopfleisch R, et al. West Nile Virus Epidemic in Germany Triggered by Epizootic Emergence, 2019. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040448
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiegler, Ute, Pauline Dianne Santos, Martin H. Groschup, Carolin Hattendorf, Martin Eiden, Dirk Höper, Philip Eisermann, Markus Keller, Friederike Michel, Robert Klopfleisch, and et al. 2020. "West Nile Virus Epidemic in Germany Triggered by Epizootic Emergence, 2019" Viruses 12, no. 4: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040448
APA StyleZiegler, U., Santos, P. D., Groschup, M. H., Hattendorf, C., Eiden, M., Höper, D., Eisermann, P., Keller, M., Michel, F., Klopfleisch, R., Müller, K., Werner, D., Kampen, H., Beer, M., Frank, C., Lachmann, R., Tews, B. A., Wylezich, C., Rinder, M., ... Lühken, R. (2020). West Nile Virus Epidemic in Germany Triggered by Epizootic Emergence, 2019. Viruses, 12(4), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040448






