Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F Gene in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains Used in This Study
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Estimation of Evolutionary Rate
2.3. Bayesian Skyline Plot Analyses
2.4. Similarity Plot Analyses and Calculation of the Phylogenetic Distances
2.5. Selective Pressure Analyses
2.6. Prediction of Conformational B-Cell Epitope and Amino Acid Substitution Sites by Mapping on the Structure of the RSV-A F Protein
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Analyses of the RSV-A F Gene
3.2. BSP Analyses
3.3. Similarity Analysis and Phylogenetic Distances
3.4. Selective Pressure Analyses
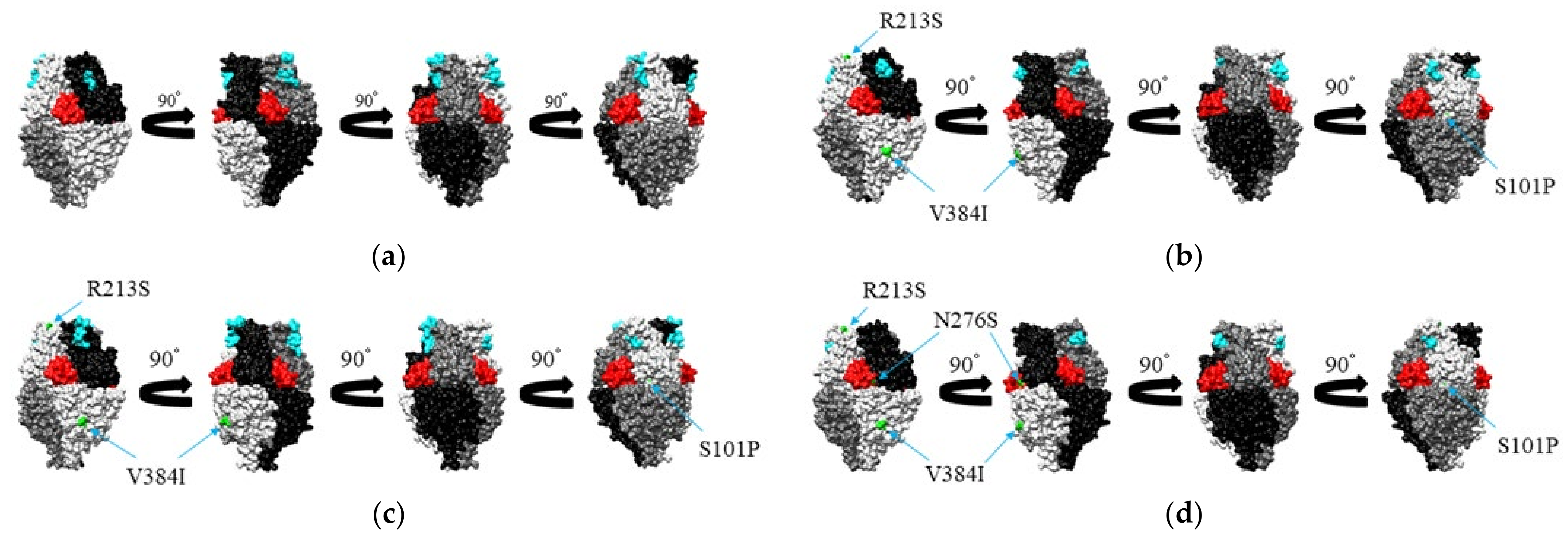
3.5. Mapping of Amino Acid Substitution Sites and Conformational B-Cell Epitopes on the Structure of the RSV-A F Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, P.L.; Karron, R.A. Respiratory syncytial virus and matapneumovirus. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Cohen, J.I., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Racaniello, V.D., Roizman, B., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 1086–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.; Kellner, J.D.; Davies, H.D. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J. Natl. Med. 2005, 97, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Shay, D.K.; Holman, R.C.; Newman, R.D.; Liu, L.L.; Stout, J.W.; Anderson, L.J. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980-1996. JAMA 1999, 282, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yorita, K.L.; Holman, R.C.; Steiner, C.A.; Effler, P.V.; Miyamura, J.; Forbes, S.; Anderson, L.J.; Balaraman, V. Severe bronchiolitis and respiratory syncytial virus among young children in Hawaii. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glezen, W.P.; Taber, L.H.; Frank, A.L.; Kasel, J.A. Risk of primary infection and reinfection with respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1986, 140, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branche, A.R.; Falsey, A.R. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in older adults: An under-recognized problem. Drugs Aging 2015, 32, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Lui, G.C.; Wong, K.T.; Li, T.C.; Tse, E.C.; Chan, J.Y.; Yu, J.; Wong, S.S.; Choi, K.W.; Wong, R.Y.; et al. High morbidity and mortality in adults hospitalized for respiratory syncytial virus infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Oliver, C.; Prince, G.A.; Hemming, V.G.; Pfarr, D.S.; Wang, S.C.; Dormitzer, M.; O’Grady, J.; Koenig, S.; Tamura, J.K.; et al. Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, C.; Grews, S.J.; Marchant, D.J. Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Infection, Detection, and New Options for Prevention and Treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 277–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, K.A.; Settembre, E.C.; Shaw, C.A.; Dey, A.K.; Rappuoli, R.; Mandl, C.W.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Carfi, A. Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Leung, S.; Graepel, K.W.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Baxa, U.; Yasuda, E.; Beaumont, T.; et al. Structure of RSV fusion glycoprotein trimer bound to a prefusion-specific neutralizing antibody. Science 2013, 340, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Killikelly, A.; Kanekiyo, M.; Graham, B. Pre-fusion F is absent on the surface of formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascough, S.; Paterson, S.; Chiu, C. Induction and subversion of human protective immunity: Contrasting influenza and respiratory syncytial virus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Escalante, J.C.; Comas-García, A.; Bernal-Silva, S.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; Gómez-Leal, G.; Noyola, D.E. Respiratory syncytial virus A genotype classification based on systematic intergenotypic and intragenotypic sequence analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; An, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, A.; Deng, L.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Genetic variations in the fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus isolated from children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Kok, J.; Fernandez, M.; Carter, I.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Dwyer, D.E.; Holmes, E.C.; Eden, J.S. Evolution of human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) over multiple seasons in New South Wales, Australia. Viruses 2018, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otieno, J.R.; Kamau, E.M.; Oketch, J.W.; Ngoi, J.M.; Gichuki, A.M.; Binter, S.; Otieno, G.P.; Ngama, M.; Agoti, C.N.; Cane, P.A.; et al. Whole genome analysis of local Kenyan and global sequences unravels the epidemiological and molecular evolutionary dynamics of RSV genotype ON1 strains. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yassine, H.M.; Sohail, M.U.; Younes, N.; Nasrallah, G.K. Systematic Review of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Prevalence, Genotype Distribution, and Seasonality in Children from the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Region. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, N.; Roux, S.; Hölzer, M.; Lamkiewicz, K.; Mock, F.; Marz, M.; Dutilh, B.E. Virus bioinformatics. In Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Nagasawa, K.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Matsushima, Y.; Fujita, K.; Yoshida, L.M.; Tanaka, R.; Ishii, H.; Shimojo, N.; Kuroda, M.; et al. Molecular evolution of the fusion protein gene in human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup A. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Nagasawa, K.; Kimura, R.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Matsushima, Y.; Fujita, K.; Hirano, E.; Ishiwada, N.; Misaki, T.; Oishi, K.; et al. Molecular evolution of the fusion protein (F) gene in human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup B. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fourment, M.; Gibbs, M.J. PATRISTIC: A program for calculating patristic distances and graphically comparing the components of genetic change. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1137, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, W.R.P.; Hünenberger, P.H.; Tironi, I.G.; Mark, A.E.; Billeter, S.R.; Fennen, J.; Torda, A.E.; Huber, T.; Krüger, P.; van Gunsteren, W.F. The GROMOS biomolecular simulation program package. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kringelum, J.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Reliable B cell epitope predictions: Impacts of method development and improved benchmarking. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweredoski, M.J.; Baldi, P. PEPITO: Improved discontinuous B-cell epitope prediction using multiple distance thresholds and half sphere exposure. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1459–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y. A simple reference state makes a significant improvement in near-native selections from structurally refined docking decoys. Proteins 2007, 69, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Zheng, D.; Standley, D.M.; Yao, B.; Zacharias, M.; Zhang, C. EPSVR and EPMeta: Prediction of antigenic epitopes using support vector regression and multiple server results. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agenbach, E.; Tiemessen, C.T.; Venter, M. Amino acid variation within the fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus subtype A and B strains during annual epidemics in South Africa. Virus Genes 2005, 30, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H.F.; Weng, L.C.; Wang, N.Y.; Chiu, N.C.; Lai, M.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chiu, Y.Y.; Hsieh, W.S.; Huang, L.M. Molecular epidemiology and phylodynamics of the human respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein in northern Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64012. [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Jansen, R.R.; Poovorawan, Y.; Templeton, K.E.; Toms, G.L.; Simmonds, P. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of human respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia, L.I.; Shaw, C.A.; Aideyan, L.O.; Jewell, A.M.; Dawson, B.C.; Haq, T.R.; Piedra, P.A. Gene sequence variability of the three surface proteins of human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) in Texas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90786. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, J.; Kimura, H.; Ishii, H.; Saraya, T.; Kurai, D.; Matsushima, Y.; Nagasawa, K.; Ryo, A.; Takizawa, H. Molecular evolution of the fusion protein (F) gene in human respirovirus 3. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, E.C. Virus evolution. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Cohen, J.I., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Racaniello, V.D., Roizman, B., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 286–313. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, J.; Rynkiewicz, M.J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, C.Y. Discovery of protective B-cell epitopes for development of antimicrobial vaccines and antibody therapeutics. Immunology 2014, 142, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, O.; Bonzel, L.; Kovacevic, A.; Mayatepek, E.; Hoehn, T.; Vogel, M. Palivizumab-resistant human respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegzyn, C.; Toh, L.K.; Notario, G.; Biguenet, S.; Unnebrink, K.; Park, C.; Makari, D.; Norton, M. Safety and effectiveness of palivizumab in children at high risk of serious disease due to respiratory syncytial virus infection: A systematic review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2014, 3, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
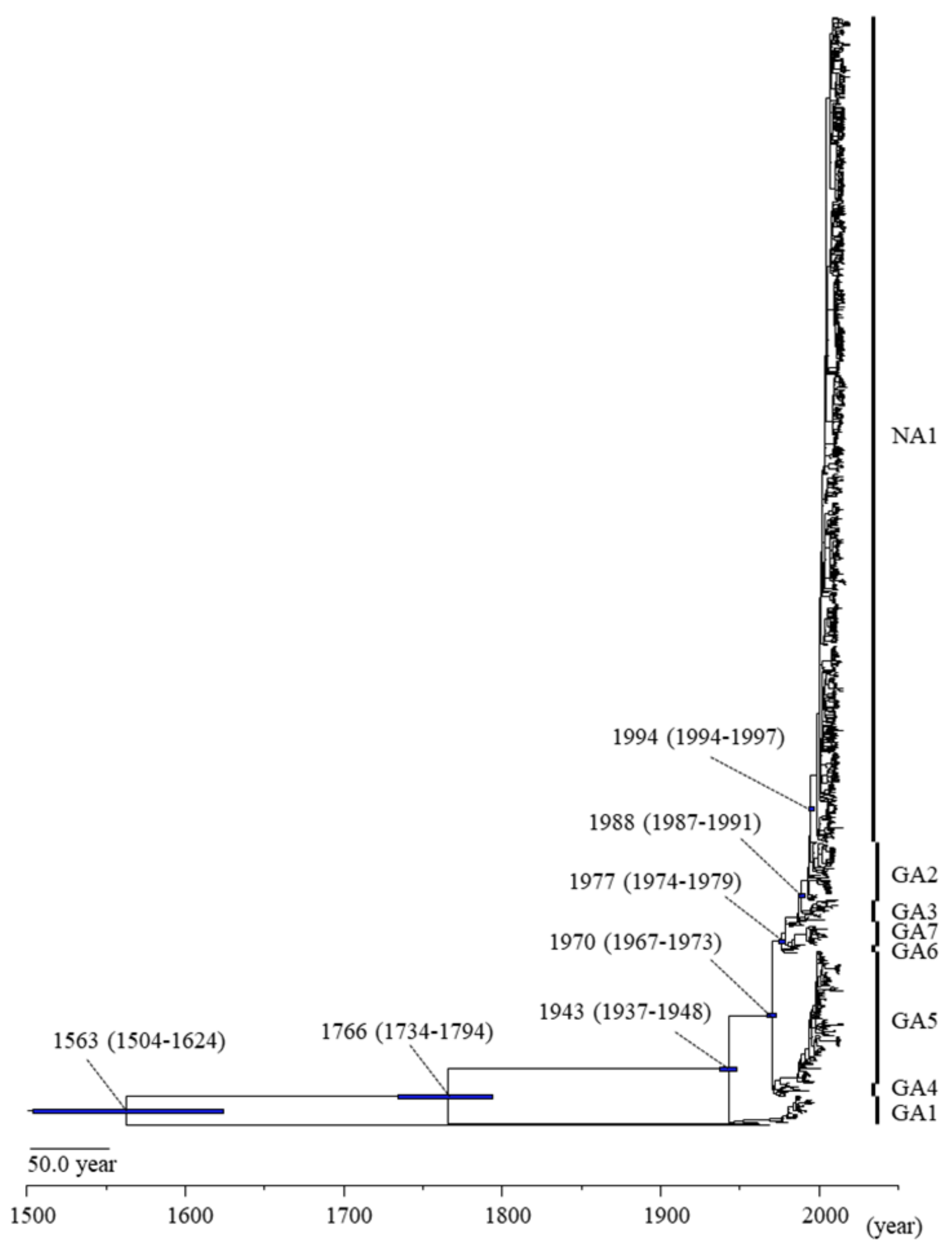
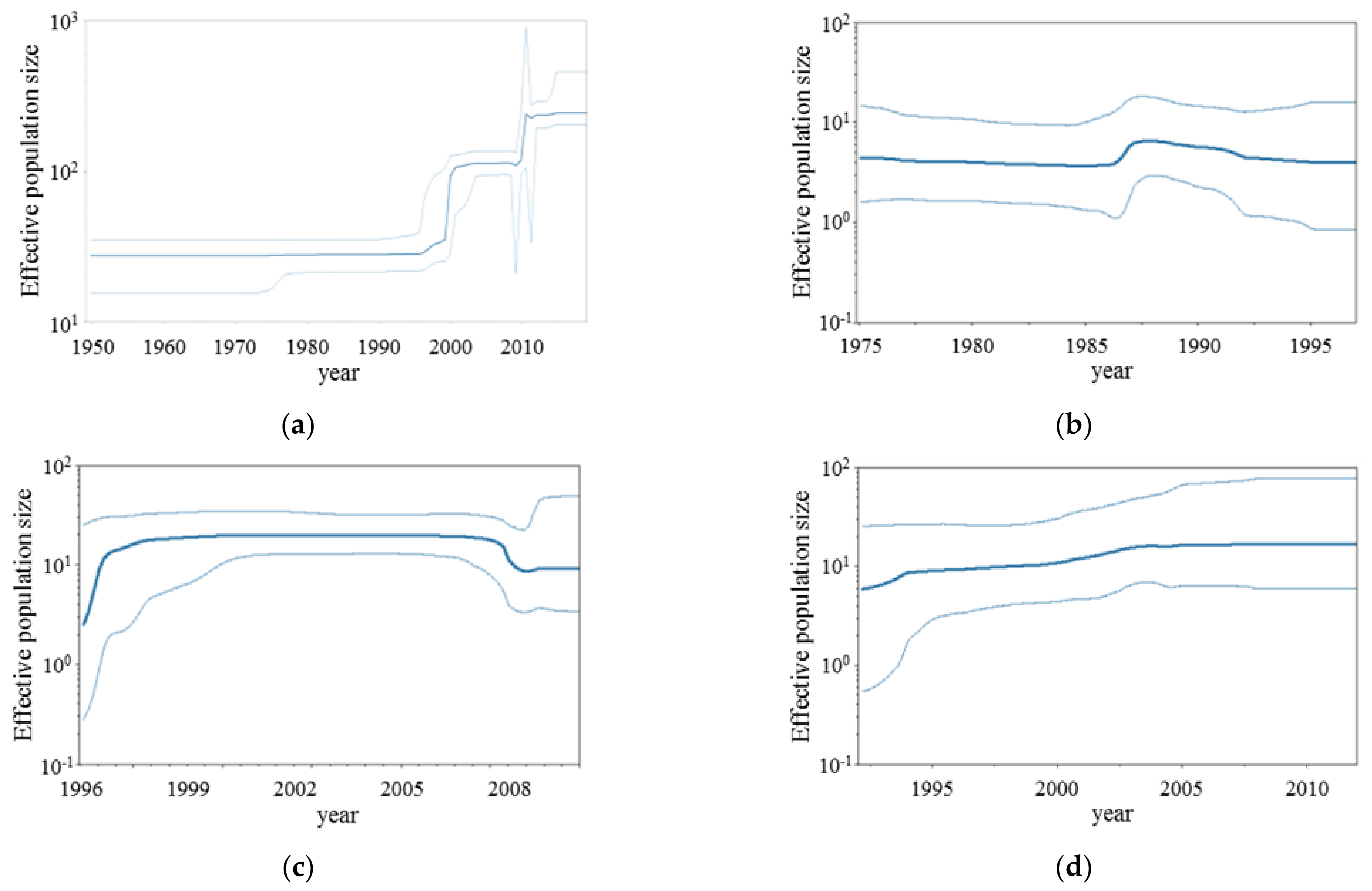
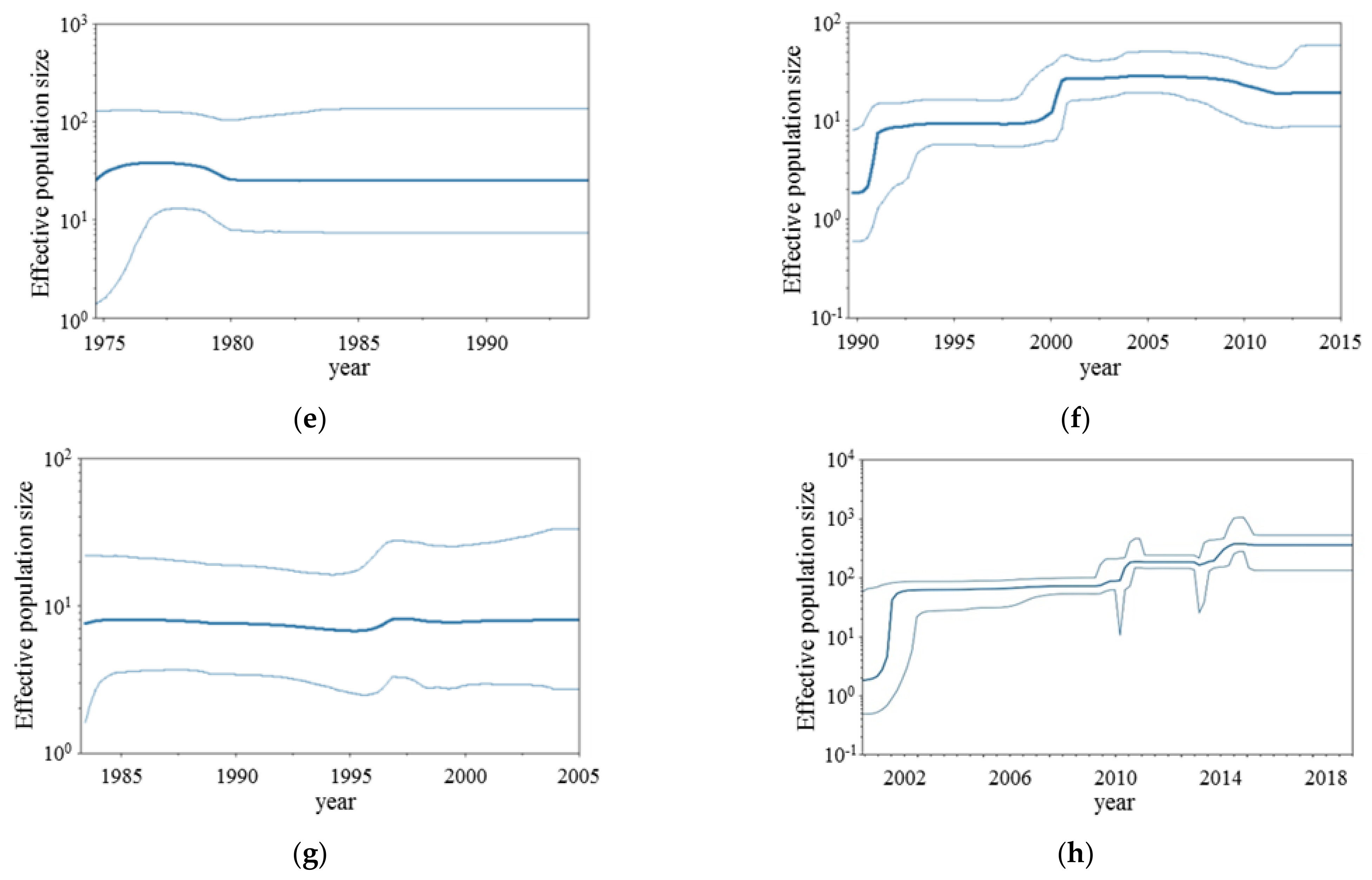
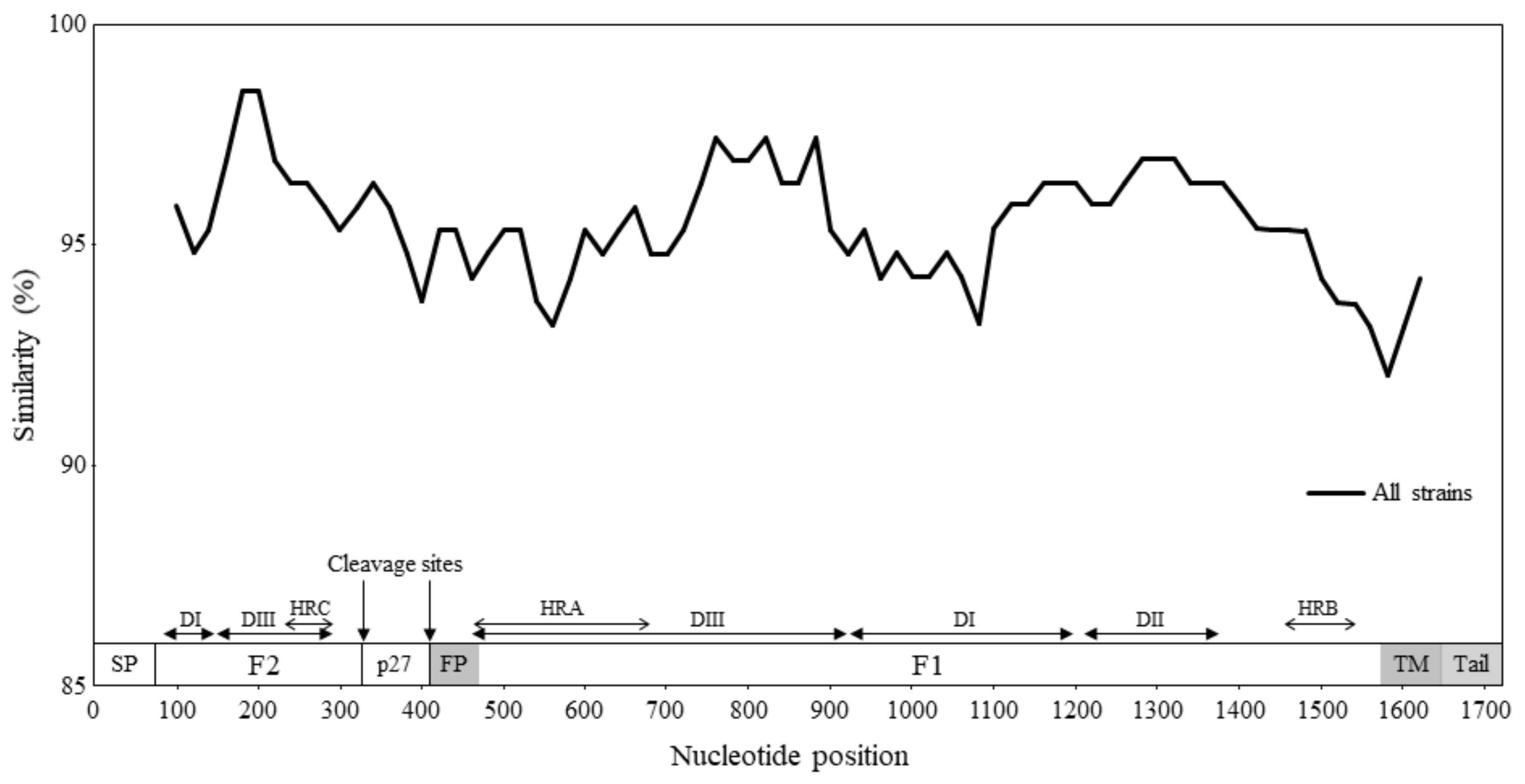

| Virus | Genotype | Diverged Year (95%HPD) | Strain Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSV-A | GA1 | 1943 (1937–1948) | 35 |
| GA4 | 1970 (1967–1973) | 17 | |
| GA5 | 1975 (1973–1977) | 174 | |
| GA6 | 1977 (1974–1979) | 6 | |
| GA7 | 1977 (1974–1979) | 34 | |
| GA3 | 1979 (1978–1981) | 28 | |
| GA2 | 1988 (1987–1991) | 77 | |
| NA1 | 1994 (1994–1997) | 1092 | |
| RSV-B | 1766 (1734–1794) | 1 | |
| Bovine-RSV | 1563 (1504–1624) | 1 | |
| Chain | A | B | C | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residue | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 210 | 211 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 209 | 210 | 211 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 209 | 210 | 211 | |
| Prototype strain | K | E | N | K | Q | S | K | E | N | K | K | Q | S | K | E | N | K | K | Q | S | |
| Genotype | NA1 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| GA1 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA2 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA3 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA4 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA5 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA6 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| GA7 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, M.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Sada, M.; Sunagawa, S.; Shirai, T.; Okayama, K.; Sugai, T.; Tsugawa, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ryo, A.; et al. Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F Gene in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup A. Viruses 2021, 13, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122525
Saito M, Tsukagoshi H, Sada M, Sunagawa S, Shirai T, Okayama K, Sugai T, Tsugawa T, Hayashi Y, Ryo A, et al. Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F Gene in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup A. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122525
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Mariko, Hiroyuki Tsukagoshi, Mitsuru Sada, Soyoka Sunagawa, Tatsuya Shirai, Kaori Okayama, Toshiyuki Sugai, Takeshi Tsugawa, Yuriko Hayashi, Akihide Ryo, and et al. 2021. "Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F Gene in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup A" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122525
APA StyleSaito, M., Tsukagoshi, H., Sada, M., Sunagawa, S., Shirai, T., Okayama, K., Sugai, T., Tsugawa, T., Hayashi, Y., Ryo, A., Takeda, M., Kawashima, H., Saruki, N., & Kimura, H. (2021). Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F Gene in the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup A. Viruses, 13(12), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122525








