Pseudorabies Virus Infection Causes Downregulation of Ligands for the Activating NK Cell Receptor NKG2D
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Infection of Swine Kidney (SK) Cells
2.2. Analysis of Cell Surface Binding of NKG2D and Cell Surface Expression of NKG2D Ligands via Flow Cytometry
2.3. Real Time-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
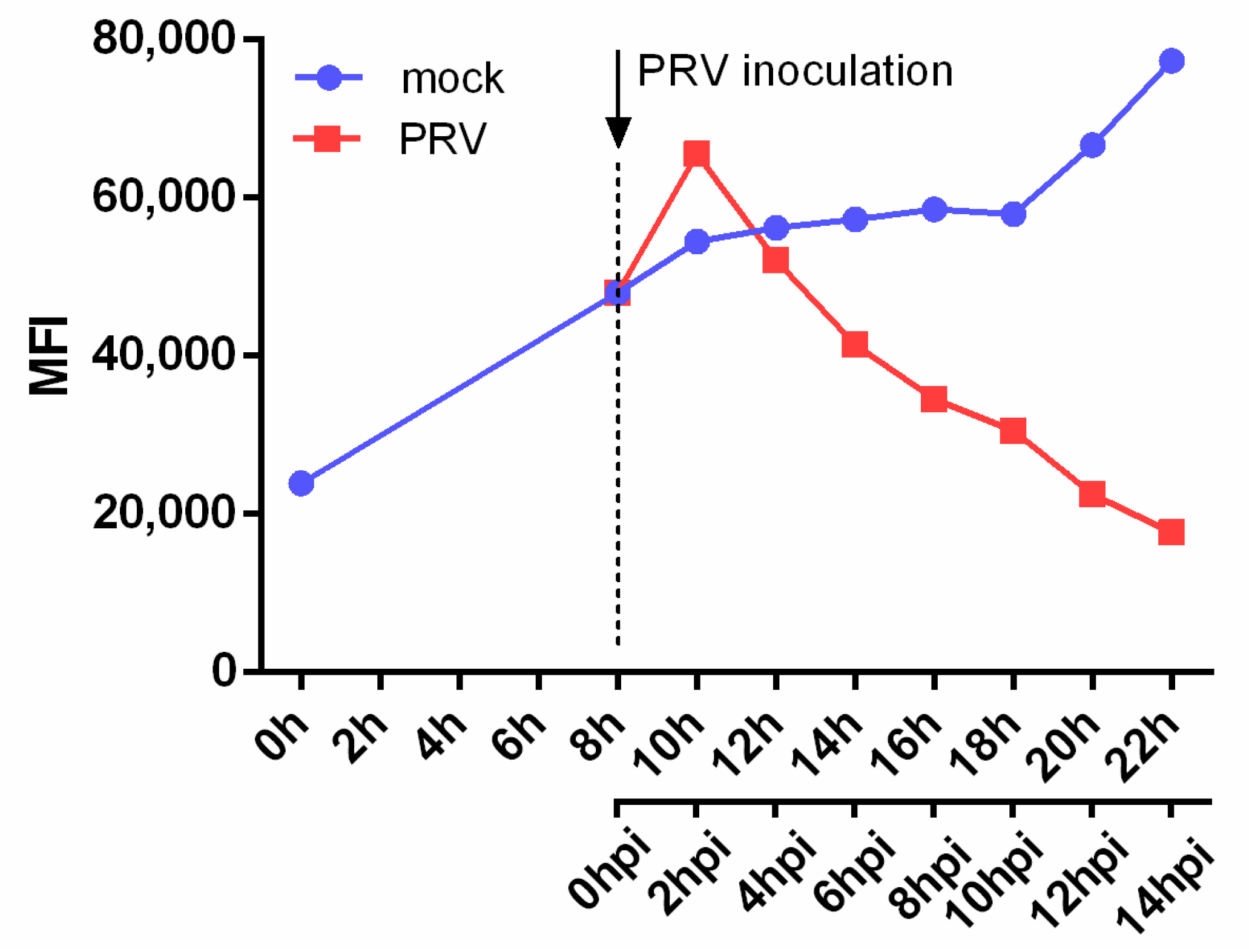
3.1. PRV Infection Suppresses NKG2D Ligand Expression on the Surface of Infected Cells
3.2. PRV Infection Leads to a Fast, Gradual and Persistent Downregulation of NKG2D Ligands
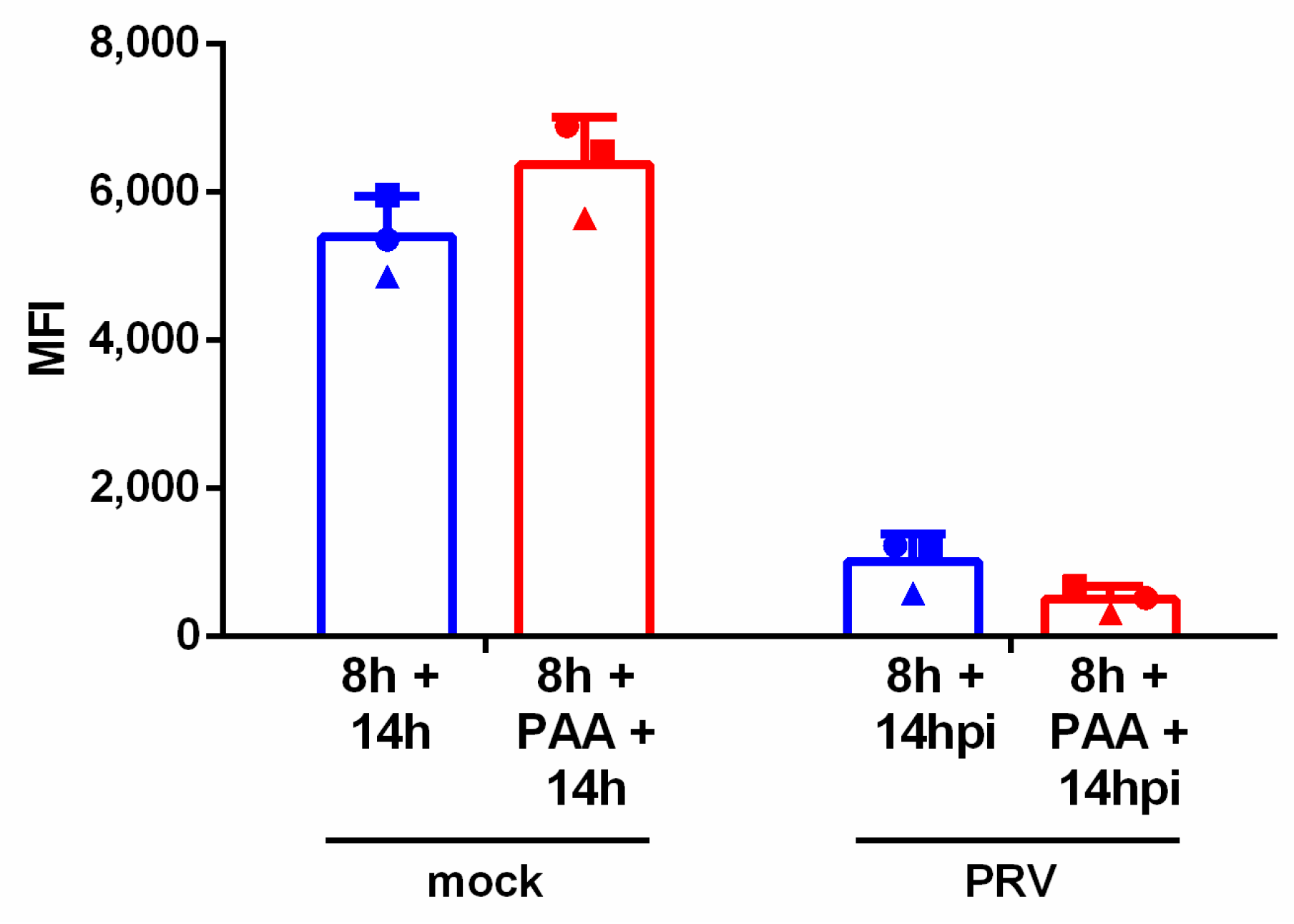
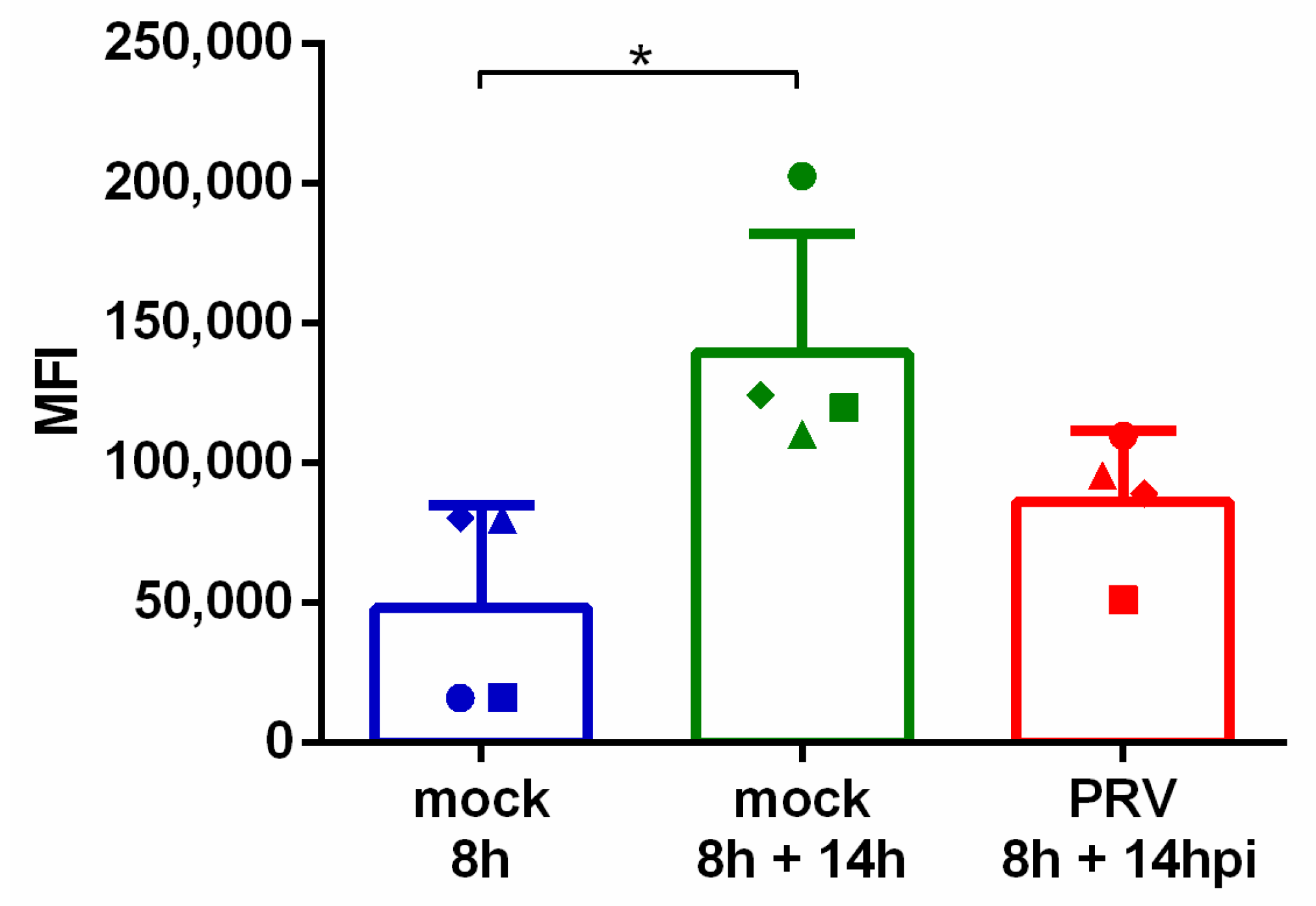
3.3. Downregulation of NKG2D Ligands Is Independent of Late Viral Gene Expression
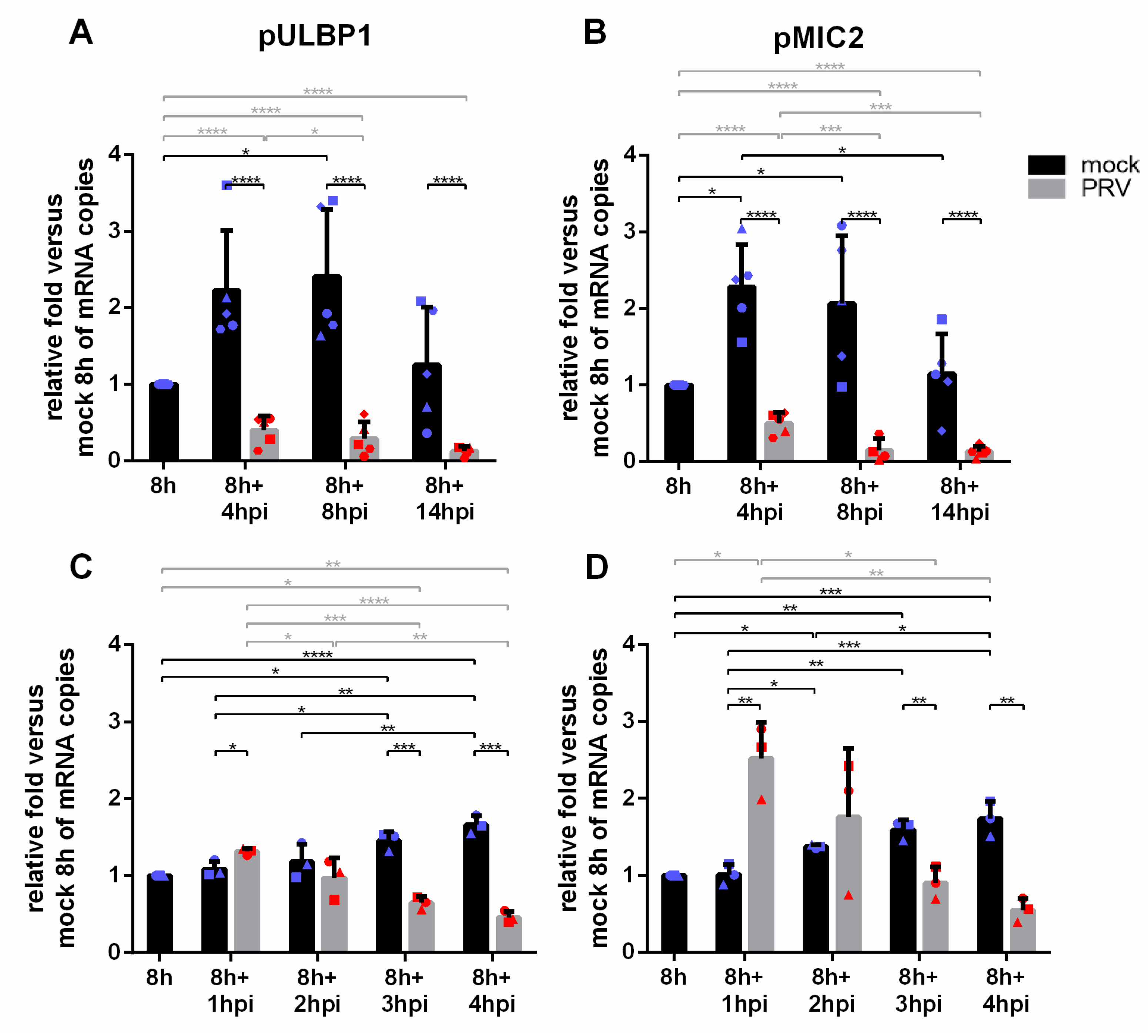
3.4. pULBP1 Expression Is Reduced after PRV Infection
3.5. PRV Infection Results in a Fast and Progressive Downregulation of pULBP1 and pMIC2 mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weis, W.I.; Taylor, M.E.; Drickamer, K. The C-type lectin superfamily in the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 163, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, D.; Call, M.E.; Feng, J.; Wucherpfennig, K.W. The activating NKG2D receptor assembles in the membrane with two signaling dimers into a hexameric structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7641–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Spies, T. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress—Inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.B.; Araki, M.; Hamerman, J.A.; Chen, T.; Yamamura, T.; Lanier, L.L. A Structural basis for the association of DAP12 with mouse, but not human, NKG2D. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensveen, F.M.; Jelenčić, V.; Polić, B. NKG2D: A Master Regulator of Immune Cell Responsiveness. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, D.; Jie, H.-B.; Sotiriadis, J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-S.; Rothschild, M.F.; Lanier, L.L.; Kim, Y.B. Molecular cloning and characterization of pig immunoreceptor DAP10 and NKG2D. Immunogenetics 2001, 53, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denyer, M.S.; Wileman, T.E.; Stirling, C.M.; Zuber, B.; Takamatsu, H.-H. Perforin expression can define CD8 positive lymphocyte subsets in pigs allowing phenotypic and functional analysis of Natural Killer, Cytotoxic T, Natural Killer T and MHC un-restricted cytotoxic T-cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 110, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, K.H.; Müllebner, A.; Essler, S.E.; Duvigneau, J.C.; Storset, A.K.; Saalmuller, A.; Gerner, W. Porcine CD8αdim/-NKp46high NK cells are in a highly activated state. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulet, D.H.; Gasser, S.; Gowen, B.G.; Deng, W.; Jung, H. Regulation of ligands for the NKG2D activating receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 413–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, A.R.; O’Callaghan, C.A. Regulation of ligands for the activating receptor NKG2D. Immunology 2007, 121, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, S.; Orsulic, S.; Brown, E.J.; Raulet, D.H. The DNA damage pathway regulates innate immune system ligands of the NKG2D receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 436, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosman, D.; Müllberg, J.; Sutherland, C.L.; Chin, W.; Armitage, R.; Fanslow, W.; Kubin, M.; Chalupny, N. ULBPs, Novel MHC Class I–Related Molecules, Bind to CMV Glycoprotein UL16 and Stimulate NK Cytotoxicity through the NKG2D Receptor. Immunity 2001, 14, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, P.; Wu, M.R.; Sentman, M.L.; Sentman, C.L. NKG2D ligands as therapeutic targets. Cancer Immun. Res. 2013, 13. Available online: www.cancerimmunity.org (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Chardon, P.; Rogel-Gaillard, C.; Cattolico, L.; Duprat, S.; Vaiman, M.; Renard, C. Sequence of the swine major histocompatibility complex region containing all non-classical class I genes. Tissue Antigens 2001, 57, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Borges, C.N.; Phanavanh, B.; Saraswati, S.; Dennis, R.A.; Crew, M.D. Molecular cloning and characterization of a porcine UL16 binding protein (ULBP)-like cDNA. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lilienfeld, B.G.; Garcia-Borges, C.; Crew, M.D.; Seebach, J.D. Porcine UL16-Binding Protein 1 Expressed on the Surface of Endothelial Cells Triggers Human NK Cytotoxicity through NKG2D. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.D.; Christiansen, D.; Winterhalter, A.; Brooks, A.; Gorrell, M.D.; Lilienfeld, B.G.; Seebach, J.D.; Sandrin, M.; Sharland, A. Porcine cells express more than one functional ligand for the human lymphocyte activating receptor NKG2D. Xenotransplantation 2008, 15, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L. Natural killer cell receptor signaling. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzl, C. How to Trigger a Killer: Modulation of Natural Killer Cell Reactivity on Many Levels, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; Romero, N.; Vitale, M.; Favoreel, H.W. Herpesvirus Evasion of Natural Killer Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeranz, L.E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Hengartner, C.J. Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: Impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine. Society 2005, 69, 462–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepis, D.; D’Amato, M.; Studahl, M.; Bergström, T.; Karre, K.; Berg, L. Herpes Simplex Virus Infection Downmodulates NKG2D Ligand Expression. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 69, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, T.M.; McSharry, B.P.; Steain, M.; Slobedman, B.; Abendroth, A. Varicella-Zoster Virus and Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Differentially Modulate NKG2D Ligand Expression during Productive Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7932–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enk, J.; Levi, A.; Weisblum, Y.; Yamin, R.; Charpak-Amikam, Y.; Wolf, D.G.; Mandelboim, O. HSV1 MicroRNA Modulation of GPI Anchoring and Downstream Immune Evasion. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauwet, K.; Cantoni, C.; Parodi, M.; De Maria, A.; Devriendt, B.; Pende, D.; Moretta, L.; Vitale, M.; Favoreel, H.W. Modulation of CD112 by the alphaherpesvirus gD protein suppresses DNAM-1–dependent NK cell-mediated lysis of infected cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16118–16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauwet, K.; Vitale, M.; De Pelsmaeker, S.; Jacob, T.; Laval, K.; Moretta, L.; Parodi, M.; Parolini, S.; Cantoni, C.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies Virus US3 Protein Kinase Protects Infected Cells from NK Cell-Mediated Lysis via Increased Binding of the Inhibitory NK Cell Receptor CD300a. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.S.; Vatter, A. A comparison of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology 1959, 7, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, N.; Van Waesberghe, C.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies Virus Infection of Epithelial Cells Leads to Persistent but Aberrant Activation of the NF-κB Pathway, Inhibiting Hallmark NF-κB-Induced Proinflammatory Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensaert, H.J.; Nauwynck, M.B. Effect of specific antibodies on the cell-associated spread of pseudorabies virus in monolayers of different types. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, D.; Tóth, J.S.; Petrovszki, P.; Boldogkői, Z. Whole-genome analysis of pseudorabies virus gene expression by real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, S.; Vantourout, P.; Wallace, G.; Antoun, A.; Vaughan, R.; Stanford, M.; Hayday, A. An NKG2D-Mediated Human Lymphoid Stress Surveillance Response with High Interindividual Variation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 113ra124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favoreel, H.W.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Van Oostveldt, P.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Pensaert, M.B. Antibody-induced and cytoskeleton-mediated redistribution and shedding of viral glycoproteins, expressed on pseudorabies virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8254–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; Dierick, E.; Klupp, B.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, M.; Favoreel, H.W. Expression of the Pseudorabies Virus gB Glycoprotein Triggers NK Cell Cytotoxicity and Increases Binding of the Activating NK Cell Receptor PILRβ. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; Devriendt, B.; De Regge, N.; Favoreel, H.W. Porcine NK Cells Stimulate Proliferation of Pseudorabies Virus-Experienced CD8+ and CD4+CD8+ T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Opdenbosch, N.; Broeke, C.V.D.; De Regge, N.; Tabares, E.; Favoreel, H.W. The IE180 Protein of Pseudorabies Virus Suppresses Phosphorylation of Translation Initiation Factor eIF2. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7235–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honess, R.W.; Watson, D.H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J. Virol. 1977, 21, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruelle, M.J.; Broeke, C.V.D.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies virus US3- and UL49.5-dependent and -independent downregulation of MHC I cell surface expression in different cell types. Virology 2009, 395, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerada, C.; Steain, M.; Campbell, T.M.; McSharry, B.P.; Slobedman, B.; Abendroth, A. Granzyme B Cleaves Multiple Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) Gene Products, and VZV ORF4 Inhibits Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.M.; McSharry, B.P.; Steain, M.; Russell, T.A.; Tscharke, D.C.; Kennedy, J.J.; Slobedman, B.; Abendroth, A. Functional paralysis of human natural killer cells by alphaherpesviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, S.A.; Sinzger, C.; Lutz, S.Z.; Singh-Jasuja, H.; Sampaio, K.L.; Eknigk, U.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Steinle, A. Selective intracellular retention of virally induced NKG2D ligands by the human cytomegalovirus UL16 glycoprotein. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chalupny, N.J.; Manley, T.J.; Riddell, S.R.; Cosman, D.; Spies, T. Intracellular Retention of the MHC Class I-Related Chain B Ligand of NKG2D by the Human Cytomegalovirus UL16 Glycoprotein. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4196–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiru, O.; Bennett, N.J.; Boyle, L.H.; Thomas, M.; Trowsdale, J.; Wills, M.R. NKG2D Ligand MICA Is Retained in the cis-Golgi Apparatus by Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL142. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12345–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, N.J.; Ashiru, O.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Pang, Y.; Okecha, G.; Eagle, R.A.; Trowsdale, J.; Sissons, J.G.P.; Wills, M.R. Intracellular Sequestration of the NKG2D Ligand ULBP3 by Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.; Krmpotic, A.; Ruzsics, Z.; Bubić, I.; Lenac, T.; Halenius, A.; Loewendorf, A.I.; Messerle, M.; Hengel, H.; Jonjić, S.; et al. Selective Down-Regulation of the NKG2D Ligand H60 by Mouse Cytomegalovirus m155 Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2920–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgill, E.R.; Malouli, D.; Hansen, S.G.; Burwitz, B.J.; Seo, S.; Schneider, C.L.; Womack, J.L.; Verweij, M.C.; Ventura, A.B.; Bhusari, A.; et al. Natural Killer Cell Evasion Is Essential for Infection by Rhesus Cytomegalovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, C.A.; Aicheler, R.; Stanton, R.J.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Han, S.; Seirafian, S.; Davies, J.; McSharry, B.P.; Weekes, M.P.; Antrobus, P.R.; et al. Two Novel Human Cytomegalovirus NK Cell Evasion Functions Target MICA for Lysosomal Degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, C.A.; Weekes, M.P.; Nobre, L.V.; Ruckova, E.; Wilkie, G.S.; Paulo, J.A.; Chang, C.; Suárez, N.M.; Davies, J.A.; Antrobus, R.; et al. Control of immune ligands by members of a cytomegalovirus gene expansion suppresses natural killer cell activation. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, D.; Tai, J.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Dovrat, S.; Mandelboim, O. Human Herpesvirus 6B Downregulates Expression of Activating Ligands during Lytic Infection To Escape Elimination by Natural Killer Cells. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9608–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölken, L.; Krmpotic, A.; Kothe, S.; Tuddenham, L.; Tanguy, M.; Marcinowski, L.; Ruzsics, Z.; Elefant, N.; Altuvia, Y.; Margalit, H.; et al. Cytomegalovirus microRNAs Facilitate Persistent Virus Infection in Salivary Glands. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Elefant, N.; Zimmermann, A.; Wolf, D.G.; Saleh, N.; Biton, M.; Horwitz, E.; Prokocimer, Z.; Prichard, M.; Hahn, G.; et al. Host Immune System Gene Targeting by a Viral miRNA. Science 2007, 317, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachmani, D.; Lankry, D.; Wolf, D.G.; Mandelboim, O. The human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-UL112 acts synergistically with a cellular microRNA to escape immune elimination. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.D.; Frenkel, N. The herpes simplex virus virion host shutoff function. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 4834–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-W.; Hsu, W.-L.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Jan, M.-S.; Wong, M.-L.; Chang, T.-J. Role of the UL41 Protein of Pseudorabies Virus in Host Shutoff, Pathogenesis and Induction of TNF-α Expression. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inverardi, L.; Samaja, M.; Motterlini, R.; Mangili, F.; Bender, J.R.; Pardi, R. Early recognition of a discordant xenogeneic organ by human circulating lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalfoun, B.; Barrat, D.; Watier, H.; Machet, M.C.; Arbeille-Brassart, B.; Riess, J.G.; Salmon, H.; Gruel, Y.; Bardos, P.; Lebranchu, Y. Development of an ex vivo model of pig kidney perfused with human lymphocytes. Analysis of xenogeneic cellular reactions. Surgery 2000, 128, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Gundry, S.R.; Hancock, W.W.; Matsumiya, G.; Zuppan, C.W.; Morimoto, T.; Slater, J.; Bailey, L.L. Prolonged discordant xenograft survival and delayed xenograft rejection in a pig-to-baboon orthotopic cardiac xenograft model. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1998, 115, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Bravery, C.; Chavez, G.; Richards, A.; Cruz, G.; Copeman, L.; Atkinson, C.; Holmes, B.; Davies, H.; Cozzi, E.; et al. Identification, detection, and in vitro characterization of cynomolgus monkey natural killer cells in delayed xenograft rejection of hDAF transgenic porcine renal xenografts. Transplant. Proc. 2000, 32, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, P.; Lilienfeld, B.G.; Baumann, B.C.; Seebach, J.D. Human NK Cytotoxicity against Porcine Cells Is Triggered by NKp44 and NKG2D. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5463–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-J.; Kim, N.; Kim, E.-O.; Choi, J.-R.; Bluestone, J.A.; Lee, J.-Y. Suppression of human anti-porcine natural killer cell xenogeneic responses by combinations of monoclonal antibodies specific to CD2 and NKG2D and extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor. Immunology 2010, 130, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Choi, S.-E.; Yun, I.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ahn, C.; Kim, S.-J.; Ha, J.; Hwang, E.-S.; Cha, C.-Y.; Miyagawa, S.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus UL18 alleviated human NK-mediated swine endothelial cell lysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antigen | Clone | Isotype/Recombinant | Labeling Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRV gB [29] | 1C11 | IgG2a | Secondary antibody R-phycoerythrin (R-PE) conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen, catalog number P-852) |
| PRV gD [29] | 13D12 | IgG1 | Secondary antibody R-PE conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG |
| NKG2D ligands | Recombinant human NKG2D Fc Chimera protein (R&D, catalog number 1299-NK-050) | Secondary antibody R-PE-conjugated Goat Fab anti-human IgG (Invitrogen, catalog number H10104) | |
| pULPBP1 [17] | IgM | Secondary antibody Alexa fluor 647 goat anti-mouse IgM (Invitrogen, catalog number A-21238) |
| Gene 1 (Encoded Protein, GenBank Accession No.) (Reference) | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| pULBP1 (ULBP1, NM_001004035.1) | 5′-TGG CTT GTG GAA GAT CCG AC-3′ | 5′-CCT GAG GTT CTG TGA TGG CA-3′ |
| pMIC2 (MIC2, XM_003128306.4) | 5′-AAC GGC TTC ACA CCA GAG AC-3′ | 5′-TTG AAT TCA GGC CTC CTG GC-3′ |
| 28S rRNA [30] | 5′-GGG CCG AAA CGA TCT CAA CC-3′ | 5′-GCC GGG CTT ACC CAT T-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Denaeghel, S.; De Pelsmaeker, S.; Van Waesberghe, C.; Favoreel, H.W. Pseudorabies Virus Infection Causes Downregulation of Ligands for the Activating NK Cell Receptor NKG2D. Viruses 2021, 13, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020266
Denaeghel S, De Pelsmaeker S, Van Waesberghe C, Favoreel HW. Pseudorabies Virus Infection Causes Downregulation of Ligands for the Activating NK Cell Receptor NKG2D. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleDenaeghel, Sofie, Steffi De Pelsmaeker, Cliff Van Waesberghe, and Herman W. Favoreel. 2021. "Pseudorabies Virus Infection Causes Downregulation of Ligands for the Activating NK Cell Receptor NKG2D" Viruses 13, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020266
APA StyleDenaeghel, S., De Pelsmaeker, S., Van Waesberghe, C., & Favoreel, H. W. (2021). Pseudorabies Virus Infection Causes Downregulation of Ligands for the Activating NK Cell Receptor NKG2D. Viruses, 13(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020266






