Robust Neutralizing Antibody Levels Detected after Either SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or One Year after Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Collective
2.2. Serological Assay
2.3. Cell Culture and Virus Propagation
2.4. Neutralization Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Longitudinal Course of S-IgG Levels after Infection or after Vaccination
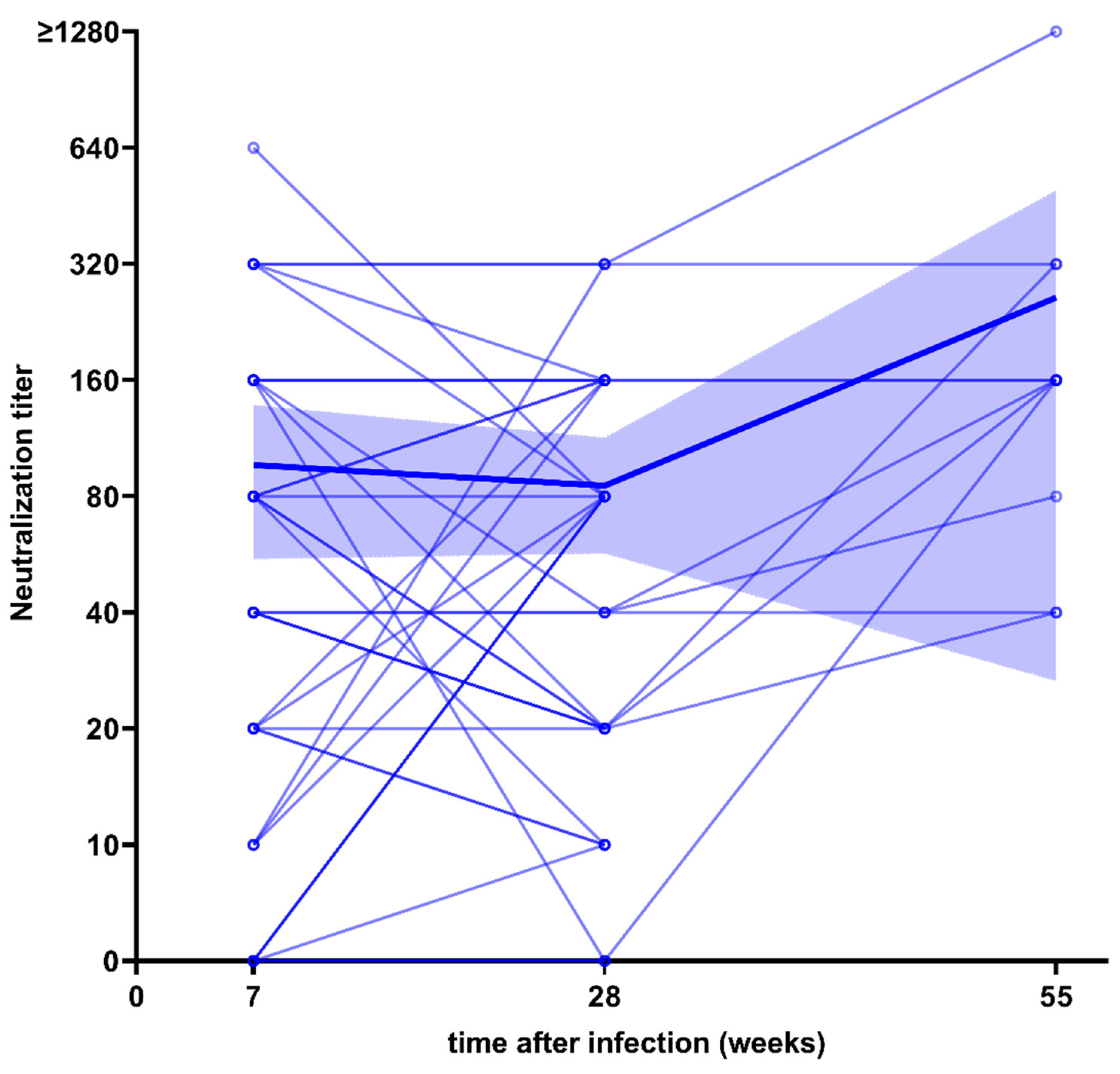
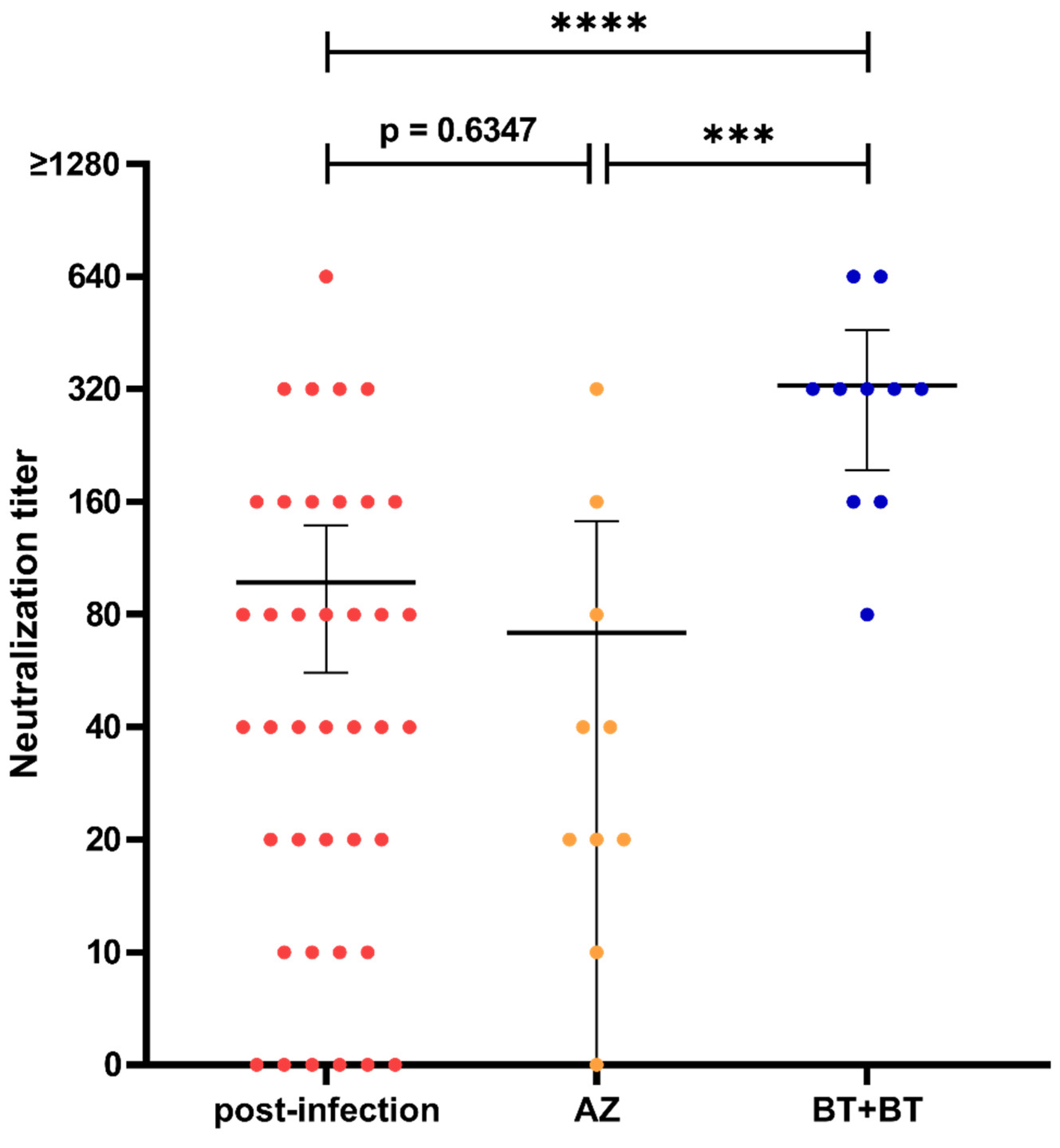
3.2. Neutralization Capacity after Infection and Vaccination
3.3. Correlation between S-IgG Levels and Neutralization Capacity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Saei, A.; Andrews, N.; Oguti, B.; Charlett, A.; Wellington, E.; Stowe, J.; Gillson, N.; Atti, A.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine coverage in health-care workers in England and effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against infection (SIREN): A prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.G.; Burgess, J.L.; Naleway, A.L.; Tyner, H.; Yoon, S.K.; Meece, J.; Olsho, L.E.W.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Fowlkes, A.L.; Lutrick, K.; et al. Prevention and Attenuation of Covid-19 with the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Vogler, I.; Derhovanessian, E.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Quandt, J.; Bidmon, N.; Ulges, A.; Baum, A.; et al. BNT162b2 vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies and poly-specific T cells in humans. Nature 2021, 595, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewer, K.J.; Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Sharpe, H.; Makinson, R.; Morter, R.; Flaxman, A.; Wright, D.; Bellamy, D.; Bittaye, M.; et al. T cell and antibody responses induced by a single dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine in a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.T.; Rouphael, N.G.; Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Durability of Responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Rha, M.S.; Sa, M.; Choi, H.K.; Jeon, J.H.; Seok, H.; Park, D.W.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, H.W.; Choi, W.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell memory is sustained in COVID-19 convalescent patients for 10 months with successful development of stem cell-like memory T cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Ling, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, M.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liang, D.; et al. Durability of neutralizing antibodies and T-cell response post SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispinseri, S.; Secchi, M.; Pirillo, M.F.; Tolazzi, M.; Borghi, M.; Brigatti, C.; De Angelis, M.L.; Baratella, M.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Venturi, G.; et al. Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in symptomatic COVID-19 is persistent and critical for survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, V.; Denolly, S.; Vogrig, M.; Boson, B.; Siret, E.; Rigaill, J.; Pillet, S.; Grattard, F.; Gonzalo, S.; Verhoeven, P.; et al. A longitudinal study of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients reveals a high correlation between neutralizing antibodies and COVID-19 severity. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.A.; Corman, V.M.; Echterhoff, A.K.C.; Muller, M.A.; Richter, A.; Schmandke, A.; Schmidt, M.L.; Schmidt, T.H.; de Vries, F.M.; Drosten, C.; et al. Seroprevalence and correlates of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies from a population-based study in Bonn, Germany. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.F.; Li, F.; Bai, C.Q.; Qin, C.F. Longitudinal dynamics of antibody responses in recovered COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Pang, X.; Du, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X.; Chen, J.; Deng, S.; et al. Antibodies Can Last for More Than 1 Year After SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Follow-Up Study From Survivors of COVID-19. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 684864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.; Scherag, A.; Baier, M.; Kiehntopf, M.; Kamradt, T.; Kolanos, S.; Ankert, J.; Glockner, S.; Makarewicz, O.; Hagel, S.; et al. Antibody response using six different serological assays in a completely PCR-tested community after a coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak-the CoNAN study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 470.e1–470.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Bottcher, S.; Haring, C.; Giebeler, L.; Henke, A.; Zell, R.; Jungwirth, J.; Jordan, P.M.; Werz, O.; Hornung, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 causes severe epithelial inflammation and barrier dysfunction. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.F.; Wei, J.; O’Donnell, D.; Stoesser, N.E.; Matthews, P.C.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; Marsden, B.D.; Cox, S.; James, T.; et al. The Duration, Dynamics, and Determinants of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Antibody Responses in Individual Healthcare Workers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e699–e709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masia, M.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, M.; Telenti, G.; Agullo, V.; Garcia, J.A.; Padilla, S.; Garcia-Abellan, J.; Galiana, A.; Gonzalo-Jimenez, N.; Gutierrez, F. Durable antibody response one year after hospitalization for COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 123, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, G.L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhan, B.D.; Duan, L.J.; Lu, B.; Shi, C.; Gao, Y.M.; Peng, H.H.; et al. Persistence of Antibody and Cellular Immune Responses in COVID-19 patients over Nine Months after Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, D.; Lu, M.; Lv, Y. Disappearance of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in a -COVID-19 patient after recovery. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1703–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.X.; Tang, X.J.; Shi, Q.L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.J.; et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Stellas, D.; Rosati, M.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Hu, X.; Politou, M.; Pappa, V.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Karaliota, S.; Bear, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibody kinetics eight months from COVID-19 onset: Persistence of spike antibodies but loss of neutralizing antibodies in 24% of convalescent plasma donors. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 89, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K.; et al. Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.S.; Vibholm, L.K.; Monrad, I.; Olesen, R.; Frattari, G.S.; Pahus, M.H.; Hojen, J.F.; Gunst, J.D.; Erikstrup, C.; Holleufer, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 elicits robust adaptive immune responses regardless of disease severity. EBioMedicine 2021, 68, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Potent and Persistent Antibody Response in COVID-19 Recovered Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 659041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Long, Q.X.; Deng, H.J.; Hu, J.; Gao, Q.Z.; Zhang, G.J.; He, C.L.; Huang, L.Y.; Hu, J.L.; Chen, J.; et al. Longitudinal Dynamics of the Neutralizing Antibody Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e531–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaaskelainen, A.J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kekalainen, E.; Ahava, M.J.; Loginov, R.; Kallio-Kokko, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Jarva, H.; Kurkela, S.; Lappalainen, M. Performance of six SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in comparison with microneutralisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.S.; Case, J.B.; Franks, C.E.; Chen, R.E.; Anderson, N.W.; Henderson, J.P.; Diamond, M.S.; Gronowski, A.M.; Farnsworth, C.W. Association between SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies and Commercial Serological Assays. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, P.J.M.; Caniels, T.G.; van der Straten, K.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Aldon, Y.; Bangaru, S.; Torres, J.L.; Okba, N.M.A.; Claireaux, M.; Kerster, G.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability. Science 2020, 369, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensels, D.; Pierlet, N.; Penders, J.; Mesotten, D.; Heylen, L. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response Following Vaccination With BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. JAMA 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shaw, R.H.; Stuart, A.S.; Greenland, M.; Dinesh, T.; Provstgaard-Morys, S.; Clutterbuck, E.; Ramasamy, M.N.; Aley, P.K.; Farooq Mujadidi, Y.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity Report from the Com-COV Study—A Single-Blind Randomised Non-Inferiority Trial Comparing Heterologous And Homologous Prime-Boost Schedules with An Adenoviral Vectored and mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. Lancet 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, D.W.; Lumley, S.F.; Wei, J.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Justice, A.; Jesuthasan, G.; O’Donnell, D.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; et al. Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike responses to Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines by previous infection status. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Stoesser, N.; Matthews, P.C.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Studley, R.; Bell, I.; Bell, J.I.; Newton, J.N.; Farrar, J.; Diamond, I.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in 45,965 adults from the general population of the United Kingdom. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.S.; O’Halloran, J.A.; Kalaidina, E.; Kim, W.; Schmitz, A.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Lei, T.; Thapa, M.; Chen, R.E.; Case, J.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines induce persistent human germinal centre responses. Nature 2021, 596, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cele, S.; Gazy, I.; Jackson, L.; Hwa, S.H.; Tegally, H.; Lustig, G.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Wilkinson, E.; Naidoo, Y.; et al. Escape of SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 from neutralization by convalescent plasma. Nature 2021, 593, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Werner, A.P.; Koch, M.; Choi, A.; Narayanan, E.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Colpitts, T.; Bennett, H.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Shi, W.; et al. Serum Neutralizing Activity Elicited by mRNA-1273 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.W.; Linderman, S.L.; Moodie, Z.; Czartoski, J.; Lai, L.; Mantus, G.; Norwood, C.; Nyhoff, L.E.; Edara, V.V.; Floyd, K.; et al. Longitudinal analysis shows durable and broad immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection with persisting antibody responses and memory B and T cells. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glöckner, S.; Hornung, F.; Baier, M.; Weis, S.; Pletz, M.W.; Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Löffler, B.; the CoNAN Study Group. Robust Neutralizing Antibody Levels Detected after Either SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or One Year after Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102003
Glöckner S, Hornung F, Baier M, Weis S, Pletz MW, Deinhardt-Emmer S, Löffler B, the CoNAN Study Group. Robust Neutralizing Antibody Levels Detected after Either SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or One Year after Infection. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlöckner, Stefan, Franziska Hornung, Michael Baier, Sebastian Weis, Mathias W. Pletz, Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer, Bettina Löffler, and the CoNAN Study Group. 2021. "Robust Neutralizing Antibody Levels Detected after Either SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or One Year after Infection" Viruses 13, no. 10: 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102003
APA StyleGlöckner, S., Hornung, F., Baier, M., Weis, S., Pletz, M. W., Deinhardt-Emmer, S., Löffler, B., & the CoNAN Study Group. (2021). Robust Neutralizing Antibody Levels Detected after Either SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination or One Year after Infection. Viruses, 13(10), 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102003








