Detection of Jingmenviruses in Japan with Evidence of Vertical Transmission in Ticks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Ticks
2.2. RNA Virome Analyses Using Next-Generation Sequencer
2.3. Virus Isolation
2.4. Retrospective Screening of Samples from Previous Virus Isolation Studies
2.5. Determination and Characterization of Viral Genome Sequence
2.6. Examination of the Presence of Endogenous Viral Element (EVE)
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
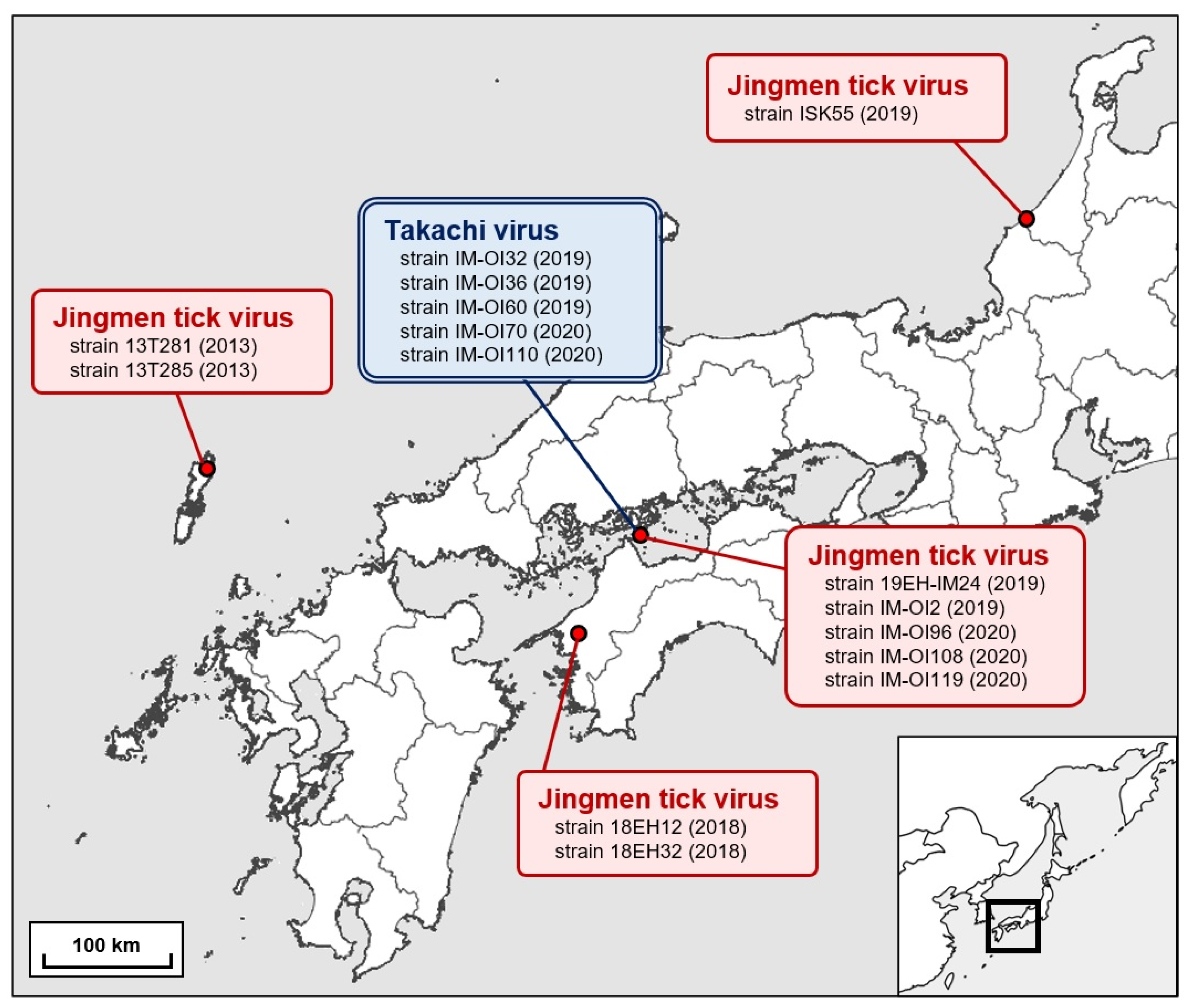
3.1. Detection of JMTV and Prevalence among Field-Collected Ticks in Japan
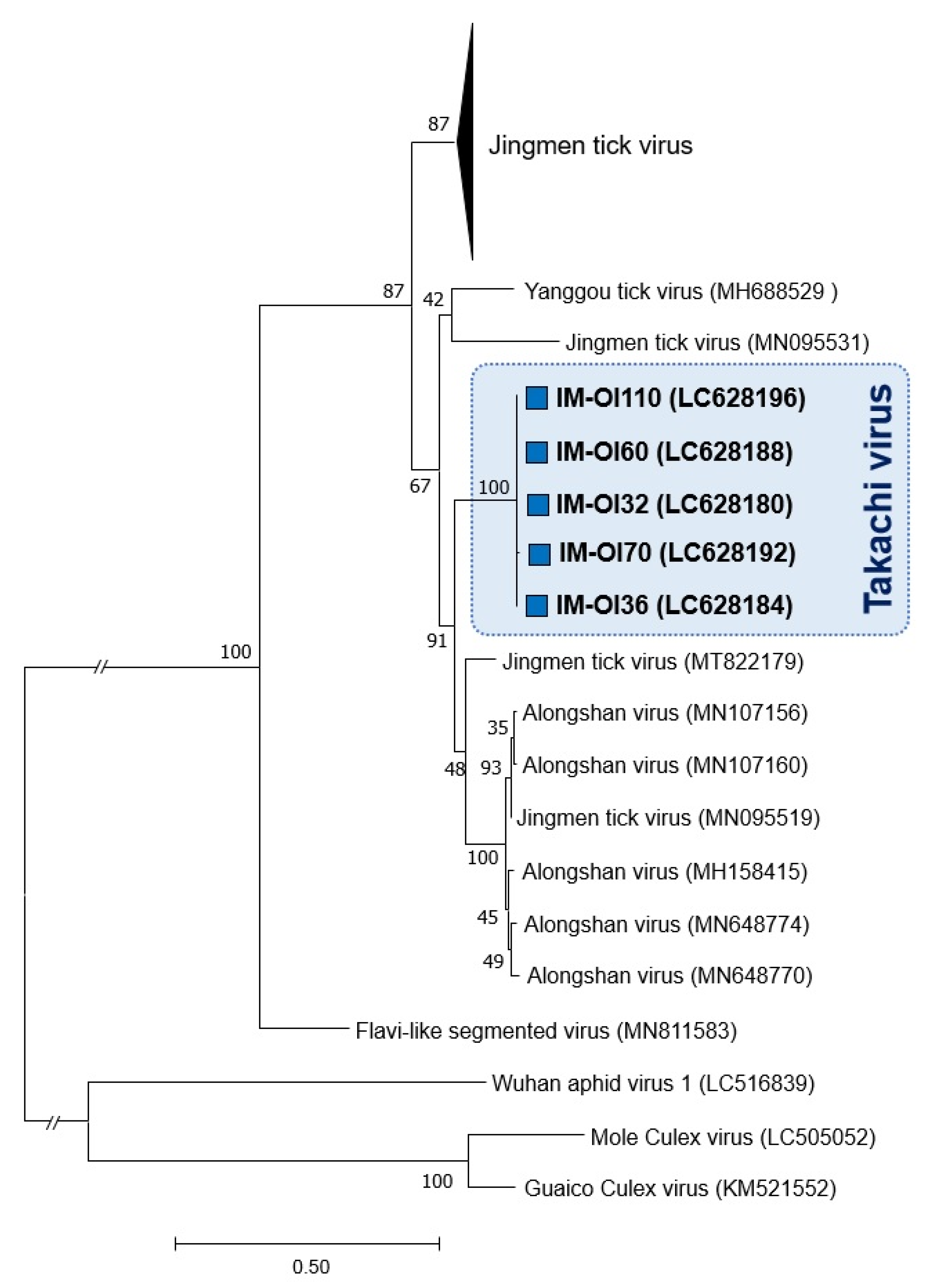
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationship between Japanese JMTV Strains and Other Known JMTV Strains
3.3. Discovery of a Novel Jingmenvirus in Hae. Formosensis Ticks Collected in Japan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madison-Antenucci, S.; Kramer, L.D.; Gebhardt, L.L.; Kauffman, E. Emerging tick-borne diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00083-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, R.; Lipkin, W.I. Discovery and Surveillance of Tick-Borne Pathogens. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Xie, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, R.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, K.; et al. A tentative tamdy orthonairovirus related to febrile illness in Northwestern China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xie, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Human Tacheng Tick Virus 2 Infection, China, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Gao, D.Y.; He, J.R.; Wang, J.B.; Li, C.X.; Kang, Y.J.; Yu, B.; et al. A tick-borne segmented RNA virus contains genome segments derived from unsegmented viral ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garry, C.E.; Garry, R.F. Proteomics computational analyses suggest that the envelope glycoproteins of segmented jingmen flavi-like viruses are class II viral fusion proteins (β-Penetrenes) with mucin-like domains. Viruses 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmerich, P.; Jakupi, X.; von Possel, R.; Berisha, L.; Halili, B.; Günther, S.; Cadar, D.; Ahmeti, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Viral metagenomics, genetic and evolutionary characteristics of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever orthonairovirus in humans, Kosovo. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Liu, H.B.; Ni, X.B.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zheng, Y.C.; Song, J.L.; Li, J.; Jiang, B.G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Emergence of human infection with Jingmen tick virus in China: A retrospective study. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.J.; Lin, X.D.; Chen, Y.M.; Hao, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Yu, Z.M.; Lu, M.; Li, K.; Qin, X.C.; Wang, W.; et al. Diversity and circulation of Jingmen tick virus in ticks and mammals. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmam, S.; Bigot, T.; Chrétien, D.; Gondard, M.; Pérot, P.; Pommelet, V.; Dufour, E.; Petres, S.; Devillers, E.; Hoem, T.; et al. Insights into the host range, genetic diversity, and geographical distribution of jingmenviruses. MSphere 2019, 4, e0064-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinçer, E.; Hacıoğlu, S.; Kar, S.; Emanet, N.; Brinkmann, A.; Nitsche, A.; Özkul, A.; Linton, Y.M.; Ergünay, K. Survey and characterization of Jingmen tick virus variants. Viruses 2019, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ternovoi, V.A.; Protopopova, E.V.; Shvalov, A.N.; Kartashov, M.Y.; Bayandin, R.B.; Tregubchak, T.V.; Yakovlev, S.A.; Nikiforov, K.A.; Konovalova, S.N.; Loktev, V.B.; et al. Complete coding genome sequence for a novel multicomponent Kindia tick virus detected from ticks collected in Guinea. Biorxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, S.R.; Castro-Jorge, L.A.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Garcia, G.R.; Brandão, L.G.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Okada, M.I.; Abrão, E.P.; Ferreira, B.R.; et al. Characterisation of divergent flavivirus NS3 and NS5 protein sequences detected in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Brazil. Mem. Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, W.M.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Carrasco, A.O.T.; Romeiro, M.F.; Modha, S.; Seki, M.C.; Gheller, J.M.; Daffre, S.; Nunes, M.; Murcia, P.R.; et al. Viral diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus parasitizing cattle in southern Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Shen, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, F. Metagenomic profiling of viruses associated with Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in Yunnan Province, China. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameroff, S.; Tokarz, R.; Charles, R.A.; Jain, K.; Oleynik, A.; Che, X.; Georges, K.; Carrington, C.V.; Lipkin, W.I.; Oura, C. Viral diversity of tick species parasitizing cattle and dogs in Trinidad and Tobago. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Han, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.T.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.C.; et al. A new segmented virus associated with human febrile illness in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. The discovery of segmented flaviviruses: Implications for viral emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 40, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegrift, K.J.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, H.; Murthy, S.; Kramer, L.D.; Ostfeld, S.; Hudson, P.J.; Kapoor, A. Presence of segmented flavivirus infections in North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Litov, A.G.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Makenov, M.T.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Aibulatov, S.V.; Bazarova, G.K.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; et al. Geographical and tick-dependent distribution of flavi-like Alongshan and Yanggou tick viruses in Russia. Viruses 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.; James, M.E.; Asgari, S. Uncovering the worldwide diversity and evolution of the virome of the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizah, A.N.; Kobayashi, D.; Isawa, H.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Murota, K.; Higa, Y.; Futami, K.; Shimada, S.; Kim, K.S.; Itokawa, K.; et al. Deciphering the virome of Culex vishnui subgroup mosquitoes, the major vectors of Japanese encephalitis, in Japan. Viruses 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, D.; Murota, K.; Itokawa, K.; Ejiri, H.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Faizah, A.N.; Watanabe, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Noda, S.; et al. RNA virome analysis of questing ticks from Hokuriku District, Japan, and the evolutionary dynamics of tick-borne phleboviruses. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Murota, K.; Faizah, A.N.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Higa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Sawabe, K.; Isawa, H. RNA virome analysis of hematophagous Chironomoidea flies (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae and Simuliidae) collected in Tokyo, Japan. Med. Entomol. Zool. 2020, 71, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Komatsu, N.; Faizah, A.N.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Sawabe, K.; Isawa, H. A novel nyavirus lacking matrix and glycoprotein genes from Argas japonicus ticks. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Watanabe, M.; Faizah, A.N.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Higa, Y.; Tsuda, Y.; Sawabe, K.; Isawa, H. Discovery of a novel Flavivirus (Flaviviridae) from the horse fly, Tabanus rufidens (Diptera: Tabanidae): The possible coevolutionary relationships between the classical insect-specific flaviviruses and host dipteran insects. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kuwata, R.; Kimura, T.; Faizah, A.N.; Higa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Sawabe, K.; Isawa, H. Toyo virus, a novel member of the Kaisodi group in the genus Uukuvirus (family Phenuiviridae) found in Haemaphysalis formosensis ticks in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2751–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kuwata, R.; Kimura, T.; Faizah, A.N.; Higa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Sawabe, K.; Isawa, H. Detection of quaranjavirus-like sequences from Haemaphysalis hystricis ticks collected in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, R.; Ejiri, H.; Lim, C.K.; Noda, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Takayama-Ito, M.; Murota, K.; Posadas-Herrera, G.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Tarumizu tick virus: A new coltivirus from Haemaphysalis flava ticks in Japan. Virus Res. 2017, 242, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Isawa, H.; Ejiri, H.; Sasaki, T.; Sunahara, T.; Futami, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Minakawa, N.; et al. Complete genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of a Getah virus strain (genus Alphavirus, family Togaviridae) isolated from Culex tritaeniorhynchus mosquitoes in Nagasaki, Japan in 2012. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Ohashi, M.; Osei, J.; Agbosu, E.; Opoku, M.; Agbekudzi, A.; Joannides, J.; Fujita, R.; Sasaki, T.; Bonney, J.; et al. Detection of a novel putative phlebovirus and first isolation of Dugbe virus from ticks in Accra, Ghana. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, N.; Fujita, H.; Takahashi, M.; Natsuaki, M. Key to species of mature ticks & specific descriptions. In Medical Acarology in Japan; Takada, N., Ed.; Hokuryukan: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; pp. 118–147. [Google Scholar]
- Natsuaki, M. Tick bites in Japan. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, R.; Shinjo, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Ogata, S.; Kusakisako, K.; Kinoshita, G.; Naguib, D.; Chatanga, E.; Mohamed, W.; Moustafa, M.; et al. Amblyomma testudinarium infestation on a brown bear (Ursus arctos yesoensis) captured in Hokkaido, a northern island of Japan. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 80, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bente, D.A.; Forrester, N.L.; Watts, D.M.; McAuley, A.J.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Bray, M. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever: History, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical syndrome and genetic diversity. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, T. A bibliographical survey of host-parasite relationships between birds and ticks from Japan. Bull. Hoshizaki Green Found. 2001, 5, 271–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, S.T.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.G.; Choi, C.Y.; Park, C.U.; Klein, T.A.; Robbins, R.G. Tick surveillance of migratory birds during 2010–2011 on Hong and Heuksan Islands, Jeollanam Province, Republic of Korea. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Kim, K.S.; Ranyuk, M.; Babaev, E.; Voloshina, I.; Bayarlkhagva, D.; Chong, J.R.; Ishiguro, N.; Yu, L.; Min, M.S.; et al. Asia-wide phylogeography of wild boar (Sus scrofa) based on mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome: Revising the migration routes of wild boar in Asia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangia, C.; Vismarra, A.; Kramer, L.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Porretta, D.; Otranto, D.; Epis, S.; Grandi, G. Evaluation of the in vitro expression of ATP binding-cassette (ABC) proteins in an Ixodes ricinus cell line exposed to ivermectin. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangada, M.N.M.; Mohamed, H.; del Carmen Castillo, L.; Hasebe, F.; Igarashi, A. Effect of incubation temperature on dengue-2 viral antigen production and viral RNA synthesis in infected Aedes albopictus clone C6/36 cell line. Tissue Cult. Res. Commun. 1995, 14, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, S.M.; Colín, G.G.; Camarillo, S.D.R.; Murguía, C.A.V. Growth properties of DH82 and RF/6A cell lines under standard laboratory conditions. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2016, 7, 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nahapetian, A.T.; Thomas, J.N.; Thilly, W.G. Optimization of environment for high density Vero cell culture: Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient supply on cell growth and changes in metabolites. J. Cell Sci. 1986, 81, 65–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbey, J.E.; Tsunoda, I.; Fujinami, R.S. Altered cell growth and morphology in a BHK-21 cell mutant that lacks a receptor for Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus. Virology 2002, 294, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Beitzel, B.; Auguste, A.J.; Dupuis, A.P., II; Lindquist, M.E.; Sibley, S.D.; Kota, K.P.; Fetterer, D.; Eastwood, G.; et al. A multicomponent animal virus isolated from mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe. 2016, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Genus | Species | Tick Hosts | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyomma | A. javanense | Pangolin | China | [8] |
| A. testudinarium | ND * | Laos | [10] | |
| NA (flagging) ** | Japan | This study | ||
| Haemaphysalis | Hae. campanulata | Dog | China | [5] |
| Hae. flava | Hedgehog, Badger | China | [5] | |
| Hae. hystricis | Mammals *** | China | [9] | |
| Badger | China | [5] | ||
| Hae. inermis | Cattle | Turkey | [11] | |
| Hae. longicornis | Cattle, Dog, Goat | China | [5] | |
| Hae. parva | Cattle | Turkey | [11] | |
| Hyalomma | Hy. marginatum | Cattle, Dog, Goat | Turkey | [11] |
| Ixodes | I. granulatus | ND | China | [5] |
| I. ricinus | NA (flagging) | France | [10] | |
| I. sinensis | Wild goat | China | [5] | |
| Rhipicephalus | R. bursa | Cattle, Goat, Sheep | Turkey | [11] |
| R. geigyi | Cattle | Guinea | [12] | |
| R. microplus | Mammals | China | [9] | |
| Cattle | Brazil | [13] | ||
| Cattle | Brazil | [14] | ||
| Cattle | China | [5] | ||
| Cattle or Buffalo | China | [15] | ||
| Cattle | Trinidad and Tobago | [16] | ||
| ND | French Antilles | [10] | ||
| R. sanguineus | Dog | Turkey | [11] | |
| ND | China | [5] | ||
| R. turanicus | Cattle | Turkey | [11] |
| Source | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus | Strain | Species | Stage and No. of Individuals | Collection Site | Collection Date |
| Jingmen tick virus | T281 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 9 larvae | Tsushima City, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan | 29 November 2013 |
| T285 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 6 nymphs | Tsushima City, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan | 15 December 2013 | |
| 18EH12 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 26 nymphs | Ozu City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 27 September 2018 | |
| 18EH32 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 6 nymphs | Ozu City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 26 September 2018 | |
| 19EH-IM24 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 7 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 16 June 2019 | |
| IM-OI2 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 5 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 21 July 2019 | |
| IM-OI96 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 5 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 13 March 2020 | |
| IM-OI108 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 4 larvae | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 6 May 2020 | |
| IM-OI119 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 3 larvae | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 6 June 2020 | |
| ISK55 | Amblyomma testudinarium | 1 nymph | Kaga City, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan | 23 April 2019 | |
| Takachi virus | IM-OI32 | Haemaphysalis formosensis | 42 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 24 November 2019 |
| IM-OI36 | Haemaphysalis formosensis | 48 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 3 December 2019 | |
| IM-OI60 | Haemaphysalis formosensis | 50 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 23 December 2019 | |
| IM-OI70 | Haemaphysalis formosensis | 50 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 17 January 2020 | |
| IM-OI110 | Haemaphysalis formosensis | 50 nymphs | Imabari City, Ehime Prefecture, Japan | 6 May 2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, D.; Kuwata, R.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, H.; Fujita, R.; Faizah, A.N.; Kai, I.; Matsumura, R.; Kuroda, Y.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Detection of Jingmenviruses in Japan with Evidence of Vertical Transmission in Ticks. Viruses 2021, 13, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122547
Kobayashi D, Kuwata R, Kimura T, Shimoda H, Fujita R, Faizah AN, Kai I, Matsumura R, Kuroda Y, Watanabe S, et al. Detection of Jingmenviruses in Japan with Evidence of Vertical Transmission in Ticks. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122547
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Daisuke, Ryusei Kuwata, Toshiya Kimura, Hiroshi Shimoda, Ryosuke Fujita, Astri Nur Faizah, Izumi Kai, Ryo Matsumura, Yudai Kuroda, Shumpei Watanabe, and et al. 2021. "Detection of Jingmenviruses in Japan with Evidence of Vertical Transmission in Ticks" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122547
APA StyleKobayashi, D., Kuwata, R., Kimura, T., Shimoda, H., Fujita, R., Faizah, A. N., Kai, I., Matsumura, R., Kuroda, Y., Watanabe, S., Kuniyoshi, S., Yamauchi, T., Watanabe, M., Higa, Y., Hayashi, T., Shinomiya, H., Maeda, K., Kasai, S., Sawabe, K., & Isawa, H. (2021). Detection of Jingmenviruses in Japan with Evidence of Vertical Transmission in Ticks. Viruses, 13(12), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122547







