Multiplex PCR-Based Nanopore Sequencing and Epidemiological Surveillance of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius, Republic of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Mitochondrial DNA Analysis
2.4. Indirect Immunofluorescence Antibody Test
2.5. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.6. Quantitative PCR
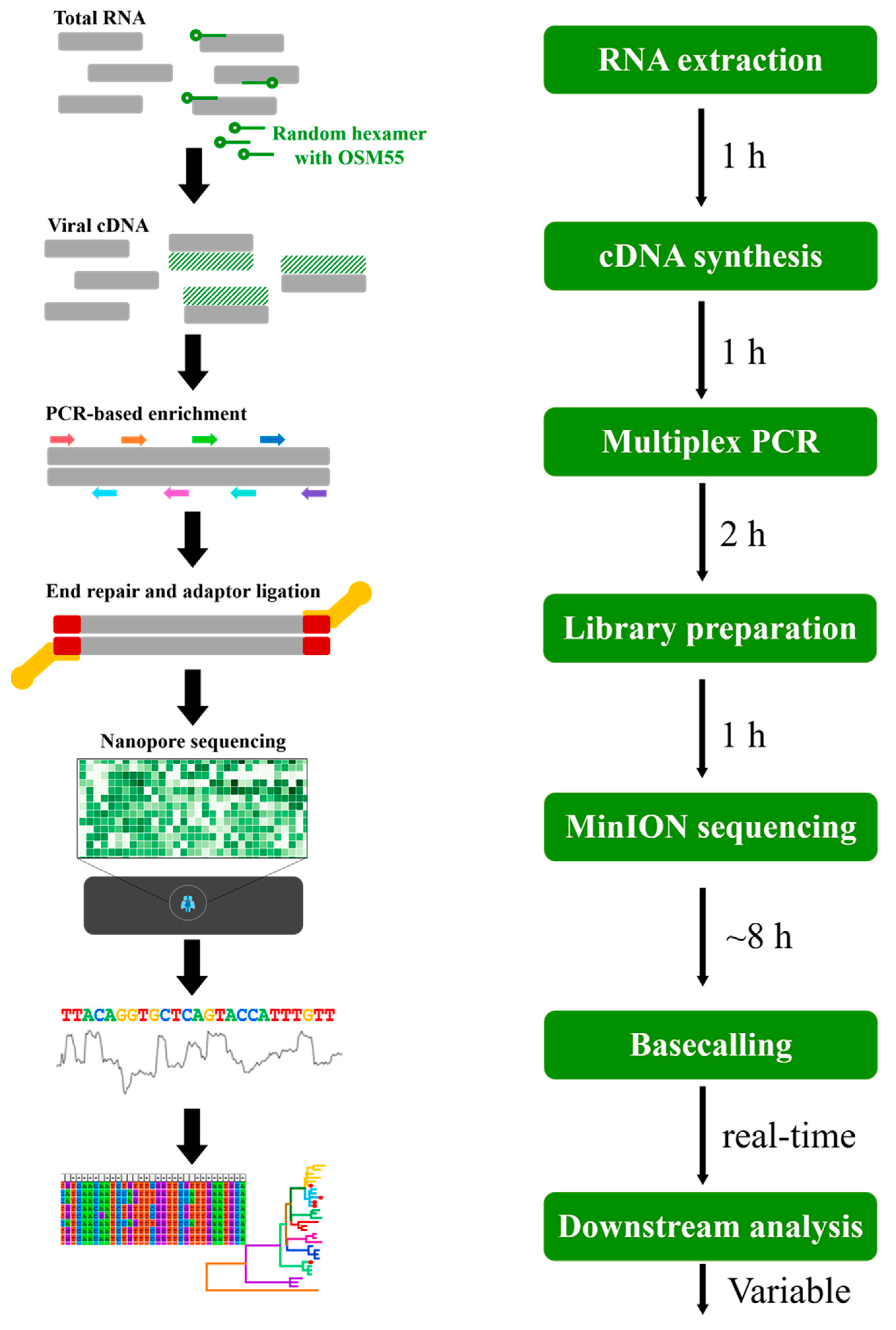
2.7. Multiplex PCR-Based Enrichment
2.8. Library Preparation for Sequencing on MinION Platform
2.9. Library Preparation for Sequencing on MiSeq Platform
2.10. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trapping Sites of Small Mammals from the ROK
3.2. Serological and Molecular Prevalence of HTNV Collected from the ROK
3.3. HTNV RNA Loads and Determination of Viral Copy Number from A. agrarius Lung Tissues
3.4. Multiplex PCR-Based NGS of HTNV Using MinION or MiSeq Platforms
3.5. Phylogeographic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaheri, A.; Henttonen, H.; Voutilainen, L.; Mustonen, J.; Sironen, T.; Vapalahti, O. Hantavirus infections in Europe and their impact on public health. Revi. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laenen, L.; Vergote, V.; Calisher, C.H.; Klempa, B.; Klingstrom, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; Maes, P. Hantaviridae: Current Classification and Future Perspectives. Viruses 2019, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.J.; Simpson, G.L.; Levy, H. Spectrum of hantavirus infection: Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Annu. Rev. Med. 1999, 50, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, M.; Delaere, B.; Weynand, B.; Clement, J.; Maes, P.; Vergote, V.; Laenen, L.; Hjelle, B.; Verroken, A.; Dive, A. Another case of “European hantavirus pulmonary syndrome” with severe lung, prior to kidney, involvement, and diagnosed by viral inclusions in lung macrophages. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagihara, R.; Gu, S.H.; Arai, S.; Kang, H.J.; Song, J.W. Hantaviruses: Rediscovery and new beginnings. Virus Res. 2014, 187, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.P.; Lin, X.D.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.H.; Cong, M.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, M.R.; Zhou, R.H.; Wang, J.B.; Li, M.H.; et al. Phylogeny and origins of hantaviruses harbored by bats, insectivores, and rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, S.N.; Gu, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Arai, S.; Yanagihara, R. Reconstructing the evolutionary origins and phylogeography of hantaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, K.M.; Sironen, T.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus maintenance and transmission in reservoir host populations. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.F. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: Mode of transmission to humans. Lab. Anim. Sci 1987, 37, 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.D.; Chapman, D.; Dixon, L.; Chantrey, J.; Darby, A.C.; Hall, N. Application of next-generation sequencing technologies in virology. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, J.G.; Kapoor, A.; Dupuis, K.; Schnurr, D.P.; Delwart, E.L. Rapid identification of known and new RNA viruses from animal tissues. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, F.-X.; Schmitz, A.; Ogor, K.; Le Prioux, A.; Guillou-Cloarec, C.; Guillemoto, C.; Allée, C.; Le Bras, M.-O.; Hirchaud, E.; Quenault, H. Emerging highly pathogenic H5 avian influenza viruses in France during winter 2015/16: Phylogenetic analyses and markers for zoonotic potential. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvala, H.; Frampton, D.; Grant, P.; Raffle, J.; Ferns, R.B.; Kozlakidis, Z.; Kellam, P.; Pillay, D.; Hayward, A.; Nastouli, E. Emergence of a novel subclade of influenza A (H3N2) virus in London, December 2016 to January 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Bahl, J.; Lycett, S.J.; Worobey, M.; Pybus, O.G.; Ma, S.K.; Cheung, C.L.; Raghwani, J.; Bhatt, S. Origins and evolutionary genomics of the 2009 swine-origin H1N1 influenza A epidemic. Nature 2009, 459, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gire, S.K.; Goba, A.; Andersen, K.G.; Sealfon, R.S.; Park, D.J.; Kanneh, L.; Jalloh, S.; Momoh, M.; Fullah, M.; Dudas, G. Genomic surveillance elucidates Ebola virus origin and transmission during the 2014 outbreak. Science 2014, 345, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neverov, A.; Chumakov, K. Massively parallel sequencing for monitoring genetic consistency and quality control of live viral vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20063–20068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnink, B.B.O.; Münger, E.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Kohl, R.; Van Der Linden, A.; Schapendonk, C.; Van Der Jeugd, H.; Kik, M.; Rijks, J.; Reusken, C. Genomic monitoring to understand the emergence and spread of Usutu virus in the Netherlands, 2016–2018. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.-K.; Kim, J.-A.; Song, D.H.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; No, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kho, J.H. Phylogeographic analysis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome patients using multiplex PCR-based next generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.H.; Kim, W.K.; Gu, S.H.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.A.; No, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Wiley, M.R.; Palacios, G.; Song, J.W.; et al. Sequence-Independent, Single-Primer Amplification Next-Generation Sequencing of Hantaan Virus Cell Culture-Based Isolates. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- No, J.S.; Kim, W.-K.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-A.; Lee, D.; Song, D.H.; Gu, S.H.; Jeong, S.T.; Wiley, M.R. Comparison of targeted next-generation sequencing for whole-genome sequencing of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius lung tissues. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Ruan, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Kreuze, J.F.; Fei, Z.; Zhu, X.; Gao, S. Using small RNA deep sequencing data to detect human viruses. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, A.L.; Roberts, H.E.; Bonsall, D.; de Cesare, M.; Mokaya, J.; Lumley, S.F.; Golubchik, T.; Piazza, P.; Martin, J.B.; de Lara, C. Illumina and Nanopore methods for whole genome sequencing of hepatitis B virus (HBV). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, N.R.; da Silva Azevedo, R.d.S.; Kraemer, M.U.; Souza, R.; Cunha, M.S.; Hill, S.C.; Thézé, J.; Bonsall, M.B.; Bowden, T.A.; Rissanen, I. Zika virus in the Americas: Early epidemiological and genetic findings. Science 2016, 352, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, C.M.; Yale, G.; Condori, R.E.; Costa, N.C.; Long, N.V.; Minh, P.Q.; Chuong, V.D.; Tho, N.D.; Thanh, N.T.; Thin, N.X. Portable Rabies Virus Sequencing in Canine Rabies Endemic Countries Using the Oxford Nanopore MinION. Viruses 2020, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paden, C.R.; Tao, Y.; Queen, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Uehara, A.; Tong, S. Rapid, sensitive, full-genome sequencing of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, J.; Loman, N.J.; Duraffour, S.; Simpson, J.T.; Severi, E.; Cowley, L.; Bore, J.A.; Koundouno, R.; Dudas, G.; Mikhail, A.; et al. Real-time, portable genome sequencing for Ebola surveillance. Nature 2016, 530, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L.; Naccache, S.N.; Federman, S.; Yu, G.; Mbala, P.; Bres, V.; Stryke, D.; Bouquet, J.; Somasekar, S.; Linnen, J.M. Rapid metagenomic identification of viral pathogens in clinical samples by real-time nanopore sequencing analysis. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M.; Kocher, T.D.; Wilson, A.C. Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 32, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, W.-K.; Park, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Hwang, J.; No, J.S.; Cho, S.; Lee, D.; Song, D.-H.; Gu, S.H.; et al. Phylogeographic diversity and hybrid zone of Hantaan orthohantavirus collected in Gangwon Province, Republic of Korea. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, J.S.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kho, J.H.; Lee, D.; Song, D.H.; Gu, S.H.; et al. Detection of Hantaan virus RNA from anti-Hantaan virus IgG seronegative rodents in an area of high endemicity in Republic of Korea. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabwe, E.; Davidyuk, Y.; Shamsutdinov, A.; Garanina, E.; Martynova, E.; Kitaeva, K.; Malisheni, M.; Isaeva, G.; Savitskaya, T.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; et al. Orthohantaviruses, Emerging Zoonotic Pathogens. Pathogens 2020, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Infectious Disease Portal. Available online: http://www.cdc.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/ist/bass/bassDissStatsMain.do (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Kim, J.A.; Kim, W.K.; No, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kho, J.H.; Lee, D.; Song, D.H.; Gu, S.H.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Reassortment of Hantaan Virus Tripartite RNA Genomes in Nature, the Republic of Korea. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryou, J.; Lee, H.I.; Yoo, Y.J.; Noh, Y.T.; Yun, S.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, E.H.; Han, M.G.; Ju, Y.R. Prevalence of hantavirus infection in wild rodents from five provinces in Korea, 2007. J. Wild Dis. 2011, 47, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, Y.P.; Kim, E.H.; Cheong, H.K. The influence of climatic factors on the development of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and leptospirosis during the peak season in Korea: An ecologic study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Moon, S.S.; Gu, S.H.; Song, K.J.; Baek, L.J.; Kim, H.C.; Kijek, T.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Lee, J.S.; Turell, M.J.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in 4 US soldiers, South Korea, 2005. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; No, J.S.; Lee, D.; Jung, J.; Park, H.; Yi, Y.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.; et al. Active Targeted Surveillance to Identify Sites of Emergence of Hantavirus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-K.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.-H.; No, J.S.; Lee, G.-Y.; Park, K.; Lee, D.; Jeong, S.T.; Song, J.-W. Genomic Epidemiology and Active Surveillance to Investigate Outbreaks of Hantaviruses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Martin, V.; Perales, C.; Grande-Perez, A.; Garcia-Arriaza, J.; Arias, A. Viruses as quasispecies: Biological implications. Quasispecies 2006, 299, 51–82. [Google Scholar]
- Vignuzzi, M.; Stone, J.K.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. Quasispecies diversity determines pathogenesis through cooperative interactions in a viral population. Nature 2006, 439, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardy, J.L.; Loman, N.J. Towards a genomics-informed, real-time, global pathogen surveillance system. Nat. Rev. Genet 2018, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.-d.; Park, W.B.; Park, S.-W.; Choe, P.G.; Bang, J.H.; Song, K.-H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, N.J. Middle East respiratory syndrome: What we learned from the 2015 outbreak in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, J.T.; Beitzel, B.; Chain, P.S.; Davenport, M.G.; Donaldson, E.; Frieman, M.; Kugelman, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; O’Rear, J.; Sabeti, P.C. Standards for sequencing viral genomes in the era of high-throughput sequencing. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macalalad, A.R.; Zody, M.C.; Charlebois, P.; Lennon, N.J.; Newman, R.M.; Malboeuf, C.M.; Ryan, E.M.; Boutwell, C.L.; Power, K.A.; Brackney, D.E. Highly sensitive and specific detection of rare variants in mixed viral populations from massively parallel sequence data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mitsuya, Y.; Gharizadeh, B.; Ronaghi, M.; Shafer, R.W. Characterization of mutation spectra with ultra-deep pyrosequencing: Application to HIV-1 drug resistance. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnink, B.B.O.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Stein, M.; O’Toole, Á.; Haverkate, M.; Mollers, M.; Kamga, S.K.; Schapendonk, C.; Pronk, M.; Lexmond, P. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 whole-genome sequencing and analysis for informed public health decision-making in the Netherlands. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina Technical Note: Sequencing. Quality scores for Next-Generation Sequencing. Assessing sequencing accuracy using Phred quality scoring. Available online: https://www.illumina.com/documents/products/technotes/technote_Q-Scores.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Jain, M.; Tyson, J.R.; Loose, M.; Ip, C.L.C.; Eccles, D.A.; O’Grady, J.; Malla, S.; Leggett, R.M.; Wallerman, O.; Jansen, H.J.; et al. MinION Analysis and Reference Consortium: Phase 2 data release and analysis of R9.0 chemistry. F1000Research 2017, 6, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, J.R.; O’Neil, N.J.; Jain, M.; Olsen, H.E.; Hieter, P.; Snutch, T.P. MinION-based long-read sequencing and assembly extends the Caenorhabditis elegans reference genome. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stancu, M.C.; Van Roosmalen, M.J.; Renkens, I.; Nieboer, M.M.; Middelkamp, S.; De Ligt, J.; Pregno, G.; Giachino, D.; Mandrile, G.; Valle-Inclan, J.E. Mapping and phasing of structural variation in patient genomes using nanopore sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Koren, S.; Miga, K.H.; Quick, J.; Rand, A.C.; Sasani, T.A.; Tyson, J.R.; Beggs, A.D.; Dilthey, A.T.; Fiddes, I.T.; et al. Nanopore sequencing and assembly of a human genome with ultra-long reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, N.J.; Quick, J.; Simpson, J.T. A complete bacterial genome assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyangwa, M.; Martynova, E.V.; Khaiboullina, S.F.; Morzunov, S.P.; Rizvanov, A.A. Hantaviral Proteins: Structure, Functions, and Role in Hantavirus Infection. Front Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiropoulou, C.F.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Shoemaker, T.R.; Peters, C.J.; Compans, R.W. Sin Nombre virus glycoprotein trafficking. Virology 2003, 308, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Ladner, J.T.; Lemey, P.; Pybus, O.G.; Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Andersen, K.G. Tracking virus outbreaks in the twenty-first century. Nat Microbiol. 2019, 4, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lewandowski, K.; Lumley, S.; Pullan, S.; Vipond, R.; Carroll, M.; Foster, D.; Matthews, P.C.; Peto, T.; Crook, D. Detection of viral pathogens with multiplex nanopore MinION sequencing: Be careful with cross-Talk. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, J.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Pullan, S.T.; Claro, I.M.; Smith, A.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Oliveira, G.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Rogers, T.F.; Beutler, N.A.; et al. Multiplex PCR method for MinION and Illumina sequencing of Zika and other virus genomes directly from clinical samples. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Species | Small Mammal Trapping Location | Total (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paju | Pocheon | Pyeongtaek | Yeoncheon | Cheorwon | Chuncheon | Hwacheon | ||
| Apodemus agrarius | 7 | 18 | 41 | 48 | 105 | 38 | 46 | 303 (86.6) |
| Crocidura lasiura | -a | - | - | 1 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 13 (3.7) |
| Crocidura shantungensis | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 (0.9) |
| Mus musculus | - | - | 7 | - | 9 | - | 1 | 17 (4.9) |
| Myodes regulus | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | 4 (1.1) |
| Micromys minutus | - | - | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | - | 5 (1.4) |
| Microtus fortis | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 (0.3) |
| Rattus norvegicus | - | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | 3 (0.9) |
| Tscherskia triton | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 (0.3) |
| Total | 9 | 18 | 53 | 50 | 125 | 45 | 50 | 350 (100) |
| Trapping Site | Number of Captured A. agrarius | Seropositivity for Anti-HTNV IgG (%) | HTNV RNA Positivity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | ||
| Paju | 7 | 0/2 | 0/5 | 0/7 | -a | - | - |
| Pocheon | 18 | 1/9 (11.1) | 0/9 | 1/18 (5.6) | 1/1 (100) | - | 1/1 (100) |
| Pyeongtaek | 41 | 0/23 | 0/18 | 0/41 | - | - | - |
| Yeoncheon | 48 | 2/22 (9.1) | 3/26 (11.5) | 5/48 (10.4) | 1/2 (50) | 1/3 (33.3) | 2/5 (40) |
| Cheorwon | 105 | 5/60 (8.3) | 2/45 (4.4) | 7/105 (6.7) | 4/5 (80) | 2/2 (100) | 6/7 (85.7) |
| Chuncheon | 38 | 0/18 | 1/20 (5) | 1/38 (2.6) | - | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| Hwacheon | 46 | 4/20 (20) | 2/26 (7.7) | 6/46 (13.0) | 3/4 (75) | 0/2 | 3/6 (50) |
| Total | 303 | 12/154 (7.8) | 8/149 (5.4) | 20/303 (6.6) | 9/12 (75) | 3/8 (37.5) | 12/20 (60) |
| Viral RNA Copy Number (Copies/µL) | Sample | Site | Anti-HTNV IgG Titer | Nested RT-PCR | Ct Value | HTNV Genomes, % Coverage (Minimum Read Depth, >10×) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L Segment | M Segment | S Segment | ||||||
| 104 to 105 | Aa19-233 | Cheorwon | 1:64 a | Pos | 20.5 | 96.8 | 98.5 | 100 |
| Aa19-278 | Cheorwon | 1:32 a | Pos | 22.2 | 92.9 | 98.4 | 100 | |
| 102 to 103 | Aa19-236 | Cheorwon | 1:32 a | Pos | 29.4 | 95.3 | 98.4 | 100 |
| Aa19-36 | Cheorwon | 1:512 b | Pos | 29.7 | 91.7 | 98.4 | 100 | |
| 10 to 102 | Aa19-89 | Yeoncheon | 1:64 a | Pos | 31.8 | 95.9 | 98.4 | 100 |
| Aa19-57 | Pocheon | 1:8096 b | Pos | 32.7 | 95.8 | 98.4 | 100 | |
| Aa19-167 | Yeoncheon | 1:256 a | Pos | 34.0 | 95.9 | 96.4 | 100 | |
| Aa19-38 | Cheorwon | 1:16,384 b | Pos | 34.4 | 92.3 | 98.4 | 100 | |
| Aa19-153 | Hwacheon | 1:4096 b | Pos | 34.5 | 92.7 | 98.4 | 100 | |
| 1 to 10 | Aa19-152 | Hwacheon | 1:512 a | Pos | 36.4 | 82.6 | 97.0 | 92.1 |
| Aa19-144 | Hwacheon | 1:256 b | Pos | 37.3 | 88.8 | 96.4 | 95.1 | |
| 0 to 1 | Aa19-39 | Cheorwon | 1:512 b | Pos | 40.0 | 65.4 | 90.6 | 92.2 |
| Viral RNA Copy Number (Copies/µL) | Sample | Site | Ct Value | L Segment | M Segment | S Segment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion | Deletion | Mismatch | Accuracy a | Insertion | Deletion | Mismatch | Accuracy | Insertion | Deletion | Mismatch | Accuracy | ||||
| 104 to 105 | Aa19-233 | Cheorwon | 20.5 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 99.8 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 99.8 |
| Aa19-278 | Cheorwon | 22.2 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 99.9 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| 102 to 103 | Aa19-236 | Cheorwon | 29.4 | 0 | 5 | 9 | 99.9 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 99.9 |
| Aa19-36 | Cheorwon | 29.7 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 99.8 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 99.9 | |
| 10 to 102 | Aa19-89 | Yeoncheon | 31.8 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 99.9 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 99.8 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 99.9 |
| Aa19-57 | Pocheon | 32.7 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 99.9 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 99.9 | |
| Aa19-167 | Yeoncheon | 34.0 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 99.9 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | |
| Aa19-38 | Cheorwon | 34.4 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 99.8 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 99.8 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 99.9 | |
| Aa19-153 | Hwacheon | 34.5 | 0 | 5 | 14 | 99.8 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 99.9 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 99.8 | |
| 1 to 10 | Aa19-152 | Hwacheon | 36.4 | 0 | 5 | 18 | 99.7 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 99.7 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 99.6 |
| Aa19-144 | Hwacheon | 37.3 | 0 | 4 | 14 | 99.8 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 99.7 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 99.6 | |
| 0 to 1 | Aa19-39 | Cheorwon | 40.0 | 0 | 2 | 59 | 99.1 | 0 | 2 | 36 | 99.0 | 0 | 1 | 28 | 98.3 |
| Total | Average (%) | 0 | 3.8 | 15.2 | 99.8 | 0 | 4.4 | 7.6 | 99.8 | 0 | 1 | 4.7 | 99.7 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.-Y.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.; No, J.S.; Budhathoki, S.; et al. Multiplex PCR-Based Nanopore Sequencing and Epidemiological Surveillance of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius, Republic of Korea. Viruses 2021, 13, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050847
Park K, Lee S-H, Kim J, Lee J, Lee G-Y, Cho S, Lee SH, Park K, No JS, Budhathoki S, et al. Multiplex PCR-Based Nanopore Sequencing and Epidemiological Surveillance of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius, Republic of Korea. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050847
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kyungmin, Seung-Ho Lee, Jongwoo Kim, Jingyeong Lee, Geum-Young Lee, Seungchan Cho, Seung Ho Lee, Kkothanahreum Park, Jin Sun No, Shailesh Budhathoki, and et al. 2021. "Multiplex PCR-Based Nanopore Sequencing and Epidemiological Surveillance of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius, Republic of Korea" Viruses 13, no. 5: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050847
APA StylePark, K., Lee, S.-H., Kim, J., Lee, J., Lee, G.-Y., Cho, S., Lee, S. H., Park, K., No, J. S., Budhathoki, S., Kim, Y.-J., Kim, Y.-S., Kim, H.-C., Klein, T. A., Kim, W.-K., & Song, J.-W. (2021). Multiplex PCR-Based Nanopore Sequencing and Epidemiological Surveillance of Hantaan orthohantavirus in Apodemus agrarius, Republic of Korea. Viruses, 13(5), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050847







