Successful Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C Normalizes IFNγ and IL2 Production in T Cells Together with TLR8 Expression and Functionality in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. TLR8 Expression in PBMCs
2.4. Assessment of TLR8 Function in Circulating PBMCs
2.5. Production of IFNγ, IL2 and IL17 in T Cells
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Evolution in the Expression profile of IFNγ, IL2, and IL17 in CD4+T Cells Pre and Post Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy
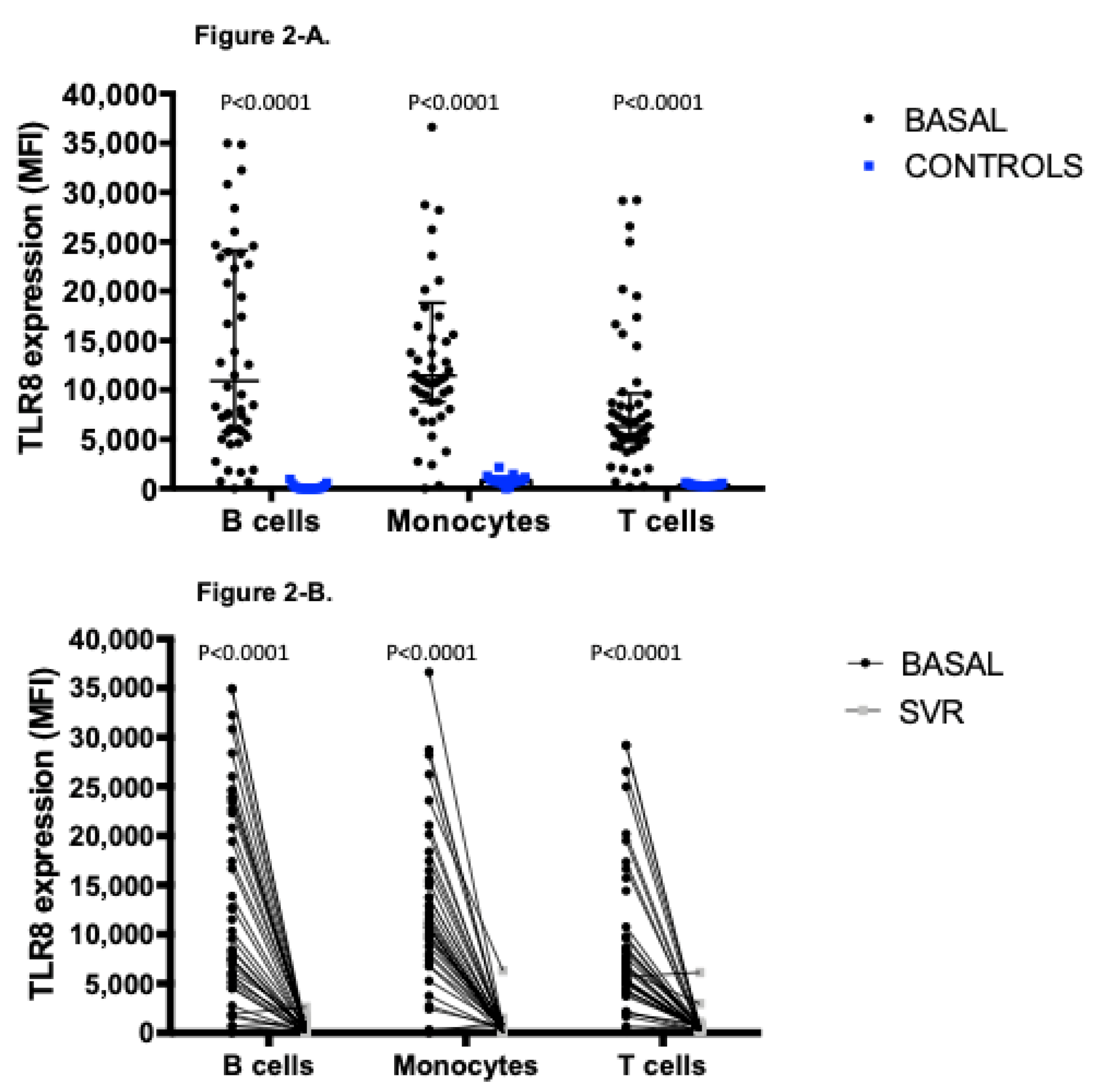
3.3. Distinctive Expression Profile of TLR8, Involved in the Recognition of Structural Components of Single Stranded-RNA Viruses
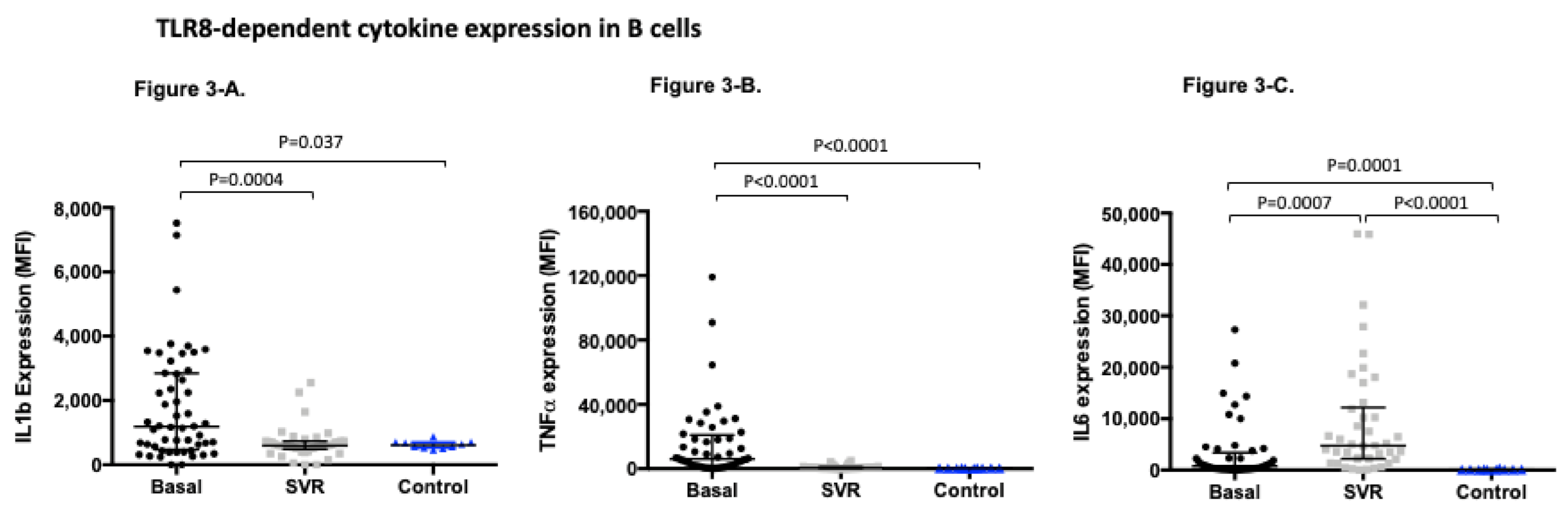
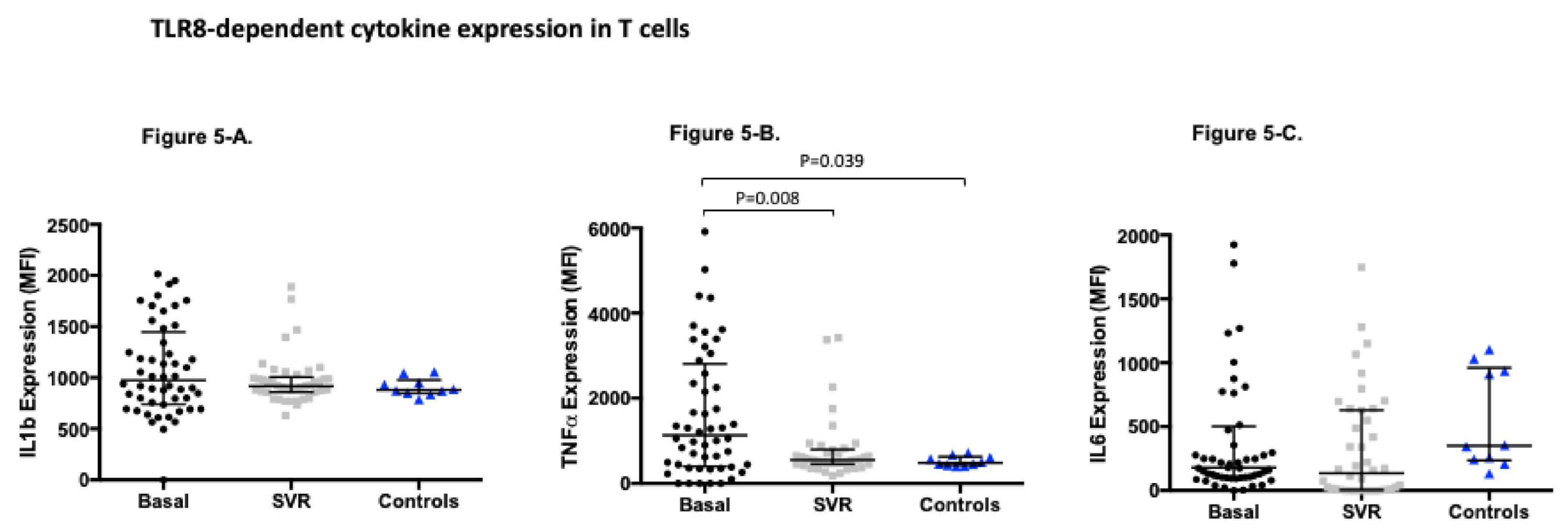
3.4. TLR8-Dependent Cytokine Expression Significantly Changes after Sustained Virological Response
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alter, M.J. The epidemiology of acute and chronic hepatitis C. Clin. Liver Dis. 1997, 1, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasley, A.; Alter, M.J. Epidemiology of hepatitis C: Geographic differences and temporal trends. Semin. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Yasuda, S.; Huang, C.F.; Iio, E.; Landis, C.; Jun, D.W.; Enomoto, M.; Ogawa, E.; Tsai, P.C.; et al. Cure with Interferon Free DAA is Associated with Increased Survival in Patients with HCV related HCC from both East and West. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, K.E.; Saeian, K.; Rizvi, S. Real-world experiences with direct-acting antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis C treatment. J. Viral. Hepat. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Bedossa, P.; Opolon, P. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The OBSVIRC, METAVIR, CLINIVIR, and DOSVIRC groups. Lancet 1997, 349, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasin-Filipowicz, M.; Oakeley, E.J.; Duong, F.H.; Christen, V.; Terracciano, L.; Filipowicz, W.; Heim, M.H. Interferon signaling and treatment outcome in chronic hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7034–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Tian, Y.; Chan, S.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, C.; Ou, J.H. TNF-alpha Induced by Hepatitis C Virus via TLR7 and TLR8 in Hepatocytes Supports Interferon Signaling via an Autocrine Mechanism. PLoS Pathog 2015, 11, e1004937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meås, H.Z.; Haug, M.; Beckwith, M.S.; Louet, C.; Ryan, L.; Hu, Z.; Landskron, J.; Nordbø, S.A.; Taskén, K.; Yin, H.; et al. Sensing of HIV-1 by TLR8 activates human T cells and reverses latency. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhir, F.Z.; Lkhider, M.; Badre, W.; Alaoui, R.; Meurs, E.F.; Pineau, P.; Ezzikouri, S.; Benjelloun, S. Genetic variations in toll-like receptors 7 and 8 modulate natural hepatitis C outcomes and liver disease progression. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Matthews, D.R. The assessment of insulin resistance in man. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Rodriguez, L.; Lopez-Hoyos, M.; Mata, C.; Fontalba, A.; Calvo Alen, J.; Marin, M.J.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L.; Aguero Balbin, J.; Aranzamendi Zaldunbide, M.; Blanco, R.; et al. Expression and function of toll-like receptors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Okumura, A.; Yamauchi, T.; Sato, S.; Ayada, M.; Matsumoto, E.; Hotta, N.; Oohashi, T.; Fukuzawa, Y.; et al. Expression of Toll-like receptors in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Cheng, K.T.; Sung, V.M.; Levine, A.M.; Foung, S.; Lai, M.M. Hepatitis C virus induces toll-like receptor 4 expression, leading to enhanced production of beta interferon and interleukin-6. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, S.M.; Skinner, N.A.; Kurtovic, J.; Locarnini, S.; McIver, C.J.; Williams, R.; Visvanathan, K. Toll-like receptor expression in chronic hepatitis C: Correlation with pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and liver injury. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Garcia, C.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Distinct Toll-like receptor expression in monocytes and T cells in chronic HCV infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, R.; Biswas, A.; Saha, K.; Mukherjee, A.; Pal, F.; Chaudhuri, S.; Chandra, A.; Konar, A.; Sadhukhan, P.C. Modulation of TLR 3, 7 and 8 expressions in HCV genotype 3 infected individuals: Potential correlations of pathogenesis and spontaneous clearance. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 491064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Yi Mei, S.L.; Burchell, J.; Skinner, N.; Millen, R.; Matthews, G.; Hellard, M.; Dore, G.J.; Desmond, P.V.; Sundararajan, V.; Thompson, A.J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Expression and Signaling in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Correlate with Clinical Outcomes in Acute Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T.; Wollschlegel, A.; Te, H.; Weiss, J.; Joshi, K.; Kinzel, B.; Billich, A.; Guntermann, C.; Lehmann, J.C.U. Interferon regulatory factor 5 and nuclear factor kappa-B exhibit cooperating but also divergent roles in the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines important for the development of TH1 and TH17 responses. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3097–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.C.; Sung, P.S.; Park, S.H. Immune responses and immunopathology in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guan, J.H.; Jiang, B.C.; Li, Z.S.; Zhu, G.Z. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Modulates the Balance of Regulatory T Cells and T Helper 17 Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C. Viral. Immunol. 2016, 29, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| N | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Regimen | |||
| Ombitasvir+paritaprevir+ritonavir | 5 | 10 | |
| Ombitasvir+paritaprevir+ritonavir+dasabuvir | 3 | 6 | |
| Sofosbuvir+daclatasvir | 13 | 26 | |
| Sofosbuvir+ledipasvir | 29 | 58 | |
| Ribavirin co-administered | 3 | 6 | |
| Treatment Duration | |||
| 8 weeks | 8 | 16 | |
| 12 weeks | 39 | 78 | |
| 24 weeks | 3 | 6 | |
| No Treatment Reasons | |||
| Loss of follow up | 2 | 4 | |
| Sustained virological response | 50 | 100 | |
| Follow up week +48 assessment | 43 | 86 | |
| Baseline Study Group Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male) | 34 | 65.38 | |
| Age | 53.00 | 10.81 | |
| BMI | 26.89 | 6.29 | |
| Genotype | |||
| 1a | 17 | 32.69 | |
| 1b | 12 | 23.08 | |
| 1 | 6 | 11.54 | |
| 3 | 13 | 25.00 | |
| 4 | 4 | 7.69 | |
| Previous antiviral treatment response | |||
| Naive | 37 | 71.15 | |
| Non-responder | 8 | 15.38 | |
| Relapser | 2 | 3.85 | |
| Adverse events | 5 | 9.62 | |
| Fibrosis (measured by transient elastography) | |||
| F1 | 26 | 50.00 | |
| F2 | 15 | 28.85 | |
| F3 | 9 | 17.31 | |
| F4 | 3 | 5.77 | |
| Leucocytes (103/µL) | 6,00 | 1.71 | |
| Neutrophils (103/µL) | 10.60 | 18.48 | |
| Haemoglobin (103/µL) | 14.62 | 1.21 | |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 195.58 | 60.43 | |
| INR | 1.00 | 0.00 | |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 82.35 | 10.48 | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 105.80 | 46.55 | |
| Insulin | 13.71 | 9.16 | |
| HOMA index | 3.77 | 3.34 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.06 | 0.47 | |
| Sodium (mg/dL) | 140.28 | 2.32 | |
| ALT (U/L) | 76.54 | 67.82 | |
| AST (U/L) | 55.82 | 42.01 | |
| GGT (U/L) | 84.86 | 115.80 | |
| Bilirrubin (mg/dL) | 0.64 | 0.53 | |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 4.14 | 0.35 | |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 123.89 | 149.72 | |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 173.24 | 32.47 | |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 54.45 | 16.03 | |
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 96.49 | 28.14 | |
| IgG (mg/dl) | 1401.92 | 458.41 | |
| IgA (mg/dl) | 238.82 | 124.34 | |
| IgM (mg/dl) | 156.02 | 107.76 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arias-Loste, M.T.; Cabezas, J.; Llerena, S.; Iruzubieta, P.; San-Segundo, D.; Merino, D.; Cuadrado, A.; Vaqué, J.P.; López-Hoyos, M.; Crespo, J. Successful Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C Normalizes IFNγ and IL2 Production in T Cells Together with TLR8 Expression and Functionality in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040635
Arias-Loste MT, Cabezas J, Llerena S, Iruzubieta P, San-Segundo D, Merino D, Cuadrado A, Vaqué JP, López-Hoyos M, Crespo J. Successful Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C Normalizes IFNγ and IL2 Production in T Cells Together with TLR8 Expression and Functionality in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Viruses. 2021; 13(4):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040635
Chicago/Turabian StyleArias-Loste, María Teresa, Joaquín Cabezas, Susana Llerena, Paula Iruzubieta, David San-Segundo, David Merino, Antonio Cuadrado, José Pedro Vaqué, Marcos López-Hoyos, and Javier Crespo. 2021. "Successful Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C Normalizes IFNγ and IL2 Production in T Cells Together with TLR8 Expression and Functionality in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells" Viruses 13, no. 4: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040635
APA StyleArias-Loste, M. T., Cabezas, J., Llerena, S., Iruzubieta, P., San-Segundo, D., Merino, D., Cuadrado, A., Vaqué, J. P., López-Hoyos, M., & Crespo, J. (2021). Successful Direct Acting Antiviral Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C Normalizes IFNγ and IL2 Production in T Cells Together with TLR8 Expression and Functionality in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Viruses, 13(4), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040635








