Abstract
The plant genome can produce long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), some of which have been identified as important regulators of gene expression. To better understand the response mechanism of rice plants to Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) infection, we performed a comparative transcriptome analysis between the RBSDV-infected and non-infected rice plants. A total of 1342 mRNAs and 22 lncRNAs were identified to be differentially expressed after RBSDV infection. Most differentially expressed transcripts involved in the plant–pathogen interaction pathway were upregulated after RBSDV infection, indicating the activation of rice defense response by RBSDV. A network of differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) and mRNAs (DEmRNAs) was then constructed. In this network, there are 56 plant–pathogen interaction-related DEmRNAs co-expressing with 20 DElncRNAs, suggesting these DElncRNAs and DEmRNAs may play essential roles in rice innate immunity against RBSDV. Moreover, some of the lncRNA–mRNA regulatory relationships were experimentally verified in rice calli by a quick and effective method established in this study. Three DElncRNAs were selected to be tested, and the results indicated that five mRNAs were found to be regulated by them. Together, we give a whole landscape of rice mRNAs and lncRNAs in response to RBSDV infection, and a feasible method to rapidly verify the lncRNA–mRNA regulatory relationship in rice.
1. Introduction
Rice black-streaked dwarf disease is an important rice disease in China, Japan, and many other Asian countries and is caused by Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) [1]. RBSDV is a member of the genus Fijivirus, family Reoviridae [2], and is transmitted by the small brown planthopper (SBPH, Laodelphax striatellus Fallén) in a persistent and circulative-propagative manner [2,3]. In addition to rice, RBSDV can also infect maize, wheat, and several species of weeds [2,3,4,5] to cause Maize rough dwarf disease and wheat dark-green dwarf disease [6,7]. RBSDV virions are non-enveloped, icosahedral, double-layered, 75–80 nm in diameter, and contain 10 double-stranded (ds) RNAs (designated as S1 to S10) with approximately 1.8 to 4.5 kilo-bases [1,8]. Microscopic analysis of ultrathin sections shows that RBSDV virions are restricted to the phloem tissues in infected plants, and the viroplasm, virus crystals, and tubular-like structures can be found in both infected plant and insect cells [9,10]. Several studies have shown that the expression of mRNAs and microRNAs in rice and maize plants can be affected by RBSDV infection. For example, the expression of rice signal transduction-associated genes can be altered after RBSDV infection, resulting in inhibition of the abscisic acid (ABA) pathway and induction of the jasmonic acid (JA) pathway [11,12]. In another study, many cell wall biosynthesis-related, chloroplast function-related, and disease resistance or stress-related genes were found to be significantly upregulated after RBSDV infection in maize [13].
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been shown as important regulators of gene expression and can be divided into two groups: small ncRNAs and long ncRNAs (lncRNAs) [14,15]. Although the function of small ncRNAs has been relatively well-studied, there is still much to learn about lncRNAs, especially in plants. Recent transcriptome-wide studies using high-throughput RNA-seq have proved that the plant genome transcribes many lncRNAs. Additionally, many studies have indicated that lncRNAs are important in almost all plant biological processes [16,17]. However, only a few lncRNAs have been identified to regulate rice growth and development. For example, a long-day-specific male-fertility-associated RNA (LDMAR) was reported to influence rice anther development by regulating photoperiod-sensitive male sterility (PSMS) [18], and an LRK Antisense Intergenic RNA (LAIR) was reported to increase rice grain yield [19]. In addition, increasing evidence has shown that multiple lncRNAs have essential roles in plant resistance to abiotic or biotic stresses [20]. In Arabidopsis thaliana, a total of 1832 lncRNAs were found to be differentially altered under drought, cold, high-salt, and abscisic acid (ABA) treatments [21]. Fusarium oxysporum infection in A. thaliana also caused differential expression of many lncRNAs, and some lncRNAs were identified to play important roles in A. thaliana anti-fungal immunity [22]. Besides, ELF18-induced long-noncoding RNA1 (ELENA1) in A. thaliana has been found to interact with Mediator subunit 19a to regulate the expression of defense-related genes including pathogenesis-related gene 1 (PR1) for enhancing the host resistance to Pseudomonas syringe infection [23]. However, only a few studies have been made to elucidate the roles of lncRNAs in plant-virus interaction. Gao and colleagues have discovered that LINC-AP2 may be responsible for the formation of shorter stamen in the flowers of the Turnip crinkle virus (TCV)-infected A. thaliana plants, through anti-cis downregulation of AP2 gene expression [24]. Moreover, a tomato lncRNA, SlLNR1, has been shown to directly interact with IR-derived vsRNAs from tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) to inhibit TYLCV disease development [25]. To date, the expression profile and function of lncRNAs during virus infection in rice are still largely unknown.
The high-throughput RNA-seq technique has been successfully used to investigate the transcriptional profiles of different plants and to identify novel lncRNAs. To better understand the rice immune defense against RBSDV infection, and to identify novel lncRNAs involved in rice antiviral response, we analyzed the transcriptomic profile of mRNAs and lncRNAs in the RBSDV-infected and non-infected rice plants using an Illumina sequencing platform. Through this study, a total of 1342 differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs) and 22 differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNA) in rice were identified after RBSDV infection. Analysis of the DElncRNA and DEmRNA co-expression network showed a complicated gene-regulating relationship, and then we focused on transcripts related to the plant–pathogen interaction pathway. To verify the regulatory relationship in this network, we silenced three DElncRNAs (TCONS_00065705, TCONS_00059822, and TCONS_00089479) in rice calli through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of hairpin constructs and then detected the expression levels of predicted co-expressed mRNAs. The qRT-PCR result indicated that DEmRNAs (LOC_01g06730, LOC_06g44010, LOC_03g18030, LOC_03g10640, and LOC_04g51660) were, respectively, regulated by these three DElncRNAs. The data presented in this paper provide new clues to further investigate the response mechanism of rice to RBSDV infection and a feasible method to screen lncRNA-regulated mRNAs in rice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth, Virus Inoculation, and RNA Isolation
Rice (Oryza sativa) cultivar Wuyujing No. 7 seedlings were grown inside an insect-free greenhouse at 28 °C and with a 16/8 h (light/dark) photoperiod. The rice seedlings were inoculated with RBSDV at 3-leaf-stage (3-L) using viruliferous small brown planthoppers (SBPH, Laodelphax striatellus) (five insects per seedling). The SBPHs were allowed to feed on the assayed seedlings for three days and were then removed. The inoculated seedlings were then grown inside individual containers in the greenhouse until the onset of disease phenotypes. Rice seedlings inoculated with non-viruliferous SBPHs were used as controls in this study. Leaf tissues were collected from individual assayed plants, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored separately at −80 °C until use. Leaf tissues harvested from a single plant were mixed and used as a biological replicate, and each treatment had three biological replicates. Total RNA was extracted from individual samples using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and virus infection in each RBSDV-inoculated sample was confirmed through RT-PCR using RBSDV-specific primers (F: 5′-GGTTGGAAAATGTTGAAAGCATTACA-3′ and R: 5′-AAACAAGGAGACACAAGATTGTAAAT-3′) targeting RBSDV segment 3.
2.2. Preparation of Transcriptome Libraries and Deep Sequencing
Total RNA (3 μg per sample) was used to construct each sequencing library. Briefly, ribosomal RNA was removed using the Epicentre Ribo-zero™ rRNA Removal Kit as instructed (Epicentre, Madison, WI, USA), followed by ethanol precipitation. The resulting mRNAs were fragmented using divalent cations under elevated temperature. The short mRNA fragments were then used to synthesize the first-strand cDNA using random hexamers primers. The second-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using DNA polymerase I and RNase H. The cDNA libraries were prepared by using the standard Illumina protocols and then sequenced on an Illumina Hiseq™ 4000 sequencing system (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) to generate reads with 150 bp paired-ends. Constructions of libraries and RNA sequencing were performed by the Zhejiang TianKe High-Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China).
2.3. Assembly and Annotation of Transcriptome Data
First, quality-control filtering was performed by removing reads containing adapter or poly-N and the low-quality bases determined with the FastQC program, and high-quality clean reads were obtained. Then, reads derived from ribosomal RNAs were removed by mapping reads to the Ribosomal Database Project (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/, accessed on 31 January 2018) with Bowtie2 v2.2.4 [26]. We obtained 41.637 Gb high-quality clean reads (6.939 Gb/per sample). All the subsequent analyses were conducted using high-quality clean reads. The resulting paired-end clean reads were aligned to the reference genome database using the TopHat v2.1.1 software (http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/index.shtml, accessed on 5 February 2018) as previously described [27]. In addition, Cufflinks v2.2.1 was used to assemble the mapped transcripts. The annotated transcripts were then used for further analyses.
2.4. Identification of lncRNAs
The assembled transcriptome data were further screened to identify lncRNAs following four steps: (i) Cuffmerge software in the Cufflinks Support Package (v2.2.1) was used to combine all assembled transcripts, and those with less than three reads coverage were removed. (ii) Transcripts were removed with less than 200 bp in length. (iii) Cuffcompare software in the Cufflinks Support Package (v2.2.1) was used to compare the transcripts with annotated rice mRNAs (http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/, accessed on 20 February 2018), and the transcripts which were overlapped with the rice mRNAs were removed. (iv) Transcripts with potential coding capabilities were removed, which were assessed by three software, namely, CPC (Coding Potential Calculator, version 2), CNCI (Coding-Non-Coding Index, 0.9-r2), and Pfam 28.0 [28,29,30]. Finally, the remaining transcripts were identified as lncRNAs.
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs
The transcript abundances of mRNAs and lncRNAs were quantified using the normalized expression values as fragments per kilo-base per million reads (FPKM) by the Cuffdiff (v2.2.1) software [31]. Differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs) or lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) between RBSDV-infected and mock plants were selected using the threshold of |log2(fold change)| ≥ 1, and a statistical significance (false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05). The expression-based sample clustering and the principal component analysis (PCA) were performed using the R package (v3.3.0) [32].
2.6. Analyses of GO and KEGG Enrichment
Gene ontology (GO) annotations were performed based on the Blast2GO database (http://www.blast2go.com, accessed on 1 March 2018), and the GO association was done using the BLASTX against the NCBI NR database. The GO enrichment analyses of DEmRNAs or the DElncRNA-targeted genes were performed using the topGO software at the Bioconductor (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/topGO.html, accessed on 15 March 2018). The GO terms with corrected p-value < 0.05 were considered to be significantly enriched, and the three terms: biological process, molecular function, and cellular component, were defined with default parameters. Moreover, the metabolic pathway analysis of the DEmRNAs or the DElncRNA-targeted genes was performed using the KEGG database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg, accessed on 16 March 2018), and the statistical enrichments were determined using the phyper package in R package (v3.3.0).
2.7. Prediction of DElncRNA-Targeted mRNAs and Construction of lncRNA–mRNA Regulatory Network
To analyze the DElncRNA cis-acting model, we searched genes in a region covering 100 kb up- to down-stream of individual DElncRNA. While the trans-acting model was analyzed using DElncRNAs and their co-expressed mRNAs. In this study, we calculated Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) based on the expression level of each DElncRNA and mRNA pair with custom Perl scripts to search the common expression module. From individual DElncRNA and its trans-acting target mRNA, the pair with a PCC > 0.95 or <−0.95 was considered as significantly correlated expressed. The DElncRNA and DEmRNA co-expression networks were constructed according to the co-expression associations between DElncRNAs and DEmRNAs, and were visualized using the Cytoscape 3.2.7 software (http://cytoscape.org/, accessed on 17 September 2018).
2.8. Validation of DEmRNAs and DElncRNAs Using Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
To validate the DEmRNAs and DElncRNAs revealed by the transcriptome data, leaves of RBSDV-infected and non-infected rice plants were collected. Total RNA (2 µg) isolated from individual leaf samples was used for cDNA synthesis using the ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix supplemented with a gRNA Remover as instructed (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). The resulting cDNA samples were individually diluted three times in RNase and DNase free water and then used (1.5 µL) in 10 µL qPCR reaction systems. Each qPCR reaction system consisted of 5 µL 2 × ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China) and 0.2 µL of each primer (10 mM), 1.5 µL diluted cDNA and 3.1 µL RNase and DNase-free water. The qPCR reaction was done on Light Cycler 480 II (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) set at 95 °C for 30 s, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, and 60 °C for 30 s. Melting curves were collected at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min, 95 °C for 15 s. Each gene expression analysis was performed using three independent biological replicates. The expression of OsUBC (LOC_Os02g42314) was used as an internal control, and the relative expression of each gene was calculated using the 2−∆∆CT method as described [33,34]. Differences were statistically evaluated with a t-test using GraphPad Prism 8. Primers used for DEmRNA and DElncRNA expression analyses are listed in Table S1.
2.9. Experimental Validation of the lncRNA–mRNA Regulatory Relationship
To construct the hairpin targeting DElncRNA, 300 to 600 bp forward and reverse sequences of the lncRNA, together with an intron from the AtRTM1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, were fused into a pCAMBIA1300 vector containing the maize polyubiquitin gene promoter by the in-fusion cloning. The hairpin targeting the gusA gene of Escherichia coli was also constructed as a control. Then, the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105 was transformed with recombinant plasmids containing hairpin constructs. The callus of rice cv. Wuyujing No. 7 was induced and then infected with the Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring different hairpin constructs according to a previous protocol [35]. The 2N6 medium was used for callus induction; the 2N6-As medium with 200 mM acetosyringone was used for co-cultivation, and the AAM medium with 200 mM acetosyringone was used to suspend Agrobacterium tumefaciens. To increase the infection efficiency, we prolonged the soaking time of callus in Agrobacterium tumefaciens suspension to 30 min. After infection, the callus tissues were co-cultivated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens for three days. Then the Agrobacterium tumefaciens was killed by washing the callus tissues with 600 mg/L cefotaxime solution, and the callus tissues were continuously cultivated for four days before extracting total RNA for qRT-PCR analysis. The qRT-PCR method has been described above, and primers used for the detection of hairpin targeted lncRNAs and related mRNAs expression analyses are listed in Table S1, primers used for vector construction are listed in Table S2.
2.10. Data Availability
Raw reads of Illumina RNA-seq generated in this study are available from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under the project ID PRJNA657713 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA657713/, accessed on 19 August 2020). The transcriptome data generated in this study are available in Gene Expression Omnibus with series entry GSE156747 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE156747, accessed on 25 August 2020).
3. Results
3.1. RNA Sequencing Results
Three RBSDV-infected rice plants (e.g., RBSDV1, RBSDV2, and RBSDV3) and three non-infected rice plants (e.g., MOCK1, MOCK2, and MOCK3) were used in this study. A total of 299,865,814 raw reads were obtained through the Illumina sequencing. After quality-control filtering, 47,629,488, 46,285,766, 46,451,138, 45,328,332, 46,432,674 and 45,452,636 clean reads were obtained from the MOCK1, MOCK2, MOCK3, RBSDV1, RBSDV2 and RBSDV3, samples, respectively (Table 1). The Q20 and Q30 values of the clean reads were, respectively, over 96.15% and 89.85%, indicating that the obtained clean reads were of high quality (Table 1). Using the TopHat software v2.1.1, we mapped a total of 215,104,641 (71.73%) clean reads to the rice genome. Based on the characteristics of lncRNAs, a total of 1273 highly reliable lncRNAs were identified through four screening steps, and a total of 46,558 annotated mRNAs were also obtained and used in the subsequent analyses.

Table 1.
Summary of RNA sequencing results.
3.2. RBSDV Infection-Induced Differential Expression Patterns of mRNAs and lncRNAs
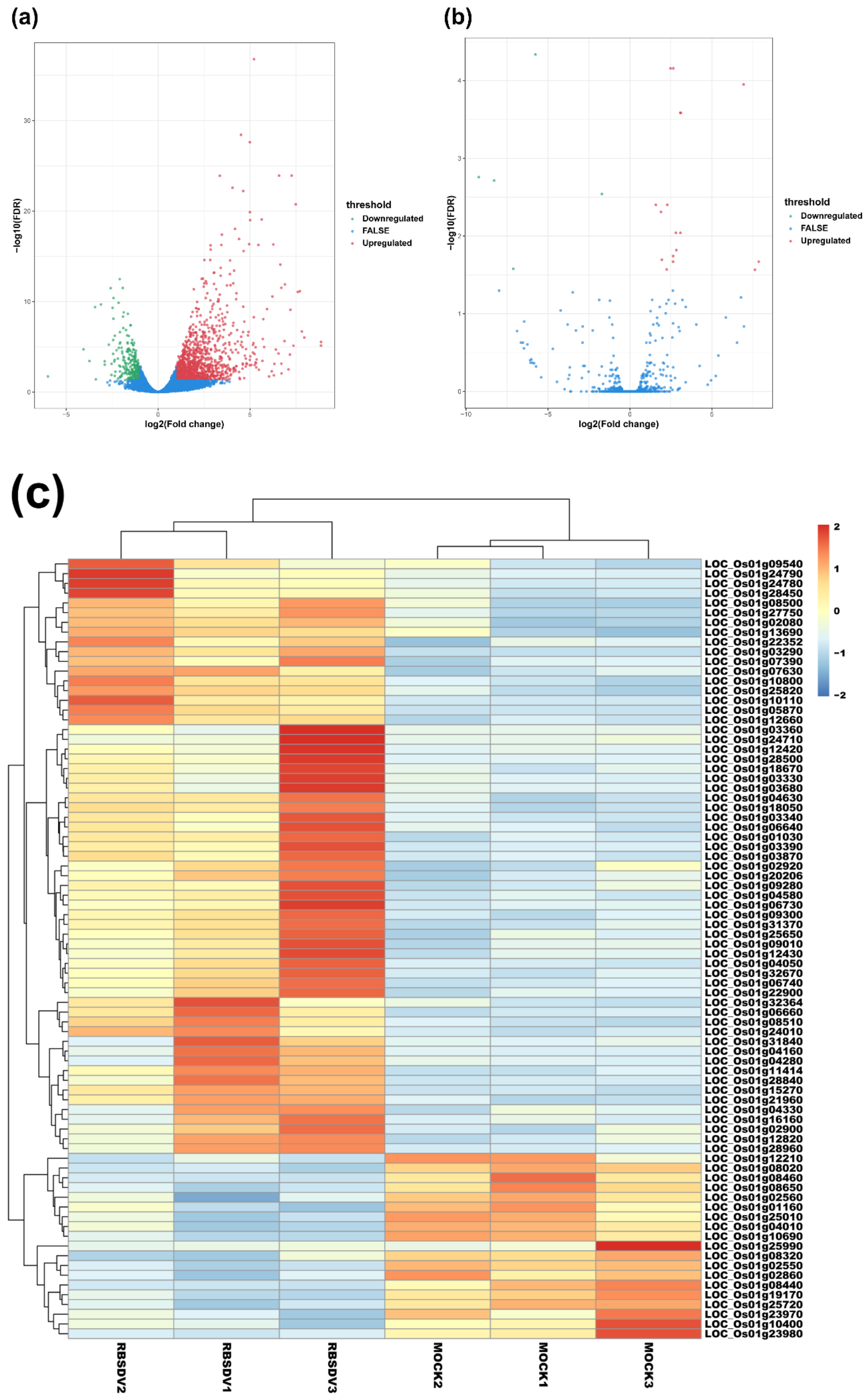
To compare the expression levels of mRNAs or lncRNAs between the RBSDV-infected and the mock plants, we normalized and analyzed the sequencing transcripts using the criteria of FDR < 0.05 and |log2(fold change)| ≥ 1 to identify DEmRNAs and DElncRNAs. The volcano plots showed the relationships between FDR and fold change of all the identified transcripts, representing the degree of difference and the statistical significance of gene expression between the RBSDV-infected and the mock plants (Figure 1a,b). We then generated heat maps using hierarchical clustering analyses of all the normalized DElncRNA values and the top 80 DEmRNAs determined by the R package software (Figure 1c,d). Hierarchical clustering analyses showed a systematic variation of mRNA or lncRNA expression between the RBSDV-infected and the mock plants. Furthermore, the principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to evaluate the sample distribution according to their expression profiles. The PCA charts showed that samples collected from the same treatment all gathered together (Figure S1a,b). As a result, we identified a total of 1342 DEmRNAs, among which 1087 were upregulated, and 255 were downregulated after RBSDV infection (Figure 1e and Table S3). Among these DEmRNAs, three genes (LOC_Os01g72370, LOC_Os01g03360, and LOC_Os06g36950) were the most affected DEmRNAs. LOC_Os01g72370, encoding a helix-loop-helix transcription factor related to the cellular response to iron ion starvation, and LOC_Os01g03360, encoding a Bowman-Birk type bran trypsin inhibitor (BBTI5) which participates in negative regulation of endopeptidase activity, were upregulated by 8.9-fold. LOC_Os06g36950, encoding a hobo/Ac/Tam (hAT) transposase, was downregulated by sixfold after RBSDV infection. At the same time, a total of 22 lncRNAs were identified to be differentially expressed. Among them, 17 lncRNAs were upregulated, and the other five lncRNAs were downregulated in the RBSDV-infected plants compared with those in the mock plants (Figure 1f and Table 2). A lncRNA (TCONS_00081336) showed the most significant upregulation (7.9-fold), while another lncRNA (TCONS_00074370) showed the most significant downregulation (9.2-fold). However, we could not predict their functions directly.
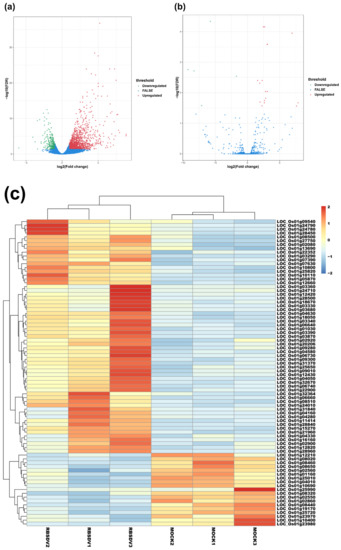
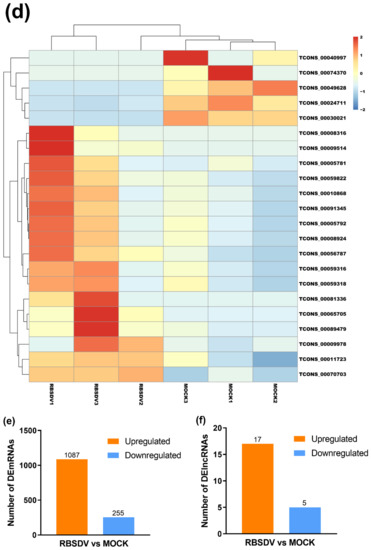
Figure 1.
Volcano maps and hierarchical clustering analysis show expression profiles of mRNAs and lncRNAs of RBSDV-infected and mock rice plants. Volcano maps show mRNA expression (a) and lncRNA expression (b) with fold change ≥ 2.0 and false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05. Red dots represent upregulated genes, and green dots represent downregulated genes in volcano maps. The heatmaps show significantly expressed mRNAs (c) and lncRNAs (d) with fold change ≥ 2.0 and FDR < 0.05. The right panel is the color key for fold-change. Red represents upregulation, blue represents downregulation, the brighter image is the greater the fold change; (e,f) the number of mRNAs or lncRNAs whose expression significantly changed are shown.

Table 2.
Identified differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (DElncRNAs) in the Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV)-infected rice plants.
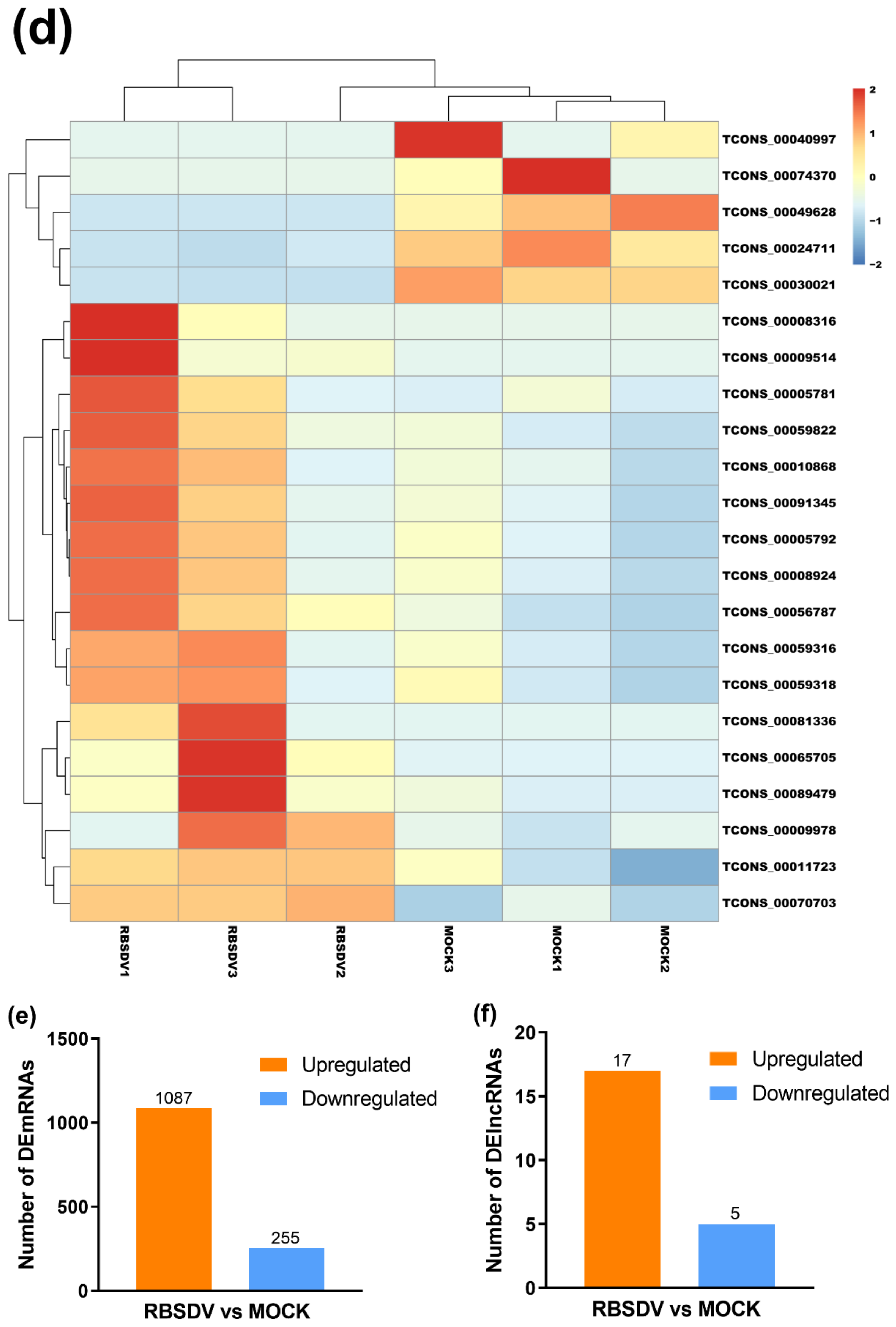
Although lncRNAs have been investigated for years, many of them have not been well annotated. To date, multiple lncRNAs have been considered to regulate gene expression and to shape 3D nuclear organization [36]. Using DElncRNAs identified in the RBSDV-infected rice plants, we investigated their general signatures, including their distributions on chromosomes and their length. The results showed that these DElncRNAs were distributed on almost all chromosomes of rice, except chromosomes 10 and 11. Among these DElncRNAs, the upregulated DElncRNAs were found on chromosomes 1, 4, 5, 7–9, while the downregulated DElncRNAs were found on chromosomes 2, 3, 6, and 12 (Figure 2a and Table 2). In contrast to DElncRNAs, the DEmRNAs were found widely distributed on all chromosomes, and more DEmRNAs were distributed on chromosome 1 (Figure 2b and Table S3). The length of DElncRNAs ranged from 430 to 12,346 bp, with the majority between 3000 and 6000 bp (Table 2).
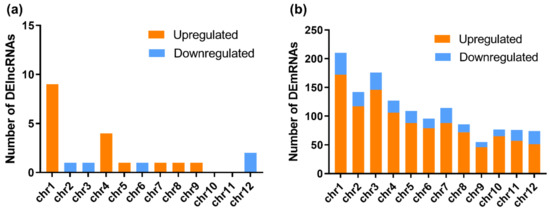
Figure 2.
Chromosomal distributions of DElncRNAs and differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs). The numbers of DElncRNAs (a) and DEmRNAs (b) on each chromosome are shown. Orange represents upregulation, while blue represents downregulation.
3.3. Functional Characteristics of DEmRNAs
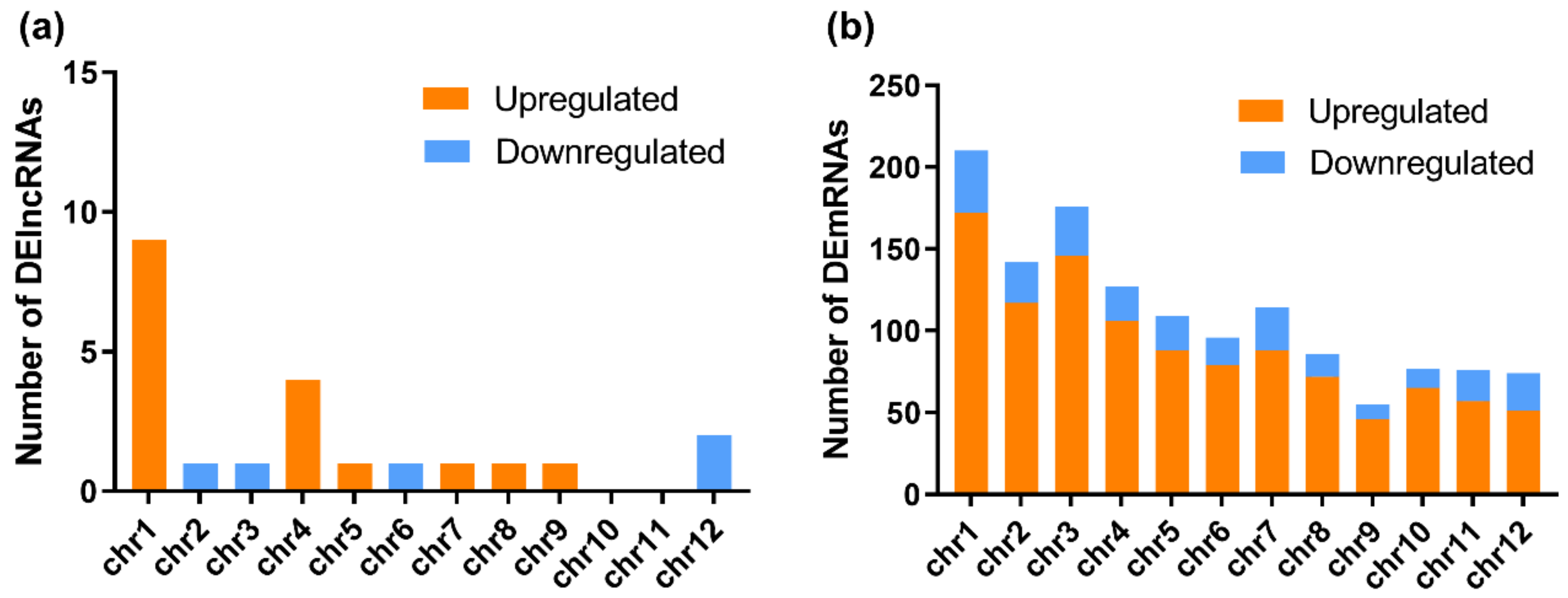
Based on the GO classification, the DEmRNAs can be separated into three categories: molecular function, cellular component, and biological process. In the molecular function category, DEmRNAs with oxidoreductase activity (GO: 0016491), iron ion binding (GO: 0005506), transferase activity and transferring hexosyl groups (GO: 0016758), and chitinase activity (GO: 0004568) were significantly enriched in the RBSDV-infected plants (Figure 3a,b). Because chitinase has been reported as one of the main plant disease-related proteins (i.e., PR proteins) [37], we considered that the upregulated expression (~4.5-fold) of genes with chitinase activities (LOC_Os11g47600 and LOC_Os04g41620) were related to rice resistance against RBSDV infection. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) plays a multitude of roles in rice defense response to RBSDV infection [12]. A lot of DEmRNAs were classified into the oxidoreductase activity (GO: 0016491), suggesting the regulation of cell redox status in response to RBSDV infection. In the cellular component category, DEmRNAs related to the integral component of membrane (GO: 0016021), cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle (GO: 0016023), and plasma membrane (GO: 0005886) were significantly enriched. These genes may be important in vesicle formation during RBSDV infection in cells (Figure 3a). In the biological process category, DEmRNAs involved in the single-organism process (GO: 0044699) were significantly enriched, and DEmRNAs involved in the oxidation-reduction process (GO: 0055114), small molecule biosynthetic process (GO: 0044283), and organic acid metabolic process (GO: 0006082) were significantly upregulated upon RBSDV infection. Besides, DEmRNAs in the polysaccharide metabolic process (GO: 0005976), defense response (GO: 0006952), and transmembrane transport (GO: 0055085) were also affected (Figure 3a).
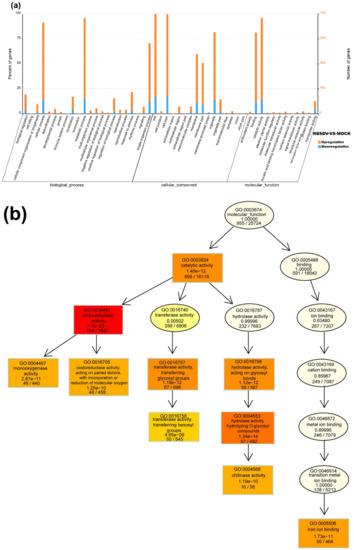
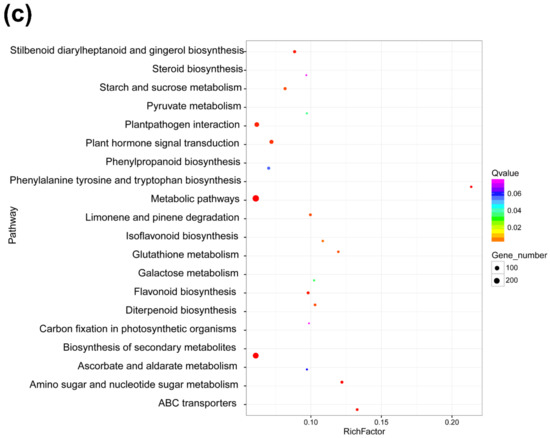
Figure 3.
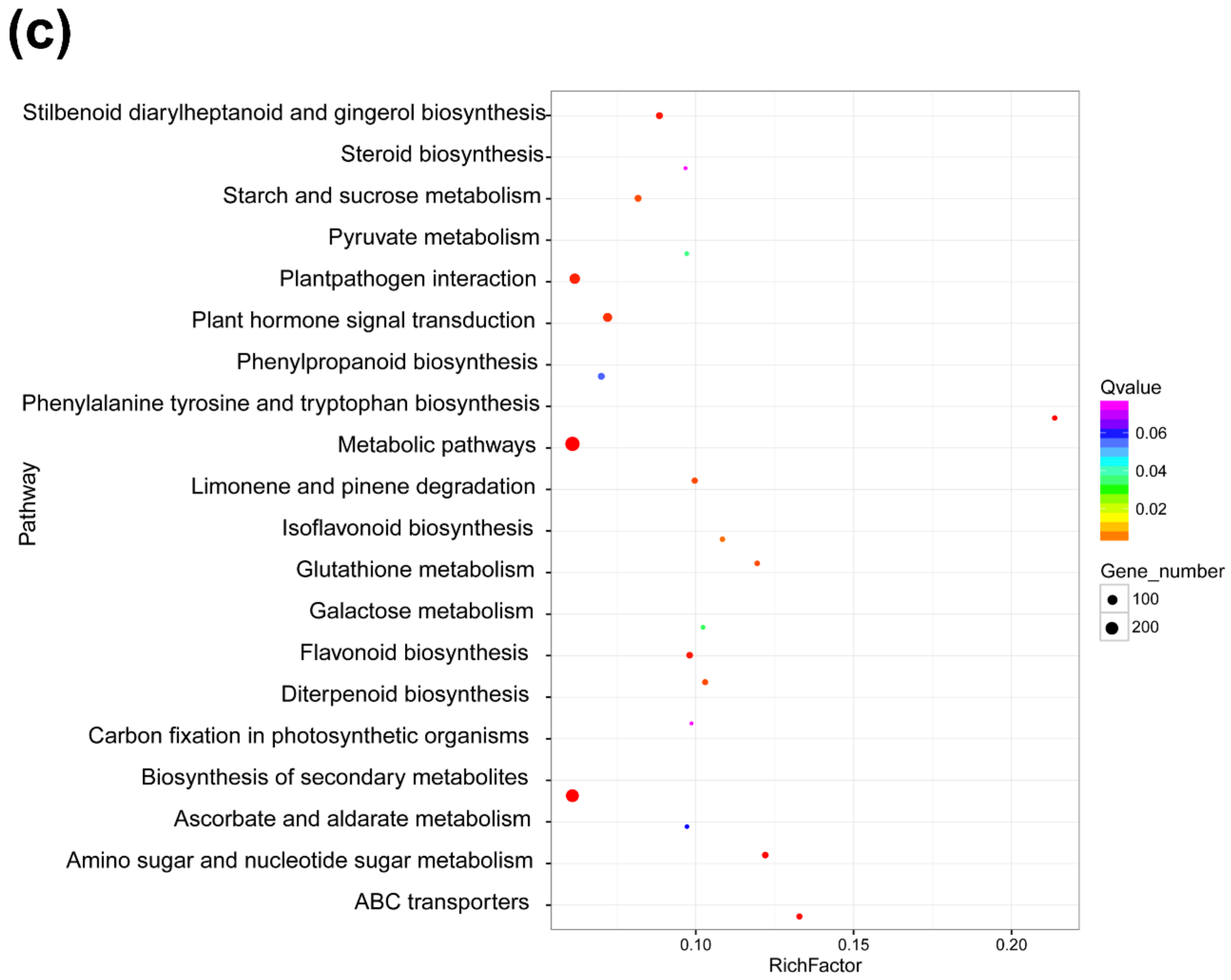
Gene ontology (GO) function enrichment analysis, GO terms, and KEGG pathway enrichment of DEmRNAs identified in RBSDV-infected rice plants. (a) GO enrichment analysis of DEmRNAs with a p-value < 0.05; (b) gene ontology terms for molecular function of DEmRNAs; (c) statistics of the top 20 KEGG pathways enriched for DEmRNAs. The size of each circle represents the number of significant DEmRNAs enriched in the corresponding pathway. The enrichment factor was calculated using the number of enriched DEmRNAs divided by the total number of background genes in the corresponding pathway. A pathway with a p-value < 0.05 is considered to be significantly over-represented.
To obtain more information on the molecular and biological responses to RBSDV infection, we searched the KEGG database using the RBSDV-induced DEmRNAs, and found 871 DEmRNAs associated with KEGG pathways. The top 20 significantly enriched pathways are shown in Figure 3c. Among these 20 KEGG pathways, the metabolic pathway (ko01100) was the most enriched pathway with 274 DEmRNAs followed by the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites (ko01110) with 208 DEmRNAs, and then, the plant–pathogen interaction (ko004626) with 115 DEmRNAs (Figure 3c and Table S4). In this study, the DEmRNAs associated with the plant–pathogen interaction pathway were significantly enriched with 86 upregulated DEmRNAs and 29 downregulated DEmRNAs, indicating the activation of this pathway by RBSDV infection (Table S5). The gene encoding PR1 protein (LOC_Os01g28500), an important defense response protein, was upregulated by 6.6-fold, suggesting that the salicylic acid pathway might be activated after RBSDV infection. The gene encoding a respiratory burst oxidase (LOC_Os04g48930) was upregulated by fivefold, but the gene encoding an ABA-responsive element binding factor (LOC_Os02g03960) was downregulated by 2.1-fold, suggesting that the abscisic acid pathway might be suppressed during RBSDV infection. Previous studies demonstrated that plant hormones played important roles in plant defense against RBSDV infection [11,12,38]. Jasmonic acid and auxin signaling pathways enhance the resistance of rice to RBSDV, while abscisic acid and brassinosteroid pathways mediate the susceptibility to RBSDV infection [11,12,38]. In our results, we found that the DEmRNAs were also enriched in the plant hormone signal transduction pathway (ko04075), indicating broad responses of plant hormone signaling pathways to RBSDV infection. Other genes involved in the phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis (ko00400), phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (ko00940), flavonoid biosynthesis (ko00941), and diterpenoid biosynthesis (ko00904) were also significantly enriched (Figure 3c and Table S4). The gene encoding chalcone synthase (LOC_Os11g32650) in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, was upregulated by 5.6-fold. These results indicate that a complex gene expression network is affected by RBSDV infection, and defense response pathways are activated.
3.4. Functional Analyses of DElncRNA-Targeted Genes
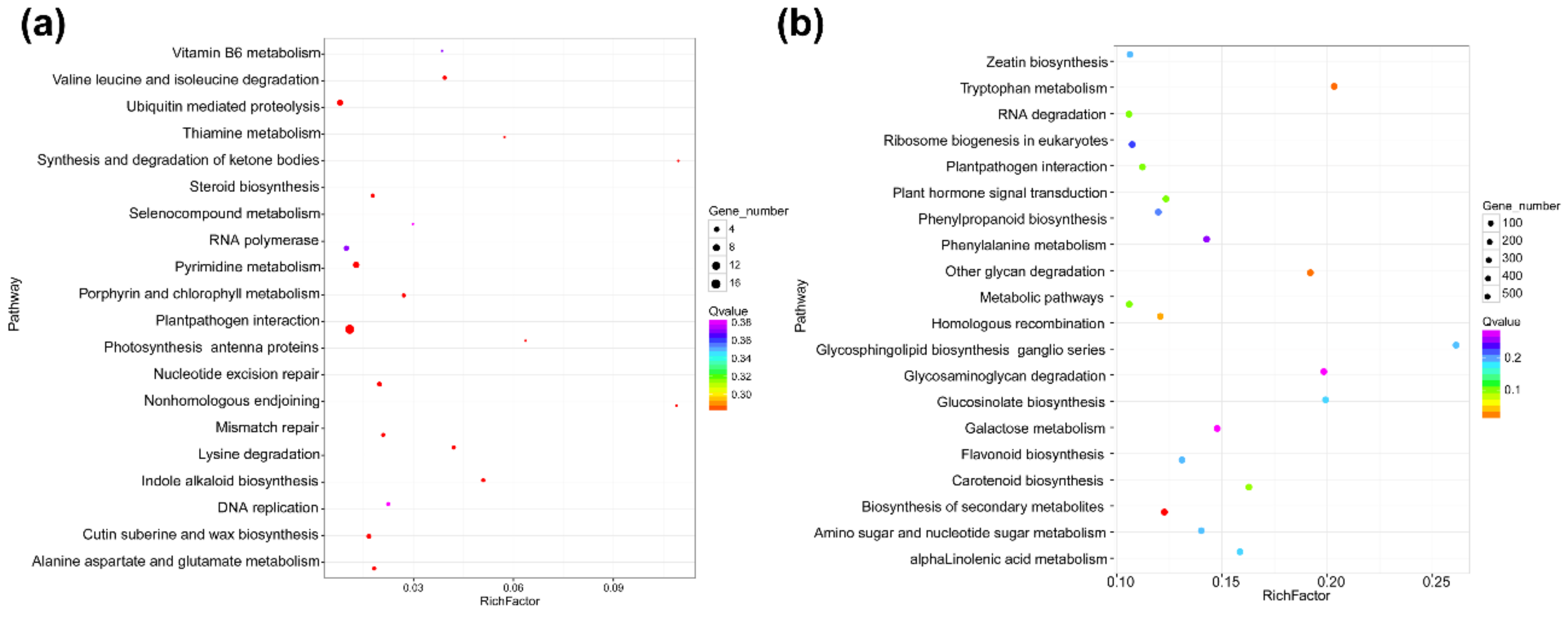
Cis-acting lncRNAs are known to repress or activate the expression of genes that are adjacent to the transcription sites of lncRNAs on the same chromosome. It is also reported that trans-acting lncRNAs regulate gene expression through a variety of transcriptional or post-transcriptional biological processes, while cis-acting lncRNAs regulate the expression of nearby genes epigenetically at the transcriptional level [39]. To elucidate the function model of cis-acting lncRNAs, we searched mRNAs adjacent to the transcription sites of DElncRNAs. In this study, we searched 100 kb sequence up- to down-stream of the 22 identified DElncRNAs for their cis-regulatory effects and defined the relationship between the lncRNA and its adjacent mRNA as co-located. The result showed that a total of 304 mRNAs were co-located to the 22 DElncRNAs, suggesting that the expression of these 304 mRNAs might be affected by DElncRNAs through their cis-regulatory activities (Table S6). GO categorization analyses of the predicted targets of these DElncRNAs showed that they were involved in a broad range of processes (Figure S2). In total, 109 targets were mapped into the KEGG pathway database and the top 20 enriched pathways are shown in Figure 4a and Table S7. These results indicated that the co-located mRNAs involved in the plant–pathogen interaction and the ubiquitin–proteasome protein degradation pathway were more enriched compared with other pathways. Many studies have shown that the ubiquitin–proteasome protein degradation pathway plays important roles in the degradation of viral proteins. In contrast, viruses can also hijack plant ubiquitin–proteasome machinery to help their infections. Recently, He and colleagues reported that the P5-1 protein encoded by RBSDV could regulate the ubiquitination activity of SCF E3 ligase to inhibit the jasmonate signaling pathway to promote RBSDV infection [40]. In this study we also noticed that five mRNAs in the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (ko04120) were co-located with DElncRNAs (Figure 4a and Table S7), suggesting that RBSDV infection in rice can regulate several genes related to the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway through lncRNAs.
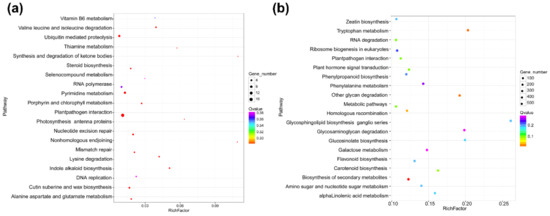
Figure 4.
Statistics of the KEGG pathways enriched for mRNAs co-located with DElncRNAs (a) and mRNAs co-expressed with DElncRNAs (b). The size of each circle represents the number of significant DEmRNAs enriched in the corresponding pathway. The enrichment factor was calculated using the number of enriched DEmRNAs divided by the total number of background genes in the corresponding pathway. A pathway with a p-value < 0.05 is considered to be significantly over-represented.
Among the mRNAs that co-located with DElncRNAs, 12 were differentially expressed, resulting in 12 co-located pairs of DElncRNA–DEmRNA in the RBSDV-infected plants (Table 3), and we speculate that these 12 DEmRNAs might be regulated by these 12 DElncRNAs, respectively. A gene that encodes a member in the transferase family (LOC_Os04g51660) was found to co-locate with TCONS_00059822 and involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, which was reported to play important roles in plant defense against pathogens and insects [41]. Thus, this finding suggested that TCONS_00059822 may regulate host flavonoid biosynthesis pathway through the cis-regulation of LOC_Os04g51660 by 1.79-fold. A previous report has indicated that a cytochrome P450 gene is significantly upregulated in RBSDV-infected maize plants [13]. In this study, we have also observed a 3.9-fold upregulated rice cytochrome P450 gene (LOC_Os01g72270) in the co-location data (Figure 4a and Table 3). We speculate that this cytochrome P450 gene is likely regulated by TCONS_00011723 in the RBSDV-infected plants. In general, the target DEmRNAs were upregulated by 1.6- to 3.9-fold by the corresponding DElncRNAs (Table 3).

Table 3.
The co-located DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs.
Next, we calculated the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) based on the expression level of each DElncRNA and mRNA pair, and the relationship of the DElncRNA–mRNA pair with a PCC > 0.95 or < −0.95 was defined as co-expressed. We analyzed the co-expressed relationships between DElncRNAs and mRNAs to predict the roles of DElncRNAs in the trans-acting model. The results showed a total of 17,335 matched co-expressed pairs (Table S8). The GO categories of the matched mRNAs are shown in Figure S3. The KEGG analysis result demonstrated that the homologous recombination (ko03440) and the plant–pathogen interaction (ko04626) pathways were significantly enriched (Figure 4b and Table S9). In these 17,335 co-expressed pairs, we filtered out 684 DEmRNAs as the potential targets of 22 DElncRNAs to investigate further (Table S10).
3.5. DElncRNA–DEmRNA Co-Expression Network
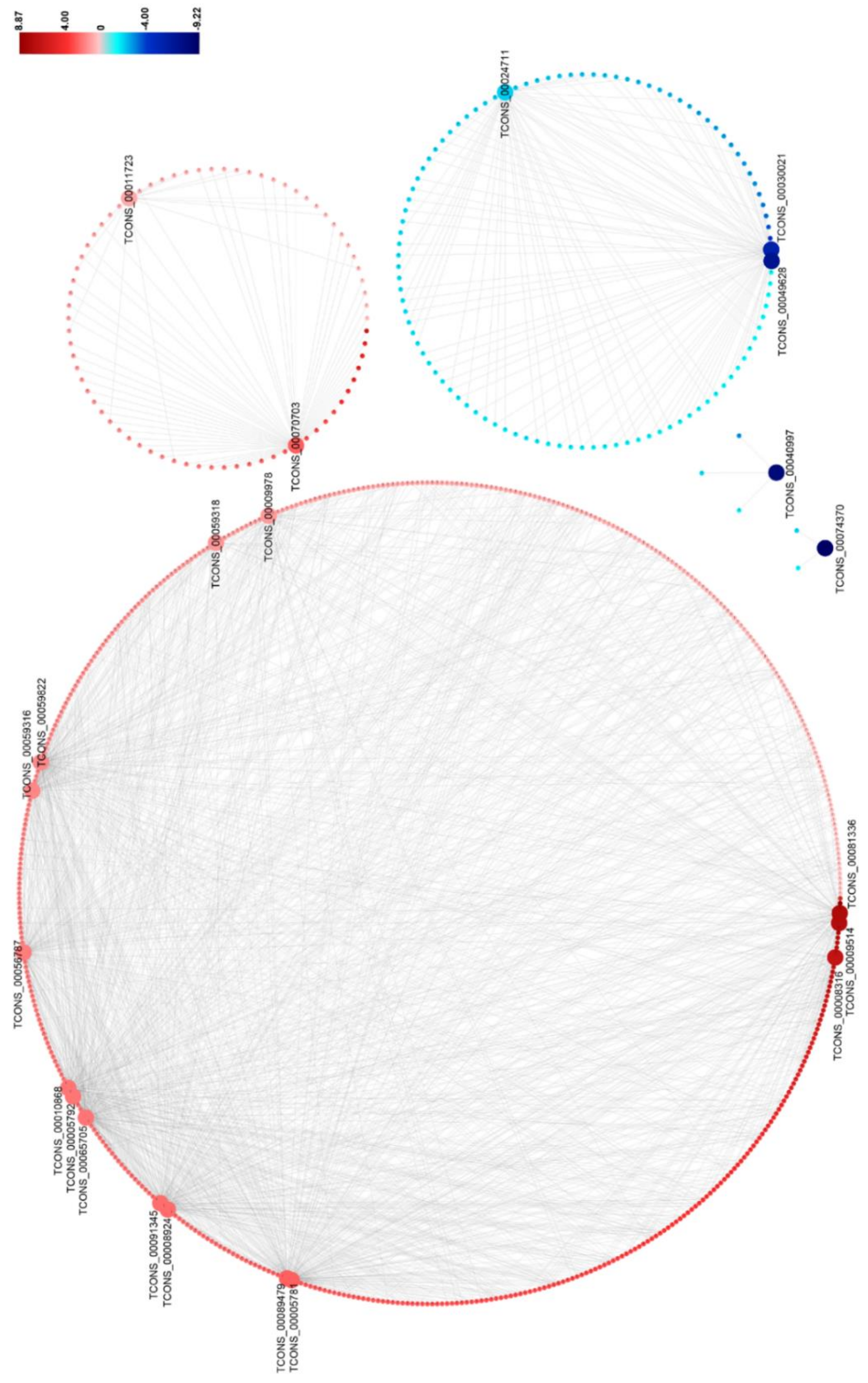
To predict the functions of DElncRNAs on DEmRNAs, we constructed the DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression network by using the 684 DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression pairs mentioned above (Figure 5 and Table S10). This network contains 15 upregulated and 7 downregulated DElnRNAs, and 579 upregulated and 105 downregulated target DEmRNAs. It could be seen that the expression of the DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs were positively correlated (Figure 5). In the network, three DElncRNAs (TCONS_00065705, TCONS_00089479, and TCONS_00056787) co-expressed with a large number of DEmRNAs, suggesting that they might play important roles during RBSDV infection (Figure 5 and Table S10).
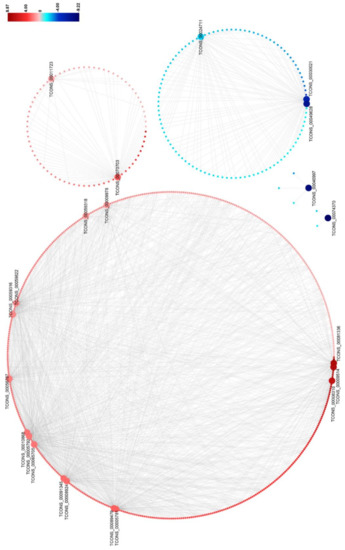
Figure 5.
The network for the predicted co-expressed DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs found in RBSDV-infected rice plants. A fold-change scale is shown on the right side. Red indicates upregulation and blue indicates downregulation. The brighter image is the greater fold change. A DElncRNA–DEmRNA pair with a person’s correlation coefficient > 0.95 or < −0.95 is considered to be co-expressed.
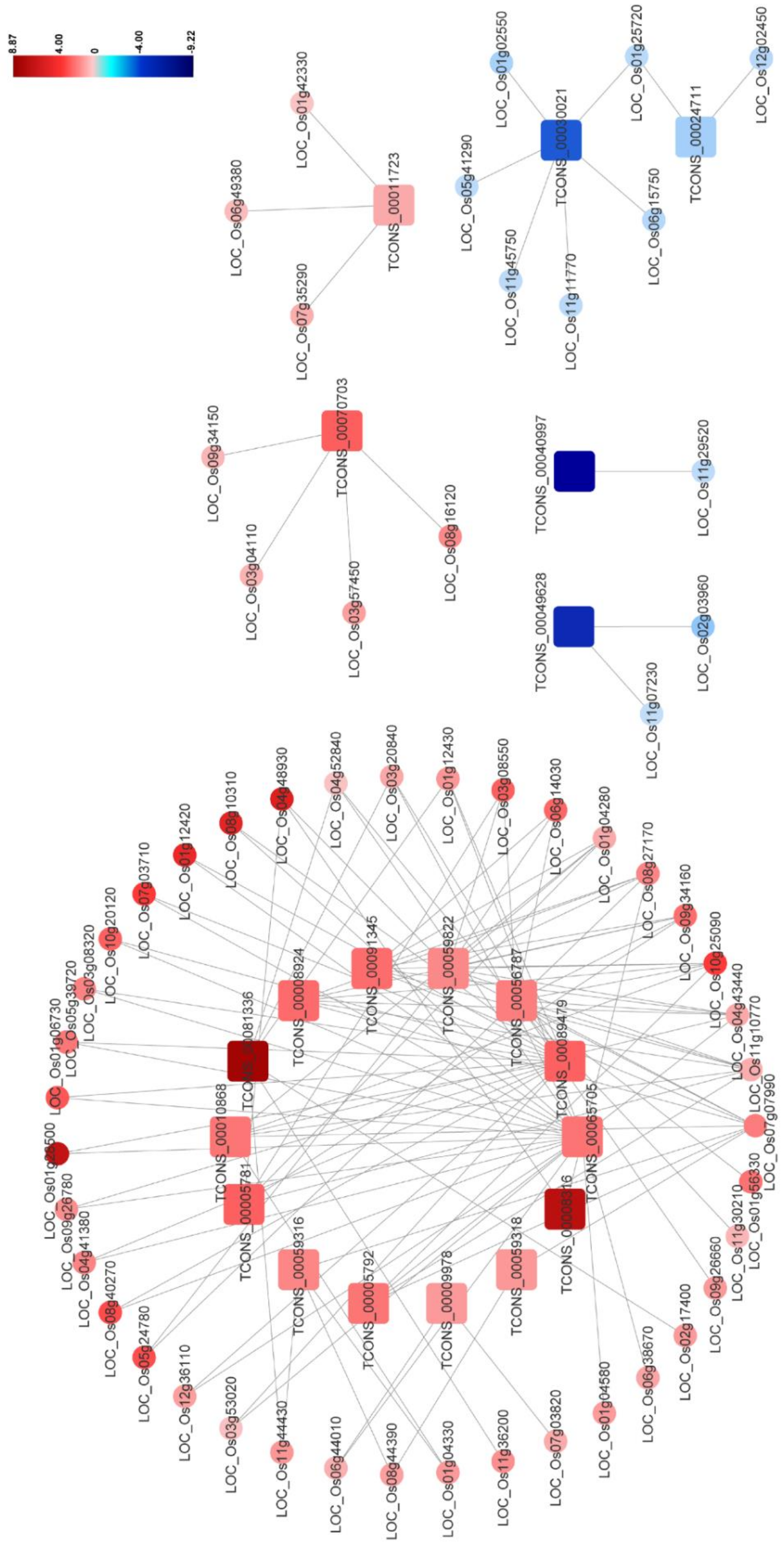
Previous studies have indicated that the plant–pathogen interaction pathway including the MAPK signaling pathway and the plant hormone signal transduction pathway participates in plant antiviral resistance. In this network, 20 DElncRNAs were found to be significantly and intricately interconnected with 56 DEmRNAs in the plant–pathogen interaction pathway, and the predicted co-expression network of these DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs was also constructed (Figure 6 and Table S11). In this network, expression levels of most DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs were upregulated after RBSDV infection, suggesting the activation of the plant defense system. Additionally, we found that some genes could be simultaneously targeted by different DElncRNAs, implying the essential roles of these genes and lncRNAs in RBSDV infection. For example, three genes (LOC_Os11g10770, LOC_Os04g43440, and LOC_Os09g34160) were found to be co-expressed with seven, six, and five DElncRNAs, respectively (Figure 6 and Table S11). Calcium (Ca2+) is an important messenger involved in plant responses, and Ca2+ concentration in the cytoplasm increases as one of the early signals of pathogen invasion [42]. In this co-expression network, two genes (LOC_Os08g27170 and LOC_Os01g04280), predicted to encode calmodulin-binding proteins, were co-expressed with five and four DElncRNAs, respectively (Figure 6 and Table S11). In addition, OsCML16 (LOC_Os01g04330) and OsCML21 (LOC_Os05g24780) encoding the plant-specific calmodulin-like proteins, were found to be co-expressed with four DElncRNAs (TCONS_00010868, TCONS_00059316, TCONS_00056787 and TCONS_00059822) (Figure 6 and Table S11). Jasmonic acid (JA) pathway is known to positively regulate plant defense against RBSDV infection [38]. In this network, OsJAZ8 (LOC_Os09g26780) and OsJAZ11 (LOC_Os03g08320), predicted to encode the key co-receptors of JA pathway, were both found to be co-expressed with two DElncRNAs (TCONS_00089479 and TCONS_00065705), indicating that the two lncRNAs might participate in the regulation of JA pathway. We also noticed that LOC_Os06g44010 which encodes OsWRKY28 was also co-expressed with lncRNA TCONS_00065705 in this network. The WRKY gene family is a large transcription factor (TFs) family in higher plants, which is involved in various plant processes in coping with diverse biotic and abiotic stresses [43]. We found mRNAs related to the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, such as LOC_Os03g18030 and LOC_Os10g16974. Taking the finding in the co-location analysis into account, we suspect flavonoids may be important compounds in the response of rice to RBSDV infection. These complex networks can provide effective evidence for estimating lncRNA function and clues for further study of the immune response induced by RBSDV invasion.
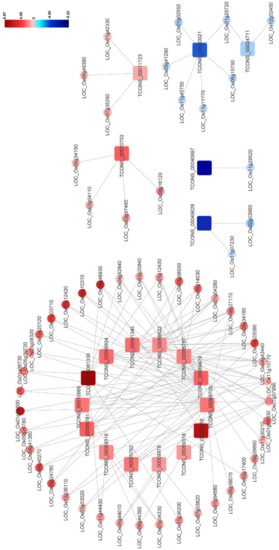
Figure 6.
The network for the predicted DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression pairs potentially involved in plant–pathogen interaction (Pathway ID:ko004626). The square represents DElncRNA and the circle represents DEmRNA. Red indicates upregulation and blue indicates downregulation. The brighter image is the greater fold change. Each selected pair is with a person’s correlation coefficient > 0.95 or < −0.95. Identitiess of DElncRNAs and DEmRNAs are shown in the figure.
3.6. Validation of DEmRNA and DElncRNA in Response to Viral Infection
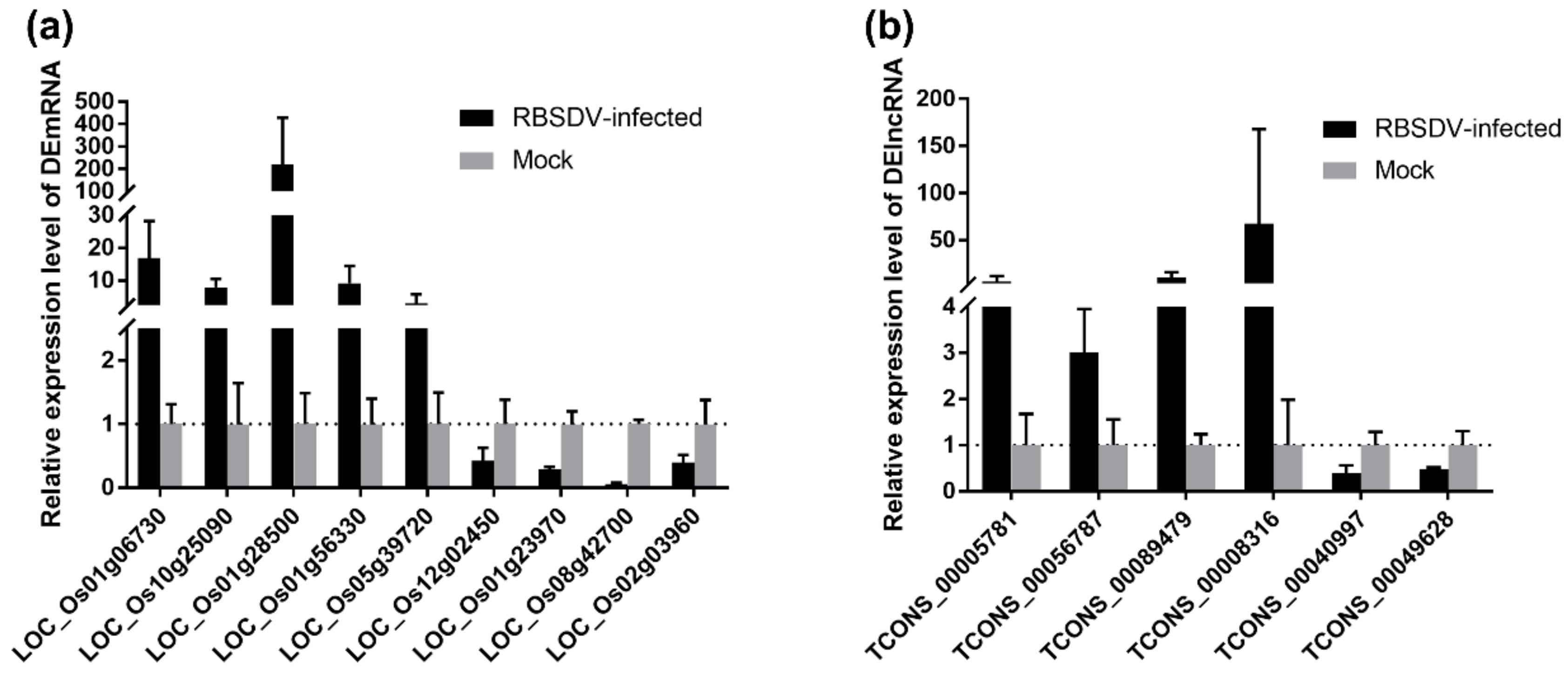
To validate the Illumina sequencing data of the rice transcriptome and the expression patterns of the DEmRNAs and DElncRNAs, nine DEmRNAs and six DElncRNAs related to the plant–pathogen interaction pathway were selected for qRT-PCR analyses. The OsUBC gene was selected as an internal reference for the relative quantification as its expression level changes little upon RBSDV infection [33]. The selected nine DEmRNAs included upregulated LOC_Os01g06730, LOC_Os10g25090, LOC_Os01g28500, LOC_Os01g56330 and LOC_Os05g39720 as well as downregulated LOC_Os12g02450, LOC_Os01g23970, LOC_Os08g42700 and LOC_Os02g03960 in RBSDV-infected rice plants, and the qRT-PCR results were consistent with the Illumina sequencing data (Figure 7a). Besides, six randomly selected DElncRNAs including upregulated TCONS_00005781, TCONS_00056787, TCONS_00089479, TCONS_00008316, and downregulated TCONS_00040997, TCONS_00049628 were also validated by qRT-PCR (Figure 7b). Thus, these data together suggest that the transcriptome results are reliable and can represent the virtual expression pattern upon RBSDV infection.
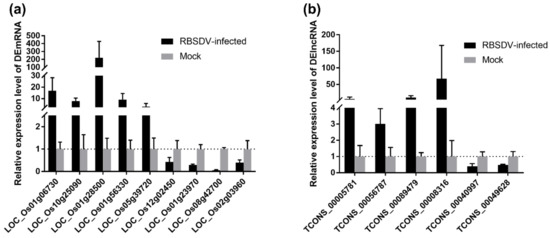
Figure 7.
Validation of expression of selected DEmRNAs (a) and DElncRNAs (b) though qRT-PCR. The total RNA from RBSDV-infected and mock rice plants was extracted for qRT-PCR analyses at 30 dpi. OsUBC gene served as an internal reference for the relative quantification. The values represented means of the gene expression levels ± standard deviations (SD) relative to the mock plants (n = 3 biological replicates).
3.7. Experimental Validation of the lncRNA–mRNA Regulatory Relationship in the DElncRNA–DEmRNA Co-Expression Network
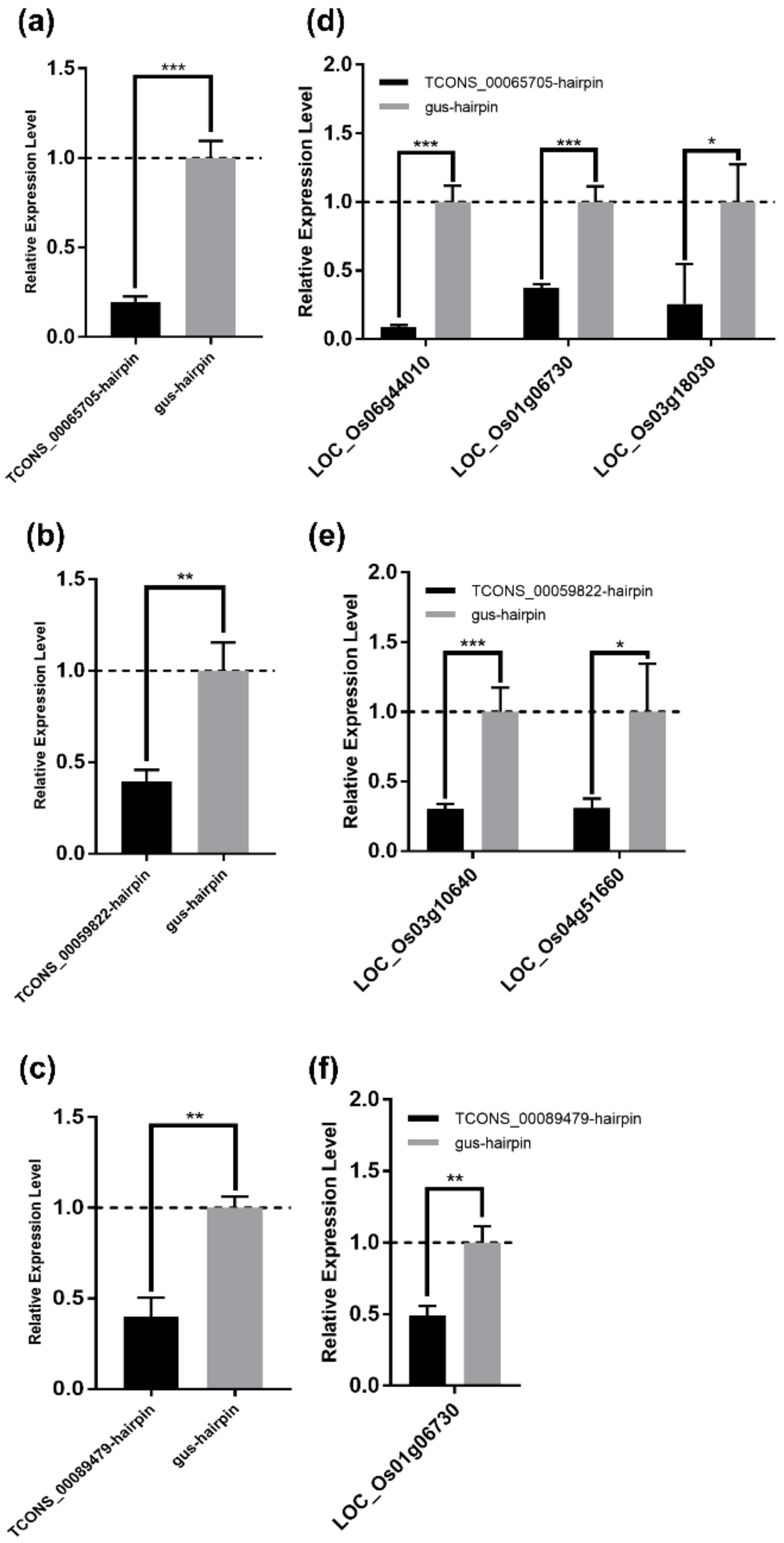
To experimentally confirm the regulatory relationship between lncRNA and mRNA in the DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression network, and to screen lncRNAs and mRNAs for future study, we attempted to detect the expression levels of DEmRNAs in their co-expressed DElncRNAs-silenced rice calli. Three DElncRNAs (TCONS_00065705, TCONS_00089479, and TCONS_00059822), and eight mRNAs were selected from the 20 DElncRNAs and 56 DEmRNAs mentioned above for further tests (Table 4). To silence these three lncRNAs, the hairpin construct targeting each lncRNA was expressed in rice calli by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, while the gus-hairpin construct was expressed as a negative control. The qRT-PCR analyses showed that these three lncRNAs were effectively silenced at 7 days after Agrobacterium infection (Figure 8a–c). In five selected mRNAs (LOC_Os01g06730, LOC_Os06g44010, LOC_Os03g18030, LOC_Os01g28500, and LOC_Os03g03034) predicted to be co-expressed with TCONS_00065705, the relative expression levels of LOC_Os01g06730, LOC_Os06g44010, and LOC_Os03g18030, which, respectively, encode a receptor-like protein, a WRKY transcription factor family protein OsWRKY28, and a leucocyanidin oxygenase, were significantly reduced after silencing TCONS_00065705 (Figure 8d and Table 4). Both LOC_Os04g51660 encoding a malonyl transferase and LOC_Os03g10640 encoding a calcium-transporting ATPase were significantly downregulated after silencing TCONS_00059822 (Figure 8e and Table 4). Interestingly, we found that the expression of LOC_Os01g06730 was also inhibited in TCONS_00089479-silenced rice calli (Figure 8f and Table 4), which suggested that LOC_Os01g06730 was regulated by the two lncRNAs (TCONS_00065705 and TCONS_00089479) and might play an important role in rice-RBSDV interaction. Whereas, there were some mRNAs that their expression levels had no significant changes in co-expressed lncRNAs-silenced rice calli (Figure S4).

Table 4.
List of tested DElncRNAs and DEmRNAs.
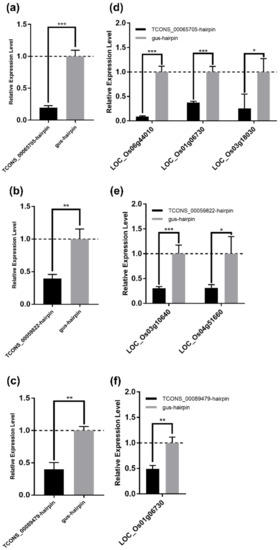
Figure 8.
Experimental validation of the lncRNA–mRNA regulatory relationship in the DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression network. (a–c) The silencing of the lncRNA TCONS_00065705 (a), TCONS_00059822 (b), and TCONS_00089479 (c) was confirmed by qRT-PCR. Total RNA of rice callus was extracted at 7 days after Agrobacterium infection. OsUBC gene served as an internal reference for the relative quantification. The values represent means of the lncRNA expression levels ± standard deviations (SD) relative to the gus-hairpin-expressed callus tissues (n = 3 biological replicates). Data were analyzed by the Student’s t-test, and asterisks denote significant differences between lncRNA-silenced and gus-hairpin-expressed callus tissues (two-sided, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). (d–f) qRT-PCR analyses of the mRNA co-expressed with TCONS_00065705 (d); TCONS_00059822 (e); and TCONS_00089479 (f). Total RNA in (a–c) was used for qRT-PCR analyses. OsUBC gene served as an internal reference for the relative quantification. The values represent means of the mRNA expression levels ± standard deviations (SD) relative to the gus-hairpin-expressed callus tissues (n = 3 biological replicates). Data were analyzed by the Student’s t-test, and asterisks denote significant differences between lncRNA-silenced and gus-hairpin-expressed callus tissues. (two-sided, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNAs that do not encode proteins and can be divided into two groups by their size: (i) small non-coding RNA, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), trans-acting siRNAs (ta-siRNAs) and natural antisense transcript siRNAs (NAT-siRNAs), and (ii) long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are longer than 200 nt [44]. Earlier studies have suggested that many of the lncRNAs and mRNAs may share the common mechanisms of transcription and processing [45]. It is noteworthy that the lncRNAs are more cell-type specific, less abundant, and conserved compared with mRNAs. Moreover, some lncRNAs have been identified diversified and essential functions in gene silencing and imprinting, transcription, mRNA splicing, translation, trafficking of nuclear factors, genome rearrangements, and regulation of chromatin modifications [46]. However, whether lncRNAs have specific biological functions or are merely transcriptional by-products remains controversial, because most of them do not have a recognizable function. Current studies on plant lncRNAs are less comprehensive than those for other eukaryotes [45]. Although multiple lncRNAs have now been identified in Arabidopsis [21], rice [47], maize [48], cotton [49] and Medicago [50], and have been shown to play roles in plant vegetative growth and reproductive development, very few studies focused on plant lncRNA functions in the gene regulatory networks associated with plant defense responses [18].
Several earlier studies have investigated the expression of mRNAs and microRNAs in the RBSDV-infected maize and rice plants and have found some molecular pathways involved in maize-RBSDV and rice-RBSDV interactions [12,13,38,51]. However, the roles of lncRNAs in RBSDV infection are still unclear. To investigate how RBSDV infection affects lncRNA expression in rice, we analyzed the expression of lncRNAs and mRNAs in RBSDV-infected and non-infected rice plants through RNA-seq. In this study, a total of 1342 DEmRNAs have been identified. Among these DEmRNAs, 1087 were upregulated and 255 were downregulated in RBSDV-infected plants (Figure 1e). Moreover, we have also identified 1273 lncRNAs. Among them, 17 were upregulated and five were downregulated in RBSDV-infected rice plants (Figure 1f). GO enrichment and KEGG enrichment analyses for DEmRNAs showed that, similar to previous findings, RBSDV infection in rice also altered the expression of many genes associated with the metabolic, plant–pathogen interaction, and hormone signaling pathways [12,13,38,51]. However, the function of DElncRNAs in RBSDV infection and the relationships of DElncRNA with DEmRNAs remain to be studied.
To identify the potential lncRNA-regulated mRNAs involved in RBSDV infection in rice, we conducted DElncRNA and mRNA co-location and co-expression analyses and mainly focused on DEmRNAs rather than all mRNAs. We found that plenty of DEmRNAs were co-expressed with specific DElncRNAs, while only a few were co-located with specific DElncRNAs (Figure 5, Table 3 and Table S10), suggesting that the regulation of mRNA expression by lncRNAs is not only dependent on their chromosomal locations but also is affected by other unidentified and possibly complex co-expressed networks. In this study we also noticed that five mRNAs in the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (ko04120) were co-localized with DElncRNAs (Figure 4a and Table S7), suggesting that RBSDV infection in rice can regulate several genes related to the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway through lncRNAs. To better understand these complex regulatory relationships of lncRNA to mRNA, the predicted co-expression network for the DElncRNAs and DEmRNAs was constructed (Figure 5 and Table S10). Due to the large quantity of DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expression pairs in this network, it is difficult for us to find the co-expression pairs of the DElncRNA–DEmRNA that are potentially related to RBSDV infection. To narrow the scope of genes in the co-expression network, we filtered out the DEmRNAs which were related to the plant–pathogen interaction (Pathway ID:ko004626) and constructed a new network for them (Figure 6 and Table S11). It is noteworthy that most predicted DElncRNA–DEmRNA pairs were upregulated in this network, suggesting that RBSDV infection in rice could robustly activate many gene expressions. The LRR domain-containing proteins are important for protein recognition and play critical roles in plant defense. Some viral proteins, such as p50 of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) and the coat protein of potato virus X (PVX), can be perceived by plant LRR proteins, and then the antiviral response will be activated [52]. We found that there were some LRR domain-containing proteins in this network, such as LOC_Os01g06730, LOC_Os08g10310, and LOC_Os02g17400 (Figure 6 and Table S11). Thus, we speculate that these LRR domain-containing proteins might participate in the recognition of viral proteins. In our co-expression network, OsCML16 (LOC_Os01g04330) and OsCML21 (LOC_Os05g24780) encoding the plant-specific calmodulin-like proteins, were found to be co-expressed with four DElncRNAs (Table S11). Calcium (Ca2+) is an important messenger involved in plant defense signal transduction, and some calmodulin-like proteins are necessary for the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) against pathogen invasion [53]. A previous study has shown that ROS is accumulated after RBSDV infection and enhances the resistance of rice to the virus [12]. These genes encoding the plant-specific calmodulin-like proteins may be upregulated by DElncRNAs to withstand viral infection by promoting ROS accumulation. We also found that genes participating in flavonoids biosynthesis could also be regulated by DElncRNAs, such as TCONS_00065705-LOC_Os03g18030, TCONS_00065705-LOC_Os10g16974, and TCONS_00059822-LOC_Os04g51660 (Figure 6 and Table S11). The flavonoids are important in plant resistance against pathogens and insects [41], and have been shown to enhance the plant resistance to PVX and tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) [54,55], as well as the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper [56]. The upregulation of these DElncRNAs and their related flavonoid biosynthesis genes suggests that rice can increase the accumulation of the flavonoids to counter viral infection and planthopper feeding, and lncRNAs may be essential regulators in this process.
Besides the DElncRNAs participating in the antiviral response against RBSDV infection, we also found that some DElncRNAs may be utilized by RBSDV to enhance viral infection. Previous studies have indicated that plant hormones: ABA, JA, BR, and auxin, play important roles in RBSDV infection in rice plants [11,12,38]. In this study, we have found that some hormone signaling- and biosynthesis-related DEmRNAs were co-expressed with specific DElncRNAs, such as both OsJAZ8 (LOC_Os09g26780) and OsJAZ11 (LOC_Os03g08320) are co-expressed with two DElncRNAs (TCONS_00089479 and TCONS_00065705) (Figure 6 and Table S11). The cytochrome P450 was reported to be implicated in brassinosteroids biosynthesis in rice [57], and in our results, a cytochrome P450 (LOC_Os01g72270) co-located with TCONS_00011723 (Table 3). The JA signaling pathway has been proved to positively regulate antiviral defense against RBSDV in rice, while the BR signaling pathway was reported to mediate susceptibility to RBSDV infection [58]. Interestingly, JAZ protein is a repressor of the JA signaling pathway, and cytochrome P450 is involved in BR biosynthesis. The upregulation of these genes may inhibit the JA signaling pathway and promote the BR signaling pathway, which may contribute to RBSDV infection on rice. In another co-expressed lncRNA–mRNA pair, OsWRKY28 (LOC_Os06g44010) was co-expressed with lncRNA TCONS_00065705 (Figure 6 and Table S11). OsWRKY28 is reported to be a negative regulator of innate immune responses against rice blast fungus in rice [59], and thus we speculate that the upregulation of OsWRKY28 would also enhance the susceptibility of rice to RBSDV.
Based on the computational prediction of DElncRNA–DEmRNA regulatory relationships, we attempted to confirm these relationships experimentally. Most studies identifying the lncRNAs in rice through high-throughput RNA-seq techniques did not verify whether the lncRNA–mRNA regulatory relationships truly exist or not, which is mainly because of the relatively long period of obtaining lncRNA-silenced transgenic rice plants. Here, we succeeded in silencing certain DElncRNAs in rice calli by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, and then the expression levels of the predicted co-expressed DEmRNAs were detected through qRT-PCR. Three DElncRNAs were selected to be silenced, and eight co-expressed DEmRNAs were tested. As a result, we found that five DEmRNAs could be regulated by the selected DElncRNAs (Figure 8 and Table 4). Moreover, LOC_Os01g06730 predicted to encode a receptor-like protein was found to be regulated by two DElncRNAs (TCONS_00065705 and TCONS_00089479), suggesting the regulation of lncRNA to mRNA may be a complex relationship (Figure 6 and Figure 8, Table 4 and Table S11). We also found that the DEmRNAs confirmed to co-express with DElncRNAs experimentally in this study were mainly located in the middle to the upstream of their related pathways, which indicates that lncRNAs are prone to alter pathways at their middle to upstream location. Genes downstream of a pathway may not be the target of lncRNAs. For example, the expression level of a PR1 gene (LOC_Os01g28500) which locates at the downstream of the plant defense pathway, did not significantly change after silencing its predicted co-expressed DElncRNAs (TCONS_00065705 and TCONS_00089479) in our test (Figure 6 and Figure S3, Table 4 and Table S11). Although not all selected co-expressed DEmRNAs were regulated by the corresponding DElncRNAs in our experiments, this method still verified a significant number of lncRNA–mRNA regulatory relationships. We think that our results here prove this method to be a feasible and efficient way to screen lncRNA–mRNA regulatory pairs for further study. Besides, this method is less time-consuming compared with the traditional transgenic method, which makes it possible to rapidly screen lncRNA–mRNA regulatory pairs from considerable computationally predicted data.
In brief, these results provide clues on the roles of DEmRNA and DElncRNA in confronting RBSDV infection and information for future functional studies of the candidate genes involved in rice-RBSDV interaction. Moreover, we also present a new method to rapidly screen lncRNA–mRNA regulatory pairs based on transient gene silencing in rice calli through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, which will be helpful to the function study of lncRNAs in rice in the future. To understand the interaction between rice and RBSDV, further investigations on regulatory mechanisms of lncRNA–mRNA and the functions of their targeted pathways are necessary.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/12/9/951/s1. Figure S1. The principal component analysis (PCA) of mRNAs and lncRNAs. Figure S2. GO enrichment analysis of mRNAs co-located with DElncRNAs. Figure S3. GO enrichment analysis of mRNAs co-expressed with DElncRNAs. Figure S4. The qRT-PCR data of the mRNAs with no significant changes after silencing lncRNAs. Table S1. PCR primer sequences used for qRT-PCR analysis. Table S2. PCR primer sequences used for vector construction. Table S3. Detail information of the DEmRNAs. Table S4. KEGG pathway enrichment for DEmRNAs. Table S5. DEmRNAs involved in the plant–pathogen interaction pathway. Table S6. The 304 mRNAs co-located with DElncRNAs. Table S7. KEGG pathway enrichment for mRNAs co-located with DElncRNAs. Table S8. The 17,335 mRNAs co-expressed with DElncRNAs. Table S9. KEGG pathway enrichment for mRNAs co-expressed with DElncRNAs. Table S10. Detail information of the DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expressed pairs. Table S11. Detail information of the DElncRNA–DEmRNA co-expressed pairs involved in the plant–pathogen interaction pathway.
Author Contributions
T.Z. and Q.L., conducted laboratory work and drafted the paper. C.L., and S.F., contributed to data analysis. J.W., X.Z. and J.K.K. conceived and designed the study. J.W. secured funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31772125; 31972234), the National Key Research and Development Project of China (No. 2016YFD0300706; 2017YFD0201604), the Bilateral Cooperation Project of Zhejiang-Czech Industrial Research and Development of China (2015C54004 and TF02000056), and the Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (nycytx-001).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Xinshun Ding (Noble Research Institute [Retired], Ardmore, USA) for his help during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Qian Liang is the employee of Zhejiang TianKe High-Technology Development Co. Ltd. Zhejiang TianKe High-Technology Development Co. Ltd. does not provide financial support for this research. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| RBSDV | Rice black-streaked dwarf virus |
| SBPH | small brown planthopper |
| FPKM | fragments per kilo-base per million reads |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| DEmRNA | differentially expressed mRNA |
| DElncRNA | differentially expressed lncRNA |
References
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Miao, H.; Hu, X.; Pang, Y.; Qiu, B. Rice black streaked dwarf virus P9-1, an α-helical protein, self-interacts and forms viroplasms in vivo. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Li, D.; Yu, J. Development of an ID-ELISA for the detection of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus in plants. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 134, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikata, E.; Kitagawa, Y. Rice black-streaked dwarf virus: Its properties, morphology and intracellular localization. Virology 1977, 77, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.W.; Qu, Z.C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.W.; Xu, J.; Ye, M.M.; Wu, H.L.; Liao, X.G.; Shen, D.L. Identification of rice black streaked dwarf virus in different cereal crops with dwarfing symptoms in China. Acta Virol. 2001, 45, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Yu, J.; Feng, J.; Han, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Identification of rice black-streaked dwarf fijivirus in maize with rough dwarf disease in China. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J. Mapping quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to rice black-streaked virus in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ni, Y.; Liu, H.; Rao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Development and use of three monoclonal antibodies for the detection of rice black-streaked dwarf virus in field plants and planthopper vectors. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Chen, J.P.; Adams, M.J. Molecular characterisation of segments 1 to 6 of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus from China provides the complete genome. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, H. Biology and Epidemiology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Lovisolo, O. Tubular Structures Associated with Maize Rough Dwarf Virus Particles in Crude Extracts: Electron Microscopy Study. J. Gen. Virol. 1971, 13, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Hong, G.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Suppression of auxin signalling promotes rice susceptibility to Rice black streaked dwarf virus infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Tan, X.; He, Y.; Hong, G.; Li, J.; Ming, F.; Yao, X.; et al. Abscisic acid negatively modulates plant defence against rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection by suppressing the jasmonate pathway and regulating reactive oxygen species levels in rice. Plant. Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Duan, C.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wu, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Yong, H.; et al. Dual transcriptome analysis reveals insights into the response to Rice black-streaked dwarf virus in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4593–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaloner, T.; van Kan, J.A.L.; Grant-Downton, R.T. RNA ‘Information Warfare’ in Pathogenic and Mutualistic Interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y. An expression atlas of miRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Liu, S.; Nie, X.; Weining, S.; Wu, L. Conservation analysis of long non-coding RNAs in plants. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulitsky, I. Evolution to the rescue: Using comparative genomics to understand long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Lu, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Mao, H.; Zhang, P.; Yao, J.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Sun, F.; Hu, J.; Zha, X.; Su, W.; Yang, J. Overexpressing lncRNA LAIR increases grain yield and regulates neighbouring gene cluster expression in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Chua, N.-H. Long noncoding RNA transcriptome of plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jung, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Deng, S.; Bernad, L.; Arenas-Huertero, C.; Chua, N.-H. Genome-Wide Analysis Uncovers Regulation of Long Intergenic Noncoding RNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4333–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.-H.; Stephen, S.; Taylor, J.; Helliwell, C.A.; Wang, M.-B. Long noncoding RNAs responsive to Fusarium oxysporum infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.S.; Sun, H.-X.; Park, B.S.; Huang, C.-H.; Yeh, S.-D.; Jung, C.; Chua, N.-H. ELF18-INDUCED LONG-NONCODING RNA Associates with Mediator to Enhance Expression of Innate Immune Response Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Liu, P.; Irwanto, N.; Loh, D.R.; Wong, S.-M. Upregulation of LINC-AP2 is negatively correlated with AP2 gene expression with Turnip crinkle virus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, D.; Wang, J.; Ling, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, W.; et al. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus intergenic siRNAs target a host long noncoding RNA to modulate disease symptoms. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.-Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. Predicting active site residue annotations in the Pfam database. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, G.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W.; Liaw, A.; Lumley, T.; Mächler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Möller, S. gplots: Various R programming tools for plotting data. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=gplots (accessed on 25 February 2018).
- Fang, P.; Lu, R.; Sun, F.; Lan, Y.; Shen, W.; Du, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, T. Assessment of reference gene stability in Rice stripe virus and Rice black streaked dwarf virus infection rice by quantitative Real-time PCR. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiei, Y.; Komari, T. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice using immature embryos or calli induced from mature seed. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinodoz, S.; Guttman, M. Long noncoding RNAs: An emerging link between gene regulation and nuclear organization. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Brar, A.; Yadav, M.; Chawade, A.; Vivekanand, V.; Pareek, N. Chitinases—Potential Candidates for Enhanced Plant Resistance towards Fungal Pathogens. Agriculture 2018, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; MacFarlane, S.; Yan, F.; Chen, J. Jasmonic acid-mediated defense suppresses brassinosteroid-mediated susceptibility to Rice black streaked dwarf virus infection in rice. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Rice black-streaked dwarf virus-encoded P5-1 regulates the ubiquitination activity of SCF E3 ligases and inhibits jasmonate signaling to benefit its infection in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierziak, J.; Kostyn, K.; Kulma, A. Flavonoids as Important Molecules of Plant Interactions with the Environment. Molecules 2014, 19, 16240–16265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldon, D.; Mbengue, M.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P. Calcium Signalling in Plant Biotic Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.P.; Somssich, I.E. The Role of WRKY Transcription Factors in Plant Immunity: Figure 1. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Niu, Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Yu, N.; Chua, N. Analysis of non-coding transcriptome in rice and maize uncovers roles of conserved lncRNAs associated with agriculture traits. Plant J. 2015, 84, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulitsky, I.; Bartel, D.P. lincRNAs: Genomics, Evolution, and Mechanisms. Cell 2013, 154, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekanova, J.A. Long non-coding RNAs and their functions in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Liao, J.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.-P.; Li, Q.-F.; Qu, L.-H.; Shu, W.-S.; Chen, Y.-Q. Genome-wide screening and functional analysis identify a large number of long noncoding RNAs involved in the sexual reproduction of rice. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Eichten, S.R.; Shimizu, R.; Petsch, K.; Yeh, C.-T.; Wu, W.; Chettoor, A.M.; Givan, S.A.; Cole, R.A.; Fowler, J.E.; et al. Genome-wide discovery and characterization of maize long non-coding RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, D.; Tu, L.; Gao, W.; He, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, N.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X. Long noncoding RNAs and their proposed functions in fibre development of cotton (Gossypium spp.). New Phytol. 2015, 207, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, M.-G.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.-H. Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.S.; Ji, W.; Wang, M.; Bian, S.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yu, M.; Liu, Q.; et al. Transcriptional changes of rice in response to rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Gene 2017, 628, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-A.; Yeom, S.-I. Plant NB-LRR proteins: Tightly regulated sensors in a complex manner. Brief. Funct. Genomics 2015, 14, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, B.W. Calcium signaling and biotic defense responses in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e973818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, L.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Fuertes, D.; Bellés, J.M.; Rodrigo, I.; Lisón, P. Tomato glycosyltransferase Twi1 plays a role in flavonoid glycosylation and defence against virus. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, C.J.; Towers, G.H.N. Inhibition of infectivity of potato virus X by flavonoids. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. The OsmiR396-OsGRF8-OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A Novel Cytochrome P450 Is Implicated in Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis via the Characterization of a Rice Dwarf Mutant, dwarf11, with Reduced Seed Length. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hong, G.; Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Kong, Y.; Sang, T.; Xie, K.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; et al. The OsGSK2 Kinase Integrates Brassinosteroid and Jasmonic Acid Signaling by Interacting with OsJAZ4. Plant Cell 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Shimogawa, T.; Shimizu, T.; Otake, Y.; Yokotani, N.; Nishizawa, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Nojiri, H.; Yamane, H.; et al. OsWRKY28, a PAMP-responsive transrepressor, negatively regulates innate immune responses in rice against rice blast fungus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).