HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Proteolytic Cleavage Protects Infected Cells from ADCC Mediated by Plasma from Infected Individuals
Abstract
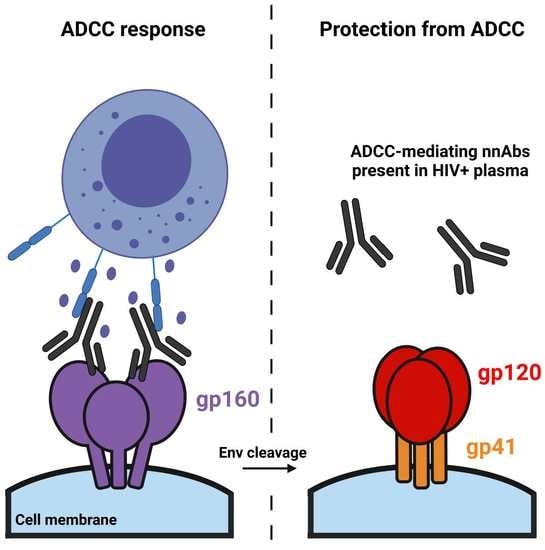
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Lines and Primary Cells
2.3. Antibodies and Sera
2.4. Small Molecules
2.5. Plasmids and Proviral Constructs
2.6. Radioactive Labeling and Immunoprecipitation of Envelope Glycoproteins
2.7. Viral Production and Infections
2.8. Virus Capture Assay
2.9. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell-Surface and Intracellular Staining
2.10. FACS-Based ADCC Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Conformation of HIV-1 Uncleaved Env at the Surface of Infected Cells and Viral Particles
3.2. Impact of HIV-1 Env Proteolytic Cleavage on ADCC Responses Mediated by HIV+ Plasma
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Earl, P.L.; Doms, R.W.; Moss, B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earl, P.L.; Moss, B.; Doms, R.W. Folding, interaction with GRP78-BiP, assembly, and transport of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantanen, M.L.; Leinikki, P.; Kuismanen, E. Endoproteolytic cleavage of HIV-1 gp160 envelope precursor occurs after exit from the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Williams, J.A.; Chu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.J.; Ding, L.; Akhirome, E.; Wen, X.; Lapierre, L.A.; Goldenring, J.R.; et al. Rab11-FIP1C and Rab14 direct plasma membrane sorting and particle incorporation of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein complex. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschman, J.; Qi, M.; Ding, L.; Hammonds, J.; Dienger-Stambaugh, K.; Wang, J.J.; Lapierre, L.A.; Goldenring, J.R.; Spearman, P. HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Trafficking through the Endosomal Recycling Compartment Is Required for Particle Incorporation. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freed, E.O.; Myers, D.J.; Risser, R. Mutational analysis of the cleavage sequence of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein precursor gp160. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 4670–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, V.; Pawlita, M. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env gene product proteolytic cleavage site. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCune, J.M.; Rabin, L.B.; Feinberg, M.B.; Lieberman, M.; Kosek, J.C.; Reyes, G.R.; Weissman, I.L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 1988, 53, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.K.; Spellman, M.W.; Riddle, L.; Harris, R.J.; Thomas, J.N.; Gregory, T.J. Assignment of intrachain disulfide bonds and characterization of potential glycosylation sites of the type 1 recombinant human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein (gp120) expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10373–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, H.B.; Tucker, S.P.; Hunter, E.; Schutzbach, J.S.; Compans, R.W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein is modified by O-linked oligosaccharides. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewar, R.L.; Vasudevachari, M.B.; Natarajan, V.; Salzman, N.P. Biosynthesis and processing of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins: Effects of monensin on glycosylation and transport. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 2452–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallenberger, S.; Bosch, V.; Angliker, H.; Shaw, E.; Klenk, H.D.; Garten, W. Inhibition of furin-mediated cleavage activation of HIV-1 glycoprotein gp160. Nature 1992, 360, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroly, E.; Vandenbranden, M.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Cogniaux, J.; Jacob, G.S.; Howard, S.C.; Marshall, G.; Kompelli, A.; Basak, A.; Jean, F.; et al. The convertases furin and PC1 can both cleave the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 envelope glycoprotein gp160 into gp120 (HIV-1 SU) and gp41 (HIV-I TM). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12240–12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroly, E.; Wouters, S.; Di Bello, C.; Lazure, C.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Seidah, N.G. Identification of the paired basic convertases implicated in HIV gp160 processing based on in vitro assays and expression in CD4(+) cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30442–30450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decroly, E.; Benjannet, S.; Savaria, D.; Seidah, N.G. Comparative functional role of PC7 and furin in the processing of the HIV envelope glycoprotein gp160. FEBS Lett. 1997, 405, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, S.S.; Thomas, L.; VanSlyke, J.K.; Stenberg, P.E.; Thomas, G. Intracellular trafficking and activation of the furin proprotein convertase: Localization to the TGN and recycling from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubay, J.W.; Dubay, S.R.; Shin, H.J.; Hunter, E. Analysis of the cleavage site of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein: Requirement of precursor cleavage for glycoprotein incorporation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4675–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrera, C.; Klasse, P.J.; Michael, E.; Kake, S.; Barnes, K.; Kibler, C.W.; Campbell-Gardener, L.; Si, Z.; Sodroski, J.; Moore, J.P.; et al. The impact of envelope glycoprotein cleavage on the antigenicity, infectivity, and neutralization sensitivity of Env-pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles. Virology 2005, 338, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasquato, A.; Dettin, M.; Basak, A.; Gambaretto, R.; Tonin, L.; Seidah, N.G.; Di Bello, C. Heparin enhances the furin cleavage of HIV-1 gp160 peptides. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, J.B.; Gorman, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Arthos, J.; Burton, D.R.; Koff, W.C.; Courter, J.R.; Smith, A.B., III; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Conformational dynamics of single HIV-1 envelope trimers on the surface of native virions. Science 2014, 346, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Lu, M.; Gorman, J.; Terry, D.S.; Hong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H.; Altman, R.B.; Arthos, J.; Blanchard, S.C.; et al. HIV-1 Env trimer opens through an asymmetric intermediate in which individual protomers adopt distinct conformations. eLife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Ma, X.; Castillo-Menendez, L.R.; Gorman, J.; Alsahafi, N.; Ermel, U.; Terry, D.S.; Chambers, M.; Peng, D.; Zhang, B.; et al. Associating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structures with states on the virus observed by smFRET. Nature 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Lu, M.; Bess, J., Jr.; Chao, C.W.; Gorman, J.; Terry, D.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, T.; Blanchard, S.C.; et al. Subnanometer structures of HIV-1 envelope trimers on aldrithiol-2-inactivated virus particles. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtmueller, B.M.; Bridges, M.D.; Dam, K.M.; Lerch, M.T.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Hubbell, W.L.; Bjorkman, P.J. DEER Spectroscopy Measurements Reveal Multiple Conformations of HIV-1 SOSIP Envelopes that Show Similarities with Envelopes on Native Virions. Immunity 2018, 49, 235–246.e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finzi, A.; Xiang, S.H.; Pacheco, B.; Wang, L.; Haight, J.; Kassa, A.; Danek, B.; Pancera, M.; Kwong, P.D.; Sodroski, J. Topological layers in the HIV-1 gp120 inner domain regulate gp41 interaction and CD4-triggered conformational transitions. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veillette, M.; Desormeaux, A.; Medjahed, H.; Gharsallah, N.E.; Coutu, M.; Baalwa, J.; Guan, Y.; Lewis, G.; Ferrari, G.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Interaction with cellular CD4 exposes HIV-1 envelope epitopes targeted by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decker, J.M.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; Levy, D.N.; Wang, W.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Derdeyn, C.A.; Allen, S.; et al. Antigenic conservation and immunogenicity of the HIV coreceptor binding site. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Yates, N.L.; Liu, P.; Qin, L.; Fouda, G.G.; Chavez, L.L.; Decamp, A.C.; Parks, R.J.; Ashley, V.C.; Lucas, J.T.; et al. Initial B-cell responses to transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1: Virion-binding immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies followed by plasma anti-gp41 antibodies with ineffective control of initial viremia. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12449–12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Haynes, B.F. HIV-1-specific antibody responses during acute and chronic HIV-1 infection. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2009, 4, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, K.L.; Gray, E.S.; Moore, P.L.; Decker, J.M.; Salomon, A.; Montefiori, D.C.; Graham, B.S.; Keefer, M.C.; Pinter, A.; Morris, L.; et al. High titer HIV-1 V3-specific antibodies with broad reactivity but low neutralizing potency in acute infection and following vaccination. Virology 2009, 387, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.M.; Easterhoff, D.; Bradley, T.; Luo, K.; Williams, W.B.; Liao, H.X.; Moody, M.A.; Phad, G.E.; Vazquez Bernat, N.; et al. Antibodies Elicited by Multiple Envelope Glycoprotein Immunogens in Primates Neutralize Primary Human Immunodeficiency Viruses (HIV-1) Sensitized by CD4-Mimetic Compounds. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5031–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.M.; Mach, L.; Ding, S.; Prevost, J.; Richard, J.; Hora, B.; Sutherland, L.; Zhao, C.A.; Conn, B.P.; et al. A CD4-mimetic compound enhances vaccine efficacy against stringent immunodeficiency virus challenge. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Pollara, J.; Kozink, D.; Harms, T.; Drinker, M.; Freel, S.; Moody, M.A.; Alam, S.M.; Tomaras, G.D.; Ochsenbauer, C.; et al. An HIV-1 gp120 envelope human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a C1 conformational epitope mediates potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity and defines a common ADCC epitope in human HIV-1 serum. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7029–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Pazgier, M.; Sajadi, M.M.; Kamin-Lewis, R.; Al-Darmarki, S.; Flinko, R.; Lovo, E.; Wu, X.; Robinson, J.E.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Diverse specificity and effector function among human antibodies to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein epitopes exposed by CD4 binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E69–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Richard, J.; Batraville, L.A.; Dagher, O.; Bernard, N.; Tremblay, C.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Roger, M.; Finzi, A. The HIV-1 gp120 CD4-Bound Conformation Is Preferentially Targeted by Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity-Mediating Antibodies in Sera from HIV-1-Infected Individuals. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Brassard, N.; Iyer, S.S.; Roger, M.; Martin, L.; Pazgier, M.; Schon, A.; Freire, E.; Routy, J.P.; et al. CD4 mimetics sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2687–E2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Prevost, J.; Scharf, L.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Ferrari, G.; Robinson, J.E.; Sturzel, C.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. A Highly Conserved Residue of the HIV-1 gp120 Inner Domain Is Important for Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses Mediated by Anti-cluster A Antibodies. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Verly, M.M.; Princiotto, A.; Melillo, B.; Moody, T.; Bradley, T.; Easterhoff, D.; Roger, M.; Hahn, B.H.; Madani, N.; et al. Small Molecule CD4-Mimetics Sensitize HIV-1-infected Cells to ADCC by Antibodies Elicited by Multiple Envelope Glycoprotein Immunogens in Non-Human Primates. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veillette, M.; Coutu, M.; Richard, J.; Batraville, L.A.; Desormeaux, A.; Roger, M.; Finzi, A. Conformational evaluation of HIV-1 trimeric envelope glycoproteins using a cell-based ELISA assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsahafi, N.; Bakouche, N.; Kazemi, M.; Richard, J.; Ding, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, D.; Anand, S.P.; Prevost, J.; Tolbert, W.D.; et al. An Asymmetric Opening of HIV-1 Envelope Mediates Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Cell Host. Microbe. 2019, 25, 578–587.e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willey, R.L.; Maldarelli, F.; Martin, M.A.; Strebel, K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhee, S.S.; Marsh, J.W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef-induced down-modulation of CD4 is due to rapid internalization and degradation of surface CD4. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5156–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madani, N.; Schon, A.; Princiotto, A.M.; Lalonde, J.M.; Courter, J.R.; Soeta, T.; Ng, D.; Wang, L.; Brower, E.T.; Xiang, S.H.; et al. Small-molecule CD4 mimics interact with a highly conserved pocket on HIV-1 gp120. Structure 2008, 16, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.M.; Schon, A.; LaLonde, J.; Feng, Y.; Freire, E.; Park, J.; Courter, J.R.; Jones, D.M.; Robinson, J.; et al. CD4-mimetic small molecules sensitize human immunodeficiency virus to vaccine-elicited antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6542–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.M.; Zhao, C.; Jahanbakhshsefidi, F.; Mertens, M.; Herschhorn, A.; Melillo, B.; Smith, A.B., III; Sodroski, J. Activation and Inactivation of Primary Human Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers by CD4-Mimetic Compounds. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Princiotto, A.M.; Vrbanac, V.D.; Melillo, B.; Park, J.; Tager, A.M.; Smith, A.B., III; Sodroski, J.; Madani, N. A Small-Molecule CD4-Mimetic Compound Protects Bone Marrow-Liver-Thymus Humanized Mice From HIV-1 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Richard, J.; Lichtfuss, M.; Smith, A.B., III; Park, J.; Courter, J.R.; Melillo, B.N.; Sodroski, J.G.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Finzi, A.; et al. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity against Reactivated HIV-1-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, J.; Pacheco, B.; Gohain, N.; Veillette, M.; Ding, S.; Alsahafi, N.; Tolbert, W.D.; Prevost, J.; Chapleau, J.P.; Coutu, M.; et al. Co-receptor Binding Site Antibodies Enable CD4-Mimetics to Expose Conserved Anti-cluster A ADCC Epitopes on HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, S.P.; Prevost, J.; Baril, S.; Richard, J.; Medjahed, H.; Chapleau, J.P.; Tolbert, W.D.; Kirk, S.; Smith, A.B., III; Wines, B.D.; et al. Two Families of Env Antibodies Efficiently Engage Fc-Gamma Receptors and Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Grenier, M.C.; Tolbert, W.D.; Vezina, D.; Sherburn, R.; Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; Chapleau, J.P.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; et al. A New Family of Small-Molecule CD4-Mimetic Compounds Contacts Highly Conserved Aspartic Acid 368 of HIV-1 gp120 and Mediates Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevost, J.; Tolbert, W.D.; Medjahed, H.; Sherburn, R.T.; Madani, N.; Zoubchenok, D.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Gaffney, A.E.; Grenier, M.C.; Kirk, S.; et al. The HIV-1 Env gp120 Inner Domain Shapes the Phe43 Cavity and the CD4 Binding Site. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezina, D.; Gong, S.Y.; Tolbert, W.D.; Ding, S.; Nguyen, D.; Richard, J.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Melillo, B.; Smith, A.B., III; Pazgier, M.; et al. Stabilizing the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein State 2A conformation. J. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, J.K.; Richard, J.; Beloor, J.; Prevost, J.; Anand, S.P.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Shan, L.; Herndler-Brandstetter, D.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; et al. Modulating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein conformation to decrease the HIV-1 reservoir. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 904–916.e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Zhang, S.; Gaffney, A.; Ding, H.; Lu, M.; Grover, J.R.; Farrell, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Zhao, C.; Anang, S.; et al. Long-Acting BMS-378806 Analogues Stabilize the State-1 Conformation of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Envelope Glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ma, X.; Reichard, N.; Terry, D.S.; Arthos, J.; Smith, A.B., III; Sodroski, J.G.; Blanchard, S.C.; Mothes, W. Shedding-Resistant HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Adopt Downstream Conformations That Remain Responsive to Conformation-Preferring Ligands. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.H.; Kwong, P.D.; Gupta, R.; Rizzuto, C.D.; Casper, D.J.; Wyatt, R.; Wang, L.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Doyle, M.L.; Sodroski, J. Mutagenic stabilization and/or disruption of a CD4-bound state reveals distinct conformations of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9888–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herschhorn, A.; Ma, X.; Gu, C.; Ventura, J.D.; Castillo-Menendez, L.; Melillo, B.; Terry, D.S.; Smith, A.B., III; Blanchard, S.C.; Munro, J.B.; et al. Release of gp120 Restraints Leads to an Entry-Competent Intermediate State of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins. MBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desormeaux, A.; Coutu, M.; Medjahed, H.; Pacheco, B.; Herschhorn, A.; Gu, C.; Xiang, S.H.; Mao, Y.; Sodroski, J.; Finzi, A. The highly conserved layer-3 component of the HIV-1 gp120 inner domain is critical for CD4-required conformational transitions. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2549–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilmen, G.; Smith, A.C.; Benet, H.C.; Shukla, R.K.; Larue, R.C.; Herschhorn, A.; Sharma, A. Conformation of HIV-1 Envelope governs rhesus CD4 usage and simian-human immunodeficiency virus replication. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Zoubchenok, D.; Richard, J.; Veillette, M.; Pacheco, B.; Coutu, M.; Brassard, N.; Parsons, M.S.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Bunupuradah, T.; et al. Influence of the Envelope gp120 Phe 43 Cavity on HIV-1 Sensitivity to Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Responses. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prevost, J.; Richard, J.; Ding, S.; Pacheco, B.; Charlebois, R.; Hahn, B.H.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Finzi, A. Envelope glycoproteins sampling states 2/3 are susceptible to ADCC by sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. Virology 2018, 515, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Menendez, L.R.; Witt, K.; Espy, N.; Princiotto, A.; Madani, N.; Pacheco, B.; Finzi, A.; Sodroski, J. Comparison of Uncleaved and Mature Human Immunodeficiency Virus Membrane Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Go, E.P.; Ding, H.; Steinbock, R.T.; Desaire, H.; et al. Asymmetric structures and conformational plasticity of the uncleaved full-length human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein trimer. J. Virol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringe, R.P.; Sanders, R.W.; Yasmeen, A.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Cupo, A.; Korzun, J.; Derking, R.; van Montfort, T.; Julien, J.P.; et al. Cleavage strongly influences whether soluble HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimers adopt a native-like conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18256–18261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakrabarti, B.K.; Pancera, M.; Phogat, S.; O’Dell, S.; McKee, K.; Guenaga, J.; Robinson, J.; Mascola, J.; Wyatt, R.T. HIV type 1 Env precursor cleavage state affects recognition by both neutralizing and nonneutralizing gp41 antibodies. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2011, 27, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, J.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Valcke, H.S.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. High expression levels of B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) by dendritic cells correlate with HIV-related B-cell disease progression in humans. Blood 2011, 117, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, J.; Coutlee, F.; Tremblay, C.; Routy, J.P.; Poudrier, J.; Roger, M. HIV infection affects blood myeloid dendritic cells after successful therapy and despite nonprogressing cl.inical disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International, H.I.V.C.S.; Pereyra, F.; Jia, X.; McLaren, P.J.; Telenti, A.; de Bakker, P.I.; Walker, B.D.; Ripke, S.; Brumme, C.J.; Pulit, S.L.; et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 2010, 330, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamya, P.; Boulet, S.; Tsoukas, C.M.; Routy, J.P.; Thomas, R.; Cote, P.; Boulassel, M.R.; Baril, J.G.; Kovacs, C.; Migueles, S.A.; et al. Receptor-ligand requirements for increased NK cell polyfunctional potential in slow progressors infected with HIV-1 coexpressing KIR3DL1*h/*y and HLA-B*57. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5949–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peretz, Y.; Ndongala, M.L.; Boulet, S.; Boulassel, M.R.; Rouleau, D.; Cote, P.; Longpre, D.; Routy, J.P.; Falutz, J.; Tremblay, C.; et al. Functional T cell subsets contribute differentially to HIV peptide-specific responses within infected individuals: Correlation of these functional T cell subsets with markers of disease progression. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 124, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, E.J.; Wehrly, K.; Kuhmann, S.E.; Chesebro, B.; Kabat, D. Effects of CCR5 and CD4 cell surface concentrations on infections by macrophagetropic isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Park, J.; Kirk, S.M.; Chen, H.C.; Li, X.; Lippincott, D.J.; Melillo, B.; Smith, A.B., III. Development of an Effective Scalable Enantioselective Synthesis of the HIV-1 Entry Inhibitor BNM-III-170 as the Bis-Trifluoroacetate Salt. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 2464–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emi, N.; Friedmann, T.; Yee, J.K. Pseudotype formation of murine leukemia virus with the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Keele, B.F.; Learn, G.H.; Giorgi, E.E.; Li, H.; Decker, J.M.; Wang, S.; Baalwa, J.; Kraus, M.H.; et al. Genetic identity, biological phenotype, and evolutionary pathways of transmitted/founder viruses in acute and early HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenbauer, C.; Edmonds, T.G.; Ding, H.; Keele, B.F.; Decker, J.; Salazar, M.G.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Shattock, R.; Haynes, B.F.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Generation of Transmitted/Founder HIV-1 Infectious Molecular Clones and Characterization of Their Replication Capacity in CD4 T Lymphocytes an.nd Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrish, N.F.; Gao, F.; Li, H.; Giorgi, E.E.; Barbian, H.J.; Parrish, E.H.; Zajic, L.; Iyer, S.S.; Decker, J.M.; Kumar, A.; et al. Phenotypic properties of transmitted founder HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fenton-May, A.E.; Dibben, O.; Emmerich, T.; Ding, H.; Pfafferott, K.; Aasa-Chapman, M.M.; Pellegrino, P.; Williams, I.; Cohen, M.S.; Gao, F.; et al. Relative resistance of HIV-1 founder viruses to control by interferon-alpha. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rho, H.M.; Poiesz, B.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gallo, R.C. Characterization of the reverse transcriptase from a new retrovirus (HTLV) produced by a human cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line. Virology 1981, 112, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Gasser, R.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; Tolbert, W.D.; Sodroski, J.; Pazgier, M.; Finzi, A. CD4 Incorporation into HIV-1 Viral Particles Exposes Envelope Epitopes Recognized by CD4-Induced Antibodies. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Phan, N.; Kiprilov, E.; Sodroski, J. Effects of HIV type 1 envelope glycoprotein proteolytic processing on antigenicity. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2003, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kurteva, S.; Lee, S.; Sodroski, J. Stoichiometry of antibody neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenberg, O.F.; Magnus, C.; Rusert, P.; Regoes, R.R.; Trkola, A. Different infectivity of HIV-1 strains is linked to number of envelope trimers required for entry. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieh, D.J.; King, D.F.; Klein, K.; Aldon, Y.; McKay, P.F.; Shattock, R.J. Discrete partitioning of HIV-1 Env forms revealed by viral capture. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Nguyen, H.T.; Ding, H.; Wang, J.; Zou, S.; Liu, L.; Guha, D.; Gabuzda, D.; Ho, D.D.; Kappes, J.C.; et al. Dual Pathways of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Envelope G.Glycoprotein Trafficking Modulate the Selective Exclusion of Uncleaved Oligomers from Virions. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Prévost, J.; Descôteaux-Dinelle, J.; Richard, J.; Nguyen, D.N.; Medjahed, H.; Chen, H.-C.; Smith, A.B.; Pazgier, M.; Finzi, A. HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Cell Surface Localization Is Associated with Antibody-Induced Internalization. Viruses 2021, 13, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, N.; Ding, S.; Richard, J.; Markle, T.; Brassard, N.; Walker, B.; Lewis, G.K.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Brockman, M.A.; Finzi, A. Nef Proteins from HIV-1 Elite Controllers Are Inefficient at Preventing Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aloia, R.C.; Tian, H.; Jensen, F.C. Lipid composition and fluidity of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope and host cell plasma membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5181–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishwanathan, S.A.; Thomas, A.; Brasseur, R.; Epand, R.F.; Hunter, E.; Epand, R.M. Large changes in the CRAC segment of gp41 of HIV do not destroy fusion activity if the segment interacts with cholesterol. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 11869–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimi, H.; Johnson, J.; Flores, M.G.; Zhang, M.S.; O’Malley, Y.; Houtman, J.C.; Schlievert, P.M.; Haim, H. The lipid membrane of HIV-1 stabilizes the viral envelope glycoproteins and modulates their sensitivity to antibody neutralization. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, L.M.; Weinhold, K.J.; Matthews, T.J.; Langlois, A.J.; Perno, C.F.; Condie, R.M.; Allain, J.P. Preparation and characterization of an intravenous solution of IgG from human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive donors. Blood 1991, 77, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevost, J.; Richard, J.; Medjahed, H.; Alexander, A.; Jones, J.; Kappes, J.C.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Finzi, A. Incomplete Downregulation of CD4 Expression Affects HIV-1 Env Conformation and Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alsahafi, N.; Richard, J.; Prevost, J.; Coutu, M.; Brassard, N.; Parsons, M.S.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Brockman, M.; Finzi, A. Impaired downregulation of NKG2D ligands by Nef protein from elite controllers sensitizes HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. J. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, E.; Hotter, D.; Koepke, L.; Zech, F.; Gross, R.; Sparrer, K.M.J.; Muller, J.A.; Pfaller, C.K.; Heusinger, E.; Wombacher, R.; et al. Guanylate-Binding Proteins 2 and 5 Exert Broad Antiviral Activity by Inhibiting Furin-Mediated Processing of Viral Envelope Proteins. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2092-2104.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lodermeyer, V.; Suhr, K.; Schrott, N.; Kolbe, C.; Sturzel, C.M.; Krnavek, D.; Munch, J.; Dietz, C.; Waldmann, T.; Kirchhoff, F.; et al. 90K, an interferon-stimulated gene product, reduces the infectivity of HIV-1. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tada, T.; Zhang, Y.; Koyama, T.; Tobiume, M.; Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Yamaoka, S.; Fujita, H.; Tokunaga, K. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, M.; Wilkins, J.; Ding, S.; Swartz, T.H.; Esposito, A.M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Freed, E.O.; Liang, C.; Chen, B.K.; et al. IFITM Proteins Restrict HIV-1 Infection by Antagonizing the Envelope Glycoprotein. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Ding, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Finzi, A.; Liu, S.L.; Liang, C. The V3 Loop of HIV-1 Env Determines Viral Susceptibility to IFITM3 Impairment of Viral Infectivity. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foster, T.L.; Wilson, H.; Iyer, S.S.; Coss, K.; Doores, K.; Smith, S.; Kellam, P.; Finzi, A.; Borrow, P.; Hahn, B.H.; et al. Resistance of Transmitted Founder HIV-1 to IFITM-Mediated Restriction. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drouin, A.; Migraine, J.; Durand, M.A.; Moreau, A.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; Beretta, M.; Roingeard, P.; Bouvin-Pley, M.; Braibant, M. Escape of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein from the restriction of infection by IFITM3. J. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp, C.; Hotter, D.; Gawanbacht, A.; McLaren, P.J.; Kluge, S.F.; Sturzel, C.M.; Mack, K.; Reith, E.; Engelhart, S.; Ciuffi, A.; et al. Guanylate Binding Protein (GBP) 5 Is an Interferon-Inducible Inhibitor of HIV-1 Infectivity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, F.; Stella, K.; Thomas, L.; Liu, G.; Xiang, Y.; Reason, A.J.; Thomas, G. alpha1-Antitrypsin Portland, a bioengineered serpin highly selective for furin: Application as an antipathogenic agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7293–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatib, A.M.; Siegfried, G.; Prat, A.; Luis, J.; Chretien, M.; Metrakos, P.; Seidah, N.G. Inhibition of proprotein convertases is associated with loss of growth and tumorigenicity of HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells: Importance of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor processing in IGF-1-mediated functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30686–30693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassi, D.E.; Lopez De Cicco, R.; Mahloogi, H.; Zucker, S.; Thomas, G.; Klein-Szanto, A.J. Furin inhibition results in absent or decreased invasiveness and tumorigenicity of human cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10326–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kibler, K.V.; Miyazato, A.; Yedavalli, V.S.; Dayton, A.I.; Jacobs, B.L.; Dapolito, G.; Kim, S.J.; Jeang, K.T. Polyarginine inhibits gp160 processing by furin and suppresses productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49055–49063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remacle, A.G.; Gawlik, K.; Golubkov, V.S.; Cadwell, G.W.; Liddington, R.C.; Cieplak, P.; Millis, S.Z.; Desjardins, R.; Routhier, S.; Yuan, X.W.; et al. Selective and potent furin inhibitors protect cells from anthrax without significant toxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klenk, H.D.; Rott, R. The molecular biology of influenza virus pathogenicity. Adv. Virus Res. 1988, 34, 247–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchkov, V.E.; Feldmann, H.; Volchkova, V.A.; Klenk, H.D. Processing of the Ebola virus glycoprotein by the proprotein convertase furin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5762–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawling, J.; Cano, O.; Garcin, D.; Kolakofsky, D.; Melero, J.A. Recombinant Sendai viruses expressing fusion proteins with two furin cleavage sites mimic the syncytial and receptor-independent infection properties of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, B.A.; Xie, X.; Bailey, A.L.; Kalveram, B.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Muruato, A.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Juelich, T.; Smith, J.K.; et al. Loss of furin cleavage site attenuates SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nature 2021, 591, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Toba, S.; Itakura, Y.; Chambaro, H.M.; Kishimoto, M.; Tabata, K.; Intaruck, K.; Uemura, K.; Sanaki, T.; Sato, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Bearing a Mutation at the S1/S2 Cleavage Site Exhibits Attenuated Virulence and Confers Protective Immunity. mBio 2021, 12, e0141521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prévost, J.; Medjahed, H.; Vézina, D.; Chen, H.-C.; Hahn, B.H.; Smith, A.B., III; Finzi, A. HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Proteolytic Cleavage Protects Infected Cells from ADCC Mediated by Plasma from Infected Individuals. Viruses 2021, 13, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112236
Prévost J, Medjahed H, Vézina D, Chen H-C, Hahn BH, Smith AB III, Finzi A. HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Proteolytic Cleavage Protects Infected Cells from ADCC Mediated by Plasma from Infected Individuals. Viruses. 2021; 13(11):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112236
Chicago/Turabian StylePrévost, Jérémie, Halima Medjahed, Dani Vézina, Hung-Ching Chen, Beatrice H. Hahn, Amos B. Smith, III, and Andrés Finzi. 2021. "HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Proteolytic Cleavage Protects Infected Cells from ADCC Mediated by Plasma from Infected Individuals" Viruses 13, no. 11: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112236
APA StylePrévost, J., Medjahed, H., Vézina, D., Chen, H.-C., Hahn, B. H., Smith, A. B., III, & Finzi, A. (2021). HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins Proteolytic Cleavage Protects Infected Cells from ADCC Mediated by Plasma from Infected Individuals. Viruses, 13(11), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112236