Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection–Success, Challenges, and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HBV Host Tropism
3. Surrogate Models Based on HBV-Related Hepadnaviruses
3.1. Woodchuck Hepatitis B Virus
3.2. Duck Hepatitis B Virus
3.3. Woolly Monkey Hepatitis B Virus
3.4. Hepadnavirus Infections in Tupaias
4. HBV-Susceptible Primate Models
4.1. Chimpanzees
4.2. Smaller Non-Human Primates
5. Non-Infection Murine Models
5.1. HBV Transgenic Mouse Model
5.2. Viral Vector-Mediated HBV Transduction
5.3. Delivery of HBV Genomes through Hydrodynamic Tail Vein Injections (HDI) into Mice
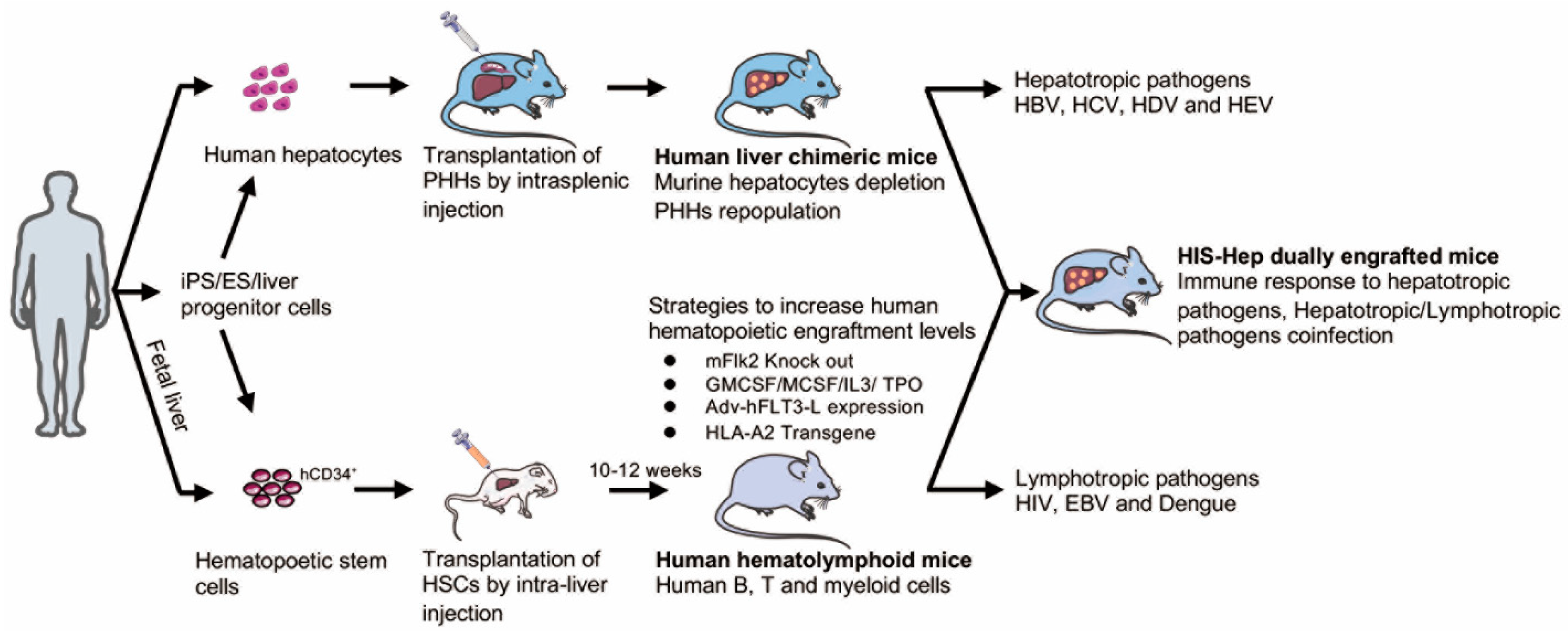
6. Humanized Xenotransplantation Models for the Study of HBV
6.1. Human Liver Chimeric Mice
6.2. Dually Engrafted Mice
6.3. Recent Progress and Improvements of Humanized Mouse Models in Other Fields
6.4. Future Directions for Humanized HBV Mouse Models
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, J.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thimme, R. Immunological cure of HBV infection. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Chen, D.S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Bzowej, N.H.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Murad, M.H.; American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, A.; Horn, J.; Mikolajczyk, R.T.; Krause, G.; Ott, J.J. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karayiannis, P. Hepatitis B virus: Virology, molecular biology, life cycle and intrahepatic spread. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: Towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.R.; Min, B.Y.; Song, J.C.; Seong, M.H.; Lee, S.S.; Jang, E.S.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; et al. Off-treatment virologic relapse and outcomes of re-treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients who achieved complete viral suppression with oral nucleos(t)ide analogs. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.C.; Hung, C.H.; Hu, T.H.; Lu, S.N.; Wang, J.H.; Lee, C.M.; Chen, C.H. Incidence and predictors of HBV relapse after cessation of nucleoside analogues in HBeAg-negative patients with HBsAg ≤ 200 IU/mL. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziyannis, S.J.; Tassopoulos, N.C.; Heathcote, E.J.; Chang, T.T.; Kitis, G.; Rizzetto, M.; Marcellin, P.; Lim, S.G.; Goodman, Z.; Ma, J.; et al. Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Gane, E.; Leung, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Wang, Y.; Lai, C.L.; Heathcote, E.J.; Manns, M.; Bzowej, N.; Niu, J.; et al. 2-Year GLOBE trial results: Telbivudine Is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Du, B.; Fang, X.; Shu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, H.; Sun, Y.; Teng, J.; Visalath, P.; Qiu, H.; et al. ALT Flare Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Antiviral Treated Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Cross-Country Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 615203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Song, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, F.; Guan, S.; Xie, J.; Gohda, J.; et al. Emergence of Lamivudine-Resistant HBV during Antiretroviral Therapy Including Lamivudine for Patients Coinfected with HIV and HBV in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, O.; Aygen, B.; Demirtürk, N.; Demirdal, T.; Inan, D.; Yıldırmak, T.; Kantürk, A.; Tütüncü, E.; Group, H.B.S. Lamivudine resistance mutations in patients infected with hepatitis B virus genotype D. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 4987–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osiowy, C. From infancy and beyond… ensuring a lifetime of hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccine-induced immunity. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Romet-Lemonne, J.L.; Mullins, J.I.; Essex, M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell 1986, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shih, C.H.; Li, L.S.; Roychoudhury, S.; Ho, M.H. In vitro propagation of human hepatitis B virus in a rat hepatoma cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6323–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, L.; Kekule, A.S.; Jakubowski, U.; Burgelt, E.; Hofschneider, P.H. The HBV-producing cell line HepG2-4A5: A new in vitro system for studying the regulation of HBV replication and for screening anti-hepatitis B virus drugs. Virology 1996, 216, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, S. Hepatitis B virus taxonomy and hepatitis B virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, A.; Brosius, J.; Schmitz, J.; Kriegs, J.O. The genome of a Mesozoic paleovirus reveals the evolution of hepatitis B viruses. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drexler, J.F.; Geipel, A.; Konig, A.; Corman, V.M.; van Riel, D.; Leijten, L.M.; Bremer, C.M.; Rasche, A.; Cottontail, V.M.; Maganga, G.D.; et al. Bats carry pathogenic hepadnaviruses antigenically related to hepatitis B virus and capable of infecting human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16151–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, C.; Meik, J.M.; Dashevsky, D.; Card, D.C.; Castoe, T.A.; Schaack, S. Endogenous hepadnaviruses, bornaviruses and circoviruses in snakes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, J.A.; Camus, A.C.; Leary, J.H.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Holmes, E.C.; Ng, T.F. Distinct Viral Lineages from Fish and Amphibians Reveal the Complex Evolutionary History of Hepadnaviruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7920–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauber, C.; Seitz, S.; Mattei, S.; Suh, A.; Beck, J.; Herstein, J.; Borold, J.; Salzburger, W.; Kaderali, L.; Briggs, J.A.G.; et al. Deciphering the Origin and Evolution of Hepatitis B Viruses by Means of a Family of Non-enveloped Fish Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 387–399.e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, W.S. Animal models and the molecular biology of hepadnavirus infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lempp, F.A.; Wiedtke, E.; Qu, B.; Roques, P.; Chemin, I.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Le Grand, R.; Grimm, D.; Urban, S. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is the limiting host factor of hepatitis B virus infection in macaque and pig hepatocytes. Hepatology 2017, 66, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Will, H.; Cattaneo, R.; Koch, H.G.; Darai, G.; Schaller, H.; Schellekens, H.; van Eerd, P.M.; Deinhardt, F. Cloned HBV DNA causes hepatitis in chimpanzees. Nature 1982, 299, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.Q.; Su, J.J.; Huang, D.R.; Gan, Y.C.; Yang, C.; Huang, G.H. Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. I. Experimental infection of tree shrews with hepatitis B virus. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 122, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, Z.Y.; Cao, C.C.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, Y.X.; Fan, D.D.; He, J.; Hou, H.L.; Hu, L.; Hu, X.T.; et al. Genome of the Chinese tree shrew. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walter, E.; Keist, R.; Niederost, B.; Pult, I.; Blum, H.E. Hepatitis B virus infection of tupaia hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 1996, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebe, D.; Aliakbari, M.; Krass, P.; Knoop, E.V.; Valerius, K.P.; Gerlich, W.H. Pre-s1 antigen-dependent infection of Tupaia hepatocyte cultures with human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9511–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dupinay, T.; Gheit, T.; Roques, P.; Cova, L.; Chevallier-Queyron, P.; Tasahsu, S.I.; Le Grand, R.; Simon, F.; Cordier, G.; Wakrim, L.; et al. Discovery of naturally occurring transmissible chronic hepatitis B virus infection among Macaca fascicularis from Mauritius Island. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, W.H.; Snitbhan, R.; Scott, R.M.; Tingpalapong, M.; Watson, W.T.; Tanticharoenyos, P.; Karwacki, J.J.; Srimarut, S. Transmission of hepatitis B virus to gibbons by exposure to human saliva containing hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Infect. Dis. 1977, 135, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, R.M.; Snitbhan, R.; Bancroft, W.H.; Alter, H.J.; Tingpalapong, M. Experimental transmission of hepatitis B virus by semen and saliva. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Njouom, R.; Mba, S.A.; Nerrienet, E.; Foupouapouognigni, Y.; Rousset, D. Detection and characterization of hepatitis B virus strains from wild-caught gorillas and chimpanzees in Cameroon, Central Africa. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Peng, B.; He, W.; Zhong, G.; Qi, Y.; Ren, B.; Gao, Z.; Jing, Z.; Song, M.; Xu, G.; et al. Molecular determinants of hepatitis B and D virus entry restriction in mouse sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7977–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, J.S.; Fukano, K.; Iwamoto, M.; Tsukuda, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Wakita, T.; Sureau, C.; Watashi, K. A Single Adaptive Mutation in Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Induced by Hepadnaviruses Determines Virus Species Specificity. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lempp, F.A.; Mutz, P.; Lipps, C.; Wirth, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Evidence that hepatitis B virus replication in mouse cells is limited by the lack of a host cell dependency factor. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, B.Y.; Shirvani-Dastgerdi, E.; Bram, Y.; Sellau, J.; Low, B.E.; Johnson, H.; Huang, T.; Hrebikova, G.; Heller, B.; Sharon, Y.; et al. Preclinical assessment of antiviral combination therapy in a genetically humanized mouse model for hepatitis delta virus infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, aap9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Guo, J.T.; Hu, J. Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation in Immortalized Mouse Hepatocytes Associated with Nucleocapsid Destabilization. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9021–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raney, A.K.; Eggers, C.M.; Kline, E.F.; Guidotti, L.G.; Pontoglio, M.; Yaniv, M.; McLachlan, A. Nuclear covalently closed circular viral genomic DNA in the liver of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-null hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2900–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Summers, J.; O’Connell, A.; Millman, I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: Restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 4597–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Summers, J.; Smolec, J.M.; Snyder, R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mason, W.S.; Seal, G.; Summers, J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1980, 36, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Brasky, K.M.; Burns, R.B.; Rico-Hesse, R. Isolation of a hepadnavirus from the woolly monkey, a New World primate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5757–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerety, R.J.; Tabor, E.; Purcell, R.H.; Tyeryar, F.J. Summary of an international workshop on hepatitis B vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 140, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payette, P.J.; Ma, X.; Weeratna, R.D.; McCluskie, M.J.; Shapiro, M.; Engle, R.E.; Davis, H.L.; Purcell, R.H. Testing of CpG-optimized protein and DNA vaccines against the hepatitis B virus in chimpanzees for immunogenicity and protection from challenge. Intervirology 2006, 49, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shata, M.T.; Pfahler, W.; Brotman, B.; Lee, D.H.; Tricoche, N.; Murthy, K.; Prince, A.M. Attempted therapeutic immunization in a chimpanzee chronic HBV carrier with a high viral load. J. Med. Primatol. 2006, 35, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asabe, S.; Wieland, S.F.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Roederer, M.; Engle, R.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. The size of the viral inoculum contributes to the outcome of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9652–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamili, S.; Sozzi, V.; Thompson, G.; Campbell, K.; Walker, C.M.; Locarnini, S.; Krawczynski, K. Efficacy of hepatitis B vaccine against antiviral drug-resistant hepatitis B virus mutants in the chimpanzee model. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Guerra, B.; Chavez, D.; Giavedoni, L.; Hodara, V.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Fosdick, A.; Frey, C.R.; Zheng, J.; Wolfgang, G.; et al. GS-9620, an oral agonist of Toll-like receptor-7, induces prolonged suppression of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected chimpanzees. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1508–1517.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieland, S.F. The chimpanzee model for hepatitis B virus infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, P.; Yang, C.; Su, J.; Cao, J.; Ou, C.; Luo, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Shi, J.; et al. Histopathological changes in the liver of tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis) persistently infected with hepatitis B virus. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menne, S.; Tumas, D.B.; Liu, K.H.; Thampi, L.; AlDeghaither, D.; Baldwin, B.H.; Bellezza, C.A.; Cote, P.J.; Zheng, J.; Halcomb, R.; et al. Sustained efficacy and seroconversion with the Toll-like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 in the Woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colonno, R.J.; Genovesi, E.V.; Medina, I.; Lamb, L.; Durham, S.K.; Huang, M.L.; Corey, L.; Littlejohn, M.; Locarnini, S.; Tennant, B.C.; et al. Long-term entecavir treatment results in sustained antiviral efficacy and prolonged life span in the woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttleman, J.S.; Pourcel, C.; Summers, J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell 1986, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, W.K.; Miller, D.S.; Scougall, C.A.; Kotlarski, I.; Colonno, R.J.; Jilbert, A.R. Effect of antiviral treatment with entecavir on age- and dose-related outcomes of duck hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5819–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, S.F.; Konig, A.; Doring, B.; Glebe, D.; Geyer, J. Characterisation of the hepatitis B virus cross-species transmission pattern via Na+/taurocholate co-transporting polypeptides from 11 New World and Old World primate species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Winer, B.Y.; Chavez, D.; Guerra, B.; Brasky, K.M.; Eng, S.; Salas, E.; Tam, D.; Simmons, J.H.; Abee, C.R.; et al. Woolly Monkey-HBV Infection in Squirrel Monkeys as a Surrogate Nonhuman Primate Model of HBV Infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, F.V.; Filippi, P.; Buras, J.; McLachlan, A.; Popper, H.; Pinkert, C.A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6909–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chisari, F.V.; Pinkert, C.A.; Milich, D.R.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 1985, 230, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, F.V.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Milich, D.R.; Riggs, M.; Lee, S.; Palmiter, R.D.; Pinkert, C.A.; Brinster, R.L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1986, 60, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.K.; Li, C.C.; Chen, H.J.; Chang, J.L.; Jeng, K.S.; Chou, C.K.; Hsu, M.T.; Tsai, T.F. Blocking of G1/S transition and cell death in the regenerating liver of Hepatitis B virus X protein transgenic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Koike, K.; Saito, I.; Miyamura, T.; Jay, G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 1991, 351, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L.; Price, J.; Raney, A.K.; McLachlan, A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6599–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Matzke, B.; Schaller, H.; Chisari, F.V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6158–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zou, Z.; Chen, S.H.; Qu, C. Immunizations with hepatitis B viral antigens and a TLR7/8 agonist adjuvant induce antigen-specific immune responses in HBV-transgenic mice. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 29, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Burda, M.R.; Török, E.; Pollok, J.M.; Iwanska, A.; Sommer, G.; Rogiers, X.; Rogler, C.E.; Gupta, S.; Will, H.; et al. Repopulation of mouse liver with human hepatocytes and in vivo infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2001, 33, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateno, C.; Kawase, Y.; Tobita, Y.; Hamamura, S.; Ohshita, H.; Yokomichi, H.; Sanada, H.; Kakuni, M.; Shiota, A.; Kojima, Y.; et al. Generation of Novel Chimeric Mice with Humanized Livers by Using Hemizygous cDNA-uPA/SCID Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azuma, H.; Paulk, N.; Ranade, A.; Dorrell, C.; Al-Dhalimy, M.; Ellis, E.; Strom, S.; Kay, M.A.; Finegold, M.; Grompe, M. Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah−/−/Rag2−/−/Il2rg−/− mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grompe, M.; Lindstedt, S.; al-Dhalimy, M.; Kennaway, N.G.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Torres-Ramos, C.A.; Ou, C.N.; Finegold, M. Pharmacological correction of neonatal lethal hepatic dysfunction in a murine model of hereditary tyrosinaemia type I. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissig, K.D.; Wieland, S.F.; Tran, P.; Isogawa, M.; Le, T.T.; Chisari, F.V.; Verma, I.M. Human liver chimeric mice provide a model for hepatitis B and C virus infection and treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, Y.P.; Dorner, M.; Mommersteeg, M.C.; Xiao, J.W.; Balazs, A.B.; Robbins, J.B.; Winer, B.Y.; Gerges, S.; Vega, K.; Labitt, R.N.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies abrogate established hepatitis C virus infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 254ra129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.F.; Wang, Q.; Chu, J.X.; Liu, A.L. Effects of retrorsine on mouse hepatocyte proliferation after liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kawai, K.; Mitsui, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Monnai, M.; Wakui, M.; Ito, M.; Suematsu, M.; Peltz, G.; Nakamura, M.; et al. The reconstituted ‘humanized liver’ in TK-NOG mice is mature and functional. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosaka, K.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Yoshimi, S.; Murakami, E.; Nakahara, T.; Honda, Y.; Ono, A.; Kawaoka, T.; Tsuge, M.; et al. A novel TK-NOG based humanized mouse model for the study of HBV and HCV infections. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billerbeck, E.; Mommersteeg, M.C.; Shlomai, A.; Xiao, J.W.; Andrus, L.; Bhatta, A.; Vercauteren, K.; Michailidis, E.; Dorner, M.; Krishnan, A.; et al. Humanized mice efficiently engrafted with fetal hepatoblasts and syngeneic immune cells develop human monocytes and NK cells. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strick-Marchand, H.; Dusséaux, M.; Darche, S.; Huntington, N.D.; Legrand, N.; Masse-Ranson, G.; Corcuff, E.; Ahodantin, J.; Weijer, K.; Spits, H.; et al. A novel mouse model for stable engraftment of a human immune system and human hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bility, M.T.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Li, F.; Chi, L.; Zhang, L.; Tu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: Induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Guo, X.; et al. HBV infection-induced liver cirrhosis development in dual-humanised mice with human bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Gut 2019, 68, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Michalak, T.I. Asymptomatic Hepadnaviral Persistence and Its Consequences in the Woodchuck Model of Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.R.; Kao, J.H.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, T.C.; Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.H.; Su, T.H.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Liu, C.J. Clinical and virological features of occult hepatitis B in patients with HBsAg seroclearance post-treatment or spontaneously. Liver Int. 2014, 34, e71–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Vikash, V.; Wang, Q.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M.; Yang, D.; Liu, J. Transcriptome Analysis and Comparison of Marmota monax and Marmota himalayana. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Cullen, J.; Moraleda, G.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.E.; Miller, D.S.; Tennant, B.; Frick, L.; Averett, D.; Condreay, L.D.; et al. Lamivudine therapy of WHV-infected woodchucks. Virology 1998, 245, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairman, J.; Liu, K.H.; Menne, S. Prevention of liver tumor formation in woodchucks with established hepatocellular carcinoma by treatment with cationic liposome-DNA complexes. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavis, J.E.; Massey, B.; Gong, Y. The duck hepatitis B virus polymerase is activated by its RNA packaging signal, epsilon. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5789–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavis, J.E.; Ganem, D. Evidence for activation of the hepatitis B virus polymerase by binding of its RNA template. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5741–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.Y.; Ma, X.Z.; Ouyang, B.; Ings, D.P.; Marwah, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, A.Y.; Gupta, R.; Manuel, J.; Chen, X.C.; et al. Nanoparticle Uptake in a Spontaneous and Immunocompetent Woodchuck Liver Cancer Model. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4698–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Kang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Li, M.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. The function of targeted host genes determines the oncogenicity of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, J.; Vogel, M.; Nassal, M. dNTP versus NTP discrimination by phenylalanine 451 in duck hepatitis B virus P protein indicates a common structure of the dNTP-binding pocket with other reverse transcriptases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junker-Niepmann, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Schaller, H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavis, J.E.; Ganem, D. RNA sequences controlling the initiation and transfer of duck hepatitis B virus minus-strand DNA. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4283–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.T.; Coates, L.; Aldrich, C.E.; Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. In hepatocytes infected with duck hepatitis B virus, the template for viral RNA synthesis is amplified by an intracellular pathway. Virology 1990, 175, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Smith, P.M.; Horwich, A.L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colledge, D.; Civitico, G.; Locarnini, S.; Shaw, T. In vitro antihepadnaviral activities of combinations of penciclovir, lamivudine, and adefovir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campagna, M.R.; Liu, F.; Mao, R.; Mills, C.; Cai, D.; Guo, F.; Zhao, X.; Ye, H.; Cuconati, A.; Guo, H.; et al. Sulfamoylbenzamide derivatives inhibit the assembly of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6931–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.; Li, J.; Wands, J.R. Carboxypeptidase D is an avian hepatitis B virus receptor. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8696–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Barrera, A.; Brasky, K.M. An infectious clone of woolly monkey hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7814–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mason, W.S.; Cullen, J.; Saputelli, J.; Wu, T.T.; Liu, C.; London, W.T.; Lustbader, E.; Schaffer, P.; O’Connell, A.P.; Fourel, I. Characterization of the antiviral effects of 2’carbodeoxyguanosine in ducks chronically infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 1994, 19, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ange-van Heugten, K.D.; Burns, R.; Verstegen, M.W.; Jansen, W.L.; Ferket, P.R.; van Heugten, E. Evaluation of diabetes determinants in woolly monkeys (Lagothrix lagotricha). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2007, 91, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagell, S.; Whipple, A.V.; Chambers, C.L. Population genetic patterns among social groups of the endangered Central American spider monkey (Ateles geoffroyi) in a human-dominated landscape. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, B.Y.; Ding, Q.; Gaska, J.M.; Ploss, A. In vivo models of hepatitis B and C virus infection. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kock, J.; Nassal, M.; MacNelly, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Blum, H.E.; von Weizsacker, F. Efficient infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes with purified human and woolly monkey hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5084–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanada, T.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Ezzikouri, S.; Benjelloun, S.; Murakami, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Tateno, C.; Kohara, M. Property of hepatitis B virus replication in Tupaia belangeri hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burwitz, B.J.; Wettengel, J.M.; Muck-Hausl, M.A.; Ringelhan, M.; Ko, C.; Festag, M.M.; Hammond, K.B.; Northrup, M.; Bimber, B.N.; Jacob, T.; et al. Hepatocytic expression of human sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide enables hepatitis B virus infection of macaques. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Guilhot, S.; Klopchin, K.; Moss, B.; Pinkert, C.A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L.; Kanagawa, O.; Chisari, F.V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science 1990, 248, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julander, J.G.; Colonno, R.J.; Sidwell, R.W.; Morrey, J.D. Characterization of antiviral activity of entecavir in transgenic mice expressing hepatitis B virus. Antivir. Res. 2003, 59, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Bertoletti, A. Tolerance and immunity to pathogens in early life: Insights from HBV infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.F.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V. Intrahepatic induction of alpha/beta interferon eliminates viral RNA-containing capsids in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, J.L.; Gardiner, L.; Nishimura, S.; Shinkai, K.; Locksley, R.; Ganem, D. Activation of a nonclassical NKT cell subset in a transgenic mouse model of hepatitis B virus infection. Immunity 2002, 16, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Publicover, J.; Goodsell, A.; Nishimura, S.; Vilarinho, S.; Wang, Z.E.; Avanesyan, L.; Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J.; Cooper, S.; Baron, J.L. IL-21 is pivotal in determining age-dependent effectiveness of immune responses in a mouse model of human hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publicover, J.; Jespersen, J.M.; Johnson, A.J.; Nishimura, S.L.; Goodsell, A.; Wakil, A.E.; Rosenthal, P.; Pai, E.; Avanesyan, L.; Cooper, S.; et al. Liver capsule: Age-influenced hepatic immune priming determines HBV infection fate: Implications from mouse to man. Hepatology 2016, 63, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Publicover, J.; Gaggar, A.; Nishimura, S.; Van Horn, C.M.; Goodsell, A.; Muench, M.O.; Reinhardt, R.L.; van Rooijen, N.; Wakil, A.E.; Peters, M.; et al. Age-dependent hepatic lymphoid organization directs successful immunity to hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3728–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprinzl, M.F.; Oberwinkler, H.; Schaller, H.; Protzer, U. Transfer of hepatitis B virus genome by adenovirus vectors into cultured cells and mice: Crossing the species barrier. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5108–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dion, S.; Bourgine, M.; Godon, O.; Levillayer, F.; Michel, M.L. Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer leads to persistent hepatitis B virus replication in mice expressing HLA-A2 and HLA-DR1 molecules. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5554–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeissig, S.; Murata, K.; Sweet, L.; Publicover, J.; Hu, Z.; Kaser, A.; Bosse, E.; Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M.M.; Balschun, K.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-induced lipid alterations contribute to natural killer T cell-dependent protective immunity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, D.; Peng, H.; Su, L.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhang, L. A mouse model for HBV immunotolerance and immunotherapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Salvetti, A.; Marniquet, X.; Mailly, L.; Testoni, B.; Fusil, F.; Inchauspe, A.; Michelet, M.; Michel, M.L.; Levrero, M.; et al. Detection of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) covalently-closed-circular DNA (cccDNA) in mice transduced with a recombinant AAV-HBV vector. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Bai, W.; Jia, B.; Hu, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Bourgine, M.M.; Michel, M.L.; et al. Adenoviral delivery of recombinant hepatitis B virus expressing foreign antigenic epitopes for immunotherapy of persistent viral infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3004–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Hirsch, M.L.; Zhang, L.; Samulski, R.J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Mediated Delivery of the HBV Genome Induces Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Cui, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus persistence in mice reveals IL-21 and IL-33 as regulators of viral clearance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Zeng, J.; Yu, Y.; Xiang, K.; Hu, H.; Zhou, X.; Gu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Young, J.A.T.; et al. HBVcircle: A novel tool to investigate hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, R.; Ding, S.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, Q.; Guan, G.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, H.; Nunes, F.; et al. The gRNA-miRNA-gRNA Ternary Cassette Combining CRISPR/Cas9 with RNAi Approach Strongly Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3090–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, P.J. Hydrodynamic HBV Transfection Mouse Model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1540, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Guo, L.; Chen, C.; Gu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, G.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Liao, X.; et al. CXCL13-mediated recruitment of intrahepatic CXCR5. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, D.; Chang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Lan, K.; Deng, Q. Recombinant covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus induces long-term viral persistence with chronic hepatitis in a mouse model. Hepatology 2018, 67, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhou, G.; Yang, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated p53 and Pten dual mutation accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis in adult hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.H.; Fang, C.C.; Tsuneyama, K.; Chou, H.Y.; Pan, W.Y.; Shih, Y.M.; Wu, P.Y.; Chen, Y.; Leung, P.S.; Gershwin, M.E.; et al. A murine model of hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular carcinoma generated by adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchida, T.; Imamura, M.; Kan, H.; Hiraga, N.; Hayes, C.N.; Tsuge, M.; Abe-Chayama, H.; Aikata, H.; Makokha, G.N.; Miki, D.; et al. Usefulness of humanized cDNA-uPA/SCID mice for the study of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus virology. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, P.; Libbrecht, L.; De Vos, R.; de Hemptinne, B.; Gevaert, K.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Roskams, T.; Leroux-Roels, G. Morphological and biochemical characterization of a human liver in a uPA-SCID mouse chimera. Hepatology 2005, 41, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, D.F.; Schiller, D.E.; Elliott, J.F.; Douglas, D.N.; Hao, C.; Rinfret, A.; Addison, W.R.; Fischer, K.P.; Churchill, T.A.; Lakey, J.R.; et al. Hepatitis C virus replication in mice with chimeric human livers. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, M.L.; Bility, M.T.; Zhang, L.; Kovalev, G.I.; Buntzman, A.; Frelinger, J.A.; Barry, W.; Ploss, A.; Rice, C.M.; Su, L. A humanized mouse model to study hepatitis C virus infection, immune response, and liver disease. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesfaye, A.; Stift, J.; Maric, D.; Cui, Q.; Dienes, H.P.; Feinstone, S.M. Chimeric mouse model for the infection of hepatitis B and C viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ling, C.; Zhong, L.; Li, M.; Su, Q.; He, R.; Tang, Q.; Greiner, D.L.; Shultz, L.D.; Brehm, M.A.; et al. Efficient and Targeted Transduction of Nonhuman Primate Liver with Systemically Delivered Optimized AAV3B Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heckel, J.L.; Sandgren, E.P.; Degen, J.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Neonatal bleeding in transgenic mice expressing urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Cell 1990, 62, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, E.P.; Palmiter, R.D.; Heckel, J.L.; Daugherty, C.C.; Brinster, R.L.; Degen, J.L. Complete hepatic regeneration after somatic deletion of an albumin-plasminogen activator transgene. Cell 1991, 66, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, B.Y.; Huang, T.; Low, B.E.; Avery, C.; Pais, M.A.; Hrebikova, G.; Siu, E.; Chiriboga, L.; Wiles, M.V.; Ploss, A. Recapitulation of treatment response patterns in a novel humanized mouse model for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Virology 2017, 502, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.; Vercauteren, K.; Mancio-Silva, L.; Andrus, L.; Jahan, C.; Ricardo-Lax, I.; Zou, C.; Kabbani, M.; Park, P.; Quirk, C.; et al. Expansion, in vivo-ex vivo cycling, and genetic manipulation of primary human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Miyagi, T.; Hikita, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Mukai, K.; Nawa, T.; Sakamori, R.; Ohkawa, K.; Hiramatsu, N.; Takahashi, T.; et al. The Hepatitis B Virus Genotype Affects the Persistence of Viral Replication in Immunodeficient NOG Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabori, T.; Hikita, H.; Murai, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Kai, Y.; Makino, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Wada, H.; Eguchi, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide inhibition efficiently blocks hepatitis B virus spread in mice with a humanized liver. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutti, T.L.; Knibbe, J.S.; Makarov, E.; Zhang, J.; Yannam, G.R.; Gorantla, S.; Sun, Y.; Mercer, D.F.; Suemizu, H.; Wisecarver, J.L.; et al. Human hepatocytes and hematolymphoid dual reconstitution in treosulfan-conditioned uPA-NOG mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, E.M.; Bial, J.; Tarlow, B.; Bial, G.; Jensen, B.; Greiner, D.L.; Brehm, M.A.; Grompe, M. Extensive double humanization of both liver and hematopoiesis in FRGN mice. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 13, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dusséaux, M.; Masse-Ranson, G.; Darche, S.; Ahodantin, J.; Li, Y.; Fiquet, O.; Beaumont, E.; Moreau, P.; Rivière, L.; Neuveut, C.; et al. Viral Load Affects the Immune Response to HBV in Mice With Humanized Immune System and Liver. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1647–1661.e1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bility, M.T.; Nio, K.; Li, F.; McGivern, D.R.; Lemon, S.M.; Feeney, E.R.; Chung, R.T.; Su, L. Chronic hepatitis C infection-induced liver fibrogenesis is associated with M2 macrophage activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Khoury, M.; Limmon, G.; Choolani, M.; Chan, J.K.; Chen, J. Human fetal hepatic progenitor cells are distinct from, but closely related to, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sze, C.W.; Keng, C.T.; Al-Haddawi, M.; Liu, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Kwek, H.L.; Her, Z.; Chan, X.Y.; Barnwal, B.; et al. Hepatitis C virus mediated chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis in the humanised immune system and liver mouse model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lunemann, S.; Schöbel, A.; Kah, J.; Fittje, P.; Hölzemer, A.; Langeneckert, A.E.; Hess, L.U.; Poch, T.; Martrus, G.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; et al. Interactions Between KIR3DS1 and HLA-F Activate Natural Killer Cells to Control HCV Replication in Cell Culture. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1366–1371.e1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploss, A.; Strick-Marchand, H.; Li, W. Animal Models for Hepatitis B: Does the Supply Meet the Demand? Gastroenterology 2021, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Khoury, M.; Chen, J. Expression of human cytokines dramatically improves reconstitution of specific human-blood lineage cells in humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21783–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douam, F.; Ziegler, C.G.K.; Hrebikova, G.; Fant, B.; Leach, R.; Parsons, L.; Wang, W.; Gaska, J.M.; Winer, B.Y.; Heller, B.; et al. Selective expansion of myeloid and NK cells in humanized mice yields human-like vaccine responses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Mention, J.J.; Court, N.; Masse-Ranson, G.; Toubert, A.; Spits, H.; Legrand, N.; Corcuff, E.; Strick-Marchand, H.; Di Santo, J.P. A novel Flt3-deficient HIS mouse model with selective enhancement of human DC development. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Balazs, A.B.; Rao, D.S.; Kivork, C.; Yang, L.; Baltimore, D. Lentiviral vector delivery of human interleukin-7 (hIL-7) to human immune system (HIS) mice expands T lymphocyte populations. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willinger, T.; Rongvaux, A.; Strowig, T.; Manz, M.G.; Flavell, R.A. Improving human hemato-lymphoid-system mice by cytokine knock-in gene replacement. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.A.; Covassin, L.; Brehm, M.A.; Racki, W.; Pearson, T.; Leif, J.; Laning, J.; Fodor, W.; Foreman, O.; Burzenski, L.; et al. Human peripheral blood leucocyte non-obese diabetic-severe combined immunodeficiency interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene mouse model of xenogeneic graft-versus-host-like disease and the role of host major histocompatibility complex. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covassin, L.; Laning, J.; Abdi, R.; Langevin, D.L.; Phillips, N.E.; Shultz, L.D.; Brehm, M.A. Human peripheral blood CD4 T cell-engrafted non-obese diabetic-scid IL2rgamma(null) H2-Ab1 (tm1Gru) Tg (human leucocyte antigen D-related 4) mice: A mouse model of human allogeneic graft-versus-host disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Saito, Y.; Najima, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Ochi, T.; Tomizawa, M.; Doi, T.; Sone, A.; Suzuki, N.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Generation of functional human T-cell subsets with HLA-restricted immune responses in HLA class I expressing NOD/SCID/IL2r gamma(null) humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13022–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strowig, T.; Gurer, C.; Ploss, A.; Liu, Y.F.; Arrey, F.; Sashihara, J.; Koo, G.; Rice, C.M.; Young, J.W.; Chadburn, A.; et al. Priming of protective T cell responses against virus-induced tumors in mice with human immune system components. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, S.; Pearson, T.; Friberg, H.; Shultz, L.D.; Greiner, D.L.; Rothman, A.L.; Mathew, A. Dengue virus infection and virus-specific HLA-A2 restricted immune responses in humanized NOD-scid IL2rgammanull mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, R.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Rosenberger, J.; Surls, J.; Richie, T.L.; Brumeanu, T.D.; Casares, S. Expression of HLA class II molecules in humanized NOD.Rag1KO.IL2RgcKO mice is critical for development and function of human T and B cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, T.; Katano, I.; Ito, R.; Ito, M.; Harigae, H.; Ishii, N.; Sugamura, K. Induction of human humoral immune responses in a novel HLA-DR-expressing transgenic NOD/Shi-scid/gammacnull mouse. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billerbeck, E.; Horwitz, J.A.; Labitt, R.N.; Donovan, B.M.; Vega, K.; Budell, W.C.; Koo, G.C.; Rice, C.M.; Ploss, A. Characterization of human antiviral adaptive immune responses during hepatotropic virus infection in HLA-transgenic human immune system mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Uchida, T.; Xia, Y.; Umarova, R.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; Gaggar, A.; Suri, V.; Mucke, M.M.; Vermehren, J.; et al. Diminished hepatic IFN response following HCV clearance triggers HBV reactivation in coinfection. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3205–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Bierwolf, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Lutgehetmann, M. Hepatitis Delta co-infection in humanized mice leads to pronounced induction of innate immune responses in comparison to HBV mono-infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giersch, K.; Helbig, M.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Mancke, L.V.; Lohse, A.W.; Polywka, S.; Pollok, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Taylor, J.; et al. Persistent hepatitis D virus mono-infection in humanized mice is efficiently converted by hepatitis B virus to a productive co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giersch, K.; Homs, M.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Allweiss, L.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Buti, M.; Pollicino, T.; Sureau, C.; et al. Both interferon alpha and lambda can reduce all intrahepatic HDV infection markers in HBV/HDV infected humanized mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Mancke, L.V.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Allweiss, L.; Bornscheuer, T.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Urban, S.; et al. Humanized chimeric uPA mouse model for the study of hepatitis B and D virus interactions and preclinical drug evaluation. Hepatology 2012, 55, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.A.; Yu, M.L.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis B reactivation during or after direct acting antiviral therapy—Implication for susceptible individuals. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 651–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.P.; Crane, M.; Audsley, J.; Avihingsanon, A.; Sasadeusz, J.; Lewin, S.R. HIV-hepatitis B virus coinfection: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. AIDS 2017, 31, 2035–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, K.; Luo, J. HIV-HBV and HIV-HCV Coinfection and Liver Cancer Development. Cancer Treat. Res. 2019, 177, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissig-Choisat, B.; Alves-Bezerra, M.; Zorman, B.; Ochsner, S.A.; Barzi, M.; Legras, X.; Yang, D.; Borowiak, M.; Dean, A.M.; York, R.B.; et al. A human liver chimeric mouse model for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JHEP Rep. 2021, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Natural HBV Variant: | Permissive to | Barrier for Natural HBV Infection: | Potential Recombination Events with: | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Human | HBV | HBV | None | chHBV; gibHBV |
 Chimpanzee | chHBV | HBV chHBV | None | HBV; gorilla-specific HBV variants |
 Cynomolgus monkey | Possibly mcHBV | HBV (in hNTCP-expressing hepatocytes) | 158R residue of NTCP receptor | N/A |
 Woolly monkey | WMHBV | WMHBV | NTCP receptor | N/A |
 Rhesus macaque | N/A | HBV (in hNTCP-expressing hepatocytes) | 158R residue of NTCP receptor | N/A |
 Gorilla | Gorilla-specific HBV | Gorilla-specific HBV; Possibly chHBV | N/A | chHBV |
 Gibbon | gibHBV | gibHBV | N/A | HBV |
 Squirrel monkey | N/A | WMHBV | Unknown (contains 158G of NTCP receptor, like human) | N/A |
 Spider monkey | N/A | WMHBV | Unknown | N/A |
| Animal Models | Hepadnavirus | Viral Entry | Infection/Replication | cccDNA Formation | Immune Status | Inbred/Outbred | Gene Modification | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chimpanzee | HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | immunocompetent | No | - | [51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Tupaia | HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | immunocompetent | No | - | [34,40,58] |
| Woodchuck | WHBV | Yes | infection | Yes | immunocompetent | No | - | [48,59,60] |
| Duck | DHBV | Yes | infection | Yes | immunocompetent | No | - | [49,61,62] |
| Woolly monkey | WMHBV | Yes | infection | Yes | immunocompetent | No | - | [50,63,64] |
| HBV transgenic mouse model | HBV | No | - | No | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBsAg | Yes | PreS1, S and x transgene | [65,66,67] |
| HBV | No | - | No | immunocompetent | Yes | x transgene | [68,69] | |
| HBV | No | - | No | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBeAg, HBcAg | Yes | PreC/C transgene | [70] | |
| HBV | No | replication | No | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBV | Yes | 1.1 mer genome transgene | [71] | |
| HBV | No | replication | No | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBV | Yes | 1.2 mer genome transgene | [71] | |
| HBV | No | replication | No | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBV | Yes | 1.3 mer genome transgene | [71,72,73] | |
| HBV | No | replication | Yes | Immunocompetent, tolerance to HBV | Yes | HNF1 α−/−/1.3×HBV-C57BL/6/Sv/129 | [46] | |
| HBV | Yes | replication | No | Immunodeficient | Yes | hNTCP/BAC/1.3×HBV-NRG | [44] | |
| Human liver chimeric mouse model | HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | Immunodeficient | Yes | Alb-uPA/Rag2+hHep | [74] |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | Immunodeficient | Yes | cDNA-uPA/SCID+hHep | [75] | |
| Yes | infection | Yes | Immunodeficient | Yes | Fah−/− /Rag2−/− / IL2rγ−/− (FRG)+hHep | [76,77,78] | ||
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | Immunodeficient | Yes | Fah−/−NODRag1−/− IL2rγcnull (FNRG)+hHep | [79,80] | |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | Immunodeficient | Yes | HSVtk-NOG(TK-NOG)+hHep | [81,82] | |
| Dual chimeric mouse model | HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | HIS | Yes | Fah−/− /Rag2−/− / IL2rγ−/− (FRG)+HSC+hHep | [83] |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | HIS | Yes | Fah−/− /NODRag1−/− / IL2rγ−/− (FNRG) +HSC+hHep | [83] | |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | HIS | Yes | BALB/c Rag2−/−Il2rγ−/−SirpaNODAlb-uPAtg/tg (BRGS-uPA)+HSC+hHep | [84] | |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | HIS | Yes | HLA-A2 NOD-SCID-IL2rγ−/−(A2/NSG)+HSC+hHep | [85] | |
| HBV | Yes | infection | Yes | HIS | Yes | Fah−/−Rag2−/−IL-2Rγc−/− SCID +hBMSC+hHep | [86] |
| Model | Features | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3×HBV tg mice | Contains 1.3×HBV integrated into murine genome |
|
| [71,112] |
| HDI-based replication-competent HBV tg mice | HBV replicons, i.e., 1.2×, 1.3×HBV or HBVcircle genomes, are hydrodynamically injected into mice through tail vein injection |
|
| [128,129,130] |
| Adeno-HBV tg mice | Adenovirus vectors containing HBV genome are injected into mice |
|
| [126,127,135] |
| AAV-HBV tg mice | AAV vectors containing HBV genome are injected into mice |
|
| [122,124,125] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Maya, S.; Ploss, A. Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection–Success, Challenges, and Future Directions. Viruses 2021, 13, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050777
Liu Y, Maya S, Ploss A. Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection–Success, Challenges, and Future Directions. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yongzhen, Stephanie Maya, and Alexander Ploss. 2021. "Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection–Success, Challenges, and Future Directions" Viruses 13, no. 5: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050777
APA StyleLiu, Y., Maya, S., & Ploss, A. (2021). Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection–Success, Challenges, and Future Directions. Viruses, 13(5), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050777








