Deletion of the L7L-L11L Genes Attenuates ASFV and Induces Protection against Homologous Challenge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Construction of Recombinant ASFV SY18△L7-11
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.5. Viral Growth Curves
2.6. Animal Tests
2.7. Quantitative PCR
2.8. Detection of Anti-ASFV Antibodies
2.9. Cytokine Assay
3. Results
3.1. Construction of the Gene-Deleted ASFV SY18△L7-11
3.2. Replication of SY18△L7-11 In Vitro
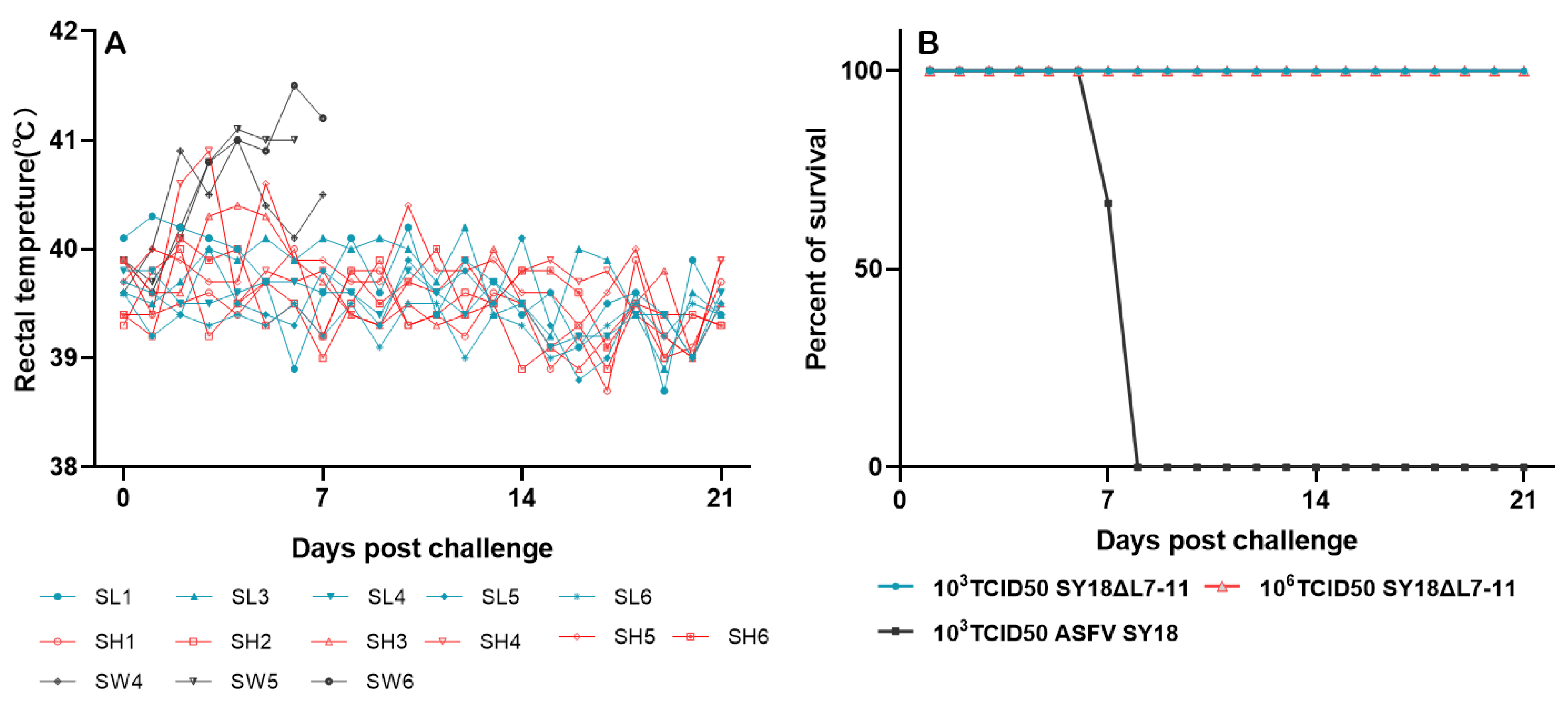
3.3. Virulence of SY18△L7-11 to Swine
3.4. Protective Effect of SY18△L7-11 against Challenge of Parental ASFV SY18
3.5. The Immune Response to SY18△L7-11
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boshoff, C.; Bastos, A.; Gerber, L.; Vosloo, W. Genetic characterisation of African swine fever viruses from outbreaks in southern Africa (1973–1999). Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 121, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achenbach, J.; Gallardo, C.; Nieto-Pelegrín, E.; Rivera-Arroyo, B.; Degefa-Negi, T.; Arias, M.; Jenberie, S.; Mulisa, D.; Gizaw, D.; Gelaye, E.; et al. Identification of a New Genotype of African Swine Fever Virus in Domestic Pigs from Ethiopia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quembo, C.; Jori, F.; Vosloo, W.; Heath, L. Genetic characterization of African swine fever virus isolates from soft ticks at the wildlife/domestic interface in Mozambique and identification of a novel genotype. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzoni, G.; Dei Giudici, S.; Loi, F.; Sanna, D.; Floris, M.; Fiori, M.; Sanna, M.; Madrau, P.; Scarpa, F.; Zinellu, S.; et al. African Swine Fever Circulation among Free-Ranging Pigs in Sardinia: Data from the Eradication Program. Vaccines 2020, 8, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, N.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, F.; Chen, T.; Zhang, S.; Cao, P.; Li, X.; Tian, K.; et al. Emergence of African Swine Fever in China, 2018. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, V.; Jeong, D.; Yoon, S.; Kwon, H.; Trinh, T.; Nguyen, T.; Bui, T.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.; Cheong, K.; et al. Outbreak of African Swine Fever, Vietnam, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1433–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cho, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Nah, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, J.; Sohn, H.; Choi, J.; et al. Outbreak of African swine fever in South Korea, 2019. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.; Chapman, D.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Fishbourne, E.; Hutet, E.; Cariolet, R.; Hutchings, G.; Oura, C.A.; Netherton, C.L.; Moffat, K.; et al. Protection of European domestic pigs from virulent African isolates of African swine fever virus by experimental immunisation. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4593–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borca, M.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Vuono, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Holinka, L.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D. Development of a Highly Effective African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine by Deletion of the I177L Gene Results in Sterile Immunity against the Current Epidemic Eurasia Strain. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e02017–e02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, A.; Cartaxeiro, C.; Coelho, R.; Cruz, B.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Portugal, F.C.; Vigario, J.D.; Martins, C.L.V. The non-haemadsorbing African swine fever virus isolate ASFV/NH/P68 provides a model for defining the protective anti-virus immune response. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulumba-Mfumu, L.; Goatley, L.; Saegerman, C.; Takamatsu, H.; Dixon, L. Immunization of African Indigenous Pigs with Attenuated Genotype I African Swine Fever Virus OURT88/3 Induces Protection Against Challenge with Virulent Strains of Genotype I. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e323–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.; Holinka, L.; Gladue, D.; Sanford, B.; Krug, P.; Lu, X.; Arzt, J.; Reese, B.; Carrillo, C.; Risatti, G.; et al. African Swine Fever Virus Georgia Isolate Harboring Deletions of MGF360 and MGF505 Genes Is Attenuated in Swine and Confers Protection against Challenge with Virulent Parental Virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6048–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, V.; Risatti, G.R.; Holinka, L.G.; Krug, P.W.; Carlson, J.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Azzinaro, P.A.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Simultaneous Deletion of the 9GL and UK Genes from the African Swine Fever Virus Georgia 2007 Isolate Offers Increased Safety and Protection against Homologous Challenge. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01760-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sang, H.; Miller, G.; Lokhandwala, S.; Sangewar, N.; Waghela, S.; Bishop, R.; Mwangi, W. Progress Toward Development of Effective and Safe African Swine Fever Virus Vaccines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Twigg, S.R.; Baylis, S.A.; Vydelingum, S.; Bristow, C.; Hammond, J.M.; Smith, G.L. Nucleotide sequence of a 55 kbp region from the right end of the genome of a pathogenic African swine fever virus isolate (Malawi LIL20/1). J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1655–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vydelingum, S.; Baylis, S.; Bristow, C.; Smith, G.; Dixon, L. Duplicated genes within the variable right end of the genome of a pathogenic isolate of African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiboeker, S.; Kutish, G.; Neilan, J.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Rock, D. A conserved African swine fever virus right variable region gene, l11L, is non-essential for growth in vitro and virulence in domestic swine. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, J.; Moreno, L.; Alejo, A.; Lacasta, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Salas, M. Genome Sequence of African Swine Fever Virus BA71, the Virulent Parental Strain of the Nonpathogenic and Tissue-Culture Adapted BA71V. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krug, P.; Holinka, L.; O’Donnell, V.; Reese, B.; Sanford, B.; Fernandez-Sainz, I.; Gladue, D.; Arzt, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Risatti, G.; et al. The progressive adaptation of a georgian isolate of African swine fever virus to vero cells leads to a gradual attenuation of virulence in swine corresponding to major modifications of the viral genome. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Miao, F.; Bo, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Construction and immunoprotective characterization of gene deleted African swine fever virus vaccine candidates. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 39, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Teklue, T.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.; Hu, R.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.-J. Generation and Evaluation of an African Swine Fever Virus Mutant with Deletion of the CD2v and UK Genes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, D.; He, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Shan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A seven-gene-deleted African swine fever virus is safe and effective as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, A.; Matamoros, T.; Guerra, M.; Andres, G. A Proteomic Atlas of the African Swine Fever Virus Particle. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01293-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salas, M.L.; Andres, G. African swine fever virus morphogenesis. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsak, L.; Caler, E.; Lu, Z.; Kutish, G.; Neilan, J.; Rock, D. A nonessential African swine fever virus gene UK is a significant virulence determinant in domestic swine. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanford, B.; Holinka, L.G.; O’Donnell, V.; Krug, P.W.; Carlson, J.; Alfano, M.; Carrillo, C.; Wu, P.; Lowe, A.; Risatti, G.R.; et al. Deletion of the thymidine kinase gene induces complete attenuation of the Georgia isolate of African swine fever virus. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.; O’Donnell, V.; Holinka, L.G.; Silva, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Carrillo, C.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Differential Effect of the Deletion of African Swine Fever Virus Virulence-Associated Genes in the Induction of Attenuation of the Highly Virulent Georgia Strain. Viruses 2019, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onisk, D.; Borca, M.; Kutish, G.; Kramer, E.; Irusta, P.; Rock, D. Passively transferred African swine fever virus antibodies protect swine against lethal infection. Virology 1994, 198, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Abrams, C.; Goatley, L.; Netherton, C.; Chapman, D.; Sanchez-Cordon, P.; Dixon, L. Deletion of African swine fever virus interferon inhibitors from the genome of a virulent isolate reduces virulence in domestic pigs and induces a protective response. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4698–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.; Jabbar, T.; Berrezaie, M.; Chapman, D.; Reis, A.; Sastre, P.; Rueda, P.; Goatley, L.; Dixon, L. Evaluation of protection induced by immunisation of domestic pigs with deletion mutant African swine fever virus BeninΔMGF by different doses and routes. Vaccine 2018, 36, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzuoli, E.; Franzoni, G.; Carta, T.; Zinellu, S.; Amadori, M.; Modesto, P.; Oggiano, A. Modulation of Type I Interferon System by African Swine Fever Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, G.; Razzuoli, E.; Dei Giudici, S.; Carta, T.; Galleri, G.; Zinellu, S.; Ledda, M.; Angioi, P.; Modesto, P.; Graham, S.; et al. Comparison of Macrophage Responses to African Swine Fever Viruses Reveals that the NH/P68 Strain is Associated with Enhanced Sensitivity to Type I IFN and Cytokine Responses from Classically Activated Macrophages. Pathogens 2020, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedumpun, T.; Wongyanin, P.; Sirisereewan, C.; Ritprajak, P.; Palaga, T.; Thanawongnuwech, R.; Suradhat, S. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: An early immunomodulatory cytokine induced by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Batorski, L.; Halfmann, P.; Marzi, A.; Lopes, T.; Neumann, G.; Feldmann, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Loss of Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist Enhances Susceptibility to Ebola Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S329–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Groups | No. | ASFV Genome Copies/mL (log10) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days Postinoculation | Days Postchallenge | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 21 | |||
| 103 TCID50 SY18△L7-11 | SL1 | - a | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SL2 | - | - | - | 6.97 | 7.87 | / b | |||||||
| SL3 | - | 6.29 | 6.70 | 5.79 | - | 5.12 | 5.39 | 5.44 | 5.19 | 4.48 | 3.62 | ||
| SL4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SL5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SL6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 106 TCID50 SY18△L7-11 | SH1 | - | 5.35 | - | 5.12 | 3.88 | 5.42 | 4.88 | 3.76 | 3.85 | - | - | |
| SH2 | - | 6.07 | 7.42 | 7.08 | 5.33 | 4.98 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SH3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SH4 | - | 5.85 | 7.25 | 5.06 | - | 5.03 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SH5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| SH6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 103 TCID50 ASFV SY18 | SW1 | - | 5.62 | 9.37 | / | ||||||||
| SW2 | - | 7.30 | / | ||||||||||
| SW3 | - | 5.47 | 8.34 | / | |||||||||
| SW4 | - | 6.37 | 8.71 | / | |||||||||
| SW5 | - | 7.20 | / | ||||||||||
| SW6 | - | 7.57 | 9.10 | / | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Yue, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Ke, J.; et al. Deletion of the L7L-L11L Genes Attenuates ASFV and Induces Protection against Homologous Challenge. Viruses 2021, 13, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020255
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Chen T, Yang J, Yue H, Wang L, Zhou X, Qi Y, Han X, Ke J, et al. Deletion of the L7L-L11L Genes Attenuates ASFV and Induces Protection against Homologous Challenge. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingyuan, Yanyan Zhang, Teng Chen, Jinjin Yang, Huixian Yue, Lidong Wang, Xintao Zhou, Yu Qi, Xun Han, Junnan Ke, and et al. 2021. "Deletion of the L7L-L11L Genes Attenuates ASFV and Induces Protection against Homologous Challenge" Viruses 13, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020255
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, T., Yang, J., Yue, H., Wang, L., Zhou, X., Qi, Y., Han, X., Ke, J., Wang, S., Yang, J., Miao, F., Zhang, S., Zhang, F., Wang, Y., Li, M., & Hu, R. (2021). Deletion of the L7L-L11L Genes Attenuates ASFV and Induces Protection against Homologous Challenge. Viruses, 13(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020255






