Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
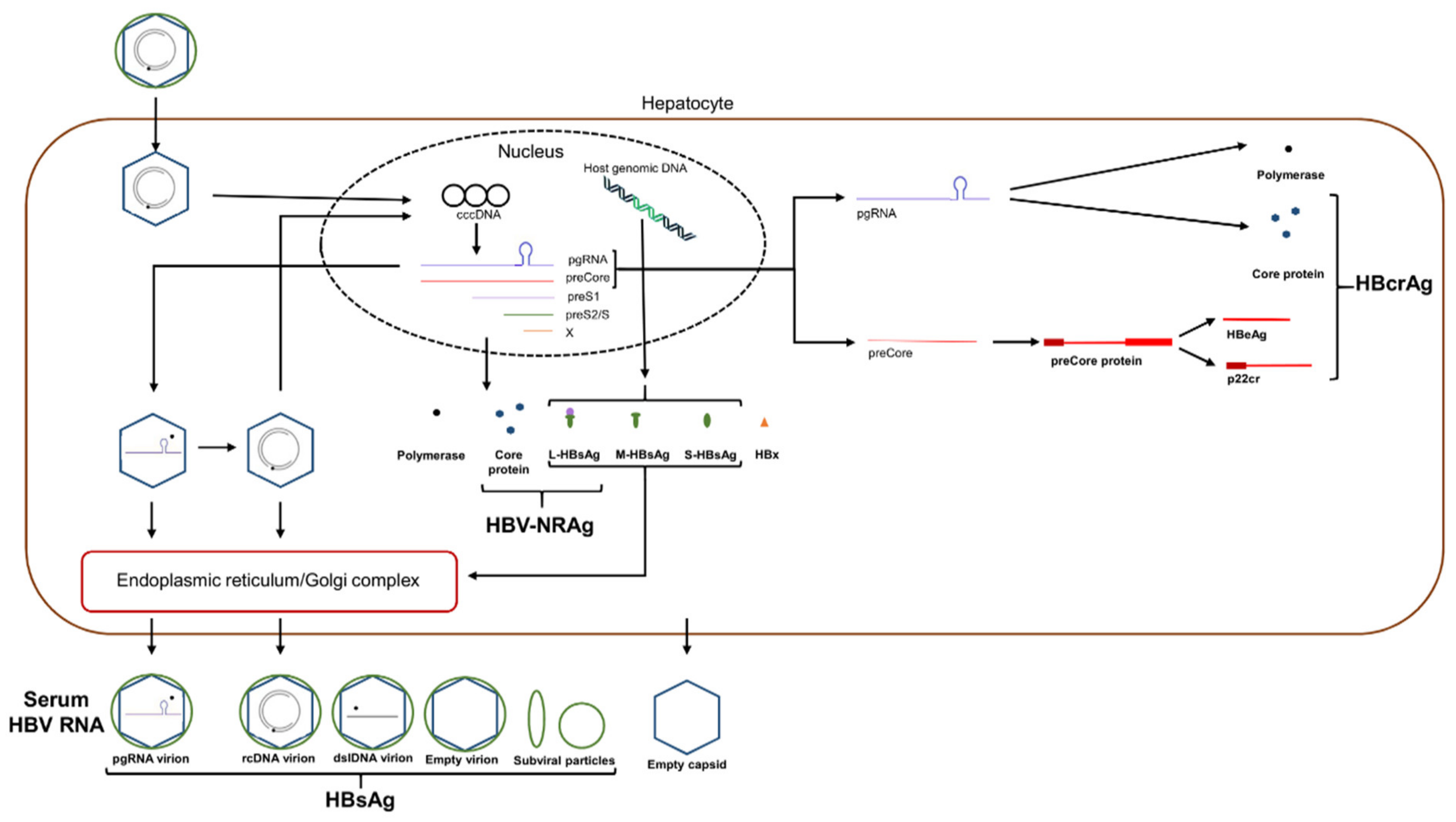
2. HBV Replication, Natural History, and Antibody Response to Infection
3. Traditional HBV Diagnostic Testing
4. HBV Treatments and Outcomes
5. Novel HBV Biomarkers
5.1. Serum HBV RNA/pgRNA
5.2. HBcrAg
5.3. HBV Nucleic Acid-Related Antigen (HBV-NRAg)
5.4. Quantitative HBsAg
5.5. Quantitative Anti-HBc Antibody (qAHBc)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 2 April 2021).
- Joshi, S.S.; Coffin, C.S. Hepatitis B and Pregnancy: Virologic and Immunologic Characteristics. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassal, M. Hepatitis B viruses: Reverse transcription a different way. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampertico, P.; Agarwal, K.; Berg, T.; Buti, M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Zoulim, F.; Tacke, F. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boeijen, L.L.; Hoodeveen, R.C.; Boonstra, A.; Lauer, G.M. Hepatitis B virus infection and the immune response: The big questions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.C.; Pape, G.R. Immunology of hepatitis B infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.E.; Kim, D.Y. Diagnosis of hepatitis B. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Almeida Pondé, R.A. Dynamic profile of the HBeAg-anti-HBe system in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A clinical-laboratory approach. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, M.W.; Piratvisuth, T.; Lau, G.K.K.; Marcellin, P.; Chow, W.C.; Cooksley, G.; Luo, K.X.; Paik, S.W.; Liaw, Y.F.; Button, P.; et al. HBeAg and hepatitis B Virus DNA as outcome predictors during therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2008, 47, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yang, R.F.; Wei, L. Quantitative serum HBsAg and HBeAg are strong predictors of sustained HBeAg seroconversion to pegylated interferon alfa-2b in HBeAg-positive patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Park, N.H.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, B.C.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Jeong, I.D.; Bang, S.J.; Kim, D.H. Clinical significance of hepatitis B e antigen level measurement during long-term lamivudine therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients with e antigen positive. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6693–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Chang, K.-K.; Lin, R.-C.; Kuo, M.-J.; Yang, C.-C.; Tseng, Y.-T. Consolidation period of 18 months no better at promoting off-treatment durability in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment than a 12-month period: A prospective randomized cohort study. Medicine 2020, 99, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Kee, K.M.; Hsu, N.T.; Wang, J.H.; Hsiao, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, S.N. Using AST-platelet ratio index and fibrosis 4 index for detecting chronic hepatitis C in a large-scale community screening. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Zheng, J.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Yan, L.; Lu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z. INR-to-platelet ratio (INPR) as a novel noninvasive index for predicting liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Wong, G.; Gane, E.; Kao, J.; Dusheiko, G. Hepatitis B Virus: Advances in Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.K.H.; Yuen, M.F.; Ngai, V.W.S.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.L. One-year entecavir or lamivudine therapy results in reduction of hepatitis B virus intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA levels. Antivir. Ther. 2006, 11, 909–916. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.R.; You, J.; Dong, J.; Zeng, D.W.; Gao, L.Y.; Chen, L.H.; Jiang, J.J. Decline in intrahepatic cccDNA and increase in immune cell reactivity after 12 weeks of antiviral treatment were associated with HBeAg loss. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, S.; Nishida, N.; Watanabe, T.; Ida, H.; Sakurai, T.; Ueshima, K.; Takita, M.; Komeda, Y.; Nishijima, N.; Osaki, Y.; et al. Sustained antiviral effects and clearance of hepatitis surface antigen after combination therapy with entecavir and pegylated interferon in chronic hepatitis B. Antivir. Ther. 2018, 23, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, E.K.; Gersch, J.; McNamara, A.; Luk, K.C.; Holzmayer, V.; de Medina, M.; Schiff, E.; Kuhns, M.; Cloherty, G.A. Hepatitis B Virus Serum DNA andRNA Levels in Nucleos(t)ide Analog-Treated or Untreated Patients During Chronic and Acute Infection. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, H.; Sajid, M.; Yan, K.; Feng, J.; He, M.; Shereen, M.A.; Li, Q.; Xu, T.; Hao, R.; Guo, D.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Interferon Alpha-Inducible Protein 27 Against Hepatitis B Virus Gene Expression and Replication. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowski, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and Nonhepatotoxic Degradation of Nuclear Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Huang, Y. Effects of pegylated interferon-α based therapies on functional cure and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligat, G.; Goto, K.; Verrier, E.; Baumert, T.F. Targeting Viral cccDNA for Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2020, 19, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F.; Dusheiko, G.; Ghany, M.G. Hepatitis B cure: From discovery to regulatory approval. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gambarin-Gelwan, M. Percutaneous Liver Biopsy. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 2, 689–690. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.; Ye, A.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Ou, Q. Diagnostic value of detection of pregenomic RNA in sera of hepatitis B virus-infected patients with different clinical outcomes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Q.; Guo, J.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, H. Insights for clinical diagnostic indicators of virus and host in chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 27, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charre, C.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Scholtès, C. Non-invasive biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B virus infection management. Antiviral Res. 2019, 169, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bömmel, F.; Bartens, A.; Mysickova, A.; Hofmann, J.; Krüger, D.H.; Berg, T.; Edelmann, A. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels as an early predictor of hepatitis B envelope antigen seroconversion during treatment with polymerase inhibitors. Hepatology 2015, 61, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmayer, B.; Diederichs, A.; Chapus, F.; Rivoire, M.; Alam, A.; Fraisse, L.; Carter, K.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Full-length 5’RACE identifies all major HBV transcripts in HBV-infected hepatocytes and patient serum. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shen, T.; Huang, X.; Kumar, G.R.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, R.; Li, T.; Zhang, T.; et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Shen, C.; Meng, Z.; Zheng, J.J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; et al. Relationship between serum HBV-RNA levels and intrahepatic viral as well as histologic activity markers in entecavir-treated patients. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, C.; Velhagen, I.; Zentgraf, H.; Schröder, C.H. Diversity of hepatitis B virus X gene-related transcripts in hepatocellular carcinoma: A novel polyadenylation site on viral DNA. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, F.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Q.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.T. Characterization of novel hepadnaviral RNA species accumulated in hepatoma cells treated with viral DNA polymerase inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 2016, 131, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayliss, J.; Lim, L.; Thompson, A.J.V.; Desmond, P.; Angus, P.; Locarnini, S.; Revill, P.A. Hepatitis B virus splicing is enhanced prior to development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, L.-Y.L.; Cloherty, G.; Wong, D.K.-H.K.; Gersch, J.; Seto, W.W.-K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.-F.M. HBV RNA profiles in chronic hepatitis B patients under different disease phases and anti-viral therapy. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Campenhout, M.J.H.; van Bömmel, F.; Pfefferkorn, M.; Fischer, J.; Deichsel, D.; Boonstra, A.; van Vuuren, A.J.; Berg, T.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A. Host and viral factors associated with serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels among patients in need for treatment. Hepatology 2018, 68, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Xue, J.; Yan, H.; Liang, X. Serum HBV RNA quantification: Useful for monitoring natural history of chronic hepatitis B infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, J.; Song, Z.; et al. Natural history of serum HBV-RNA in chronic HBV infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Liao, J.; Ye, F.; Tao, Y.C.; Wu, D.B.; He, M.; Tang, H.; Chen, E.Q. Distribution and factors associated with serum HBV pregenomic RNA levels in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P. Serum Hepatitis B Virus DNA, RNA, and HBsAg: Which Correlated Better with Intrahepatic Covalently Closed Circular DNA before and after Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Treatment? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2972–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Tan, N.; Kang, Q.; Pan, J.; Chen, H.; Xi, H.; Yu, M.; Xu, X. Hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA status can reveal the long-term prognoses of chronic hepatitis B patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Campenhout, M.J.H.; van Bömmel, F.; Pfefferkorn, M.; Fischer, J.; Deichsel, D.; Boonstra, A.; van Vuuren, A.J.; Berg, T.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA predicts response to peginterferon treatment in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, G.; Lou, B.; Lv, F.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. HBcrAg and pgRNA and the therapeutic effect in HBeAg-positive patients receiving anti-viral therapy, baseline serum HBV-RNA is a powerful predictor of response. J. Viral Hepat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuge, M.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, T.C.; Abe, H.; Hu, J.T.; Chen, D.S.; Yang, S.S.; Chayama, K.; et al. On-treatment low serum HBV RNA level predicts initial virological response in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleoside analogue therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2015, 20, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuge, M.; Murakami, E.; Imamura, M.; Abe, H.; Miki, D.; Hiraga, N.; Takahashi, S.; Ochi, H.; Hayes, C.N.; Ginba, H.; et al. Serum HBV RNA and HBeAg are useful markers for the safe discontinuation of nucleotide analogue treatments in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, I.; Gersch, J.; Wang, B.; Moigboi, C.; Kuhns, M.; Cloherty, G.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. Pre-genomic HBV RNA and HBcrAg predict outcomes in HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B patients suppressed on nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-L.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Wong, G.T.-Y.; Seto, W.-K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.-F. Rebound of HBV DNA after cessation of nucleos/tide analogues in chronic hepatitis B patients with undetectable covalently closed circular DNA. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, J.; Theilmann, L.; Galle, P.; Schlicht, H.J. Hepatitis B virus nucleic acids associated with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells do not originate from replicating virus. Hepatology 1996, 23, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limothai, U.; Chuaypen, N.; Poovorawan, K.; Chotiyaputta, W.; Tanwandee, T.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR vs reverse transcriptase quantitative real-time PCR for serum HBV RNA quantification. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3365–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Mendenhall, M.; Walsh, R.; Cabuang, L.; Soppe, S.; Revill, P.A.; Burdette, D.; Feierbach, B.; Delaney, W.; et al. Characterization of Hepatitis B Precore/Core-Related Antigens. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, F.; Miyakoshi, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H. Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus core-related antigen and intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, V.; Asselah, T. Editorial: HBV cure - the quest for biomarkers to predict off-treatment sustained response. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 53, 552–554. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Iio, E.; Ogawa, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yagi, S.; Kaneko, A.; Matsuura, K.; Aoyagi, K.; Tanaka, Y. Clinical efficacy of a novel, high-sensitivity HBcrAg assay in the management of chronic hepatitis B and HBV reactivation. J. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Perlman, D.; Revill, P.A.; Wieland, S.F.; Menne, S.; Hu, J. Characterization and Application of Precore/Core-Related Antigens in Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-W.; Kao, J.-H.; Tseng, T.-C. Three Heads are Better than Two: HBcrAg as a New Predictor of HBV-related HCC. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Shirasaki, T.; Terashima, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Oishi, N.; Wang, X.; Shimakami, T.; Okada, H.; Arai, K.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) core-related antigen during nucleos(t)ide analog therapy is related to intra-hepatic HBV replication and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Q.; Feng, S.; Wang, M.L.; Liang, L.B.; Zhou, L.Y.; Du, L.Y.; Yan, L.B.; Tao, C.M.; Tang, H. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen is a satisfactory surrogate marker of intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Armandi, A.; Rosso, C.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S. Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, M.; Feng, H.; Guan, W.; Ji, J.; Gao, Z.; Gao, C. Clinical evaluation of hepatitis B core-related antigen in chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Seto, W.; Cheung, K.-S.; Chong, C.-K.; Huang, F.-Y.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int. 2016, 2017, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.H.; Tanaka, Y.; Lai, C.L.; Mizokami, M.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigens as markers for monitoring chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3942–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetto, M.R.; Carey, I.; Maasoumy, B.; Marcos-Fosch, C.; Boonstra, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Loglio, A.; Cavallone, D.; Scholtes, C.; Ricco, G.; et al. Incremental value of HBcrAg to classify 1582 HBeAg-negative individuals in chronic infection without liver disease or hepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 1, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, B.; Lebossé, F.; Scholtes, C.; Berby, F.; Miaglia, C.; Subic, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; Lampertico, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Q.; Wang, M.L.; Tao, Y.C.; Wu, D.B.; Liao, J.; He, M.; Tang, H. Serum HBcrAg is better than HBV RNA and HBsAg in reflecting intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Wong, D.K.H.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Liu, K.S.H.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Linearized hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core-related antigen in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maasoumy, B.; Wiegand, S.B.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Bremer, B.; Lehmann, P.; Deterding, K.; Taranta, A.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Glebe, D.; et al. Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection in a large European cohort predominantly infected with genotypes A and D. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 606.e1–606.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Bes, M.; Rodríguez-Frías, F.; Tabernero, D.; Ruiz, A.; Casillas, R.; Vidal-González, J.; Homs, M.; Nieto, L.; Sauleda, S.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen is more accurate than hepatitis B surface antigen to identify inactive carriers, regardless of hepatitis B virus genotype. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Carey, I.; Bruce, M.; Montague, S.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. HBsAg and HBcrAg as predictors of HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Deng, R.; Chen, E.Q.; Tao, C.M.; Liao, J.; Zhou, T.Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, H. Performance of serum HBcrAg in chronic hepatitis B patients with 8-year nucleos(t)ide analogs therapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.H.C.J.; Yang, W.T.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hong, C.M.; Su, T.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, H.C.; Liu, C.H.C.J.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen level stratifies risk of disease progression in chronic hepatitis B patients with intermediate viral load. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Komatsu, N.; Sato, M.; Tatsumi, A.; Miura, M.; Matsuda, S.; Muraoka, M.; Nakakuki, N.; Shindo, H.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients with low hepatitis B surface antigen and high hepatitis B core-related antigen titers have a high risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, K.-S.; Seto, W.-K.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Relationship between HBsAg, HBcrAg and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with undetectable HBV DNA under nucleos(t)ide therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Ishigami, M.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Honda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakano, I.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H. Cumulative incidence and risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B who achieved sustained disappearance of viremia by nucleos(t)ide analog treatment. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, E240–E251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Impact of hepatitis B core-related antigen on the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Niinomi, T.; Yasuda, S.; Andou, Y.; et al. Effect of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy on hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B patients: A propensity score analysis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.P.; Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.H.; Fung, J.; Liu, F.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B core-related antigen levels after HBeAg seroconversion is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Toyoda, H.; Tse, Y.K.; Yip, T.C.F.; Yuen, B.W.Y.; Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Lee, H.W.; Lui, G.C.Y.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen predicts hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Min, J.J.; Tan, W.; Zheng, J.H. Targeted cancer immunotherapy with genetically engineered oncolytic Salmonella typhimurium. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Yama, T.; Tanaka, J. HBcrAg predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Lou, B.; Lv, F.; Zhao, D.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Chen, Y. HBcrAg, pg RNA and HBsAg dynamically supervise the seroconversion of HBsAg with anti-viral therapy: “Loss of HBsAg” maybe not a good end-point of anti-viral therapy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Campenhout, M.J.H.; Brouwer, W.P.; van Oord, G.W.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Guo, S.; Tabak, F.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Hepatitis B core-related antigen levels are associated with response to entecavir and peginterferon add-on therapy in hepatitis B e antigen–positive chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 571.e5–571.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuaypen, N.; Posuwan, N.; Chittmittraprap, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinkai, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Predictive role of serum HBsAg and HBcrAg kinetics in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B receiving pegylated interferon–based therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 306.e7–306.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, J.H.; Hung, C.H.; Lu, S.N.; Hu, T.H.; Chen, C.H. Combining end-of-treatment HBsAg and baseline hepatitis B core-related antigen reduce HBV relapse rate after tenofovir cessation. Hepatol. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.F.; Seto, W.K.; Wong, D.; Cheung, K.S.; Fung, J.; Mak, L.Y.; Yuen, J.; Chong, C.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Seven-year treatment outcome of entecavir in a real-world cohort: Effects on clinical parameters, HBsAg and HBcrag levels. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakenhoff, S.M.; de Man, R.A.; Boonstra, A.; van Campenhout, M.J.H.; de Knegt, R.J.; van Bömmel, F.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Berg, T.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A.; et al. Hepatitis B virus RNA decline without concomitant viral antigen decrease is associated with a low probability of sustained response and hepatitis B surface antigen loss. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, J.M.; Lou, J.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Yan, Y.; Sun, G.Z.; Li, N. Correlation between hepatitis B virus DNA levels and diagnostic tests for HBsAg, HBeAg, and PreS1-Ag in chronic hepatitis B. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriungi, N.G.; Ueda, K. TIMM29 interacts with hepatitis B virus preS1 to modulate the HBV life cycle. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 792–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffello-Le Guillou, D.; Duclos-Vallée, J.; Eberle, F.; Capel, F.; Petit, M.A. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus PreS1 envelope antigen in serum samples: Comparison with two commercial assays for monitoring hepatitis B virus DNA. J. Viral Hepat. 2000, 7, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferkorn, M.; Böhm, S.; Schott, T.; Deichsel, D.; Bremer, C.M.; Schröder, K.; Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D.; Berg, T.; Van Bömmel, F. Quantification of large and middle proteins of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) as a novel tool for the identification of inactive HBV carriers. Gut 2018, 67, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferkorn, M.; Schott, T.; Böhm, S.; Deichsel, D.; Felkel, C.; Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D.; Wat, C.; Pavlovic, V.; Heyne, R.; et al. Composition of HBsAg is predictive of HBsAg loss during treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2020, 74, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinker, F.; Bremer, C.M.; Schröder, K.; Wiegand, S.B.; Bremer, B.; Manns, M.P.; Kraft, A.R.; Wedemeyer, H.; Yang, L.; Pavlovic, V.; et al. Quantitation of large, middle and small hepatitis B surface proteins in HBeAg-positive patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Ge, S.; Niu, J. The detection of serum HBV-NRAg and HBV DNA correlation analysis. Mod. Prev. Med. 2007, 34, 4632–4636. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise WANTAI HBV NRAg ELISA; Beijing, 2007. Available online: https://www.ystwt.cn/hepatitis-b/ (accessed on 2 April 2021).
- Zhang, H.; Luo, Z.; Huang, S.; Liu, Q.; Ye, Z.; Liu, G.; Fei, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, S. Detecting Nucleic Acid Related Antigen of Hepatitis B Virus: A Clinical Study. Chin. J. Nosocomiol. 2008, 19, 930–932. [Google Scholar]
- Alawad, A.S.; Auh, S.; Suarez, D.; Ghany, M.G.; Branch, D.; Diseases, K.; Diseases, K. Durability of Spontaneous and Treatment-related Loss of Hepatitis B s Antigen. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, J.; Bulkow, L.; McMahon, B.J.; Homan, C.; Snowball, M.; Negus, S.; Williams, J.; Livingston, S.E. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Sinn, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kang, W.; et al. Risk and Risk Score Performance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Patients With Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Seroclearance. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollicino, T.; Caminiti, G. HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, D.; Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Cheng, J. Sequence analysis of the Pre-S gene in chronic asymptomatic HBV carriers with low-level HBsAg. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Cao, L.; Chen, X.W.; Lu, M.J. Hepatitis B virus infection: Defective surface antigen expression and pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3488–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.E.; Seiz, P.L.; Schüttler, C.G.; Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D.; Scheiblauer, H.; Nick, S.; Chudy, M.; Dougall, T.; Stone, L.; et al. International collaborative study on the 3rd WHO International Standard for hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 82, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burdino, E.; Ruggiero, T.; Proietti, A.; Milia, M.G.; Olivero, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Marietti, M.; Rizzetto, M.; Smedile, A.; Ghisetti, V. Quantification of hepatitis B surface antigen with the novel DiaSorin LIAISON XL Murex HBsAg Quant: Correlation with the ARCHITECT quantitative assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaras, R.; Tabak, F.; Tahan, V.; Ozturk, R.; Akin, H.; Mert, A.; Senturk, H. Correlation of quantitative assay of HBsAg and HBV DNA levels during chronic HBV treatment. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2995–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Feng, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ming, K.; Liang, G.; Lei, X.X.; Xu, B.L. Relationship between serum quantitative HBsAg and HBV DNA levels in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, T.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Wachtler, P.; Jacob, A.; Quaas, A.; Murray, J.M.; Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. Impaired Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Productivity Contributes to Low Viremia in Most HBeAg-Negative Patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungtrakul, T.; Sriprayoon, T.; Kusuman, P.; Chunnuan, P.; Soonklang, K.; Sornsamdang, G.; Auewarakul, C.U.; Tanwandee, T. Role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen in predicting inactive carriers and HBsAg seroclearance in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients. Medicine 2017, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günal, Ö.; Barut, Ş.; Etikan, İ.; Duygu, F.; Tuncel, U.; Sünbül, M. Relation between serum quantitative HBsAg, ALT and HBV DNA levels in HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection. Turkish J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werle-Lapostolle, B.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Lau, G.; Trepo, C.; Marcellin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Delaney, W.E., IV; et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.L.Y.H.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Tse, A.M.L.; Tse, C.H.; Chim, A.M.L.; Chan, H.L.Y.H.Y.; Wong, G.L.H.; Sung, J.J.Y. Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantitation Can Reflect Hepatitis B Virus in the Liver and Predict Treatment Response. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodella, A.; Galli, C.; Terlenghi, L.; Perandin, F.; Bonfanti, C.; Manca, N. Quantitative analysis of HBsAg, IgM anti-HBc and anti-HBc avidity in acute and chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 37, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P. HBsAg quantification to optimize treatment monitoring in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Lai, H.C.; Li, Y.F.; Su, W.P.; Chuang, P.H.; Kao, J.T. Early serum HBsAg level as a strong predictor of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijckborst, V.; Hansen, B.E.; Cakaloglu, Y.; Ferenci, P.; Tabak, F.; Akdogan, M.; Simon, K.; Akarca, U.S.; Flisiak, R.; Verhey, E.; et al. Early on-treatment prediction of response to peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B using HBsAg and HBV DNA levels. Hepatology 2010, 52, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijckborst, V.; Ferenci, P.; Akdogan, M.; Pinarbasi, B.; Ter Borg, M.J.; Simon, K.; Flisiak, R.; Akarca, U.S.; Raptopoulou-Gigi, M.; Verhey, E.; et al. Long-term follow-up of hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients treated with peginterferon α-2a: Progressive decrease in hepatitis B surface antigen in responders. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghiţǎ, V.I.; Cǎruntu, F.A.; Curescu, M.; Olaru, I.; Radu, M.N.; Colţan, G.; Streinu-Cercel, A. Use of quantitative serum HBsAg for optimization of therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with pegylated interferon alfa-2a: A Romanian cohort study. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2013, 22, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.G.; Phyo, W.W.; Ling, J.Z.J.; Cloherty, G.; Butler, E.K.; Kuhns, M.C.; McNamara, A.L.; Holzmayer, V.; Gersch, J.; Yang, W.L.; et al. Comparative biomarkers for HBsAg loss with antiviral therapy shows dominant influence of quantitative HBsAg (qHBsAg). Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Simon, K.G.; Mauss, S.; Schott, E.; Heyne, R.; Klass, D.M.; Eisenbach, C.; Welzel, T.M.; Zachoval, R.; Felten, G.; et al. Long-term response after stopping tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in non-cirrhotic HBeAg-negative patients – FINITE study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Li, Z.; Hansen, B.E.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Hou, J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Peng, J. Serum Level of Antibodies Against Hepatitis B Core Protein Is Associated With Clinical Relapse After Discontinuation of Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Therapy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 182–191.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Rinker, F.; Maasoumy, B.; Wiegand, S.B.; Filmann, N.; Falk, C.S.; Deterding, K.; Port, K.; Mix, C.; Manns, M.P.; et al. Viral and host responses after stopping long-term Nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in HBeAg-negative chronic Hepatitis B. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hadziyannis, S.J.; Sevastianos, V.; Rapti, I.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Hadziyannis, E. Sustained responses and loss of HBsAg in HBeAg-negative patients with chronic hepatitis B who stop long-term treatment with adefovir. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 629–636.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.H.C.J.; Yang, H.C.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Kuo, S.F.T.; Liu, C.H.C.J.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, N.; Çam, H. Quantitative HBsAg titers in relation to disease progression and serum markers of iron metabolism among chronic hepatitis B patients. Int. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, B.; Acar, A.; Adar, P.; Kose, S. Role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen levels in predicting liver biopsy time in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Ghosh, A.; Ayithan, N.; Romani, S.; Khanam, A.; Park, J.J.; Rijnbrand, R.; Tang, L.; Sofia, M.J.; Kottilil, S.; et al. Circulating serum HBsAg level is a biomarker for HBV-specific T and B cell responses in chronic hepatitis B patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Yao, C.Y. Rapid and quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11954–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Taylor, R.; Pearce, S.; Kuhns, M.; Leary, T. An ultra-sensitive Abbott ARCHITECT ® assay for the detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg). J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 105, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickinger, E.; Braun, H.B.; Meyer, T.; Schmid, K.; Daghfal, D.; Oer, M.; Schultess, J. Performance characteristics of the high sensitivity Alinity i & ARCHITECT HBsAg Next Qualitative/Confirmatory assays. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, M.; Kagita, M.; Yoshioka, N.; Tsukamoto, H.; Takao, M.; Tahara, K.; Maeda, I.; Hidaka, Y.; Yamauchi, S.; Kaneko, A.; et al. Evaluation of the highly sensitive chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay “Lumipulse HBsAg-HQ” for hepatitis B virus screening. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Maruki, M.; Yamagaito, T.; Muramatsu, M.; Sakai, Y.; Tobimatsu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y. Highly sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen by use of a semiautomated immune complex transfer chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2238–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhns, M.C.; Holzmayer, V.; McNamara, A.L.; Sickinger, E.; Schultess, J.; Cloherty, G.A. Improved detection of early acute, late acute, and occult Hepatitis B infections by an increased sensitivity HBsAg assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 118, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Song, G.; Guan, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wei, L. The Lumipulse G HBsAg-Quant assay for screening and quantification of the hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 228, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Imaizumi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Nishiguchi, S.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Ishida, T.; Moriyama, K.; Aoyagi, K.; Tanaka, E. Novel and highly sensitive immunoassay for total hepatitis B surface antigen, including that complexed with hepatitis B surface antibody. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Watanabe, T.; Nakata, M.; Sakai, R.; Fukushima, N.; Fukushima, T.; Moriuchi, Y.; Itoh, K.; et al. Ultra-high sensitivity HBsAg assay can diagnose HBV reactivation following rituximab-based therapy in patients with lymphoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Tanaka, Y.; Lo, R.; Wong, T.; Chok, K.S.-H.; Chan, A.C.-Y.; Cheung, T.-T.; Dai, W.-C.; Ng, K.; et al. Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen in predicting recurrence of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Hepatoma Res. 2018, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumida, K.; Kaneko, A.; Takahashi, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Narita, T.; Takami, A.; Iida, S.; Aoyagi, K.; Tanaka, Y. Clinical evaluation of a novel and highly sensitive immunoassay for anti-hepatitis B core antigen using a fully automated immunochemical analyzer. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency WHO International Standard: First International Standard for anti-Hepatitis B core antigen. NIBSC: Herts, UK, 2013. Available online: https://www.nibsc.org/documents/ifu/95-522.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2021).
- Vanwolleghem, T.; Groothuismink, Z.M.A.; Kreefft, K.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Boonstra, A. Hepatitis B core-specific memory B cell responses associate with clinical parameters in patients with chronic HBV. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.R.; Lu, J.H.; Ye, L.H.; Sun, X.L.; Zheng, Y.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lv, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody level is associated with inflammatory activity in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients. Medicine 2016, 95, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.W.; Liu, P.G.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Cheng, X.D.; Wu, H.L.; Yang, H.C.; Hao, X.K.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.R.; Zheng, H.W.; Lu, J.H.; Ma, S.M.; Ye, L.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lv, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core antibody titer use in screening for significant fibrosis in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11063–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Q.; Song, L.W.; Cavallone, D.; Moriconi, F.; Cherubini, B.; Colombatto, P.; Oliveri, F.; Coco, B.A.; Ricco, G.; Bonino, F.; et al. Total hepatitis B core antigen antibody, a quantitative non-invasive marker of hepatitis B virus induced liver disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.R.; Zheng, H.W.; Ma, S.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Qie, L.X.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Sun, X.L.; Ren, G.F.; Zheng, Y.H.; et al. Correlations between serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core antibody titers and liver fibrosis in treatment-naïve CHB patients. J. Chinese Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, B.; et al. Monitoring of serum HBV RNA, HBcrAg, HBsAg and anti-HBc levels in patients during long-term nucleoside/nucleotide analogue therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2019, 24, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Tsou, H.H.; Pei, S.N.; Chang, C.S.; Chen, J.H.; Yao, M.; Lin, S.J.; Lin, J.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.; et al. Quantification of HBV core antibodies may help predict HBV reactivation in patients with lymphoma and resolved HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Shi, B.S.; Lu, W.; Liu, D.P.; Huang, D.; Feng, Y.L. Quantitative Anti-HBc in Liver Pathological States in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marinos, G.; Smith, H.M.; Naoumov, N.V.; Williams, R. Quantitative assessment of serum IgM anti-HBc in the natural course and during interferon treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1994, 19, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, G.; Navarra, G.; Mondello, S.; Costantino, L.; Colloredo, G.; Cucinotta, E.; Di Vita, G.; Scisca, C.; Squadrito, G.; Pollicino, T. Occult hepatitis B virus in liver tissue of individuals without hepatic disease. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandoi, F.; Caviglia, G.P.; Pittaluga, F.; Abate, M.L.; Smedile, A.; Romagnoli, R.; Salizzoni, M. Prediction of occult hepatitis B virus infection in liver transplant donors through hepatitis B virus blood markers. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Olivero, A.; Ciancio, A.; Tandoi, F.; Troshina, G.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Younes, R.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Smedile, A.; et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a novel assay for anti-HBc IgG measurement in serum of subjects with overt and occult HBV infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Liu, J.; Chang, C.L.; Jen, C.L.; Lee, M.H.; Lu, S.N.; Wang, L.Y.; Quan, Y.; Xia, N.S.; Chen, C.J.; et al. Level of Hepatitis B (HB) Core Antibody Associates With Seroclearance of HBV DNA and HB Surface Antigen in HB e Antigen-Seronegative Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 172–181.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Tandoi, F.; Ciancio, A.; Amoroso, A.; Salizzoni, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Rizzetto, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Smedile, A. Quantitation of HBV cccDNA in anti-HBc-positive liver donors by droplet digital PCR: A new tool to detect occult infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Song, L.W.; Liu, C.J.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.G.; Huang, C.H.; Yan, Y.; Ge, S.X.; Wang, Y.B.; Peng, C.Y.; et al. Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody level may help predict treatment response in chronic hepatitis B patients. Gut 2013, 62, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Q.; Xie, Q.; Bai, X.; Ning, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yu, Y.; Niu, J.; Shi, G.; et al. Baseline quantitative hepatitis B core antibody titre alone strongly predicts HBeAg seroconversion across chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon or nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gut 2016, 65, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Tseng, T.C.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T.; Kao, J.H. Quantification of serum hepatitis B core antibody to predict off-entecavir relapse in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, C.; Chen, X. Quantitative of serum hepatitis B core antibody is a potential predictor of recurrence after interferon-induced hepatitis B surface antigen clearance. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. New perspectives of biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loureiro, D.; Tout, I.; Narguet, S.; Benazzouz, S.M.; Mansouri, A.; Asselah, T. miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Viral Hepatitis B and C. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tout, I.; Lampertico, P.; Berg, T.; Asselah, T. Perspectives on stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antiviral Res. 2021, 185, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacob, D.G.; Rosca, A.; Ruta, S.M. Circulating microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for hepatitis B virus liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R.E.; De Battista, D.; Danoff, E.J.; Nguyen, H.; Chen, Z.; Lusso, P.; Purcell, R.H.; Farci, P. Distinct cytokine profiles correlate with disease severity and outcome in longitudinal studies of acute hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus infection in chimpanzees. MBio 2020, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Ran, C.P.; Hao, H.X.; Zhang, D.; Qu, X.J.; Shen, G.; Wu, S.L.; et al. Association of cytokines with alanine aminotransferase, Hepatitis B virus surface antigen and Hepatitis B envelope antigen levels in chronic Hepatitis B. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Mo, Z.; Zhu, J.; Pang, X.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Xie, D.; Gao, Z. Soluble ST2 plasma concentrations predict mortality in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhao, C. NLRP3 inflammasome and related cytokines reflect the immune status of patients with HBV-ACLF. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 120, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, S.H. Hepatitis B virus cure: Targets and future therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Gane, E.J.; Kim, D.J.; Weilert, F.; Yuen Chan, H.L.; Lalezari, J.; Hwang, S.G.; Nguyen, T.; Flores, O.; Hartman, G.; et al. Antiviral Activity, Safety, and Pharmacokinetics of Capsid Assembly Modulator NVR 3-778 in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1392–1403.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoulim, F.; Lenz, O.; Vandenbossche, J.J.; Talloen, W.; Verbinnen, T.; Moscalu, I.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Bourgeois, S.; Buti, M.; Crespo, J.; et al. JNJ-56136379, an HBV Capsid Assembly Modulator, Is Well-Tolerated and Has Antiviral Activity in a Phase 1 Study of Patients With Chronic Infection. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 521–533.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Park, J.Y.; Hong, T.; Park, M.S.; Ahn, S.H. Efficacy of Lenvervimab, a Recombinant Human Immunoglobulin, in Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 3043–3045.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HBV Biomarker | Summary of Uses and Limitations | Laboratory Tests Available |
|---|---|---|
| Serum HBV RNA |
|
|
| HBcrAg |
|
|
| HBV-NRAg |
|
|
| qHBsAg |
|
|
| Ultrasensitive HBsAg |
| Qualitative:
|
| qAHBc |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vachon, A.; Osiowy, C. Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management. Viruses 2021, 13, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060951
Vachon A, Osiowy C. Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060951
Chicago/Turabian StyleVachon, Alicia, and Carla Osiowy. 2021. "Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management" Viruses 13, no. 6: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060951
APA StyleVachon, A., & Osiowy, C. (2021). Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management. Viruses, 13(6), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060951






