The Oncolytic Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cisplatin in Mesothelioma Cell Lines: A New Potential Virotherapy Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. Virus Production
2.3. Cell Infection with CpHV-1, MTS, and Clonogenic Assay
2.4. Viral DNA Extraction and Quantification by Real-Time PCR
2.5. Cytofluorimetric Analysis of Cell Cycle Profile and Cell Death
2.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Drug Combination Studies
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
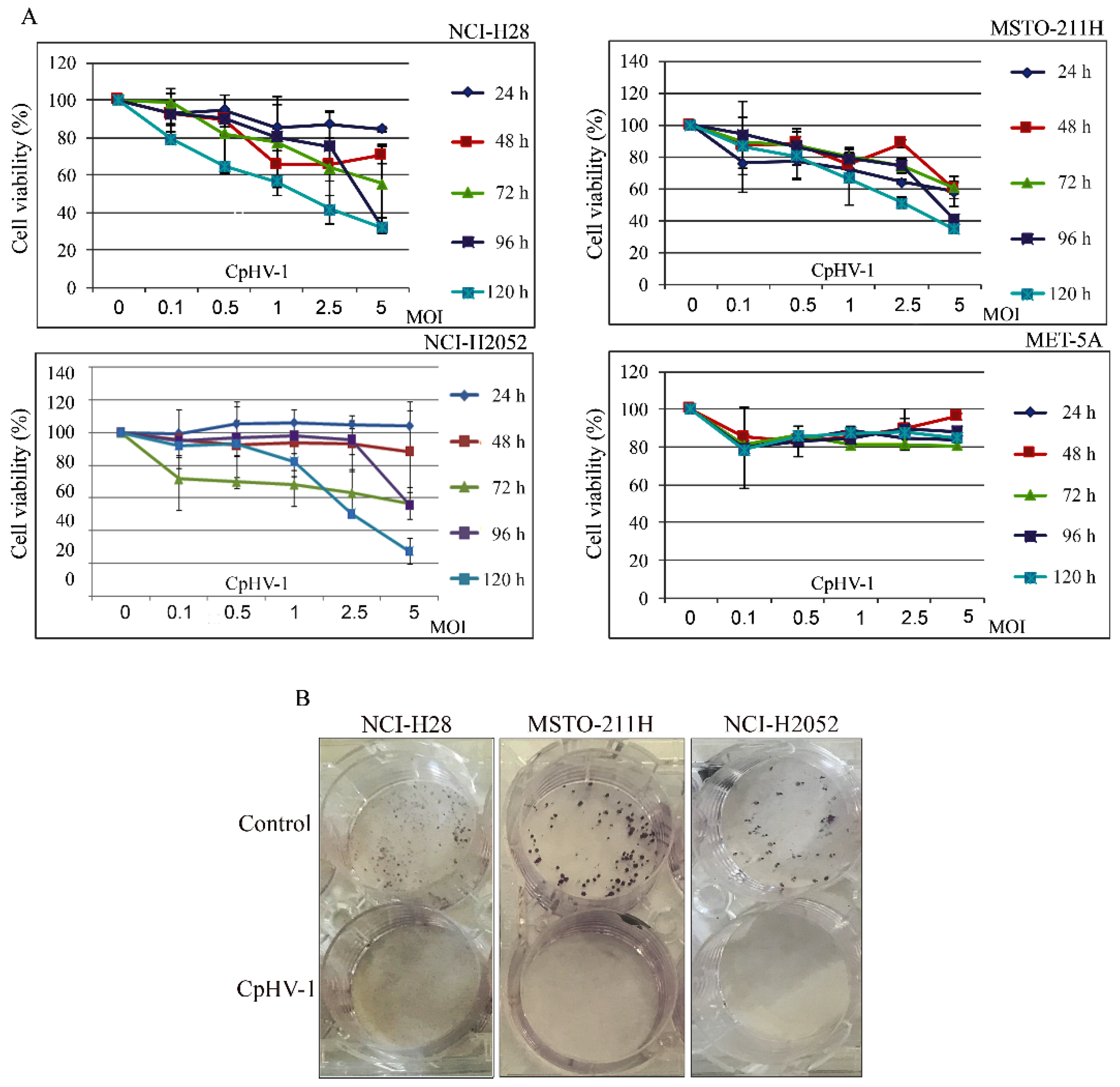
3.1. CpHV-1 Reduces MM Cell Viability and Clonogenic Potential
3.2. Detection of CpHV-1 DNA in MM Cells and Not in Normal Mesothelial Cells
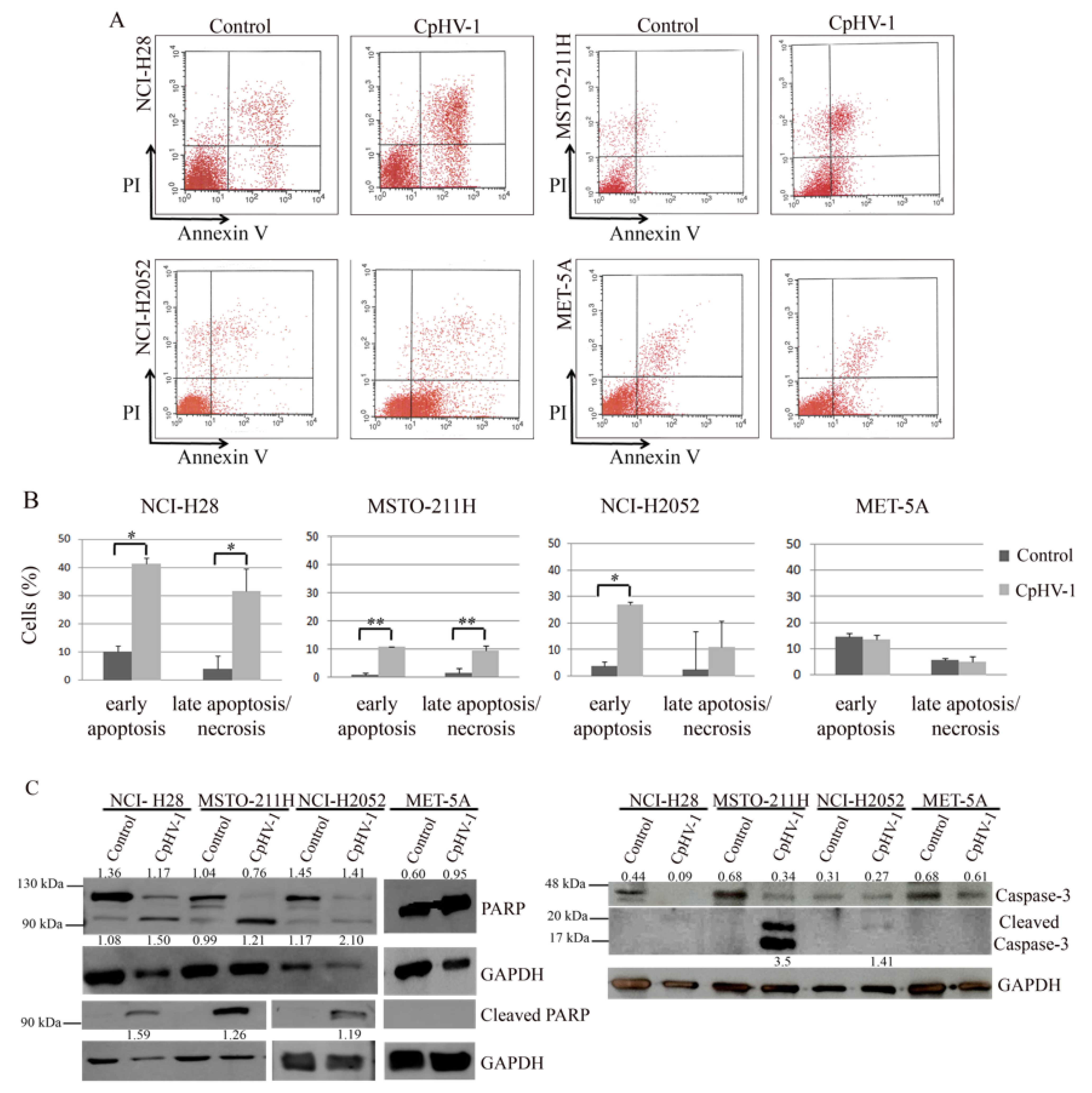
3.3. CpHV-1 Induces Apoptosis in MM Cells
3.4. CpHV-1 Perturbs MM Cell Cycle Progression
3.5. CpHV-1 Synergizes with Cisplatin in Suppressing MM Cell Viability
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Combination index |
| CpHV-1 | Caprine Herpesvirus-1 |
| Fa | Fraction affected |
| gH | glycoprotein H |
| HSV-1 | Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| ISGs | IFN-stimulated antiviral genes |
| MM | Malignant Mesothelioma |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| oHSV-1 | Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OV | Oncolytic Virus |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| p.i. | Post-Infection |
| PKR | RNA-dependent protein kinase |
| PTCID50 | Median Tissue Culture Infectious Dose |
| T-VEC | Talimogenelaherparepvec |
| VSV | Vesicular stomatitis virus |
References
- Nicholson, A.G.; Sauter, J.L.; Nowak, A.K.; Kindler, H.L.; Gill, R.R.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Armato, S.G.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bueno, R.; Alcala, N.; et al. EURACAN/IASLC Proposals for Updating the Histologic Classification of Pleural Mesothelioma: Towards a More Multidisciplinary Approach. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 15, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salle, F.G.; Churg, A.; Roggli, V.; Travis, W.D. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Mesothelioma: Recent highlights. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alpert, N.; Van Gerwen, M.; Taioli, E. Epidemiology of mesothelioma in the 21st century in Europe and the United States, 40 years after restricted/banned asbestos use. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, S28–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehl, K.; Vrugt, B.; Opitz, I.; Meerang, M. Heterogeneity in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blum, Y.; Meiller, C.; Quetel, L.; Elarouci, N.; Ayadi, M.; Tashtanbaeva, D.; Armenoult, L.; Montagne, F.; Tranchant, R.; Renier, A.; et al. Dissecting heterogeneity in malignant pleural mesothelioma through histo-molecular gradients for clinical applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, T.K.; Heasley, L.E. Translating mesothelioma molecular genomics and dependencies into precision oncology-based therapies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 61, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indovina, P.; Forte, I.M.; Pentimalli, F.; Giordano, A. Targeting SRC Family Kinases in Mesothelioma: Time to Upgrade. Cancers 2020, 12, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiddinga, B.I.; Rolfo, C.; van Meerbeeck, J.P. Mesothelioma treatment: Are we on target? A review. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 6, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Wallyn, F.; Albelda, S.M.; Munck, C. Novel therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e161–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Mazieres, J.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Dô, P.; Bylicki, O.; Monnet, I.; Corre, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Locatelli-Sanchez, M.; et al. Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.; Bocchini, M.; Bronte, G.; Delmonte, A.; Guidoboni, M.; Crinò, L.; Mazza, M. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State-of-the-Art on Current Therapies and Promises for the Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Perrot, M.; Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Cho, B.C.J. Radiotherapy for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e532–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.J.; Donahoe, L.; Bradbury, P.A.; Leighl, N.; Keshavjee, S.; Hope, A.; Pal, P.; Cabanero, M.; Czarnecka, K.; McRae, K.; et al. Surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma after radiotherapy (SMART): Final results from a single-centre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.W.; Musk, A.W.; Lake, R.A. Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet 2005, 366, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.-W.; Bell, J.C. Oncolytic virotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.S.; Liu, Z.; Kowalsky, S.; Feist, M.; Kalinski, P.; Lu, B.; Storkus, W.J.; Bartlett, D.L. Oncolytic Immunotherapy: Conceptual Evolution, Current Strategies, and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fountzilas, C.; Patel, S.; Mahalingam, D. Review: Oncolytic virotherapy, updates and future directions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102617–102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malfitano, A.M.; Di Somma, S.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Pentimalli, F.; Portella, G. Virotherapy: From single agents to combinatorial treatments. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davola, M.E.; Mossman, K.L. Oncolytic viruses: How “lytic” must they be for therapeutic efficacy? OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1581528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pease, D.F.; Kratzke, R.A. Oncolytic Viral Therapy for Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Somma, S.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Passaro, C.; Forte, I.M.; Iannone, R.; Gigantino, V.; Indovina, P.; Botti, G.; Giordano, A.; Formisano, P.; et al. The Oncolytic Virus dl922-947 Triggers Immunogenic Cell Death in Mesothelioma and Reduces Xenograft Growth. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iannuzzi, C.; Indovina, P.; Forte, I.; Di Somma, S.; Malfitano, A.; Bruno, M.; Portella, G.; Pentimalli, F.; Giordano, A. Pharmacological Inhibition of WEE1 Potentiates the Antitumoral Effect of the dl922-947 Oncolytic Virus in Malignant Mesothelioma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Nemunaitis, J. Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) for cancer treatment. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menotti, L.; Avitabile, E. Herpes Simplex Virus Oncolytic Immunovirotherapy: The Blossoming Branch of Multimodal Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Diao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Feng, Q.; Tang, Y. The oncolytic efficacy and safety of avian reovirus and its dynamic distribution in infected mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, J.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. First oncolytic virus approved for melanoma immunotherapy. OncoImmunology 2015, 5, e1115641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-Q.; Xin, H.-Y.; Lyu, Y.-N.; Ma, Z.-W.; Peng, X.-C.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wu, Z.-J.; Cheng, J.-T.; Ji, J.-F.; et al. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus tumor targeting and neutralization escape by engineering viral envelope glycoproteins. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1950–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Kern, E.R.; Whitley, R.J.; Roizman, B. Mapping of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Neurovirulence to γ 134.5, a Gene Nonessential for Growth in Culture. Science 1990, 250, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T. Oncolytic Virus Therapy Using Genetically Engineered Herpes Simplex Viruses. Hum. Cell 2002, 15, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Cuddington, B.; Mossman, K. Bovine herpesvirus type 1 as a novel oncolytic virus. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 17, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burman, B.; Pesci, G.; Zamarin, D. Newcastle Disease Virus at the Forefront of Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretscher, C.; Marchini, A. H-1 Parvovirus as a Cancer-Killing Agent: Past, Present, and Future. Viruses 2019, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, B.; Ebling, R.C.; Martins, M.; Diel, D.G.; Weiblen, R.; Flores, E.F. Antigenic relationships between Caprine alphaherpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) and Bovine alphaherpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) and experimental CpHV-1 infection of kids and calves. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnaro, S.; Damiano, S.; Ciarcia, R.; Puzio, M.V.; Ferrara, G.; Iovane, V.; Forte, I.M.; Giordano, A.; Pagnini, U. Caprine herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) as a potential candidate for oncolytic virotherapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 20, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, F.; Engels, M.; Wild, P.; Bivetti, A. Herpesvirus infection in kids in Switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 1979, 121, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Pagnini, U.; Montagnaro, S.; Di Monteforte, E.S.; Pacelli, F.; De Martino, L.; Roperto, S.; Florio, S.; Iovane, G. Caprine herpesvirus-1 (CapHV-1) induces apoptosis in goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Veter.-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 103, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Kawasaki, Y.; Yamaoka, N.; Tagawa, M.; Kasahara, N.; Terada, N.; Okamura, H. Complete regression of human malignant mesothelioma xenografts following local injection of midkine promoter-driven oncolytic adenovirus. J. Gene Med. 2010, 12, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colao, I.; Pennisi, R.; Venuti, A.; Nygårdas, M.; Heikkilä, O.; Hukkanen, V.; Sciortino, M.T. The ERK-1 function is required for HSV-1-mediated G1/S progression in HEP-2 cells and contributes to virus growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobbs, W.E.; DeLuca, N.A. Perturbation of Cell Cycle Progression and Cellular Gene Expression as a Function of Herpes Simplex Virus ICP0. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8245–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Sanyal, S.; Bruzzone, R. Breaking Bad: How Viruses Subvert the Cell Cycle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, D.; Forte, I.M.; Indovina, P.; Di Gennaro, E.; Rizzo, V.; Giorgi, F.; Mattioli, E.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Budillon, A.; Giordano, A.; et al. Pharmacological targeting of p53 through RITA is an effective antitumoral strategy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cell Cycle 2013, 13, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.-C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Clarke, C.; Henderson, D.; Musk, A.W.; Fong, K.; Nowak, A.; Loneragan, R.; McCaughan, B.; Boyer, M.; Feigen, M.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, E254–E307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suavet, F.; Champion, J.-L.; Bartolini, L.; Bernou, M.; Alzieu, J.-P.; Brugidou, R.; Darnatigues, S.; Reynaud, G.; Perrin, C.; Adam, G.; et al. First Description of Infection of Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) in Goats in Mainland France. Pathogens 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirn, D.H.; Martuza, R.L.; Zwiebel, J.A. Replication-selective virotherapy for cancer: Biological principles, risk management and future directions. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, F.; Kennedy, P.E.; Locatelli, G.; Malnati, M.; Berger, E.A.; Lusso, P. CD46 Is a Cellular Receptor for Human Herpesvirus 6. Cell 1999, 99, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauvrit, A.; Brandler, S.; Sapede-Peroz, C.; Boisgerault, N.; Tangy, F.; Gregoire, M. Measles Virus Induces Oncolysis of Mesothelioma Cells and Allows Dendritic Cells to Cross-Prime Tumor-Specific CD8 Response. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4882–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoro, F.; Greenstone, H.L.; Insinga, A.; Liszewski, M.K.; Atkinson, J.P.; Lusso, P.; Berger, E.A. Interaction of Glycoprotein H of Human Herpesvirus 6 with the Cellular Receptor CD46. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25964–25969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, G.; Thiry, E.; Hanon, E.; Pastoret, P.P.; Georlette, D. Bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein H is essential for penetration and propagation in cell culture. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vile, R.; Ando, D.; Kirn, D. The oncolytic virotherapy treatment platform for cancer: Unique biological and biosafety points to consider. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parato, K.A.; Senger, D.; Forsyth, P.A.J.; Bell, J.C. Recent progress in the battle between oncolytic viruses and tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloura, V.; Wang, L.-C.S.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Cheng, G.; Kapoor, V.; Sterman, D.H.; Harty, R.N.; Okumura, A.; Barber, G.N.; et al. Evaluation of an Attenuated Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector Expressing Interferon-β for Use in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Heterogeneity in Interferon Responsiveness Defines Potential Efficacy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grégoire, M.M.; Boisgerault, N.; Achard, C.; Delaunay, T.; Cellerin, L.; Tangy, F.; Fonteneau, J.-F. Oncolytic virotherapy for human malignant mesothelioma: Recent advances. Oncolytic Virotherapy 2015, 4, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Chan, M.-K.; Chun, Y.S.; Hezel, M.; Chou, T.-C.; Rusch, V.W.; Fong, Y. Cisplatin-induced GADD34 upregulation potentiates oncolytic viral therapy in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forte, I.M.; Indovina, P.; Montagnaro, S.; Costa, A.; Iannuzzi, C.A.; Capone, F.; Camerlingo, R.; Malfitano, A.M.; Pentimalli, F.; Ferrara, G.; et al. The Oncolytic Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cisplatin in Mesothelioma Cell Lines: A New Potential Virotherapy Approach. Viruses 2021, 13, 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122458
Forte IM, Indovina P, Montagnaro S, Costa A, Iannuzzi CA, Capone F, Camerlingo R, Malfitano AM, Pentimalli F, Ferrara G, et al. The Oncolytic Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cisplatin in Mesothelioma Cell Lines: A New Potential Virotherapy Approach. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122458
Chicago/Turabian StyleForte, Iris Maria, Paola Indovina, Serena Montagnaro, Aurora Costa, Carmelina Antonella Iannuzzi, Francesca Capone, Rosa Camerlingo, Anna Maria Malfitano, Francesca Pentimalli, Gianmarco Ferrara, and et al. 2021. "The Oncolytic Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cisplatin in Mesothelioma Cell Lines: A New Potential Virotherapy Approach" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122458
APA StyleForte, I. M., Indovina, P., Montagnaro, S., Costa, A., Iannuzzi, C. A., Capone, F., Camerlingo, R., Malfitano, A. M., Pentimalli, F., Ferrara, G., Quintiliani, M., Portella, G., Giordano, A., & Ciarcia, R. (2021). The Oncolytic Caprine Herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cisplatin in Mesothelioma Cell Lines: A New Potential Virotherapy Approach. Viruses, 13(12), 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122458









