Abstract
Aspergillus and Pseudomonas compete in nature, and are the commonest bacterial and fungal pathogens in some clinical settings, such as the cystic fibrosis lung. Virus infections of fungi occur naturally. Effects on fungal physiology need delineation. A common reference Aspergillus fumigatus strain, long studied in two (of many) laboratories, was found infected with the AfuPmV-1 virus. One isolate was cured of virus, producing a virus-free strain. Virus from the infected strain was purified and used to re-infect three subcultures of the virus-free fungus, producing six fungal strains, otherwise isogenic. They were studied in intermicrobial competition with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pseudomonas culture filtrates inhibited forming or preformed Aspergillus biofilm from infected strains to a greater extent, also seen when Pseudomonas volatiles were assayed on Aspergillus. Purified iron-chelating Pseudomonas molecules, known inhibitors of Aspergillus biofilm, reproduced these differences. Iron, a stimulus of Aspergillus, enhanced the virus-free fungus, compared to infected. All infected fungal strains behaved similarly in assays. We show an important consequence of virus infection, a weakening in intermicrobial competition. Viral infection may affect the outcome of bacterial–fungal competition in nature and patients. We suggest that this occurs via alteration in fungal stress responses, the mechanism best delineated here is a result of virus-induced altered Aspergillus iron metabolism.
1. Introduction
Viruses naturally infecting Aspergillus wild-type strains have been known since 1970 [1]. These viruses have double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) RNA genomes and may be conventionally encapsidated. They do not have an extracellular phase in their replication cycle but can be transmitted horizontally via hyphal fusion and vertically via spore production. However, little is known about how they affect Aspergillus physiology or virulence.
The virus family Polymycoviridae was initially reported in 2015 [2] and was officially recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses in 2020 (https://talk.ictvonline.org/; accessed on 5 April 2020). Polymycoviridae currently accommodate one genus Polymycovirus and 10 species, including Aspergillus fumigatus polymycovirus 1. Members of the Polymycoviridae family and related viruses have usually four [2,3] and up to eleven [4] dsRNA genomic segments. A majority of polymycoviruses are not conventionally encapsidated [2,3], although filamentous particles have been reported in one case [5] and are infectious as dsRNA [2,5].
There has been extensive research in many laboratories, for decades, regarding intermicrobial interactions, particularly Pseudomonas–Aspergillus interactions (recently reviewed [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]), two microbes that coexist, and likely compete, in nature and in patients, particularly persons with cystic fibrosis and immunocompromised hosts. A central facet of the competition is the mutual battle to withhold iron from the competitor. The Pseudomonas siderophore and pyoverdin are its principal weapons used against Aspergillus in iron-restricted liquid environments [14], along with the Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS) [15] and pyocyanin, which is likely a more direct toxin in iron-rich environments [16]. Aspergillus counters the battle for iron with its own siderophores [17]. In a non-liquid air environment, Pseudomonas can also generate volatiles that can inhibit Aspergillus [18]. Presently we studied one aspect of the possible effect of virus infection of Aspergillus fumigatus on this intermicrobial interaction, using tools that have previously been quantitatively standardized.
AF293 is a very common A. fumigatus laboratory strain, and its genome has been fully sequenced [19]. Two versions, one in the USA and one in the UK, separated by at least 10 years, were studied, and both were found to carry the same virus, Aspergillus fumigatus polymycovirus 1 (AfuPmV-1) [2]. The UK strain was cured of AfuPmV-1, resulting in virus-free and virus-infected isogenic lines as previously described [2]. To control for differences found between infected and uninfected strains, the virus-cleared strain was re-infected in three experiments with the same virus that was present in the original strain, producing three re-infected strains, as previously described [2].
2. Materials and Methods
Isolates: The USA and UK AF293 strains were designated by the California Institute for Medical Research (CIMR) # 10-53 and 18-95, respectively. A. fumigatus AF293 strain (18-95) was cured from AfuPmV-1, using the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide [2], producing a strain now designated 18-42. AfuPmV-1 was purified by differential polyethylene glycol precipitation and ultracentrifugation [2]. Purified AfuPmV-1 was re-introduced in the virus-free Aspergillus by protoplast transfection [2]. This was done 3 times, producing infected strains, designated CIMR 19-40 1A, 19-41 2A, and 19-42 3A. The presence or absence of AfuPmV-1 was confirmed by dsRNA extraction, Northern blotting, and RT-qPCR as previously described [2] (Figure S1).
PAO1 and PA14 are extensively studied widely distributed laboratory reference P. aeruginosa strains [16]. The use of all microbes in the CIMR laboratory is approved by the CIMR Biological Use Committee (approval no. 001-03Yr.14, 001-05 Yr.1).
In brief, methods used for generating and testing Pseudomonas aeruginosa supernatants and molecules on Aspergillus biofilms, as well as sources for materials, were as previously described [14,15,16,17,20].
Materials: Pyoverdin, PQS (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal, 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone), XTT (2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide inner salt), menadione, iron (FeCl3), and RPMI 1640 medium were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Trypticase soy agar (TSA) was purchased (Lonza, Walkersville, MD, USA) and prepared per manufacturer instructions. RPMI 1640 agar was prepared: Briefly, 7.5 g Bacto Agar (Carolina Biological Supply Co., Burlington, NC, USA) in 100 mL distilled water was autoclaved and mixed with 400 mL pre-warmed RPMI-1640 medium.
Methods: P. aeruginosa supernatants were prepared as detailed previously [20]. Briefly, P. aeruginosa (5 × 107 cells/mL) was incubated in RPMI 1640 medium with or without addition of FeCl3 at 37 °C and 100 rpm for 24 h. Bacterial growth was measured at 600 nm, using a spectrophotometer (Genesys 20, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Bacterial cultures were centrifuged at 200× g for 30 min, at room temperature, and filtered for sterility (0.22 micron).
Plate assays for the determination of Pseudomonas effects on Aspergillus forming or preformed biofilms forming biofilm assay: A. fumigatus conidia (2.5 × 104/mL) was seeded in test substances in RPMI 1640 medium, in 96-well plates, at 37 °C, overnight (16 h). Preformed biofilm assay: A. fumigatus conidia (2.5 × 104/mL) was seeded in RPMI 1640 medium, in 96-well plates, at 37 °C, for 24 h. The plates were washed with phosphate-buffered saline, and test substances were added. Plates were incubated at 37 °C, overnight (16 h).
All assays were evaluated by XTT metabolic assay [20,21]. Briefly, 150 microliters of an XTT-menadione mixture was added to each test well and incubated at 37 °C, for one hour. Supernatants from each well (100 microliters) were assayed, using a plate reader (Vmax, Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) at 490 nm.
Assays for testing inhibition of planktonic Aspergillus growth, by Pseudomonas supernatants or antifungal drugs, were as described [22]; Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC) was defined as ≥96% killing of the inoculum [23].
As in the manner of previous studies [18], the effect of Pseudomonas volatiles on Aspergillus growth was assessed by cutting away a 3 mm–wide strip, with a scalpel, out of the agar of an 8 cm diameter TSA agar plate, along a diameter, to separate the plate into 2 semicircular noncontiguous agar halves. The halves were inoculated with 10 microliters of a 107/mL suspension, in RPMI1640 of Pseudomonas, or of Aspergillus conidia, and this co-culture incubated for 72 h, at 37 °C, and then the Aspergillus colony area (πr2) was measured. Each experiment involved 3 replicates.
Statistical analysis: Results were analyzed with Student’s t-test if two groups were compared, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) combined with Tukey’s post-test for multiple comparisons. All data are expressed as the mean and standard deviation. Data reported as percentages of the control value were compared with Student’s t-test after arcsin transformation of the proportions; these data are presented as percentages. Assays used 4–8 replicate wells for each group studied, for statistical purposes.
3. Results
Effect of virus infection on A. fumigatus physiology in the context of the assays to be performed: To assist in interpretation of possible P. aeruginosa effects on A. fumigatus in the assays selected to test such effects, we needed to assess A. fumigatus function in the absence of P. aeruginosa, which is the A. fumigatus control we would use for assessing P. aeruginosa effects. Seven experiments assessing A. fumigatus biofilm metabolism were performed in the milieu to be used for later testing P. aeruginosa effects: RPMI 1640, in the plates, temperature, etc., described. There were 5 to 17 replicates for each of the three A. fumigatus strains (Af 18-42, virus-free, and isogenic controls, infected, 10-52 and 18-95) under study, in each of the seven experiments (a total of 212 replicates). The mean ± SD for the XTT assays, A490, for the seven experiments was 0.359 ± 0.12, 0.387 ± 0.13, and 0.455 ± 0.14, for the three isolates, respectively. None of these is significantly different from the others, p > 0.05.
Aside from metabolism (assessed by XTT), the other assay of P. aeruginosa effects (below) involved effects of volatiles on A. fumigatus growth on TSA agar. As will be reiterated, there were, again, not any differences found in the A. fumigatus controls (absence of P. aeruginosa) under the same culture conditions, as described for those assays.
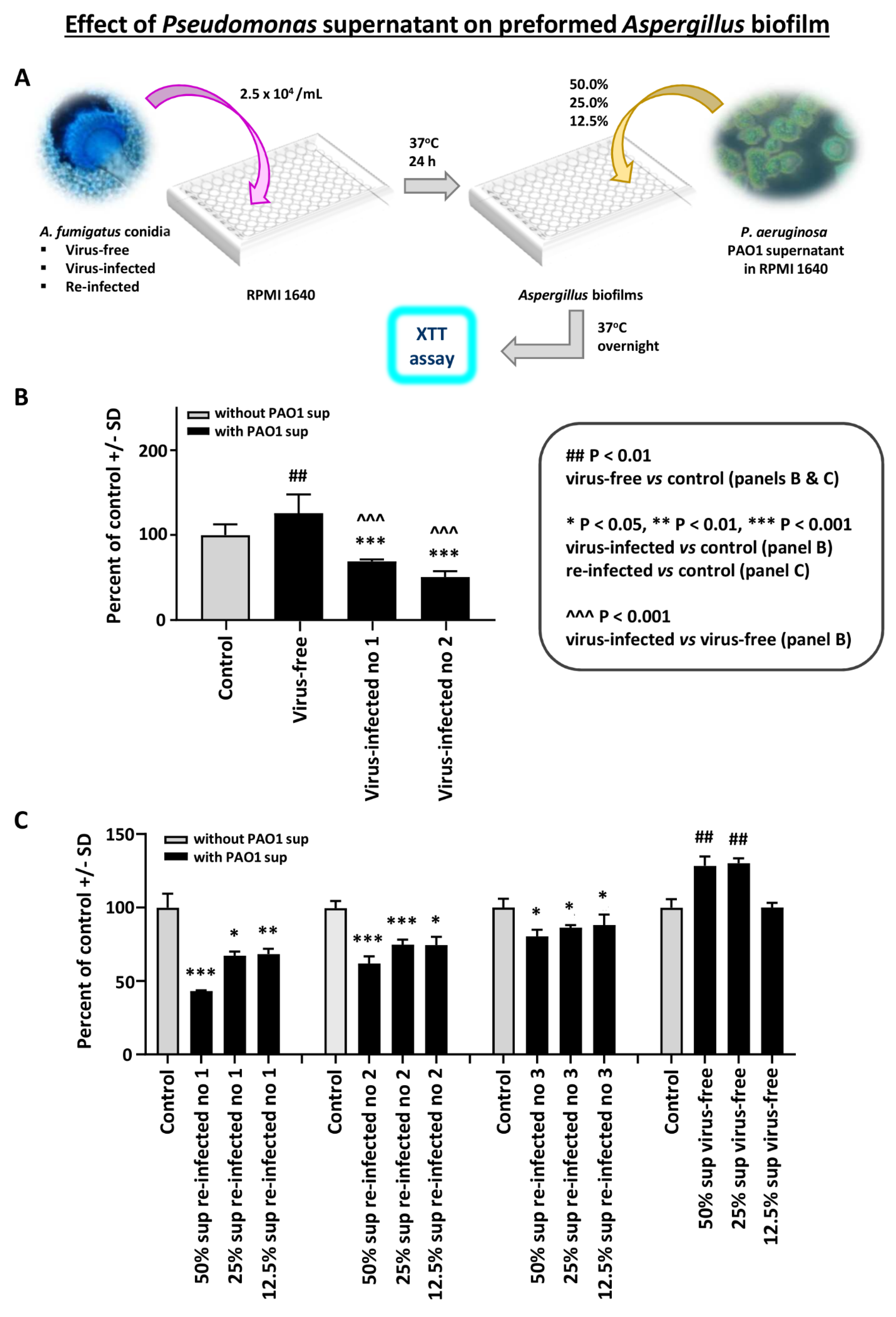
Effect of Pseudomonas planktonic supernatant on preformed Aspergillus biofilm: In the first study with preformed Aspergillus biofilm (i.e., after 16 h, till 40 h culture), and P. aeruginosa PAO1 planktonic supernatants, we found the virus-free preformed biofilm resistant to Pseudomonas supernatant (Figure 1B). In contrast, the two infected strains were significantly inhibited.
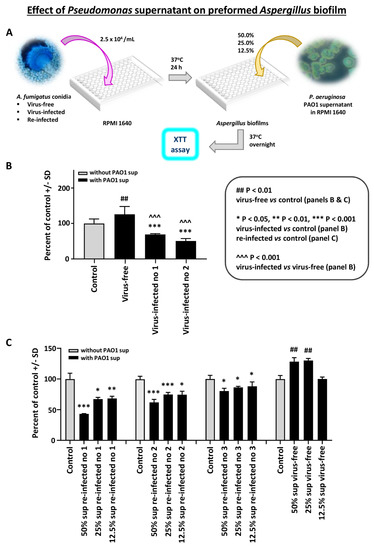
Figure 1.
Effect of Pseudomonas planktonic supernatant on preformed Aspergillus biofilm. We studied preformed Aspergillus biofilm (i.e., 16–40 h culture) and Pseudomonas (PAO1) supernatants. The read-out is the XTT assay, to quantitate Aspergillus metabolism. Data are presented as % of control (medium alone). (A). Diagram of methods. (B). We see the virus-free preformed biofilm (left dark bar) is resistant to Pseudomonas supernatant. In contrast, the 2 infected strains (10-53 no. 1; 18-95 no. 2) are significantly inhibited. The virus-free Aspergillus strain even appears to be stimulated by the Pseudomonas supernatant. (C). This shows a dose titration of the Pseudomonas supernatant (50% to 12.5%) effect, comparing the virus-free Aspergillus (18-95) to that same strain, re-infected. The 3 re-infected Aspergillus strains (19-40 1A, 19-41 2A, and 19-42 3A) are re-infected nos. 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The 4 bars, black and gray, at the right are the virus-free Aspergillus, and the stimulatory effect of Pseudomonas supernatant is again seen on the virus-free strain, at the lower dilutions. The re-infected strains (all the remaining quartets of bars) are inhibited by Pseudomonas supernatant. All Aspergillus strains show a dose-response.
In a dose titration of Pseudomonas supernatant (Figure 1B), we compared the virus-free Aspergillus to the three re-infected Aspergillus strains. The re-infected strains were inhibited by Pseudomonas supernatant. These observations were confirmed in two additional experiments.
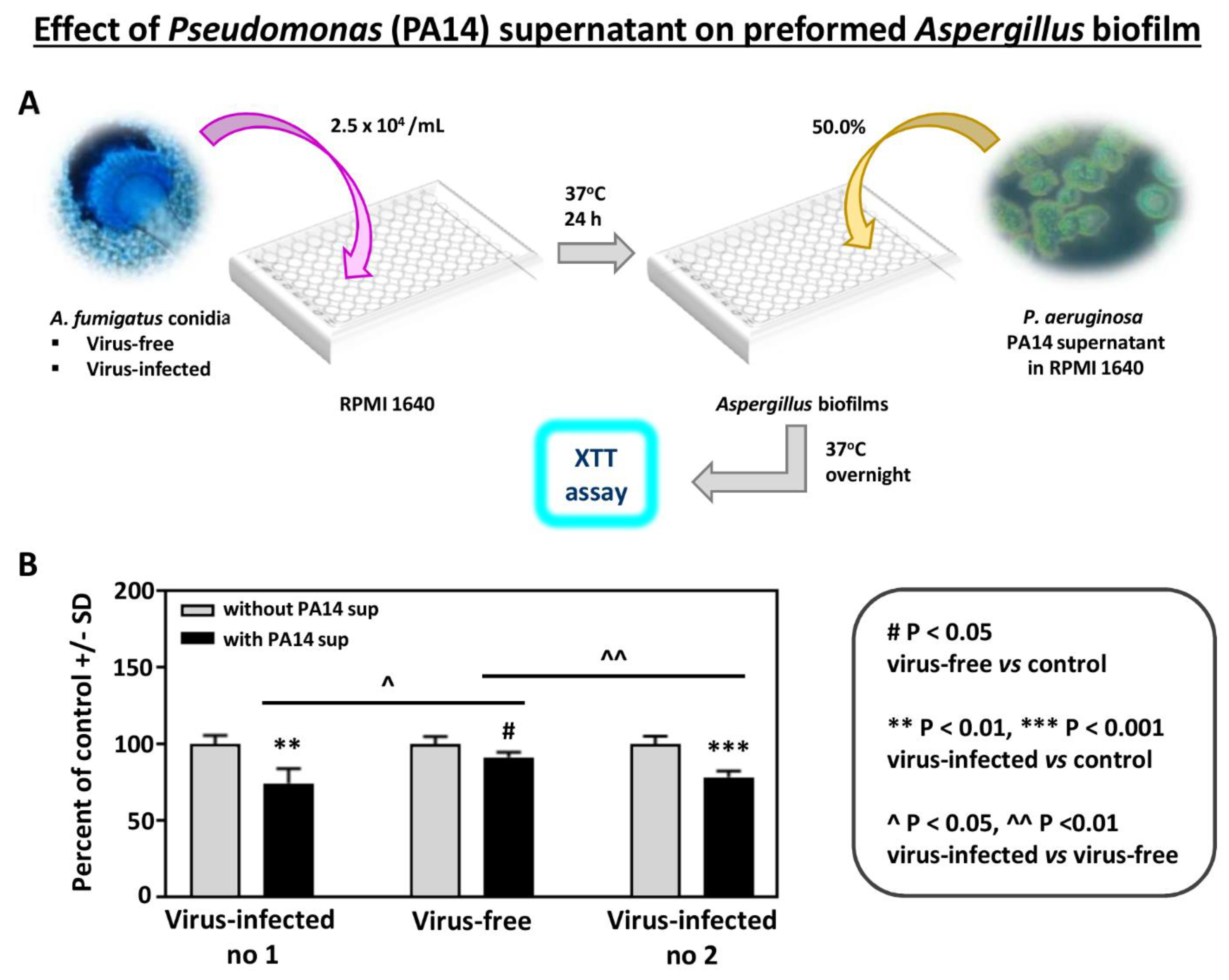
In addition, to study the effects of another Pseudomonas strain, we compared the effect of supernatant of Pseudomonas strain PA14 on preformed Aspergillus biofilm (Figure 2). As with PAO1, the effects were significantly stronger on the infected strains.
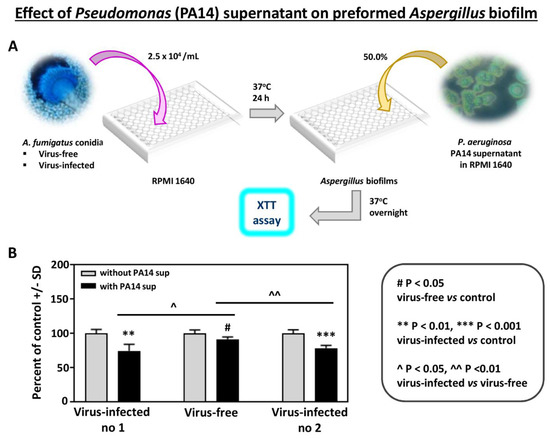
Figure 2.
Effect of Pseudomonas (PA14) planktonic supernatant on preformed Aspergillus biofilm. (A). Diagram of methods. (B). All 3 Aspergillus strains are inhibited (XTT assay) at a 1:2 dilution of Pseudomonas supernatant (black bars), comparing to their own controls (medium alone)). The virus-free Aspergillus is less inhibited compared to the infected isolates, compared to 10-53 (left), and to 18-95 (right).
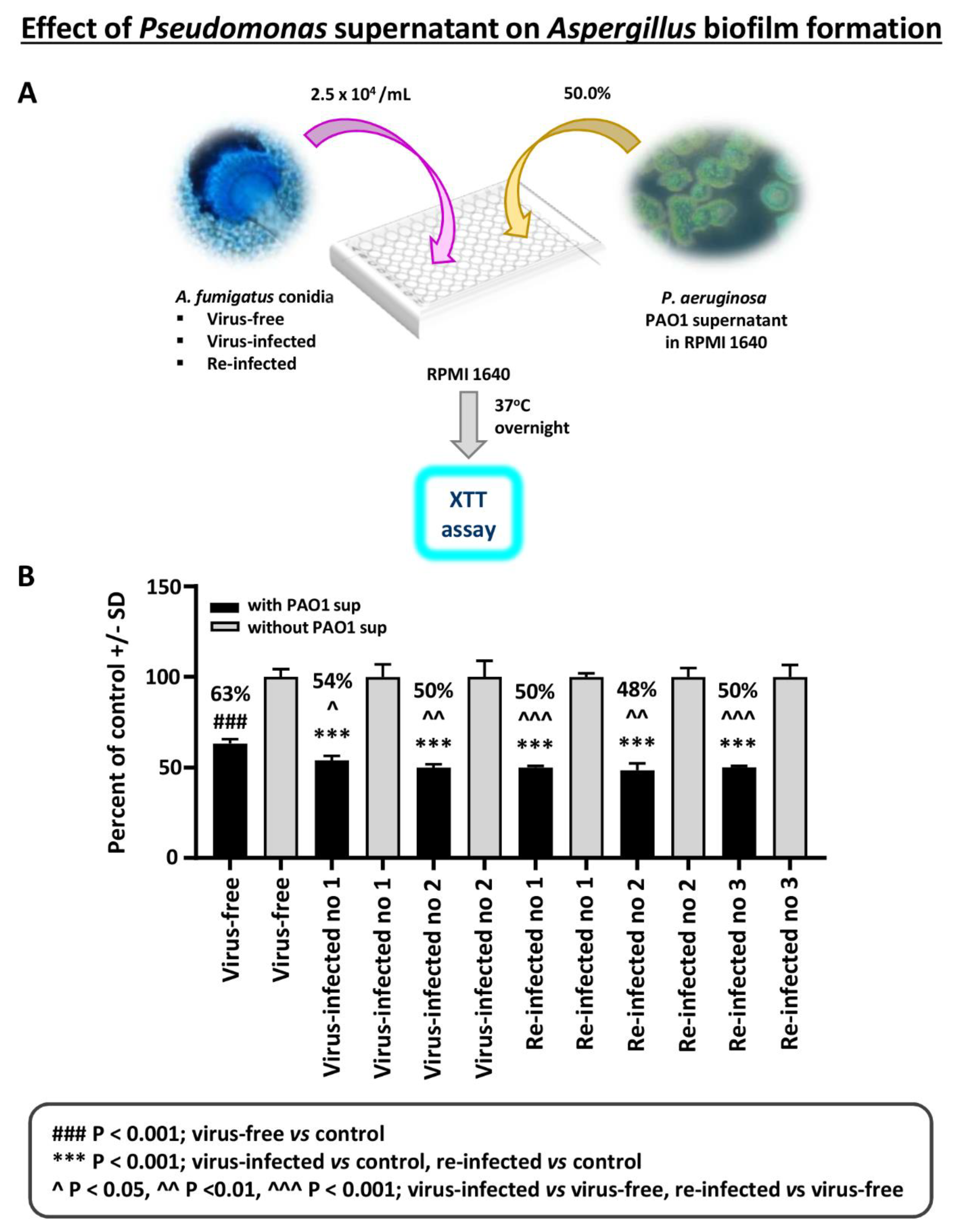
Effect of Pseudomonas planktonic supernatant on AF293-virus free or AF293-infected biofilm formation: The effect of planktonic Pseudomonas (PAO1) supernatant on biofilm formation (i.e., initial 16 h of culture) by A. fumigatus was studied (Figure 3). All isolates are inhibited by Pseudomonas supernatant. The virus-free Aspergillus is significantly inhibited less.
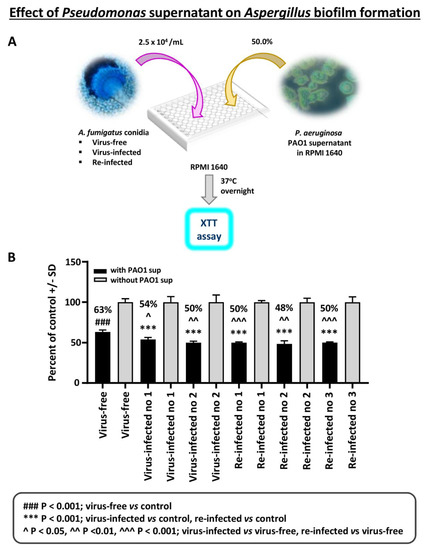
Figure 3.
Effect of Pseudomonas planktonic supernatant on AF293-virus free or AF293-infected biofilm formation. (A). Diagram of methods. (B). Black bars are the result of treatment; gray bars are the control (medium alone) value, set at 100%. The 2 bars at the left are the virus-free Aspergillus. “Infected nos. 1 and 2” are the 2 infected strains, 18-95 and 10-53, respectively; and the remainder the re-infected strains, as indicated (19-40 1A, 19-41 2A, and 19-42 3A are re-infected nos. 1, 2, and 3, respectively). All isolates are inhibited by a 1:2 dilution of Pseudomonas PAO1 supernatant; the % inhibition compared to their controls is indicated above the black bars. The virus-free Aspergillus is significantly less inhibited, comparing the virus-free to the other isolates.
A second experiment of this type was performed with PA14 supernatant. PA14 supernatants proved to be much more inhibitory in these experiments with biofilm formation than PAO1 supernatants, consistent with the reported greater virulence of PA14 compared to PAO1 [24], owing to a mutation. At a 1:100 dilution, the two infected and the virus-free strains were all greatly inhibited, to <25% of controls (p < 0.001). At a 1:500 dilution, all three strains were inhibited ≤50% of controls, but the virus-free was inhibited significantly less than either two infected strains (p < 0.05 compared to 18-95, and p < 0.001 compared to 10-53; the two infected strains were not significantly different from each other). At a 1:1000 dilution, none of the three Aspergillus strains was inhibited.
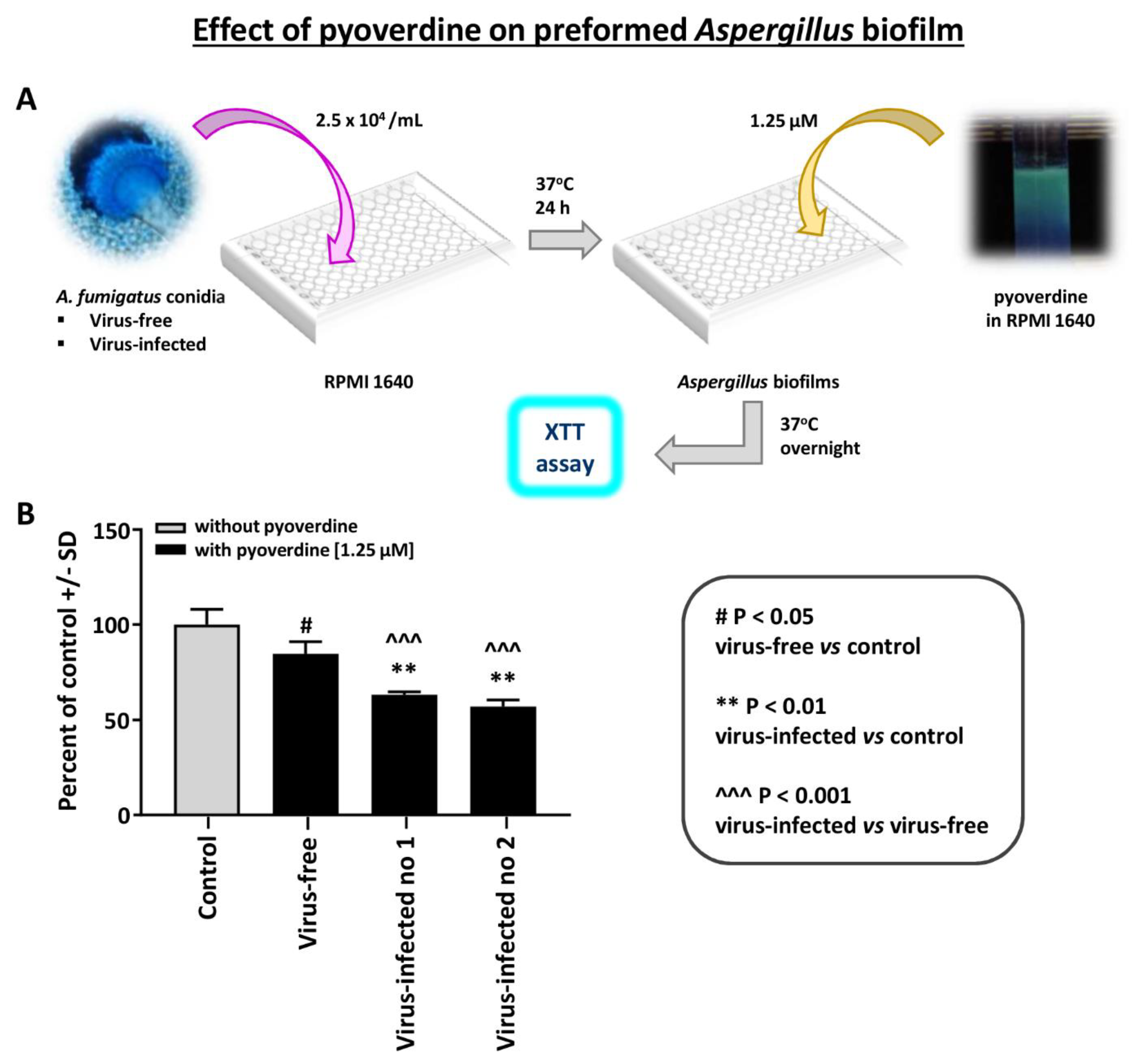
The effect of pyoverdine on Aspergillus strain pyoverdine is a Pseudomonas siderophores that is inhibitory to Aspergillus [14]. We compared the effect of pyoverdine on preformed Aspergillus biofilm (XTT assay) (Figure 4). The virus-free Aspergillus was significantly less inhibited by pyoverdine. A similar difference was noted with 12.5 micromolar pyoverdine (not shown); the two infected Aspergillus strains were inhibited more at this higher concentration, and p < 0.001 compared to the virus-free.
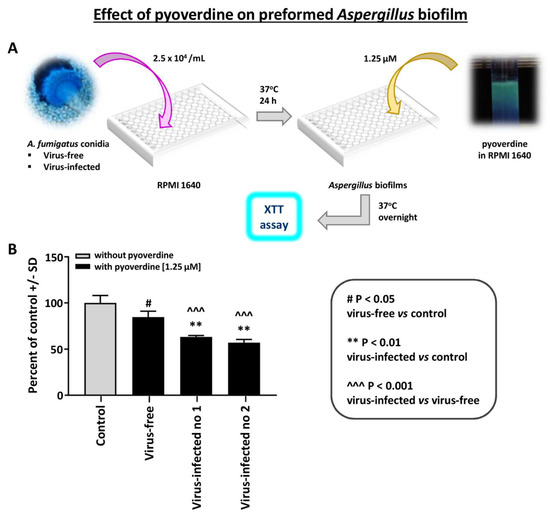
Figure 4.
Effect of pyoverdine on Aspergillus strains. This figure compares the effect of pyoverdine, 1.25 micromolar, on preformed Aspergillus biofilm (XTT assay). (A). Diagram of methods. (B). The virus-free Aspergillus (black bar, second bar from left) is significantly less inhibited. “Infected nos. 1 and 2” are the two infected strains, 18-95 and 10-53, respectively.
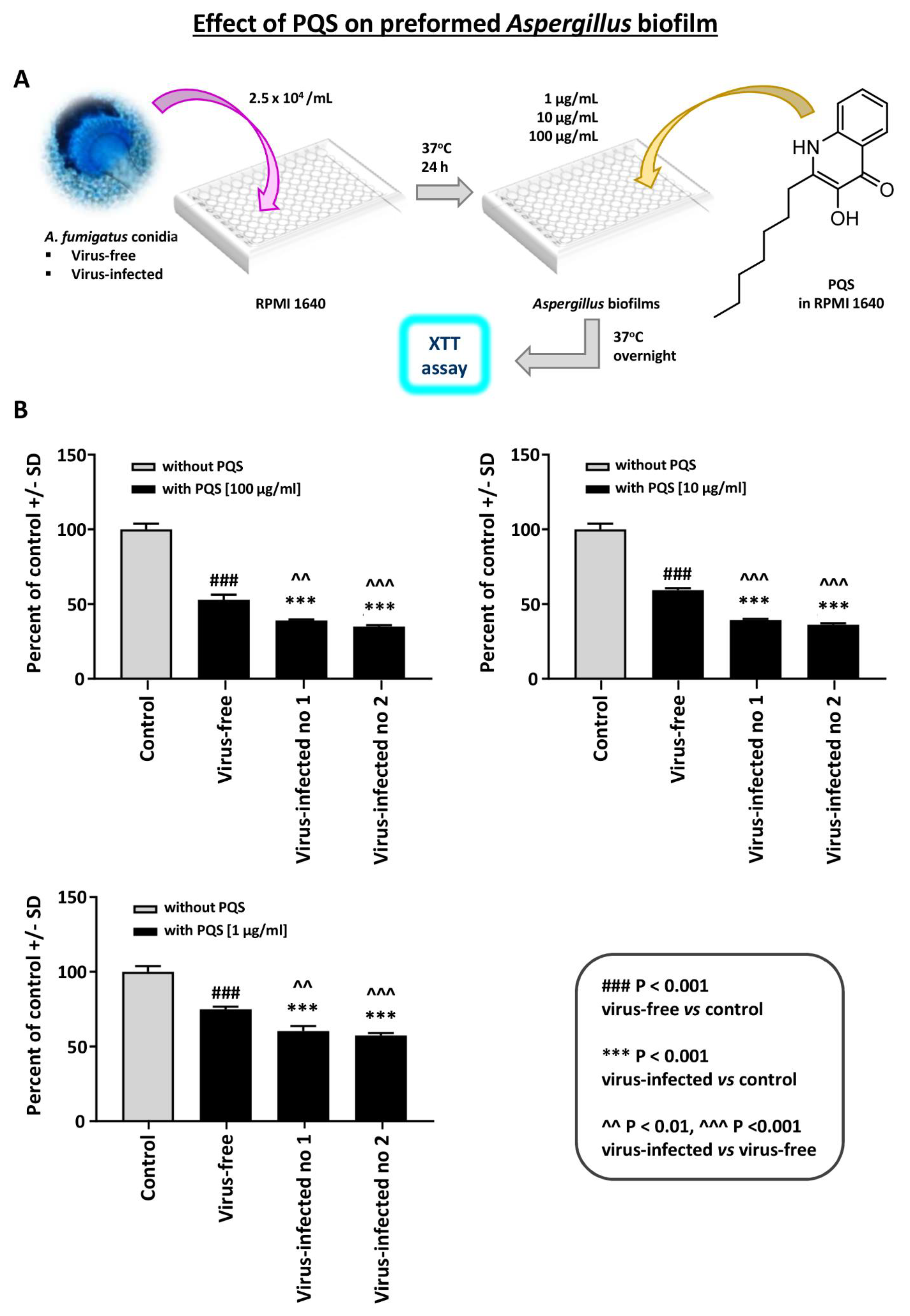
Effect of PQS on preformed Aspergillus biofilm: PQS is an important Pseudomonas exoproduct that is involved in quorum sensing and the production of virulence factors, and it also has iron-binding properties. It inhibits Aspergillus [15] under iron-restricted conditions (e.g., RPMI1640 medium). We performed a dose-titration of PQS effect on preformed Aspergillus biofilm metabolism (Figure 5). At every concentration, the two virus-infected strains were significantly more inhibited than the virus-free.
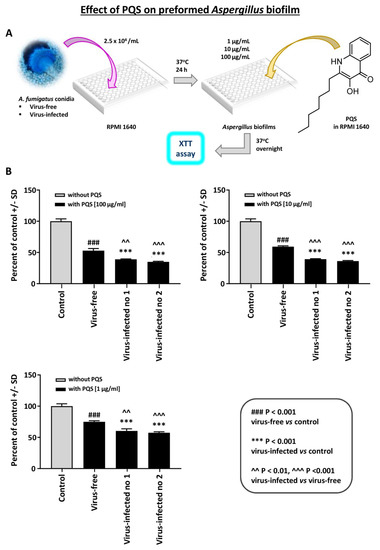
Figure 5.
Effect of Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS) on preformed Aspergillus biofilm. This figure shows a dose-titration of 100, 10, and 1 mcg/mL PQS on preformed Aspergillus biofilm metabolism. (A). Diagram of methods. (B). At every concentration, the 2 virus-infected strains (“Infected nos. 1 and 2” are 18-95 and 10-53, respectively) are significantly more inhibited than the virus-free, which is the black bar, second bar from the left, of each segment. Control, RPMI 1640 medium with ethanol concentrations equivalent to that in PQS test reagent.
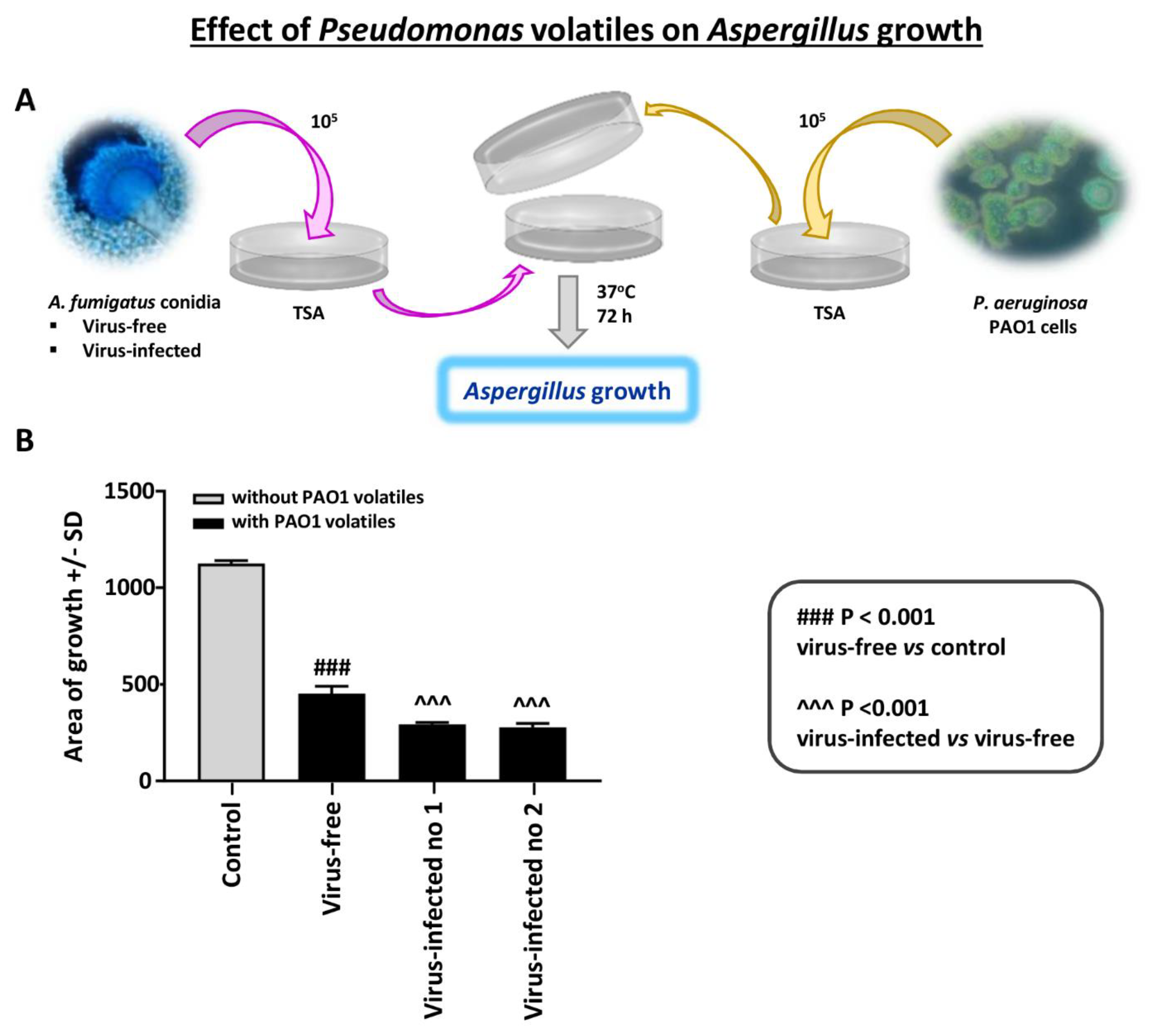
Effect of Pseudomonas volatiles on Aspergillus strains with the assay method and media described (see Methods): In studies with many Pseudomonas laboratory strains and clinical isolates, and several Aspergillus isolates, we find Pseudomonas volatiles to be inhibitory to Aspergillus [18]. The entities responsible appear to be small lipophilic organic molecules.
We here tested Aspergillus growth on agar in the presence of Pseudomonas growth on the same plate, as described. In the absence of Pseudomonas, the virus-free and the two virus-infected strains grew equally well on TSA agar. We found that the virus-free Aspergillus was inhibited significantly less by Pseudomonas than the infected (Figure 6). The experiment shown is representative of three experiments with identical results.
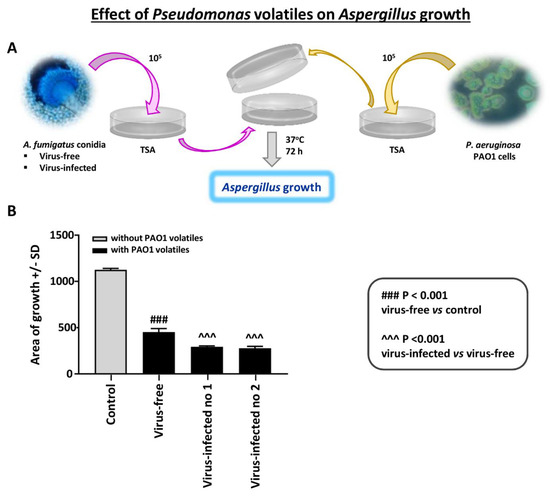
Figure 6.
Effect of Pseudomonas volatiles on Aspergillus strains. An Aspergillus isolate was inoculated on trypticase soy agar (TSA) agar and sealed together with an inverted plate with Pseudomonas PAO1 growing on it; there was no direct contact between the plates. There were 4 plates prepared for each Aspergillus–Pseudomonas combination; means and SD are shown. The control is the same 2-plate apparatus, with no Pseudomonas on the inverted plate; two plates/Aspergillus isolate. (A). Diagram of methods. (B). The 3 Aspergillus isolates’ growth in the absence of Pseudomonas were not different (colony area) on TSA; thus, these growth results are merged and shown as “Control”. After ≥3 days of incubation, the virus-free Aspergillus (left black bar) was inhibited significantly less than the infected (“Infected nos. 1 and 2” are 10-53 and 18-95, respectively). The areas of growth here were measured after 72 h of co-exposure; prior to that, there were no statistically significant differences, as all the Aspergillus colonies continued to slowly enlarge over time.
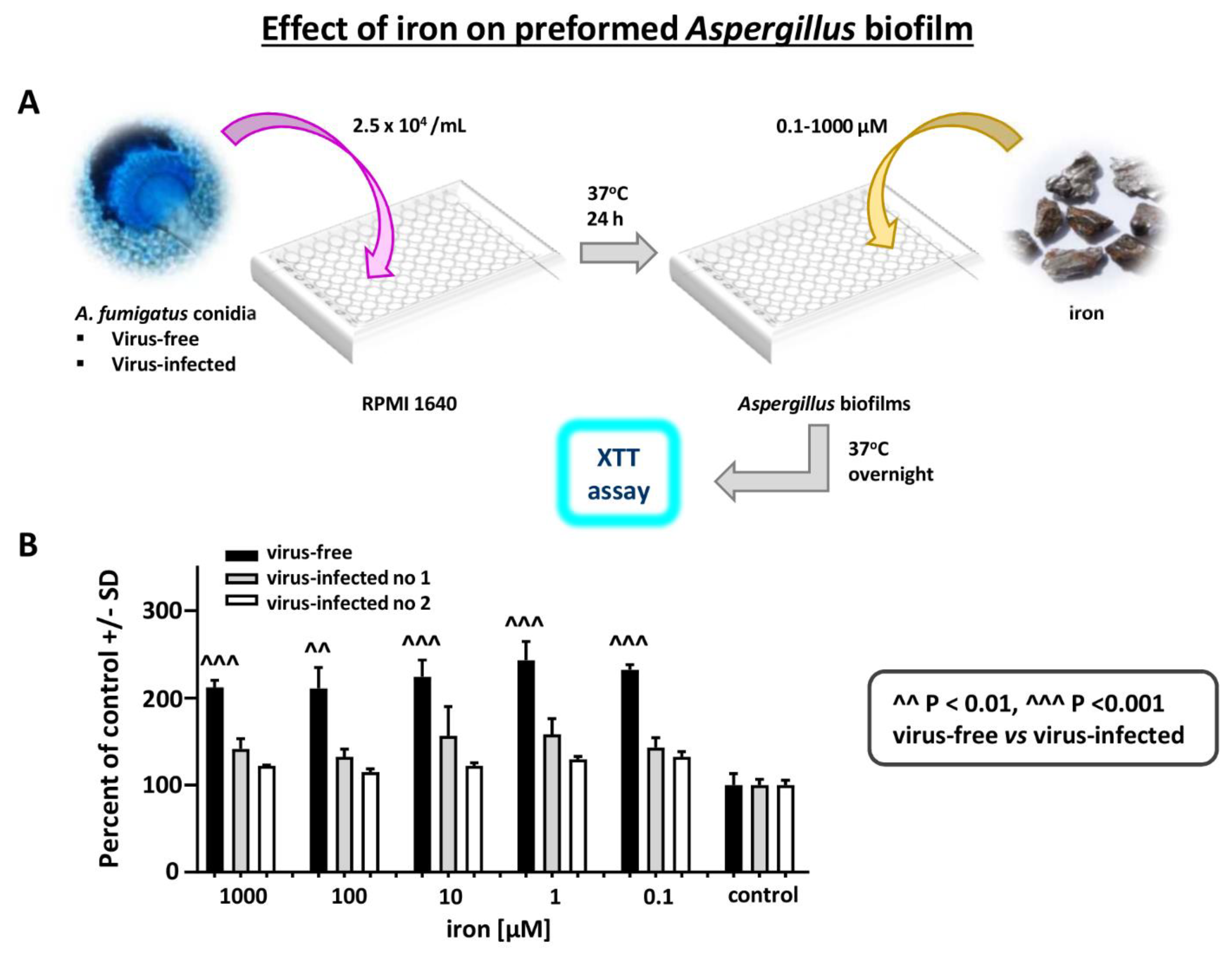
Effect of iron on Aspergillus strains: Iron stimulates Aspergillus biofilm growth [25]. We examined a possible differential effect of FeCl3 on virus-free vs. virus-infected Aspergillus preformed biofilm metabolism (XTT assay), over a range of iron concentrations (Figure 7). Iron stimulated the virus-free strain to a significantly greater extent, at all iron concentrations.
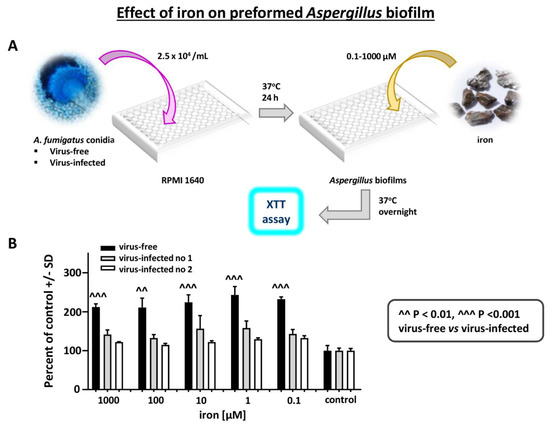
Figure 7.
Effect of iron on Aspergillus strains. Differential effect of FeCl3 on virus-free compared to virus-infected Aspergillus preformed biofilm, XTT assay, over a range of iron concentrations. (A). Diagram of methods. (B). The 3 bars at the right are the control in RPMI1640 without added iron. Within each triplet, from left to right, are the virus-free Aspergillus (the black bars), and flanking the black bar each time, the infected Aspergillus strains (“infected nos. 1 and 2” are 10-53 and 18-95, respectively). Iron stimulates the virus-free strain to a significantly greater extent, at all iron concentrations.
Effect of PAO1 planktonic filtrate on AF293-virus free or AF293-infected planktonic growth: The differential effect of Pseudomonas on planktonic Aspergillus growth was marginal (Supplementary Text and Figure S2), compared to the effects described above (Figure 1 and Figure 2) on Aspergillus biofilm.
Drug susceptibility: We compared the susceptibility of virus-free vs. virus-infected Aspergillus strains to amphotericin B, voriconazole, and caspofungin and found no differences. The MICs and MFCs (mcg/mL) for the virus-free and virus-infected Aspergillus strains were, for amphotericin B, 1 and >8, respectively; for caspofungin, 12.5 and >50; and for voriconazole, ≤0.5 and >8.
4. Discussion
Fungal viruses have been described in 22 viral taxa, with five in the genus Aspergillus, including members of the established families Chrysoviridae, Narnaviridae, Partitiviridae, Polymycoviridae, and Totiviridae [26]. It has been estimated that 30–80% of fungal species are infected, and >100 fungal species [27,28]. Most mycoviruses are dsRNA, un-enveloped; ssRNA viruses appear to be increasingly common [26,29,30]. They are less common in teleomorphs [26]. Most are transmitted by cell-to-cell transmission, and most are vertically transmitted via conidiospores [26,30,31]. Extracellular transmission [32] and transmission via mycophagous insects have been described [33] for the only DNA mycovirus known to date [34]. Most mycoviruses do not appear to integrate in the host genome, with the exception of families Metaviridae and Pseudoviridae. The viruses tend to be latent, persist, and are difficult to eliminate [26,30]. Multiple different virus infections in a fungus are common [27], for example, the A. foetidus mycovirus complex [35,36,37]. Whereas the majority of mycoviruses appears to cause no obvious phenotypic changes, nor a debilitating effect on the host fungus, some mycoviruses are lytic, and some have been described that can cause plaques in fungal lawns in vitro, and the dsRNA has been implicated [27,29,38]. Treatment with an antifungal is one stimulus described that can trigger a lytic virus in Candida albicans [38]. Fungal antiviral defense has been associated with RNA silencing [26,28].
All known mycovirus genomes encode for replication enzymes, such as RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Conversely, not all encode capsid polypeptides or are enclosed in traditional, spherical, or filamentous, protein capsids. This is the case for polymycoviruses and related viruses [2,4], that can produce infections with only naked dsRNA [2,5,31]. In some yeasts, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, mycoviruses encode protein toxins that kill other fungi, in some by inhibiting glucan synthesis [29,39] or DNA synthesis [40]. Some fungal viruses trigger or suppress production of fungal toxins harmful to mammalian species [31], such as aflatoxin in A. flavus [1]. Fungal phytopathogens have been associated preferentially with virus-free strains [27], and virus-induced hypovirulence has been utilized in the field against Cryphonectria parasitica, the fungus causing chestnut blight [28]. There has been interest in these viruses, as to what the effects on mammalian hosts might be, because of the known immunological effects of dsRNA [29].
In Aspergillus, ~10–50% of isolates in a species have been described as infected [26]. Seven to 19% of A. fumigatus clinical isolates are virus-infected [41,42]. The viruses do not appear to integrate in the host genome. Infection even across fungal genera has been described in this group of viruses [1], and some Aspergillus viruses can produce infections with only naked dsRNA [2,5,31].
Whereas the preponderance of evidence associates non-latent virus infection with fungal hypovirulence, as is the case for a variant of AfuPmV-1 that has one additional dsRNA element and was tested in a murine model [43], there is evidence in Aspergillus that some viruses may increase virulence [1,31,44], or have no effect on virulence [1,44,45]. Other studies have indicated that viruses in two Aspergillus viral taxa have no effect on antifungal drug susceptibility [45], as was the observation in our study.
In our study, we showed that an Aspergillus virus alters A. fumigatus phenotype. There is evidence for an active competition between Aspergillus and Pseudomonas, a competition that may occur in soil and water. As these two microbes are the most common fungal and bacterial pathogens in many patient groups, the outcome of the competition could be very important for the long-term welfare in the patients (summarized in References [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]). We have studied here well-documented Pseudomonas weaponry against Aspergillus in biofilm form, a competition that is likely most important to certain microbial residences, such as in the lung, in immunocompromised hosts, and also, particularly, in persons with cystic fibrosis. The studies employed well-described assays, in defined media, that have previously quantitated Pseudomonas inhibition of Aspergillus [14,15,16,17,20]. The physical microscopic correlates of the inhibition, as we have described metabolically, of Aspergillus biofilm by these Pseudomonas products have recently been documented and detailed by novel observational, computer-driven techniques [46]. Our studies here clearly indicate that virus infection weakens A. fumigatus in intermicrobial competition.
The differences demonstrated in susceptibility to Pseudomonas were unrelated to any underlying differences in metabolism or growth under the control conditions for the assays. The two reference Aspergillus strains, which are infected, despite prolonged storage in, and multiple passes in vitro, in laboratories in different continents, showed negligible differences in susceptibility to Pseudomonas. The virus-free Aspergillus under those conditions grew slightly, but insignificantly, less well in the absence of Pseudomonas than the infected. Had the virus-free grown better than infected, such as might be owing to an impairing effect of infection, one could have considered that the virus-free was more resistant to the predations of Pseudomonas merely because it grew better under the study conditions, but the latter was not the case. We would emphasize that the demonstrated equivalence of growth (in the absence of Pseudomonas) may not apply to all other growth conditions; other growth conditions would need to be studied individually. Indeed, as yet unpublished studies, with a related virus, in an entomopathogenic fungus, indicate differences between that infected and uninfected fungus, with respect to growth, are medium-dependent [47].
The differential effect of virus on iron-stimulated fungal growth, particularly when coupled with the findings of effects of iron-chelating molecules, such as pyoverdine and PQS, may be a clue that at least some of the resistance differences to Pseudomonas products are linked to a virus-induced alteration in Aspergillus iron metabolism; iron metabolism is key to Aspergillus physiology, as recently reviewed [48]. Subsequent to the findings reported here, in studies in collaboration with other researchers, significant differences in timing of, and amount of, siderophore production between these virus-infected and uninfected isogenic Aspergillus strains were discovered, which would explain the strain differences in response to iron-denying Pseudomonas products (R. Patil et al., submitted for publication). It is also probable that virus infection weakens Aspergillus’ ability to respond to any stresses, of which iron denial is one. The best evidence for that hypothesis is the differential susceptibility to Pseudomonas volatiles, since small lipophilic organic molecules appear to be the mechanism of such inhibition [18].
5. Conclusions
Our novel observations about altered susceptibility of a fungus, Aspergillus, to another microbe, Pseudomonas, coupled with studies indicating fungal virulence may be depressed by viral infection, and that some viruses may lyse fungi [27,28,29,38], might also have applications in the future for the design of viruses as antifungal treatment [30,31], analogous to phage therapy of bacteria.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v13040686/s1. Figure S1: Representative electrophoretic profiles of AF293 infected, virus-free, and re-infected strains. Figure S2: Effect of PAO1 planktonic filtrate on AF293 virus-free or AF293 infected planktonic growth. Supplementary text.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.S.; formal analysis, validation, and writing—review and editing, H.N., I.K.-L., G.S., R.H.A.C., and D.A.S.; data curation, investigation, methodology, and visualization, H.N., I.K.-L., G.S., and D.A.S.; writing—original draft, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, software, and supervision, I.K.-L. and D.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All supplementary materials referred to are available from cimr_admin@cimr.org.
Acknowledgments
Presented in part as Nazik, H.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; and Stevens, D.A. Virus infection of Aspergillus fumigatus compromises A. fumigatus in intermicrobial competition. Program of the 9th Advances Against Aspergillosis and Mucormycosis meeting, Lugano, Switzerland, 2020, Abstract no. 92 (selected for oral presentation, given by I. Kotta-Loizou). IK-L and RHAC wish to acknowledge the support of the Samuel Scott of Yews Trust. All images (96-well plate, flaskPetri dish, Petri dish lid, Aspergillus fumigatus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pyoverdine and iron) used in diagrams of methods in figures were obtained from Wikimedia Commons under a Creative Commons license.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H.A. Mycoviruses in Aspergilli: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhayuwa, L.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Özkan, S.; Gunning, A.P.; Coutts, R.H.A. A novel mycovirus from Aspergillus fumigatus contains four unique dsRNAs as its genome and is infectious as dsRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9100–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H.A. Studies on the virome of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana reveal novel dsRNA elements and mild hypervirulence. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Shamsi, W.; Jamal, A.; Bhatti, M.F.; Kondo, H.; Suzuki, N. Hadaka virus 1: A capsidless eleven-segmented positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus from a phytopathogenic fungus, Fusarium oxysporum. MBio 2020, 11, e00450–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Dong, K.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Hong, N.; Jiang, D.; Xu, W. A dsRNA virus with filamentous viral particles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Fothergill, J.L. The role of multispecies social interactions in shaping Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity in the cystic fibrosis lung. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, W.; He, X.; Liu, Y. The co-colonization prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, W. Interaction between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Penner, J.; Shah, H.; Ansari, S.R.; Clemons, K.V.; Groleau, M.-C.; Dietl, A.-M.; Visca, P.; Haas, H.; et al. Aspergillus-Pseudomonas interaction, relevant to competition in airways. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S228–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briard, B.; Mislin, G.; Latgé, J.P.; Beauvais, A. Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and pulmonary bacteria: Current state of the field, new data, and future perspective. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Sass, G.; Swietnicki, W.; Stevens, D.A. Review of potential Pseudomonas weaponry, relevant to the Pseudomonas-Aspergillus interplay, for the mycology community. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, E.; Amich, J.; Gago, S. Factoring in the complexity of the cystic fibrosis lung to understand Aspergillus fumigatus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa interactions. Pathogens 2020, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y. Subtle relationships between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and fungi in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Clin. Belgica 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Penner, J.; Shah, H.; Ansari, S.R.; Clemons, K.V.; Groleau, M.-C.; Dietl, A.-M.; Visca, P.; Haas, H.; et al. Studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants indicate pyoverdine as the central factor in inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00345-17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nazik, H.; Sass, G.; Ansari, S.R.; Ertekin, R.; Haas, H.; Deziel, E.; Stevens, D.A. Novel intermicrobial molecular interaction: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quinolone Signal (PQS) modulates Aspergillus fumigatus response to iron. Microbiology 2020, 166, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, G.; Nazik, H.; Chatterjee, P.; Stevens, D.A. In high iron environment, pyocyanin is a major anti-fungal molecule; differences in prototype P. aeruginosa strains. Med. Mycol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, G.; Ansari, S.R.; Dietl, A.-M.; Deziel, E.; Haas, H.; Stevens, D.A. Intermicrobial interaction: Aspergillus fumigatus siderophores protect against competition by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazik, H.; Sass, G.; Deziel, E.; Stevens, D.A. Aspergillus is inhibited by Pseudomonas aeruginosa volatiles. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C.; et al. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.A.G.; Penner, J.; Moss, R.B.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Clemons, K.V.; Spormann, A.M.; Nazik, H.; Cohen, K.; Banaei, N.; Carolino, E.; et al. Inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus and its biofilm by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on the source, phenotype and growth conditions of the bacterium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Document M38-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008.
- Denning, D.W.; Hanson, L.H.; Perlman, A.M.; Stevens, D.A. In vitro susceptibility and synergy studies of Aspergillus species to conventional and new agents. Diag. Micro. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, H.; McMullan, R.; Filloux, A. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa reference strain PA14 displays increased virulence due to a mutation in ladS. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazik, H.; Penner, J.C.; Ferreira, J.A.G.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Cohen, K.; Spormann, A.M.; Martinez, M.; Chen, V.; Hsu, J.L.; Clemons, K.V.; et al. Effect of iron chelators on the formation and development of Aspergillus fumigatus biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6514–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotta-Loizou, I. Diversity of mycoviruses in Aspergilli. In Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th ed.; Bamford, D.H., Mark Zuckerman, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 4, pp. 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S. Effects of fungal viruses on their hosts. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1980, 18, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S.; Caston, J.R.; Jiang, D.; Nibert, M.L.; Suzuki, N. 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 2015, 479–480, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Moore, J. Subcellular particles in pathogenic fungi. In Fungi Pathogenic for Humans and Animals; Pathogenicity, Detection, II; Howard, D.H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 103–121, Part B. [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande, W.; Lo-Ten-Foe, J.R.; van Belkum, A.; Netea, M.G.; Kullberg, B.J.; Vonk, A.G. Mycoviruses: Future therapeutic agents of invasive fungal infections in humans? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Sande, W.W.J.; Vonk, A.G. Mycovirus therapy for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis? Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S179–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Extracellular transmission of a DNA mycovirus and its use as a natural fungicide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Jin, H.; Wan, H.; et al. Fungal DNA virus infects a mycophagous insect and utilizes it as a transmission vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12803–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Huang, J.; et al. A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlakidis, Z.; Herrero, N.; Coutts, R.H.A. The complete nucleotide sequence of a totivirus from Aspergillus foetidus. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlakidis, Z.; Herrero, N.; Özkan, S.; Bhatti, M.F.; Coutts, R.H.A. A novel dsRNA element isolated from the Aspergillus foetidus mycovirus complex. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2625–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlakidis, Z.; Herrero, N.; Özkan, S.; Kanhayuwa, L.; Jamal, A.; Bhatti, M.F.; Coutts, R.H.A. Sequence determination of a quadripartite dsRNA virus isolated from Aspergillus foetidus. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.J.; Nash, C.H.; Bozzola, J.J. Virus-like particles and lytic plaque formation in lawns of Candida albicans. J. Bact. 1982, 152, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magliani, W.; Conti, S.; Arseni, S.; Frazzi, R.; Salati, A.; Polonelli, L. Killer anti-idiotypes in the control of fungal infections. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2001, 2, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M.J.; Breinig, F. Yeast viral killer toxins: Lethality and self-protection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regos, J.M.; Vonk, A.G.; Eadie, K.; Lo-Ten-Foe, J.R.; Verbrugh, H.A.; van Diepeningen, A.D.; van de Sande, W.W.J. Double-stranded RNA mycovirus infection of Aspergillus fumigatus is not dependent on the genetic make-up of the host. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77381. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, M.F.; Jamal, A.; Bignell, E.M.; Petrou, M.A.; Coutts, R.H.A. Incidence of dsRNA mycoviruses in a collection of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. Mycopathologia 2012, 174, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Shishido, E.; Yahara, M.; Urayama, S.I.; Ninomiya, A.; Chiba, Y.; Sakai, K.; Hagiwara, D.; Chibana, H.; Moriyama, H.; et al. Phenotypic and molecular biological analysis of polymycovirus AfuPmV-1M from Aspergillus fumigatus: Reduced fungal virulence in a mouse infection model. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 607795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.; Coutts, R.H.A. Aspergillus fumigatus mycovirus causes mild hypervirulent effect on pathogenicity when tested on Galleria mellonella. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 76, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, M.F.; Jamal, A.; Petrou, M.A.; Cairns, T.C.; Bignell, E.M.; Coutts, R.H.A. The effects of dsRNA mycoviruses on growth and murine virulence of Aspergillus Fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurster, S.; Sass, G.; Albert, N.D.; Nazik, H.; Deziel, E.; Stevens, D.A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Live imaging and quantitative analysis of Aspergillus fumigatus growth and morphology during inter-microbial interaction with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Virulence 2020, 11, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippou, C.; Diss, R.M.; Daudu, J.O.; Coutts, R.H.A.; Kotta-Loizou, I. The polymycovirus-mediated growth enhancement of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana is dependent on carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 606366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthaiou, E.I.; Sass, G.; Stevens, D.A.; Hsu, J.L. Iron: An essential nutrient for Aspergillus fumigatus and a fulcrum for pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).