Abstract
Carassius auratus herpesvirus (CaHV) has been identified as a high-virulence pathogenic virus that infects aquatic animals, but the key factor for virus–host interaction is still unclear. Five Really interesting new genes (RING) finger proteins (39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R) of CaHV were screened to determine structural diversity. RING finger proteins were also predicted in other known fish herpesviruses, with an arrangement and number similar to CaHV. We performed multifaceted analyses of the proteins, including protein sizes, skeleton structures, subcellular localizations, and ubiquitination activities, to determine their precise roles in virus–host interactions. The five proteins were overexpressed and detected different levels of ubiquitination activities, and 143R showed the highest activity. Then, the prokaryotic expressed and purified full-length proteins (131R and 136L), RING domain isolates (131R12–43 and 136L45–87), and RING domain-deleted mutants (131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87) were prepared to detect their activities through ubiquitination assays. The results indicate that both full-length proteins and their isolates have activities that catalyze ubiquitination, and the full-length proteins possess higher activity than the isolates, but RING domain-deleted mutants lose their activities. Furthermore, the activities of the five proteins were verified as E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, showing that the RING domains determine the ubiquitination activity. These proteins present different subcellular localization. RING domain-deleted mutants showed similar subcellular localization with their full-length proteins, and all the isolates diffused in whole cells. The current results indicate that the sequence outside the RING domain determines subcellular localization and the level of ubiquitination activity, suggesting that the RING finger proteins of fish herpesviruses might have diverse functions in virus–host interaction.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of the aquaculture industry has made outstanding contributions to protecting global food nutrition and safety [1,2]. Aquaculture is recognized as a highly efficient system for producing protein for human consumption, including the important economic fish crucian carp (Carassius auratus), with an annual output of nearly three million tons in China [3,4,5]; however, the prevalence of viral diseases, especially herpesvirus diseases, reported to be widespread in aquatic animals [6,7], has seriously affected the production and quality of aquatic products [8]. Carassius auratus herpesvirus (CaHV), isolated from diseased crucian carp, is a member of the genus Cyprinivirus within the family Alloherpesviridae in the order Herpesvirales that includes cyprinid herpesvirus 1 (CyHV-1), cyprinid herpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2), and cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) [9,10,11,12]. A genome sequence was completed, and genome architecture, some open reading frames’ (ORFs) insertion or deletion, and nucleotide sequence were found to be different from other members of the genus Cyprinivirus [13]. Several studies have also been carried out on the viral genes, subcellular localization of CaHV core protein, or host response to the virus [14,15,16], and some information about hosts immune to CaHV have also been obtained [17]. Furthermore, the viral protein targets for mitochondria FoF1-ATPase that might provide energy for virus replication were also reported [18]. In contrast, little is known about the key factor for virus–host interactions or whether RING finger proteins encoded by aquatic animal herpesviruses are involved in viral biological processes [19,20].
RING finger proteins are a large family of proteins containing a C3HC4-type RING domain (RD) (Cys–X2–Cys–X9–39–Cys–Xl–3–His–X2–3–Cys–X2–Cys–X4–48–Cys–X2–Cys; C is cysteine, H is histidine), widely involved in diverse aspects of biological processes of cellular organisms [21,22] and human–virus life cycles [23] with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. E3 ubiquitin ligase is a member of an enzymatic cascade for protein ubiquitination, including E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme and E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme [24]. Regarding aquatic viruses, RING finger proteins are only reported in infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) [25] and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). The latter functions in virus latency, replication, and host protein degradation [26]; however, limited information about the RING finger proteins is known in fish herpesvirus [9].
The trend in studying pathogenic viruses is to offer a scientific basis for prevention and control tactics [27]. Understanding virus pathogenicity, its molecular biological characteristics, and viral gene function will contribute to more effective prevention of viral diseases and ensure the health of the aquaculture industry [28]; therefore, in this study, five RING finger-containing proteins (39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R) encoded by CaHV were screened based on comparison with previously described consensus sequences (C3HC4). These genes were cloned and expressed, subcellular localizations were observed, and their functions in ubiquitination were evaluated, respectively. Our research will lay a foundation for the detailed understanding of the functions of these viral proteins, and the molecular mechanism of fish herpesvirus–host interaction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus, Cell Lines, and Reagents
The virus suspension and purified CaHV were previously stored in our laboratory at −80 °C [29,30]. Its complete genome was sequenced by our laboratory [13]. CaHV was isolated from challenged crucian carps (Carassius auratus) and used for further DNA extraction assay. Epithelioma papulosum cyprinid (EPC) cells were maintained in Medium 199 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 25 °C [31], and used for transfection and fluorescence observation. Human embryonic kidney (HEK293T) cells were cultured under an atmosphere of 5% CO2 (37 °C) in fresh Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS [32], and used for transfection and ubiquitination detection. Ubiquitin, E1, and E2 enzymes were purchased from Boston Biochem. UbcH5a has been widely used and has proved to participate in ubiquitination more effectively with most identified E3 ubiquitin ligase proteins compared to other types of E2 [33]. Therefore, UbcH5a was chosen for our ubiquitination assays to identify the E3 activity of these RING finger proteins.
2.2. Sequence Analysis of RING Finger Protein Homologs
Five RING family genes were BLAST in the CaHV genome (Genbank accession: KU199244) [13], which encodes five RING finger proteins: 39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R. Their homologs were also BLAST and predicted in other fish herpesviruses according to their genome sequence. Then, the genes were labeled in their respective genomes and compared. The sequences are illustrated via Genbank accession numbers, SY-C1 (KM200722), ST-J1 (JQ815364), CyHV2-SY (KT387800), YZ-01 (MK260012), CNDF-TB2015 (MN201961), KHV-U (DQ657948), CyHV3-Cavoy (MG925485), CyHV3-E (MG925486), CyHV3-FL (MG925487), GZ11-SC (MG925488), CyHV3-I (MG925489), CyHV3-M3 (MG925490), CyHV3-T (MG925491), and CyHV1 (JQ815363) [34,35,36]. Positions of conserved domains on the RING finger proteins were analyzed using the BLAST and SMART programs. Nuclear localization signals (NLSs) in 52L were predicted using the cNLS Mapper program. Further analysis of RING domains was performed by taking domain sequences from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) for multiple sequence alignment using ClastalX 1.83, followed by GENEDOC.
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Plasmid Construction
CaHV genome DNA was extracted from purified viruses by methods described previously [14], and used as a template to amplify the five genes and their isolated or truncated fragments. Amplified products were cloned into different vectors to produce recombinant plasmids used for fluorescence observation, prokaryotic expression, and eukaryotic expression. Detailed information is as follows. Primers used and the information about recombinant plasmids are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primers to amplify DNA and construct plasmids for localization, prokaryotic expression, and eukaryotic expression.
To produce plasmids for transfection and fluorescence observation, 39L, 131R, 136L, and 143R were amplified with pairs of primers 39L-F/R, 131R-F/R, 136L-F/R, and 143R-F/R, respectively. The PCR reaction was performed in a volume of 50 µL containing 0.5 µL of Fastpfu polymerase (TransGen, Beijing, China), 10 µL of 5× PCR buffer, 1 µL of each primer (10 mM), 4 µL of dNTPs (2.5 mM), and 1 µL of purified DNA. PCR conditions were carried out as follows: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min; 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 20 s, annealing at 55 °C for 20 s, and extension at 72 °C for 1 min; followed by a final extension step of 72 °C for 5 min. The PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel. Since there is an intron in the DNA sequence of 52L in the genome, an overlap extension PCR was employed, including two rounds of PCR. Briefly, two DNA fragments were obtained from the first round PCR with the primers of 52L-F/52L-linkerR and 52L-linkerF/52L-R. PCR products were purified and then used as a template for the second round of PCR with the primers of 52L-F/R. Then, 52L with the intron deletion was obtained. Five target fragments were 1389 bp, 1953 bp, 1353 bp, 702 bp, and 1812 bp, conforming to expectation as shown in Table 1. According to the manufacturer’s protocol, these fragments were purified using a Silica Bead DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Fermentas, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, digested with corresponding restriction enzymes, and inserted into pEGFP-N3 to produce recombinant plasmids pEGFP-39L, pEGFP-52L, pEGFP-131R, pEGFP-136L, and pEGFP-143R.
RING domain-deleted mutants 39LΔ6–47, 131RΔ12–43, and 143RΔ7–51 were amplified with primers 39LΔ6–47-F/R, 131RΔ12–43-F/R, and 143RΔ7–51-F/R, respectively, and subsequently cloned into plasmid pEGFP-N3 to construct recombinant plasmids pEGFP-39LΔ6–47, pEGFP-131RΔ12–43, and pEGFP-143RΔ7–51. 52LΔ565–607-N and 52LΔ565–607-C were obtained from the first round of PCR with the primers of 52LΔ565–607-F/52LΔ565–607-R1 and 52LΔ565–607-F1/52LΔ565–607-R, then purified and used as a template for the second round of PCR with the primers of 52LΔ565–607-F/R to get the fragment of 52LΔ565–607. 136LΔ45–87 were obtained using the same method with primers of 136LΔ45–87-F/136LΔ45–87-R1, 136LΔ45–87-F1/136LΔ45–87-R, and 136LΔ45–87-F/R. Then, they were subsequently cloned into plasmid pEGFP-N3 to construct recombinant plasmids pEGFP-52LΔ565–607 and pEGFP-136LΔ45–87.
Isolated RING domain coding fragments (39L6–47, 52L565–607, 131R12–43, 136L45–87, 143R7–51) were amplified with primers 39L6–47-F/R, 52L565–607-F/R, 131R12–43-F/R, 136L45–87-F/R, and 143R7–51-F/R, respectively, and subsequently cloned into plasmid pEGFP-N3 to construct recombinant plasmids pEGFP-39L6–47, pEGFP-52L565–607, pEGFP-131R12–43, pEGFP-136L45–87, and pEGFP-143R7–51.
To produce plasmids for ubiquitination detection in cell culture, the five genes were amplified with primers 39L-C-F/R, 52L-C-F/R, 131R-C-F/R, 136L-C-F/R, and 143R-C-F/R and inserted into pCMV-Tag2A, respectively, to construct recombinant plasmids pCMV-39L, pCMV-52L, pCMV-131R, pCMV-136L, and pCMV-143R. The cDNA fragment encoding ubiquitin (Ub) (GenBank accession no. M26880.1) was amplified with primers Ub-F/Ub-His-R by RT-PCR from the total RNA of HEK293T cells as described previously [37], and then cloned into the pcDNA3.1(+) to construct plasmid pcDNA3.1-Ub-His.
To construct plasmids for prokaryotic expression, two full-length genes (131R and 136L) were amplified with primers 131R-E-F/R, 136L-E-F/R, respectively, their isolated RING domain coding fragments (131R12–43 and 136L45–87) were amplified with primers 131R12–43-E-F/R and 136L45–87-E-F/R, and their RING domain-deleted mutants (131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87) were amplified using pEGFP-131RΔ12–43 and pEGFP-136LΔ45–87 as a template with primers 131RΔ12–43-E-F/R and 136LΔ45–87-E-F/R, respectively. Subsequently, the obtained fragments were cloned into plasmid pET32a to construct recombinant plasmids pET131R, pET136L, pET131R12–43, pET136L45–87, pET131RΔ12–43, and pET136LΔ45–87.
2.4. Transfection and Fluorescence Observation
EPC cells were inoculated on a microscopic coverslip in 6-well plates grown to 90% confluence. Then, 1.25 μg of each recombinant plasmid were transfected into EPC cells using the lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, MA, USA) reagent (according to the manufacturer’s instruction). At 24 h post-transfection (hpt), cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 30 min, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 15 min, and stained with Hoechst 33342 (Sigma, MO, USA) for 15 min. The cells were observed under a Leica DMIRB fluorescence microscope (objective 100×), as described previously [16].
2.5. Ubiquitination Detection in Cell Culture
Ubiquitination assays were performed in HEK293T cells to detect whether these five RING finger proteins could cause ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were inoculated in 6-well plates grown to 90 % confluence. Each recombinant plasmid (1.25 μg) plus pcDNA3.1-Ub-His (1.25 μg) were transfected into HEK293T cells, respectively, using the lipofectamine 3000 reagent as mentioned above, and an empty pCMV-Tag2A was used as control. For the protein stability experiment, HEK293T cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (20 μM) at 28 hpt for 8 h. Then cells were harvested for immunoprecipitation at 36 hpt. Harvested HEK293T cells were washed with pre-cooled PBS three times, then lysed with 200 μL lysis buffer (20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, pH 7.5) (Byotime, Shanghai, China) containing 2 μL protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma) and 2 μL Phenylmethylsulfonyl Fluoride (PMSF) (100 mM). The mixtures were inverted at 4 °C for 1 h, and centrifuged at 15,493× g for 5 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was transferred to a new tube, followed by adding 10 μL of Anti-Flag Affinity Gel (Sigma) and gently inverted at 4 °C overnight. The immuno-precipitates were washed three times with pre-cooled PBS, and finally resuspended by 30 μL PBS. Then, 7 μL 5× loading buffers were added to each sample, boiled at 100 °C for 10 min, and subjected to 8% and 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane (Millipore) and detected by western blot after sequential incubation with the primary antibodies (anti-Ub and anti-His) against the indicated target proteins and corresponding horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies. The membranes were incubated with an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Millipore). The chemiluminescent signals were detected using imager Tanon 5200. If a high molecular smear on the membrane was detected using an anti-Ub antibody, it would indicate that the corresponding product has ubiquitination catalyzing activity. The relative levels of ubiquitination were calculated as ratios to the corresponding protein normalization using Image J software. High values indicate high activities.
2.6. Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of Proteins
Recombinant plasmids were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells. The positive clones were cultured in an Luria-Bertani (LB) medium with 0.1 mg/mL ampicillin to mid-log phase at 37 °C and then induced with 0.1 mM Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for 4 h at 24 °C. Bacterial pellets were resuspended in a 1× binding buffer (300 mM NaCl, 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer, 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0), lysed by sonication on ice, and clarified by centrifugation at 16,000× g for 20 min. The supernatant containing recombinant proteins were then purified by Ni-NTA beads according to the manufacturer’s protocol with slight modifications as previously reported [38,39]. Un-induced bacteria, induced bacteria, and purified proteins were then verified on 12% SDS-PAGE by Coomassie blue staining. Purified proteins were dialyzed against ice-cold 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5). Protein concentrations were determined using an Enhanced BCA Protein Assay Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Beyotime), adjusted to 0.4 μg/μL, respectively, and stored at −80 °C.
2.7. Ubiquitination Assays of Purified Proteins
To detect whether these five proteins have E3 ubiquitin ligase activity or not, purified proteins were used for ubiquitination assays, respectively. Reactions were performed as follows: 5 μL of mixtures (50 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM ATP, 50 nM E1 enzyme, 250 nM E2 enzyme, 5μg ubiquitin, pH 7.5) were mixed with 5 μL (2 μg) of each purified protein (131R, 136L, 131R12–43, 136L45–87, 131RΔ12–43, and 136LΔ45–87), respectively, to final volumes of 10 μL, and then incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. Each reaction was quenched with 5× loading buffer, boiled for 10 min, and subjected to electrophoresis on 8% or 12% SDS-PAGE, then analyzed by western blot with anti-Ub and anti-Flag antibodies as described in Section 2.5.
3. Results
3.1. Fish Herpesvirus Encoding RING Finger Proteins
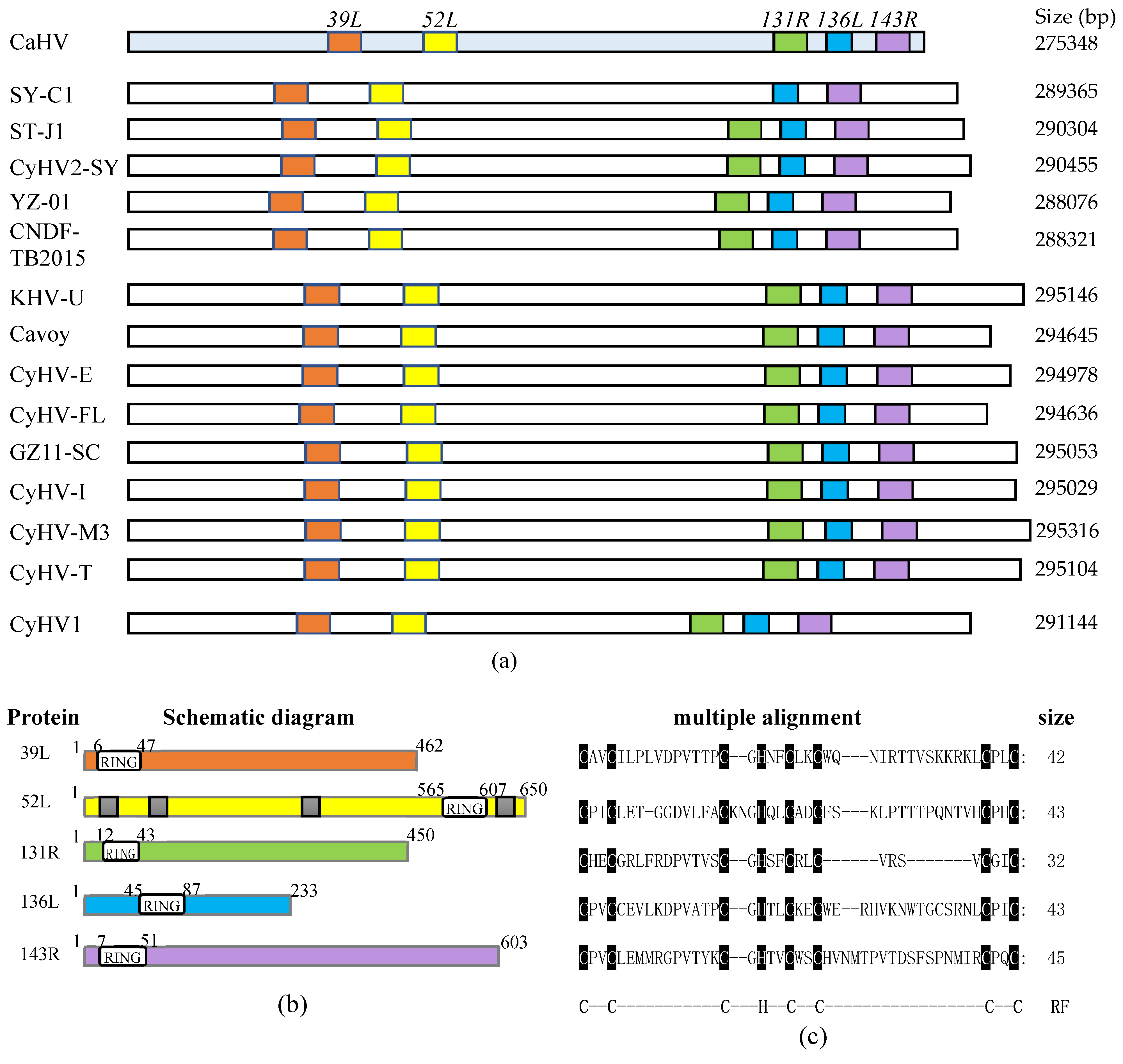
As shown in Figure 1a, five RING family genes (39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R) were screened in the CaHV genome. Further analysis showed that homologs of these five genes also exist in 14 other known fish herpesvirus genomes, with similar arrangements and number, except for SY-C1, which lacks the homolog of CaHV-52L. This indicates that RING family genes widely exist in fish herpesvirus, and probably play vital roles in virus infection.
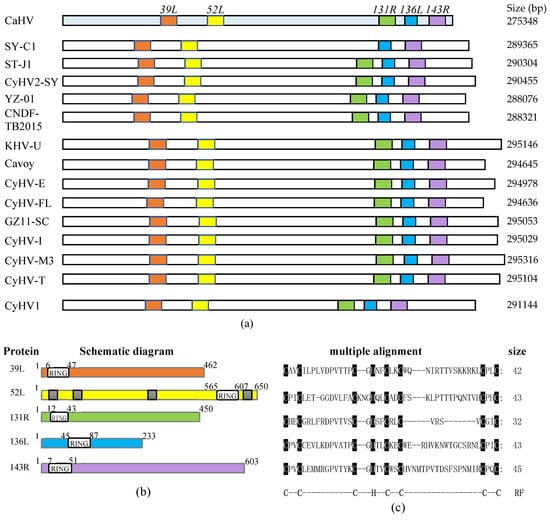
Figure 1.
RING family genes layout in genome and sequences and structural characteristics of five proteins. (a) The genomes are shown to scale as horizontal bars. Colored squares indicate RING family genes in the Carassius auratus herpesvirus (CaHV) genome and their homologs in other fish herpesvirus genomes. (b) Schematic diagrams. White boxes, RING domain; Gray boxes in 52L, predicted nuclear localization signals (NLSs). (c) The multiple alignments of RING domains. The conserved amino acid residues in RING domains were covered by black shade. RF: RING domain. C, cysteine; H, histidine.
Structural characteristics of the five proteins are shown in Figure 1b, and the lengths of these proteins were 462, 650, 450, 233, and 603 amino acids, respectively. All of them contain the RING domain. The sizes and positions of the domains are different, four of which are located at the N-terminal, and only 52L is located at the C-terminal. Besides, four nuclear localization signals (NLSs) were predicted in 52L. Multiple alignments are shown in Figure 1c. Sizes of RING domains were 42, 43, 32, 43, and 45 amino acids, respectively, containing conserved C3HC4 residues, which conformed to the classical RING domain.
3.2. Subcellular Localization of RING Finger Proteins
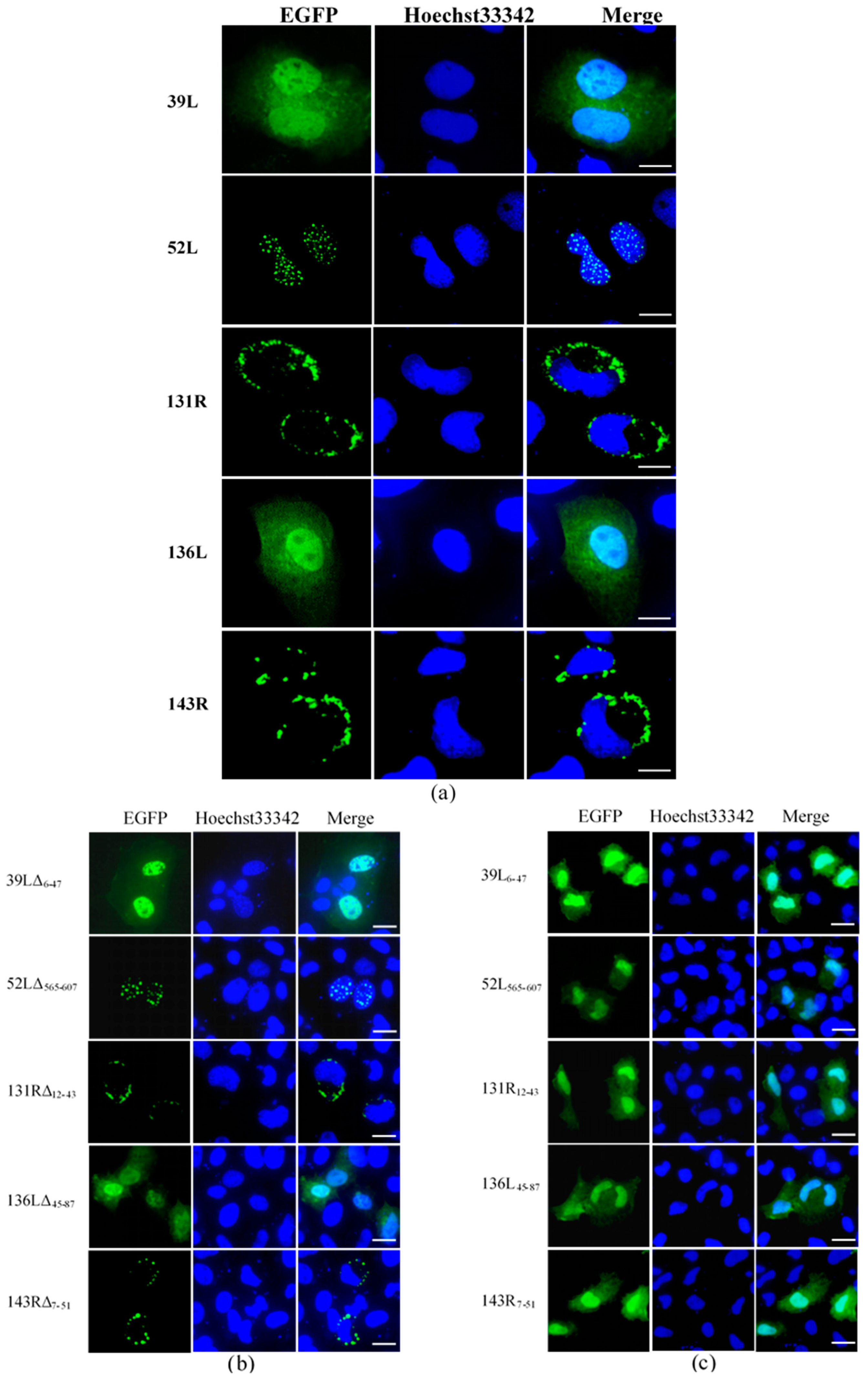
Subcellular localization was determined by detecting the fluorescence distribution of the EGFP fusion proteins. As shown in Figure 2a, 39L and 136L diffused in the whole cell. 52L localized speckled at the nucleus. Both 131R and 143R localized on cytomembrane. After the RING domain deletion, 39LΔ6–47 and 136LΔ45–87 diffused in the whole cell, 52LΔ565–607 localized at the nucleus, 131RΔ12–43 and 143RΔ7–51 localized on cytomembrane, similar to their corresponding wild-type proteins (Figure 2b). This indicates that no effects of deleting RING domains on subcellular localization were detected. The isolates 39L6–47, 52L565–607, 131R12–43, 136L45–87, and 143R7–51 all diffused in the whole cell (Figure 2c), implying that the RING domain does not determine the subcellular localization here. The results above indicate that five RING finger proteins present different subcellular localization, determined by the sequences outside the RING domain.
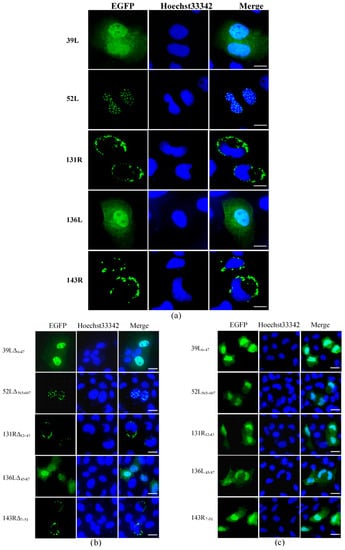
Figure 2.
Fluorescence micrographs. (a) Five RING finger proteins (39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R). 39L and 136L diffused in the whole cell. 52L signaled punctate in the nucleus. 131R and 143R localized on cytomembrane. (b) RING domain-deleted mutants. The mutants showed similar localizations with corresponding full-length proteins. (c) RING domain isolates. The isolates are diffused in the whole cell. Bar = 10 μm.
3.3. Ubiquitination Activity of RING Finger Proteins in Cell Culture
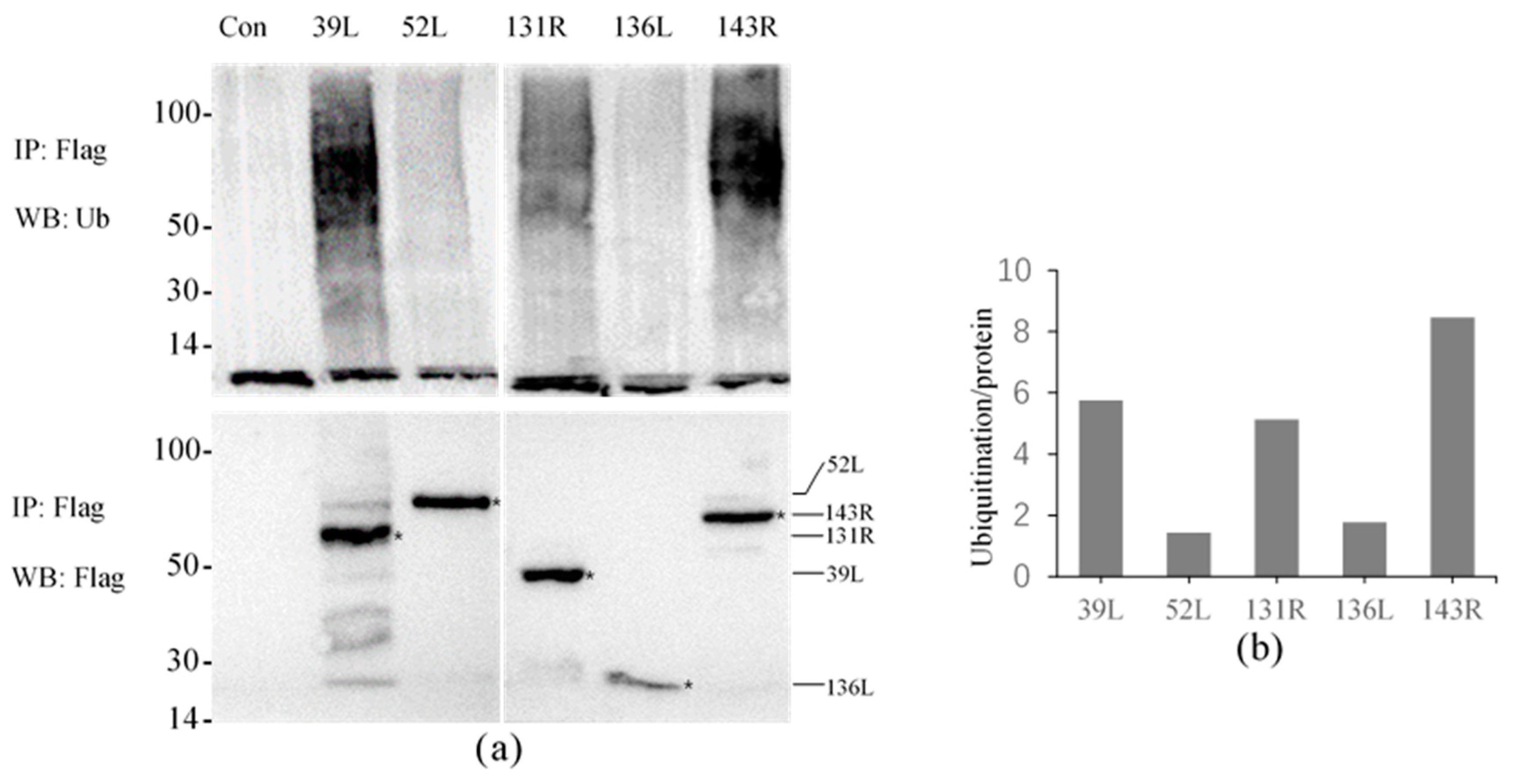
The results showed that high molecular weight smears were detected in all samples except for the control using the anti-Ub antibody, and the molecular weights were mainly concentrated in 50–100 kDa (Figure 3a). This indicates that all five proteins presented ubiquitination activity, though the displayed activities were different. Proteins were obtained by co-IP, and detected molecular weights were approximately 51, 72, 49, 27, and 66 kDa by anti-Flag antibody, confirming that the Flag-tagged fusion proteins were effectively expressed and immunoprecipitated.
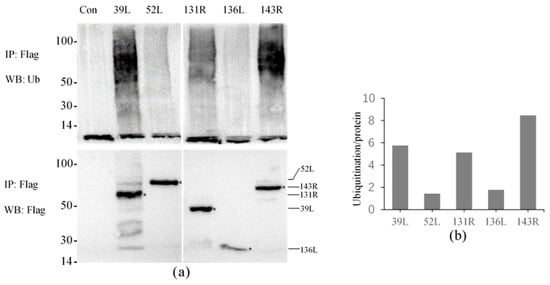
Figure 3.
Ubiquitination activity of five RING finger proteins 39L, 52L, 131R, 136L, and 143R in cell culture. (a) Ubiquiti nation detection. The upper part shows ubiquitination detection, and the below expresses immunoprecipitated proteins detection. IP: Immunoprecipitation; WB: Western blot; Ub: ubiquitin. (b) Graph of the relative ubiquitination values. The values of 39L and 131R were approximately 5–6, 52L and 136L approximately 1–2, and 143R approximately 8–9.
The relative activities were compared by analyzing the intensity of the ubiquitination smear. As shown in Figure 3b, the relative activity values of 52L and 136L were only 1–2, other proteins about 5–9, and 143R showed the highest value about 8–9, which indicates its highest activity.
3.4. Identification of Prokaryotic Expression Products
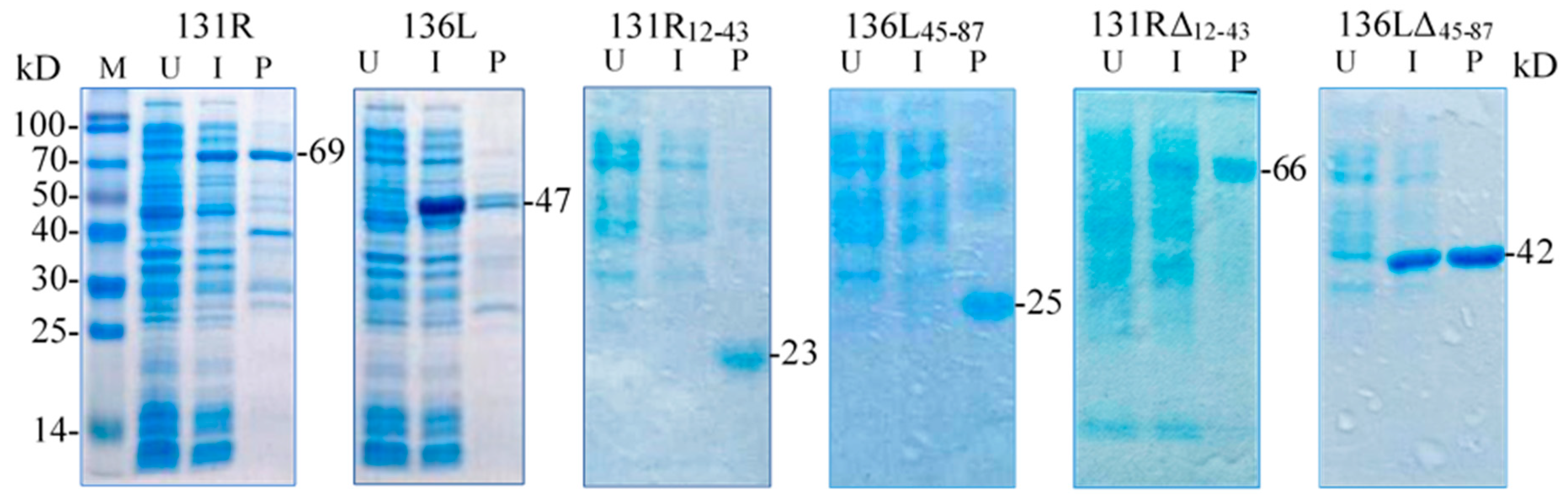
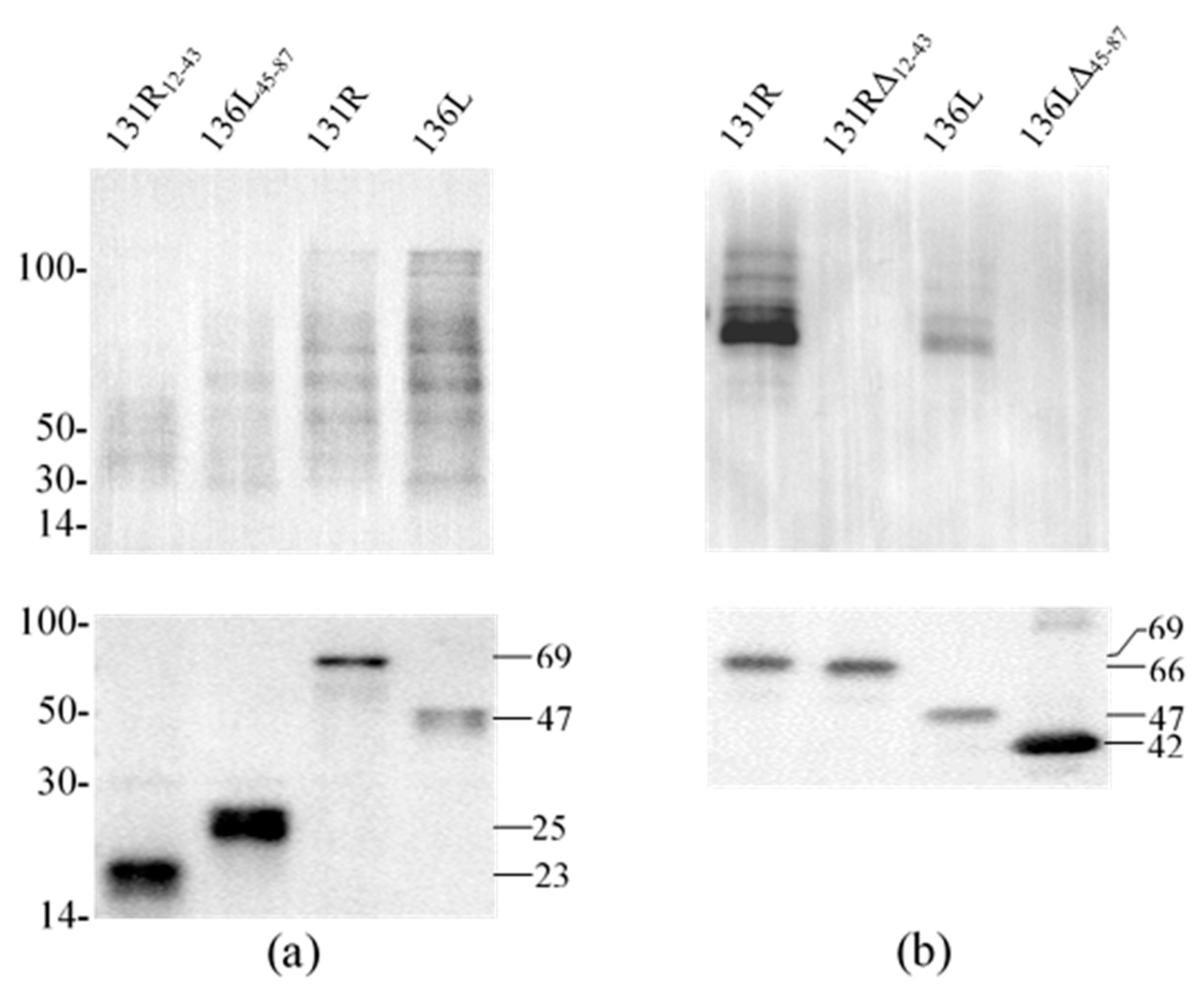
131R and 136L, their RING domain isolates 131R12–43 and 136L45–87, and their RING domain-deleted mutants 131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87 were expressed and purified. As shown in Figure 4, compared to the lanes of un-induced products, specific bands were detected in lanes of induced and purified products, respectively. The detected protein molecular weights were approximately 69, 47, 23, 25, 66, and 42 kDa, which conformed to the predicted molecular weights, implying that the recombinant proteins were expressed and purified. Note the recombinant proteins were increased in size due to an approximately 21 kDa fused Trx-His-S-His tag from the vector pET32a. The purified proteins were then used in the ubiquitination assays to detect ubiquitination activity.
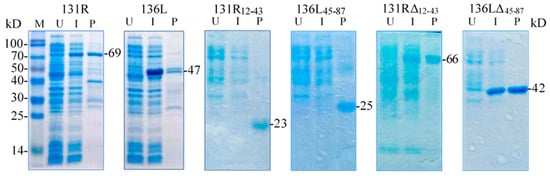
Figure 4.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) detected prokaryotic expression products of two recombinant full-length proteins 131R and 136L, two recombinant isolates 131R12–43 and 136L45–87, and two recombinant mutants 131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87. M: Protein marker; U: Un-induced bacteria; I: Induced bacteria; P: Purified protein. The recombinant proteins are indicated with short lines, and predicted molecular weights are shown on the right.
3.5. Ubiquitination Activity of the Recombinant Proteins
To reveal the effects of the RING domain on ubiquitination activity, ubiquitination catalyzed by full-length proteins (131R and 136L), RING domain isolates (131R12–43 and 136L45–87), and RING domain-deleted mutants (131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87) were further compared. Recombinant 131R12–43 (23 kDa), 136L45–87 (25 kDa), 131R (69 kDa), 136L (47 kDa), 131RΔ12–43 (66 kDa), and 136LΔ45–87 (42 kDa) were detected by anti-His antibody (Figure 5a,b). Compared to full 131R and 136L, ubiquitination formed bands were detected fewer and weaker by anti-Ub in 131R12–43 and 136L45–87 catalyzing products, but not detected in 131RΔ12–43 and 136LΔ45–87.
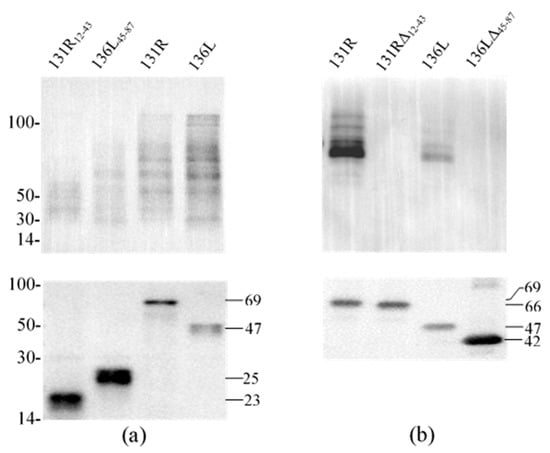
Figure 5.
Western blot analysis for ubiquitination reaction products of purified proteins. Each subfigure contains two parts, detection of target proteins using anti-His antibody and detection of ubiquitination using anti-Ub antibody by western blot. (a) Ubiquitination reaction products of purified proteins (131R12–43, 136L45–87, 131R, and 136L) were detected using anti-Ub and anti-His, respectively. (b) Ubiquitination reaction products of purified proteins (131R, 131RΔ12–43, 136L, and 136LΔ45–87) were detected using anti-Ub and anti-His, respectively. WB: Western blot; Ub: ubiquitin.
To confirm the precise activity of RING finger proteins, we performed ubiquitination assays in the incomplete reaction mixtures. Ubiquitinylated smears could be detected after respectively incubating 131R and 136L in the complete reaction mixtures. In the incomplete reaction mixtures lacking Mg2+, ATP, Ub, E1, E2, and purified RING finger proteins, no ubiquitination smear was detected. Because the complete reaction buffers used in the assays were free of any E3 enzymes other than the purified proteins, each recombinant protein functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which confirmed their activity as an E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Furthermore, in the incomplete reaction mixtures containing recombinant protein but lacking Mg2+, ATP, Ub, E1, or E2, no bands formed by ubiquitination were detected, indicating the necessity of these components for E3 ubiquitin ligase activities of these proteins [40]. This indicates that the RING finger proteins have E3 ligase activity, determined by the RING domain and influenced by the sequences outside the domain.
4. Discussion
In this study, multiple RING family genes were found to exist in the 15 known fish herpesviruses that were first reported; however, their relative locations in the genomes were uneven, and the sizes of the sequences among the homologs were also different. RING family genes were also predicted in other fish herpesvirus genomes, such as Anguillid herpesvirus 1 (AngHV-1), indicating that they widely exist in fish herpesviruses [41]. Whether these divergences related to gene expression or functions in virus-host interaction or infection needs further study. Genes layout, protein structures, subcellular localization, and ubiquitination activities were analyzed through bioinformatic analysis, fluorescence observation, and ubiquitination assay as shown in Table 2. Many questions need further study. As far as we know, this is the first report describing the ubiquitination and activity of RING finger proteins in fish herpesvirus.

Table 2.
Ubiquitination of full-length proteins, isolates, and mutants.
This study indicates that RING finger proteins possess E3 ligase activity, and the RING domain determined the identified activity because the domain deletion abrogated the activity, as previously reported [42,43]. In addition, this study showed that the RING finger proteins catalyze ubiquitination in collaboration with E1 ubiquitin-activating enzymes and E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes [44,45,46], and some viral RING finger proteins were directly or indirectly identified to interact with cellular E2 enzymes to mediate ubiquitination, providing evidence that these proteins probably hijack the host ubiquitination machine to function [47,48,49]. Here, CaHV encodes five RING finger proteins that can catalyze ubiquitination in complete reactions outside the cell. Incomplete reactions containing these proteins but lacking neither E1 nor E2 enzymes can catalyze ubiquitination. These proteins were able to catalyze ubiquitination, but no potential E1 and E2 enzymes were predicted in the CaHV genome that could participate in this process, meaning that these virus proteins hijacked cellular E1 and E2 enzymes to complete this process. This suggests that fish herpesvirus showed remarkable abilities in exploiting their hosts. Fish herpesviruses, especially cyprinid herpesviruses, were reported to infect fish that are not their specific host, even hybrids [50], which may connect to the similar cellular E1 E2 that also exist in the nonspecific host and hybrids.
Subcellular localization can provide clues for protein biological function [51], and different subcellular localizations suggest different functions. As previously reported, viral proteins such as ICP0 encoded by HSV-1 and core protein 91R encoded by Rana grylio virus (RGV) were localized at the nucleus, which has a nuclear localization signal (NLS), and play an important role in promoting the successful onset of lytic infection and productive reactivation of viral genomes from latency or virus genome replication [32,52,53,54]. Here, 52L of CaHV were observed localized at the nucleus and predicted containing an NLS, and probably have similar functions. Proteins localized in cytoplasm or whole cells might relate to virus incorporation, maturation or release, and sometimes targets viral replication factories, which might also involve virus replication and processing [55,56,57,58,59]. 39L and 136L showed similar locations here. Furthermore, those localized at membrane proteins were mostly related to viral entry or release, whereas viral membrane E3 ubiquitin ligase usually regulates cellular protein traffic, which probably helps virus maintenance, representing the potential functions of 131R and 143R [60,61]. As our results have shown, three types of subcellular localization among five proteins were observed. Various subcellular localization probably suggests that they perform functions in the different stages of virus infection.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we identified that the RING finger proteins exist widely in fish herpesviruses and that protein structure affects subcellular localization, relative to the level of activity, except for the RING domain, which determines the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The five virus RING finger proteins can exploit cellular E1 and E2 to complete the procedure of ubiquitination, which shows that the RING finger proteins directly participate in virus–host interaction. This indicates the multiparameter diversity of fish herpesvirus (CaHV) RING finger proteins. These results regarding fish herpesvirus encoded RING finger proteins may help us to further understand the interactions between virus and host.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: J.-F.G. and Q.-Y.Z. Performed the experiments: Z.-H.W. and F.K. Contributed reagents, materials, and analyzed the data: Z.-H.W., F.K., and Q.-Y.Z. Wrote the paper and approved the final manuscript: Z.-H.W., F.K., Q.-Y.Z., and J.-F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772890, 31972839), the Strategic Pilot Science and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Project (XDA24030203), and the National Key R&D Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (2018YFD0900302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Goldburg, R.J.; Primavera, J.H.; Kautsky, N.; Beveridge, M.C.; Clay, J.; Folke, C.; Lubchenco, J.; Mooney, H.; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.F.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.J. Research Advances and Prospects for Fish Genetic Breeding. Bull Chin. Acad. Sci. 2018, 33, 932–939. [Google Scholar]
- Belton, B.; Little, D.C.; Zhang, W.; Edwards, P.; Skladany, M.; Thilsted, S.H. Farming fish in the sea will not nourish the world. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.; Du, W.X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, Z.W.; Gui, J.F. Regain of sex determination system and sexual reproduction ability in a synthetic octoploid male fish. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Biotechnological innovation in genetic breeding and sustainable green development in Chinese aquaculture. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 49, 1409–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, L.; Dishon, A.; Kotler, M. Herpesviruses that infect fish. Viruses 2011, 3, 2160–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibenge, F.S. Emerging viruses in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Zhang, Q.Y. A brief review on aquatic animal virology researches in China. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 168–187, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.J.; Kurobe, T.; Gatherer, D.; Cunningham, C.; Korf, I.; Fukuda, H.; Hedrick, R.P.; Waltzek, T.B. Comparative genomics of carp herpesviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2908–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Virus genomes and virus-host interactions in aquaculture animals. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, L.; Zhang, Q.Y. Disease prevention and control. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends; Gui, J.F., Tang, Q.S., Li, Z.J., Liu, J.S., Sena, S.S.D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2018; pp. 577–598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y. An overview on several large DNA viruses in freshwater ecosystems. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica 2020, 5, 28–42, (Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Deng, Y.S.; Gui, J.F.; Zhang, Q.Y. Complete genome sequence and architecture of crucian carp Carassius auratus herpesvirus (CaHV). Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gui, L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y. Mutations in the Cterminal region affect subcellular localization of crucian carp herpesvirus (CaHV) GPCR. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gao, F.X.; Li, Z.; Tong, J.F.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Differential interferon system gene expression profiles in susceptible and resistant gynogenetic clones of gibel carp challenged with herpesvirus CaHV. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 86, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.Y. Characterization of Carassius auratus herpesvirus ORF31R (CaHV-31R) and the encoded protein colocalize with cellular organs. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1263–1270, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.J.; Gao, F.X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Differential expression of innate and adaptive immune genes in the survivors of three gibel carp gynogenetic clones after herpesvirus challenge. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Zeng, X.T.; Zhang, Q.Y. Fish herpesvirus protein (CaHV-138L) can target to mitochondrial protein FoF1 ATPase. Virus Res. 2020, 275, 197754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, M.; Zhang, Y.; Geiser, V.; Jones, C. The zinc ring finger in the bICP0 protein encoded by bovine herpesvirus-1 mediates toxicity and activates productive infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, V.J.; Yuziuk, J.A.; Chiarella, A.M.; Tyson, T.O.; Meganck, R.M.; Elmore, Z.C.; Tse, L.V.; Hathaway, N.A.; Asokan, A. Ring finger protein 121 is a potent regulator of adeno-associated viral genome transcription. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joazeiro, C.A.; Weissman, A.M. RING finger proteins: Mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 2000, 102, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Hara, Y.; Oka, Y.; Komine, O.; Van den Heuvel, D.; Guo, C.; Daigaku, Y.; Isono, M.; He, Y.; Shimada, M.; et al. Ubiquitination of DNA Damage-Stalled RNAPII Promotes Transcription-Coupled Repair. Cell 2020, 180, 1228–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.C.; Dybas, J.M.; Hughes, J.; Weitzman, M.D.; Boutell, C. The HSV-1 ubiquitin ligase ICP0: Modifying the cellular proteome to promote infection. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Joazeiro, C.A.P. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Weng, S.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Xie, Q.; Li, M.; He, J. RNFs of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) function as ubiquitin ligase enzymes. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, M.; Venugopal, M.N. Identification and characterization of novel double zinc fingers encoded by putative proteins in genome of white spot syndrome virus. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, D.M.; Archin, N.M.; Cohen, M.S.; Eron, J.J.; Ferrari, G.; Garcia, J.V.; Gay, C.L.; Goonetilleke, N.; Joseph, S.B.; Swanstrom, R.; et al. Curing HIV: Seeking to Target and Clear Persistent Infection. Cell 2020, 181, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerset, I.; Krossøy, B.; Biering, E.; Frost, P. Vaccines for fish in aquaculture. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Gui, J.F.; Gao, X.C.; Pei, C.; Hong, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.Y. Genome architecture changes and major gene variations of Andrias davidianus ranavirus (ADRV). Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Deng, Y.S.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.Y. Pathological changes of acute viral hemorrhages in the gills of crucian carp. J. Fish. Sci. China 2016, 23, 336–343, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.T.; Gao, X.C.; Zhang, Q.Y. Rana grylio virus 43R encodes an envelope protein involved in virus entry. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.T.; Zhang, Q.Y. Interaction between Two Iridovirus Core Proteins and Their Effects on Ranavirus (RGV) Replication in Cells from Different Species. Viruses 2019, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, T.; Waisner, H.; Dogrammatzis, C.; Roy, A.; Chacko, S.; Perera, C.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kalamvoki, M. Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 ICP0 Protein Using an in vitro High-Throughput Screening Assay. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00619-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Hirono, I.; Kurokawa, K.; Fukuda, H.; Nahary, R.; Eldar, A.; Davison, A.J.; Waltzek, T.B.; Bercovier, H.; Hedrick, R.P. Genome sequences of three koi herpesvirus isolates representing the expanding distribution of an emerging disease threatening koi and common carp worldwide. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5058–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Luo, Y.Z.; Gao, Z.X.; Huang, J.; Zheng, X.H.; Nie, H.H.; Zhang, J.M.; Lin, L.; Yuan, J.F. Molecular characterisation and prevalence of a new genotype of Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 in mainland China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Suárez, N.M.; Wilkie, G.S.; Dong, C.; Bergmann, S.; Lee, P.A.; Davison, A.J.; Vanderplasschen, A.F.C.; Boutier, M. Genomic and biologic comparisons of cyprinid herpesvirus 3 strains. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Functional domains and the antiviral effect of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR from Paralichthys olivaceus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6889–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ke, F.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhao, J.G.; Gui, J.F.; Zhang, Q.Y. Identification and characterization of a novel envelope protein in Rana grylio virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Ming, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y. Ranaviruses Bind Cells from Different Species through Interaction with Heparan Sulfate. Viruses 2019, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H. (State Key Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China). Personal communication, 2020.
- Van Beurden, S.J.; Bossers, A.; Voorbergen-Laarman, M.H.; Haenen, O.L.; Peters, S.; Abma-Henkens, M.H.; Peeters, B.P.; Rottier, P.J.; Engelsma, M.Y. Complete genome sequence and taxonomic position of anguillid herpesvirus 1. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhidarmo, R.; Nakatani, Y.; Day, C.L. RINGs hold the key to ubiquitin transfer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, R.; Gao, J.; Miao, S.; Wang, L. Characterisation of human RING finger protein TRIM69, a novel testis E3 ubiquitin ligase and its subcellular localisation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 429, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorick, K.L.; Jensen, J.P.; Fang, S.; Ong, A.M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Weissman, A.M. 1999. RING fingers mediate ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2)-dependent ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11364–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branigan, E.; Penedo, J.C.; Hay, R.T. Ubiquitin transfer by a RING E3 ligase occurs from a closed E2~ubiquitin conformation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Chacin, R.C.; Bodrug, T.; Bolhuis, D.L.; Kedziora, K.M.; Bonacci, T.; Ordureau, A.; Gibbs, M.E.; Weissmann, F.; Qiao, R.; Grant, G.D.; et al. Ubiquitin chain-elongating enzyme UBE2S activates the RING E3 ligase APC/C for substrate priming. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Fenner, B.J.; Godwin, A.K.; Kwang, J. White spot syndrome virus open reading frame 222 encodes a viral E3 ligase and mediates degradation of a host tumor suppressor via ubiquitination. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3884–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, E.; Gatherer, D.; Tong, L.; Everett, R.D.; Boutell, C. Functional characterization of residues required for the herpes simplex virus 1 E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 to interact with the cellular E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2D1 (UbcH5a). J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6323–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; An, R.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.; Qu, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, J. BICP0 Negatively Regulates TRAF6-Mediated NF-κB and Interferon Activation by Promoting K48-Linked Polyubiquitination of TRAF6. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 8, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Sadowski, J.; Kiełpiński, M.; Bartłomiejczyk, M.; Fichtner, D.; Riebe, R.; Lenk, M.; Kempter, J. Susceptibility of koi x crucian carp and koi x goldfish hybrids to koi herpesvirus (KHV) and the development of KHV disease (KHVD). J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thul, P.J.; Åkesson, L.; Wiking, M.; Mahdessian, D.; Geladaki, A.; Ait Blal, H.; Alm, T.; Asplund, A.; Björk, L.; Breckels, L.M.; et al. A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science 2017, 356, eaal3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, W.P.; Schaffer, P.A. ICP0 is required for efficient reactivation of herpessimplex virus type 1 from neuronal latency. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3240–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gu, H. Identification of three redundant segments responsible for herpes simplex virus 1 ICP0 to fuse with ND10 nuclear bodies. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4214–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mostafa, H.H.; Thompson, T.W.; Davido, D.J. N-terminal phosphorylation sites of herpes simplex virus 1 ICP0 differentially regulate its activities and enhance viral replication. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerenberg, B.T.; Taylor, J.; Bartee, E.; Gouveia, K.; Barry, M.; Früh, K. The poxviral RING protein p28 is a ubiquitin ligase that targets ubiquitin to viral replication factories. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardieu, C.; Vigan, R.; Wilson, S.J.; Calvi, A.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.; Kellam, P.; Towers, G.J.; Neil, S.J. The RING-CH ligase K5 antagonizes restriction of KSHV and HIV-1 particle release by mediating ubiquitin-dependent endosomal degradation of tetherin. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareiss, B.; Barry, M. Fowlpox virus encodes two p28-like ubiquitin ligases that are expressed early and late during infection. Virology 2014, 462–463, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Said, A.; Osterrieder, N. Equine herpesvirus type 1 (EHV-1) open reading frame 59 encodes an early protein that is localized to the cytosol and required for efficient virus growth. Virology 2014, 449, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Brownlie, R.; Snider, M.; Van Drunen, L.; Van den Hurk, S. Phosphorylation of Bovine Herpesvirus 1 VP8 Plays a Role in Viral DNA Encapsidation and Is Essential for Its Cytoplasmic Localization and Optimal Virion Incorporation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4427–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscoy, L.; Sanchez, D.J.; Ganem, D. A novel class of herpesvirus-encoded membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases regulates endocytosis of proteins involved in immune recognition. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadwell, K.; Coscoy, L. Ubiquitination on nonlysine residues by a viral E3 ubiquitin ligase. Science 2005, 309, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).