Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Testing Compared with Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Specimens
2.2. Quantification of Viral Load
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients
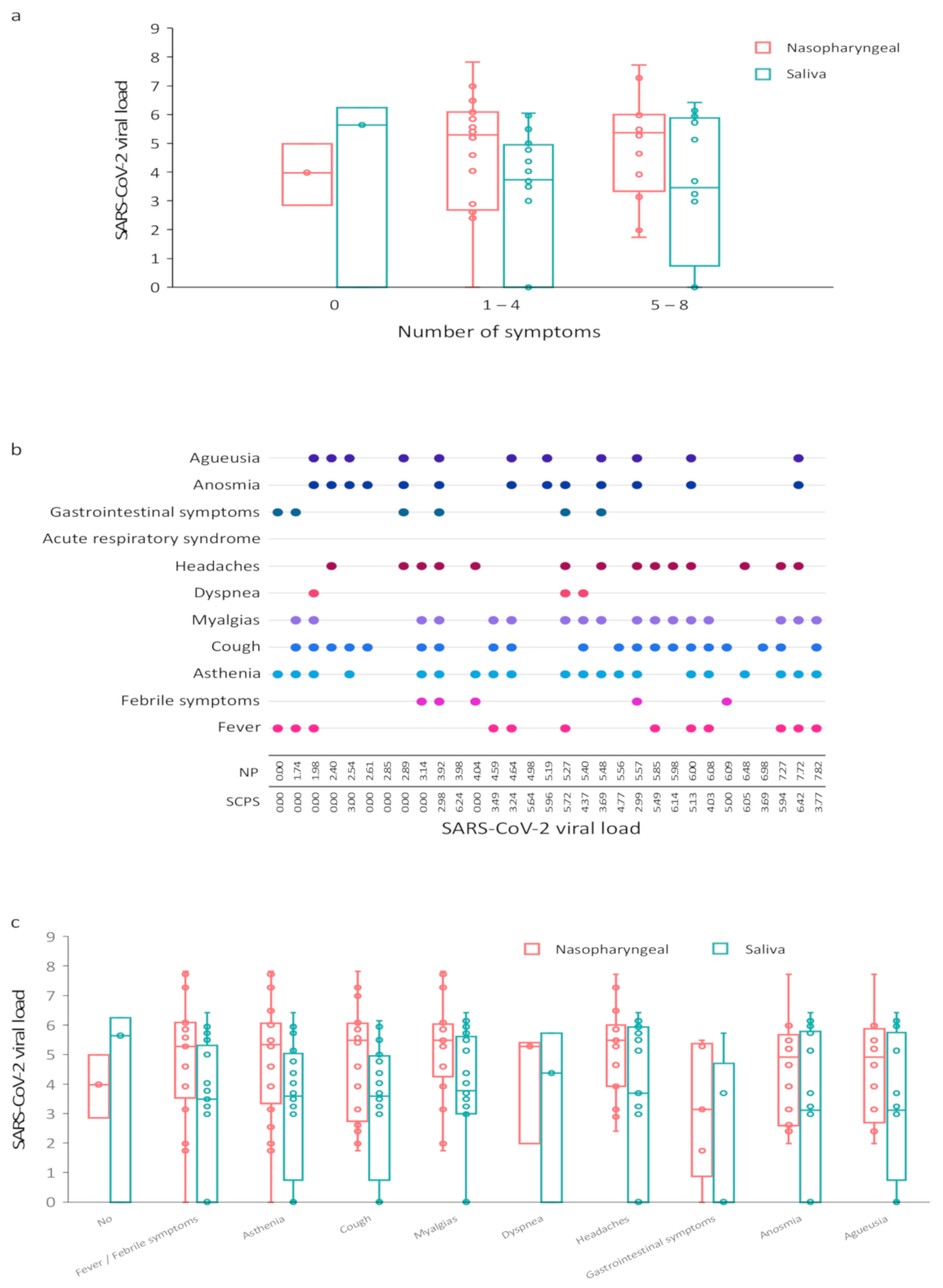
3.2. Comparison of Salivary and Nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load
3.3. Correlation between SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and COVID-19 Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, J.G.; Yoon, J.; Song, J.Y.; Yoon, S.Y.; Lim, C.S.; Seong, H.; Noh, J.Y.; Cheong, H.J.; Kim, W.J. Clinical Significance of a High SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in the Saliva. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.K.-W.; Tsang, O.T.-Y.; Chik-Yan Yip, C.; Chan, K.-H.; Wu, T.-C.; Chan, J.M.C.; Leung, W.-S.; Chik, T.S.-H.; Choi, C.Y.-C.; Kandamby, D.H.; et al. Consistent Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Saliva. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, I.; Shane, P.Y.; Okada, K.; Unoki, Y.; Yang, Y.; Inao, T.; Sakamaki, K.; Iwasaki, S.; Hayasaka, K.; Sugita, J.; et al. Mass Screening of Asymptomatic Persons for SARS-CoV-2 Using Saliva. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.C.-M.; Chow, V.C.-Y.; Lee, M.K.-P.; Lai, R.W.-M. Deep Throat Saliva as an Alternative Diagnostic Specimen Type for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procop, G.W.; Shrestha, N.K.; Vogel, S.; Van Sickle, K.; Harrington, S.; Rhoads, D.D.; Rubin, B.P.; Terpeluk, P. A Direct Comparison of Enhanced Saliva to Nasopharyngeal Swab for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Symptomatic Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, E.; Poulopoulos, A.; Tzimagiorgis, G. Salivary Diagnostics of the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Oral. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülsen, A. Simple Classification of COVID-19 Patients. J. Lung Pulm. Respir. Res. 2020, 7, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrouel, F.; Viennot, S.; Valette, M.; Cohen, J.-M.; Dussart, C.; Bourgeois, D. Salivary and Nasal Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus After Antiviral Mouthrinses (BBCovid): A Structured Summary of a Study Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial. Trials 2020, 21, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghoul, L.; Salmona, M.; Cherot, J.; Fahd, M.; Dalle, J.-H.; Vachon, C.; Perrod, A.; Bourgeois, P.; Scieux, C.; Baruchel, A.; et al. Evaluation of a New Device for Simplifying and Standardizing Stool Sample Preparation for Viral Molecular Testing with Limited Hands-On Time. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migueres, M.; Mengelle, C.; Dimeglio, C.; Didier, A.; Alvarez, M.; Delobel, P.; Mansuy, J.-M.; Izopet, J. Saliva Sampling for Diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Symptomatic Patients and Asymptomatic Carriers. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 130, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasomsub, E.; Watcharananan, S.P.; Boonyawat, K.; Janchompoo, P.; Wongtabtim, G.; Suksuwan, W.; Sungkanuparph, S.; Phuphuakrat, A. Saliva Sample as a Non-Invasive Specimen for the Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 285.e1–285.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Warren, J.L.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J.; et al. Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Bond, K.; Zhang, B.; Putland, M.; Williamson, D.A. Saliva as a Noninvasive Specimen for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Watkins, A.E.; Harden, C.A.; Brackney, D.E.; Shafer, J.; Wang, J.; Caraballo, C.; Kalinich, C.C.; Ott, I.M.; Fauver, J.R.; et al. SalivaDirect: A Simplified and Flexible Platform to Enhance SARS-CoV-2 Testing Capacity. Medicine 2021, 2, 263–280.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Fujisawa, S.; Nakakubo, S.; Kamada, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Fukumoto, T.; Sato, K.; Oguri, S.; Taki, K.; Senjo, H.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Nasopharyngeal Swab and Saliva. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e145–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahallawi, W.H.; Alsamiri, A.D.; Dabbour, A.F.; Alsaeedi, H.; Al-Zalabani, A.H. Association of Viral Load in SARS-CoV-2 Patients With Age and Gender. Front. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, M.; Tate, M.; Lloyd, O.; Maraolo, A.E.; Schafers, J.; Ho, A. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV Viral Load Dynamics, Duration of Viral Shedding, and Infectiousness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e13–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, I.; Hattori, T.; Shane, P.Y.; Konno, S.; Nagasaka, A.; Takeyabu, K.; Fujisawa, S.; Nishida, M.; Teshima, T. Equivalent SARS-CoV-2 Viral Loads by PCR between Nasopharyngeal Swab and Saliva in Symptomatic Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete, M.G.; Valenzuela, I.M.; Garcés, P.C.; Massó, I.C.; González, M.J.; Providell, S.G. Saliva Sample for the Massive Screening of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler-Laporte, G.; Lawandi, A.; Schiller, I.; Yao, M.; Dendukuri, N.; McDonald, E.G.; Lee, T.C. Comparison of Saliva and Nasopharyngeal Swab Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing for Detection of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, M.L.; Perlman-Arrow, S.; Menzies, D.; Campbell, J.R. The Sensitivity and Costs of Testing for SARS-CoV-2 Infection With Saliva Versus Nasopharyngeal Swabs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequences (5′-3′) | PCR Product |
|---|---|---|
| RdRp gen/nCoV_IP2 | 108 pb | |
| nCoV_IP2-12669Fw 1 | ATGAGCTTAGTCCTGTTG | |
| nCoV_IP2-12759Rv 1 | CTCCCTTTGTTGTGTTGT | |
| nCoV_IP2-12669bProbe (+) 1 | [5′]HEX-AGATGTCTTGTGCTGCCGGTA-[3′]BHQ-1 | |
| RdRp gene/nCoV_IP4 | 107 pb | |
| nCoV_IP4-14059Fw 1 | GGTAACTGGTATGATTTCG | |
| nCoV_IP4-14146Rv 1 | CTGGTCAAGGTTAATATAGG | |
| nCoV_IP4-14084Probe (+) 1 | [5′]Fam-TCATACAAACCACGCCAGG-[3′]BHQ-1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrouel, F.; Valette, M.; Perrier, H.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Dussart, C.; Tramini, P.; Bourgeois, D. Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Testing Compared with Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050895
Carrouel F, Valette M, Perrier H, Bouscambert-Duchamp M, Dussart C, Tramini P, Bourgeois D. Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Testing Compared with Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050895
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrouel, Florence, Martine Valette, Hervé Perrier, Maude Bouscambert-Duchamp, Claude Dussart, Paul Tramini, and Denis Bourgeois. 2021. "Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Testing Compared with Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2" Viruses 13, no. 5: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050895
APA StyleCarrouel, F., Valette, M., Perrier, H., Bouscambert-Duchamp, M., Dussart, C., Tramini, P., & Bourgeois, D. (2021). Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Testing Compared with Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses, 13(5), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050895








