High Prevalence of Genogroup I and Genogroup II Picobirnaviruses in Dromedary Camels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. RT-PCR for PBVs and DNA Sequencing
2.4. Genome Sequencing of Genogroups I and II PBVs
2.5. Genome Analysis
3. Results
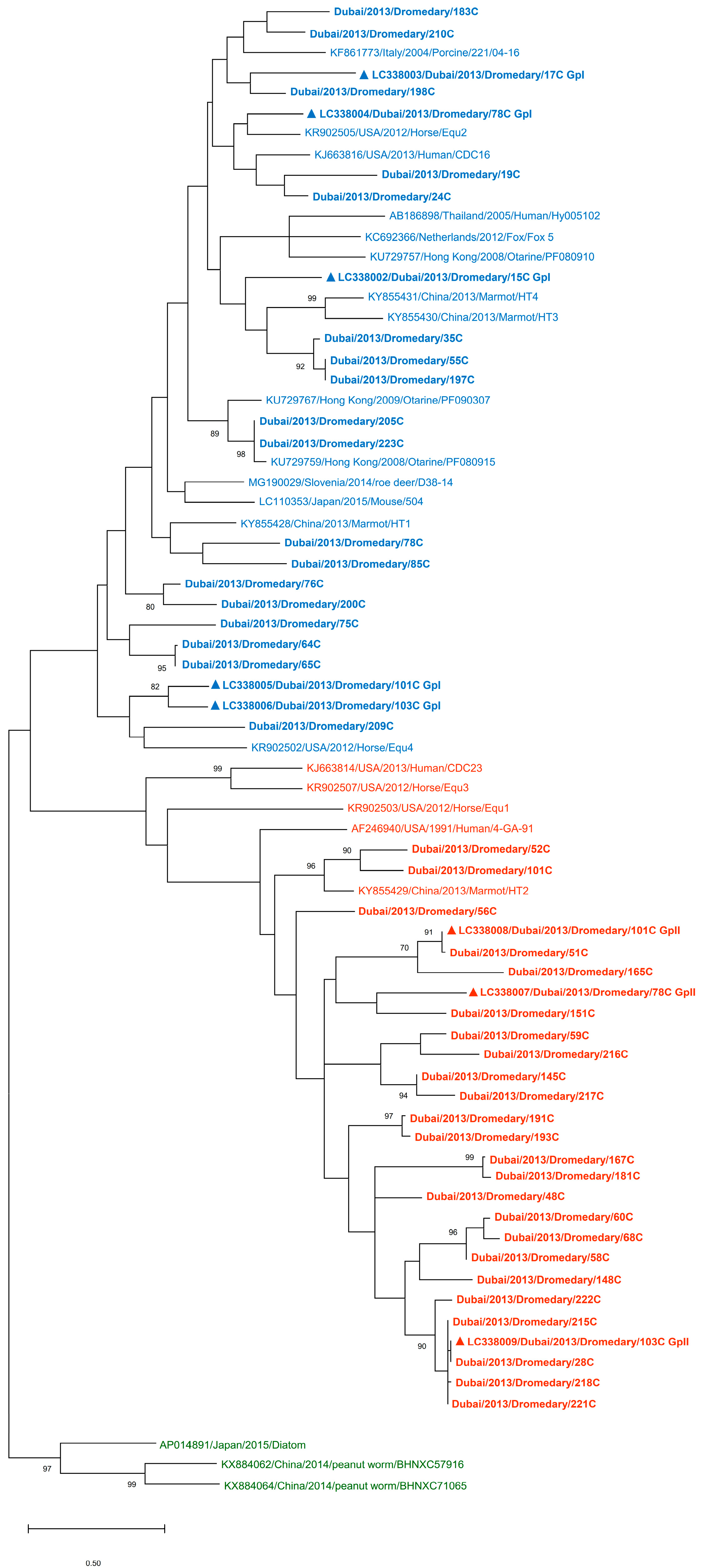
3.1. Detection of PBVs in Dromedary Fecal Samples and Phylogenetic Analysis
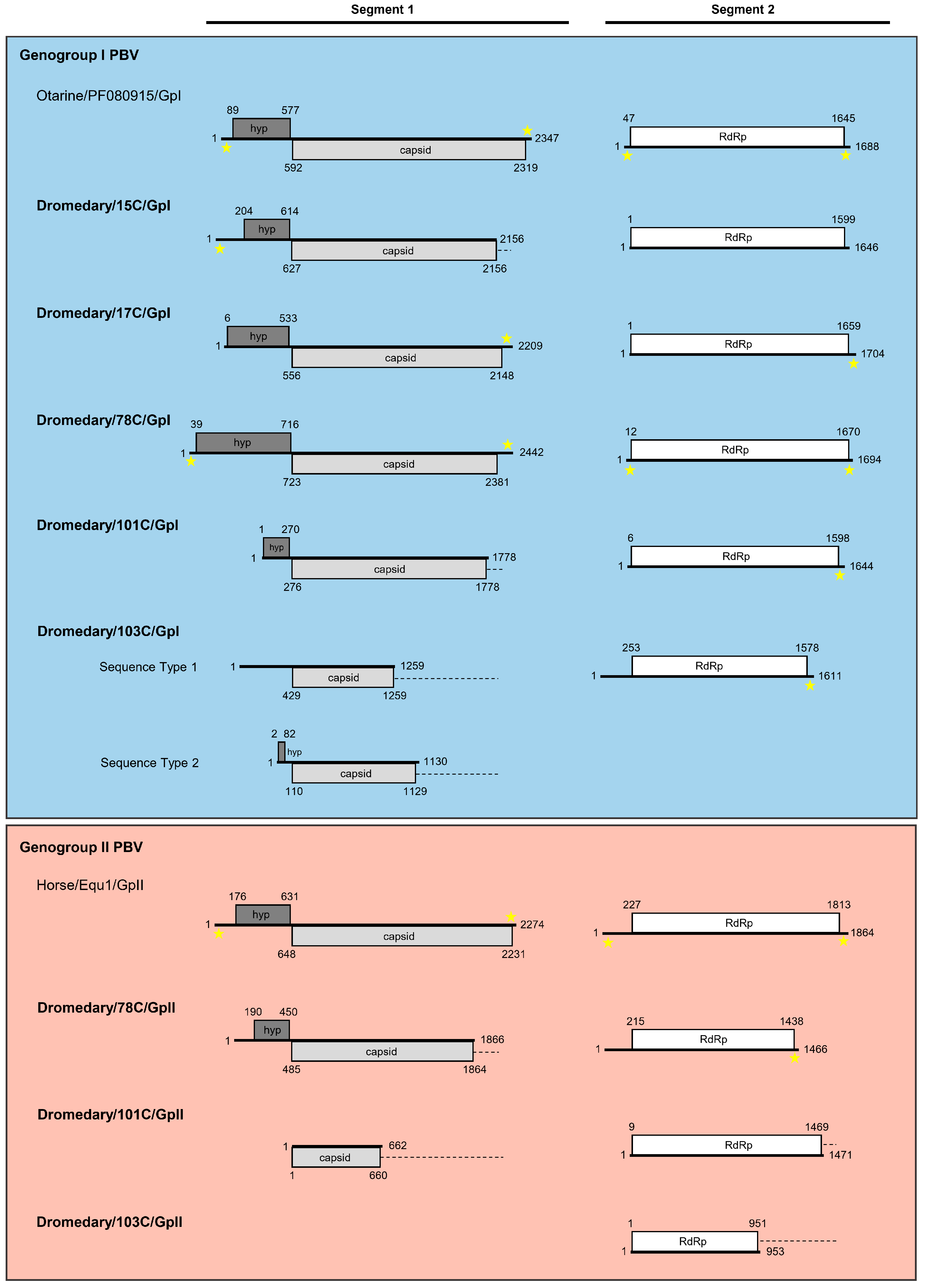
3.2. Sequence Analysis of Genogroup I Dromedary PBVs Segments 1 and 2
3.2.1. Analysis of Six Genogroup I Segment 1 Sequences (One Complete, One Near-Complete, and Four Partial Sequences)
3.2.2. Analysis of Five Genogroup I Segment 2 Sequences (One Complete and Four Near-Complete Sequences)
3.3. Sequence Analysis of Genogroup II Dromedary PBVs Segments 1 and 2
3.3.1. Analysis of Two Partial Genogroup II Segment 1 Sequences
3.3.2. Analysis of Three Genogroup II Segment 2 Sequences (One Near-Complete and Two Partial Sequences)
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of Capsid and RdRp Sequences of Dromedary PBVs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, H.G.; Fialho, A.M.; Flewett, T.H.; Teixeira, J.M.; Andrade, Z.P. Novel viruses in human faeces. Lancet 1988, 2, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.G.; Flewett, T.H.; Candeias, J.A.; Barth, O.M. A virus with a bisegmented double-stranded RNA genome in rat (Oryzomys nigripes) intestines. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 2749–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Sahoo, G.C.; Nayak, M.K.; Rajendran, K.; Dutta, P.; Mitra, U.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Naik, T.N.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Krishnan, T. Detection of Genogroup I and II human picobirnaviruses showing small genomic RNA profile causing acute watery diarrhoea among children in Kolkata, India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2007, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Sun, H.; Lan, D.; Hua, X.; Cui, L.; Yuan, C.; Yang, Z. Molecular detection of genogroup I and II picobirnaviruses in pigs in China. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição-Neto, N.; Mesquita, J.R.; Zeller, M.; Yinda, C.K.; Álvares, F.; Roque, S.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; Godinho, R.; Heylen, E.; Van Ranst, M.; et al. Reassortment among picobirnaviruses found in wolves. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2859–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duraisamy, R.; Akiana, J.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O.; Michelle, C.; Robert, C.; Parra, H.J.; Raoult, D.; Biagini, P.; Desnues, C. Detection of novel RNA viruses from free-living gorillas, Republic of the Congo: Genetic diversity of picobirnaviruses. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregolente, M.C.; de Castro-Dias, E.; Martins, S.S.; Spilki, F.R.; Allegretti, S.M.; Gatti, M.S. Molecular characterization of picobirnaviruses from new hosts. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, C.A.; Navarro, R.; Cruz, K.; Aung, M.S.; Ng, A.; Bajak, E.; Beierschmitt, A.; Lawrence, M.; Dore, K.M.; Ketzis, J.; et al. Detection of picobirnaviruses in vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus sabaeus): Molecular characterization of complete genomic segment-2. Virus Res. 2017, 230, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, B.; Masachessi, G.; Mladenova, Z. Animal picobirnavirus. Virusdisease 2014, 25, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Shiokawa, K.; Aung, M.S.; Malik, Y.S.; Kobayashi, N. High detection rates of picobirnaviruses in free roaming rats (Rattus spp.): Molecular characterization of complete gene segment-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillman, L.; Sánchez, A.M.; Arbiza, J. Picobirnavirus in captive animals from Uruguay: Identification of new hosts. Intervirology 2013, 56, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhar, U.; Jamnikar-Ciglenecki, U. High detection rate and high genetic diversity of genogroup I Picobirnaviruses from roe deer. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.F.; Possatti, F.; de Freitas, J.A.; Alfieri, A.A.; Takiuchi, E. High detection rate and genetic diversity of picobirnavirus in a sheep flock in Brazil. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.S.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, K.; Dhama, K.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Ganesh, B.; Kobayashi, N.; Banyai, K. Epidemiology, phylogeny, and evolution of emerging enteric Picobirnaviruses of animal origin and their relationship to human strains. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 780752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malik, Y.S.; Sircar, S.; Dhama, K.; Singh, R.; Ghosh, S.; Bányai, K.; Vlasova, A.N.; Nadia, T.; Singh, R.K. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of picobirnaviruses in small ruminant populations in India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, L.C.; Masachessi, G.; Carruyo, G.; Ferreyra, L.J.; Barril, P.A.; Isa, M.; Giordano, M.O.; Ludert, J.E.; Nates, S.V. Picobirnavirus causes persistent infection in pigs. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, E.M.; Griffin, D.W.; Breitbart, M. Eukaryotic viruses in wastewater samples from the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, H.; Mor, S.K.; Erber, J.; Goyal, S.M. Prevalence and complete genome characterization of turkey picobirnaviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bányai, K.; Tu, X.; Jiang, B. Simian genogroup I picobirnaviruses: Prevalence, genetic diversity, and zoonotic potential. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2779–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Lee, P.; Martelli, P.; Hui, S.W.; Yuen, K.Y. Complete genome sequence of a novel picobirnavirus, otarine picobirnavirus, discovered in California sea lions. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6377–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, A.K.; Joseph, M.; Wong, E.Y.; Tang, Y.; Sivakumar, S.; Bai, R.; Wernery, R.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of viromes of dromedary camel fecal samples reveals large number and high diversity of circoviruses and picobirnaviruses. Virology 2014, 471–473, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Teng, J.; Bai, R.; Tang, Y.; Wong, A.; Li, K.; Lam, C.; Fan, R.; Lau, S.; Yuen, K. Novel Picobirnaviruses in Respiratory and Alimentary Tracts of Cattle and Monkeys with Large Intra- and Inter-Host Diversity. Viruses 2019, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Bai, R.; Feng, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Detection and evolutionary analysis of picobirnaviruses in treated wastewater. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakuda, M.; Pongsuwanna, Y.; Taniguchi, K. Complete nucleotide sequences of two RNA segments of human picobirnavirus. J. Virol. Methods. 2005, 126, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, B.I.; Fang, Z.Y.; Glass, R.I.; Monroe, S.S. Cloning of human picobirnavirus genomic segments and development of an RT-PCR detection assay. Virology 2000, 277, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smits, S.L.; Schapendonk, C.M.; van Beek, J.; Vennema, H.; Schurch, A.C.; Schipper, D.; Bodewes, R.; Haagmans, B.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Koopmans, M.P. New viruses in idiopathic human diarrhea cases, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Teng, J.L.; Bai, R.; Wong, A.Y.; Martelli, P.; Hui, S.W.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, C.C.; Ahmed, S.S.; Yip, C.C.; et al. High Diversity of Genogroup I Picobirnaviruses in Mammals. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attoui, H.; Billoir, F.; Cantaloube, J.F.; Biagini, P.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Strategies for the sequence determination of viral dsRNA genomes. J. Virol. Methods 2000, 89, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sayers, E.W.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bolton, E.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; DiCuccio, M.; Federhen, S.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D38–D51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, B.; Attoui, H.; Ghosh, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Mundt, E.; Vakharia, V.N.; ICTV Report Consortium. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Picobirnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányai, K.; Potgieter, C.; Gellért, Á.; Ganesh, B.; Tempesta, M.; Lorusso, E.; Buonavoglia, C.; Martella, V. Genome sequencing identifies genetic and antigenic divergence of porcine picobirnaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewes, R.; van der Giessen, J.; Haagmans, B.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Smits, S.L. Identification of multiple novel viruses, including a parvovirus and a hepevirus, in feces of red foxes. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7758–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, B.; Duquerroy, S.; Tarus, B.; Delmas, B. Picobirnaviruses encode a protein with repeats of the ExxRxNxxxE motif. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Nagashima, S.; Naik, T.N. Molecular characterization of full-length genomic segment 2 of a bovine picobirnavirus (PBV) strain: Evidence for high genetic diversity with genogroup I PBVs. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2519–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, B.; Nataraju, S.M.; Rajendran, K.; Ramamurthy, T.; Kanungo, S.; Manna, B.; Nagashima, S.; Sur, D.; Kobayashi, N.; Krishnan, T. Detection of closely related Picobirnaviruses among diarrhoeic children in Kolkata: Evidence of zoonoses? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.; Bányai, K.; Martella, V.; Jakab, F.; Masachessi, G.; Kobayashi, N. Picobirnavirus infections: Viral persistence and zoonotic potential. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Presence/Absence of Polymorphism | Number (%) of Samples Positive for: | |
|---|---|---|
| Genogroup I PBV | Genogroup II PBV | |
| 94/121 (77.7) | 50/121 (41.3) | |
| With polymorphism | 71/94 (75.5) | 23/50 (46.0) |
| Without polymorphism | 23/94 (24.5) | 27/50 (54.0) |
| PBV Strain | ORF Features | 5′ UTR Features | 3′ UTR Features | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | Protein | Location (nt) | Length (nt) | Length (aa) | Frame | Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | 5′ Bases | Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | 3′ Bases | |
| Genogroup I PBV | |||||||||||||
| a 15C/GpI | 2156 | 44.3 | hypothetical | 204–614 | 411 | 136 | 3 | 203 | 41.4 | GUAAA | - | - | - |
| capsid | 627–2156 | 1530 | 509 | 3 | |||||||||
| b 17C/GpI | 2209 | 45.5 | hypothetical | 6–533 | 528 | 175 | 3 | - | - | - | 61 | 45.9 | CCUGC |
| capsid | 556–2148 | 1593 | 530 | 1 | |||||||||
| c 78C/GpI | 2442 | 40.8 | hypothetical | 39–716 | 678 | 225 | 3 | 38 | 26.3 | GUAAA | 61 | 44.3 | GGAUC |
| capsid | 723–2381 | 1659 | 552 | 3 | |||||||||
| a 101C/GpI | 1778 | 43.6 | hypothetical | 1–270 | 270 | 89 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| capsid | 276–1778 | 1503 | 500 | 3 | |||||||||
| a 103C/GpI (ST1) | 1259 | 39.8 | hypothetical | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| capsid | 429–1259 | 831 | 276 | 3 | |||||||||
| a 103C/GpI (ST2) | 1130 | 38.9 | hypothetical | 2–82 | 81 | 26 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| capsid | 110–1129 | 1020 | 339 | 2 | |||||||||
| Genogroup II PBV | |||||||||||||
| a 78C/GpII | 1866 | 30.4 | hypothetical | 190–450 | 261 | 86 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| capsid | 485–1864 | 1380 | 459 | 2 | |||||||||
| a 101C/GpII | 662 | 36.9 | hypothetical | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| capsid | 1–660 | 660 | 219 | 1 | |||||||||
| PBV Genome | Length (aa) | Number of Repeated Motifs | Length between Repeats (aa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a LC337994/Dromedary/15C/GpI | 136 | 7 | 1–8 |
| a LC337995/Dromedary/17C/GpI | 175 | 2 | 1 |
| a LC337996/Dromedary/78c/GpI | 225 | 10 | 1–33 |
| a,b LC337997/Dromedary/101C/GpI | 89 | 1 | 0 |
| a,b LC338000/Dromedary/78C/GpII | 86 | 2 | 8 |
| KU729746/Otarine/PF080915/GpI | 194 | 5 | 1–44 |
| KU729754/Otarine/PF080910/GpI | 223 | 9 | 1–22 |
| NC007026/Human/Hy005102/GpI | 224 | 5 | 1–19 |
| KY855431/Marmot/HT4/GpI | 190 | 2 | 8 |
| KY855430/Marmot/HT3/GpI | 184 | 2 | 8 |
| LC110352/Mouse/504/GpI | 241 | 7 | 1–44 |
| KR902502/Horse/Equ4/GpI | 212 | 3 | 8 |
| KC692367/Fox/Fox_5/GpI | 201 | 7 | 1–15 |
| KF861772/Porcine/221/04–16/GpI | 199 | 4 | 8–22 |
| KR902506/Horse/Equ2/GpI | 222 | 6 | 1–45 |
| KJ663813/Human/CDC23/GpII | 116 | 5 | 1–12 |
| KR902504/Horse/Equ1/GpII | 151 | 3 | 8–15 |
| KR902508/Horse/Equ3/GpII | 251 | 4 | 1–26 |
| KY855429/Marmot/HT2/GpII | 311 | 2 | 8 |
| PBV Strain | ORFs Features | 5′ UTR Features | 3′ UTR Features | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | Protein | Location (nt) | Length (nt) | Length (aa) | Frame | Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | 5′ Bases | Length (nt) | G+C Content (%) | 3′ Bases | |
| Genogroup I PBV | |||||||||||||
| a 15C/GpI | 1646 | 44.4 | RdRp | 1–1599 | 1599 | 532 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| a 17C/GpI | 1704 | 45.5 | RdRp | 1–1659 | 1659 | 552 | 1 | - | - | - | 45.0 | 46.7 | CUGC |
| b 78C/GpI | 1694 | 41.8 | RdRp | 12–1670 | 1659 | 552 | 3 | 11.0 | 18.2 | GUAAA | 24.0 | 45.8 | CCAUU |
| a 101C/GpI | 1644 | 44.3 | RdRp | 6–1598 | 1593 | 530 | 3 | - | - | - | 46.0 | 47.8 | CUGC |
| a 103C/GpI | 1611 | 43.4 | RdRp | 253–1578 | 1326 | 441 | 1 | - | - | - | 33.0 | 48.5 | CUCA |
| Genogroup II PBV | |||||||||||||
| a 78C/GpII | 1466 | 40.4 | RdRp | 215–1438 | 1224 | 407 | 2 | - | - | - | 28.0 | 57.1 | UUUC |
| c 101C/GpII | 1471 | 42.0 | RdRp | 9–1469 | 1461 | 486 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| c 103C/GpII | 953 | 45.2 | RdRp | 1–951 | 951 | 316 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, J.L.L.; Wernery, U.; Wong, P.C.; Chan, E.; Lee, H.H.; Joseph, S.; Bai, R.; Tang, Y.; Wong, E.Y.M.; Lau, S.K.P.; et al. High Prevalence of Genogroup I and Genogroup II Picobirnaviruses in Dromedary Camels. Viruses 2021, 13, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030430
Teng JLL, Wernery U, Wong PC, Chan E, Lee HH, Joseph S, Bai R, Tang Y, Wong EYM, Lau SKP, et al. High Prevalence of Genogroup I and Genogroup II Picobirnaviruses in Dromedary Camels. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030430
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Jade L. L., Ulrich Wernery, Po Chun Wong, Elaine Chan, Hwei Huih Lee, Sunitha Joseph, Ru Bai, Ying Tang, Emily Y. M. Wong, Susanna K. P. Lau, and et al. 2021. "High Prevalence of Genogroup I and Genogroup II Picobirnaviruses in Dromedary Camels" Viruses 13, no. 3: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030430
APA StyleTeng, J. L. L., Wernery, U., Wong, P. C., Chan, E., Lee, H. H., Joseph, S., Bai, R., Tang, Y., Wong, E. Y. M., Lau, S. K. P., & Woo, P. C. Y. (2021). High Prevalence of Genogroup I and Genogroup II Picobirnaviruses in Dromedary Camels. Viruses, 13(3), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030430









