Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HCV Envelope Epitopes and Immune Protection
2.1. Variance in the Protection of Antibodies Directed at Distinct Epitopes
2.2. NAbs Targeting Hypervariable Region 1
2.3. Ab Immunodominance
3. The Interplay of HCV Infection and B-Cell Receptors (BCRs)
Variable Region Immunoglobulin Heavy (VH) and Light (VL) Chain Gene Usage
4. An HCV Public Ab Repertoire
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Hepatitis C; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Combating Hepatitis B and C to Reach Elimination by 2030; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grebely, J.; Page, K.; Sacks-Davis, R.; van der Loeff, M.S.; Rice, T.M.; Bruneau, J.; Morris, M.D.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Amin, J.; Cox, A.L.; et al. The effects of female sex, viral genotype, and IL28B genotype on spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2014, 59, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fénéant, L.; Levy, S.; Cocquerel, L. CD81 and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection. Viruses 2014, 6, 535–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pileri, P.; Uematsu, Y.; Campagnoli, S.; Galli, G.; Falugi, F.; Petracca, R.; Weiner, A.J.; Houghton, M.; Rosa, D.; Grandi, G.; et al. Binding of Hepatitis C Virus to CD81. Science 1998, 282, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankwitz, D.; Steinmann, E.; Bitzegeio, J.; Ciesek, S.; Friesland, M.; Herrmann, E.; Zeisel, M.B.; Baumert, T.F.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Foung, S.K.H.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Hypervariable Region 1 Modulates Receptor Interactions, Conceals the CD81 Binding Site, and Protects Conserved Neutralizing Epitopes. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5751–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forns, X.; Thimme, R.; Govindarajan, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.; Bukh, J. Hepatitis C virus lacking the hypervariable region 1 of the second envelope protein is infectious and causes acute resolving or persistent infection in chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13318–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prentoe, J.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Foung, S.K.H.; Law, M.; Bukh, J. Hypervariable region 1 shielding of hepatitis C virus is a main contributor to genotypic differences in neutralization sensitivity. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, E.; Dorner, M.; Prentoe, J.C.; Dreux, M.; Evans, M.J.; Bukh, J.; Rice, C.M.; Ploss, A.; Burton, D.R.; Law, M. Human broadly neutralizing antibodies to the envelope glycoprotein complex of hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6205–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keck, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lau, P.; Carlsen, T.H.R.; Prentoe, J.; Xia, J.; Patel, A.H.; Bukh, J.; Foung, S.K.H. Cooperativity in Virus Neutralization by Human Monoclonal Antibodies to Two Adjacent Regions Located at the Amino Terminus of Hepatitis C Virus E2 Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2012, 87, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drummer, H.E. Challenges to the development of vaccines to hepatitis C virus that elicit neutralizing antibodies. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, M.; Maruyama, T.; Lewis, J.T.; Giang, E.; Tarr, A.W.; Stamataki, Z.; Gastaminza, P.; Chisari, F.; Jones, I.M.; I Fox, R.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies protect against hepatitis C virus quasispecies challenge. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; De Beeck, A.O.; Hadlock, K.G.; Xia, J.; Li, T.-K.; Dubuisson, J.; Foung, S.K.H. Hepatitis C Virus E2 Has Three Immunogenic Domains Containing Conformational Epitopes with Distinct Properties and Biological Functions. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9224–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broering, T.J.; Garrity, K.A.; Boatright, N.K.; Sloan, S.E.; Sandor, F.; Thomas, W.D.; Szabo, G.; Finberg, R.W.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Babcock, G.J. Identification and Characterization of Broadly Neutralizing Human Monoclonal Antibodies Directed against the E2 Envelope Glycoprotein of Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12473–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadlock, K.G.; Lanford, R.E.; Perkins, S.; Rowe, J.; Yang, Q.; Levy, S.; Pileri, P.; Abrignani, S.; Foung, S.K.H. Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Inhibit Binding of Hepatitis C Virus E2 Protein to CD81 and Recognize Conserved Conformational Epitopes. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10407–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Krey, T.; Prentoe, J.; Carlsen, T.; Li, A.Y.-J.; Patel, A.H.; Lemon, S.M.; et al. Human Monoclonal Antibodies to a Novel Cluster of Conformational Epitopes on HCV E2 with Resistance to Neutralization Escape in a Genotype 2a Isolate. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sautto, G.A.; Tarr, A.W.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M. Structural and Antigenic Definition of Hepatitis C Virus E2 Glycoprotein Epitopes Targeted by Monoclonal Antibodies. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 450963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Giang, E.; Nieusma, T.; Kadam, R.U.; Cogburn, K.E.; Hua, Y.; Dai, X.; Stanfield, R.L.; Burton, D.R.; Ward, A.B.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus E2 Envelope Glycoprotein Core Structure. Science 2013, 342, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinchen, V.J.; Cox, A.L.; Bailey, J.R. Can Broadly Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Lead to a Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine? Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, D.X.; Voisset, C.; Tarr, A.W.; Aung, M.; Ball, J.K.; Dubuisson, J.; Persson, M.A.A. Human combinatorial libraries yield rare antibodies that broadly neutralize hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16269–16274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Tarr, A.W.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Li, T.-K.; Witteveldt, J.; Adair, R.; Foung, S.K.H.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Xia, J.; Cai, Z.; Li, T.-K.; Owsianka, A.M.; Patel, A.H.; Luo, G.; Foung, S.K.H. Immunogenic and Functional Organization of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Glycoprotein E2 on Infectious HCV Virions. J. Virol. 2006, 81, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Saha, A.; Xia, J.; Conrad, F.; Lou, J.; Eckart, M.; Marks, J.D.; Foung, S.K.H. Affinity Maturation to Improve Human Monoclonal Antibody Neutralization Potency and Breadth against Hepatitis C Virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44218–44233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Center, R.J.; Boo, I.; Phu, L.; McGregor, J.; Poumbourios, P.; Drummer, H.E. Enhancing the antigenicity and immunogenicity of monomeric forms of hepatitis C virus E2 for use as a preventive vaccine. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7179–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owsianka, A.; Tarr, A.W.; Juttla, V.S.; Lavillette, D.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.-L.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Monoclonal Antibody AP33 Defines a Broadly Neutralizing Epitope on the Hepatitis C Virus E2 Envelope Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11095–11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alhammad, Y.M.; Gu, J.; Boo, I.; Harrison, D.N.; McCaffrey, K.; Vietheer, P.T.; Edwards, S.; Quinn, C.; Coulibaly, F.; Poumbourios, P.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies Directed toward the Hepatitis C Virus Glycoprotein E2 Detect Antigenic Differences Modulated by the N-Terminal Hypervariable Region 1 (HVR1), HVR2, and Intergenotypic Variable Region. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12245–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlsen, T.H.; Pedersen, J.; Prentoe, J.C.; Giang, E.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Mikkelsen, L.S.; Law, M.; Foung, S.K.; Bukh, J. Breadth of neutralization and synergy of clinically relevant human monoclonal antibodies against HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 2c, and 3a. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachko, A.V.; Frey, S.E.; Sirota, L.; Ray, R.; Wells, F.; Zubkova, I.; Zhang, P.; Major, M.E. Antibodies to an interfering epitope in hepatitis C virus E2 can mask vaccine-induced neutralizing activity. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1670–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mankowski, M.C.; Kinchen, V.J.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Flyak, A.I.; Ray, S.C.; Crowe, J.E.; Bailey, J.R. Synergistic anti-HCV broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies with independent mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E82–E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brasher, N.A.; Eltahla, A.A.; Underwood, A.; Boo, I.; Rizzetto, S.; Walker, M.R.; Rodrigo, C.; Luciani, F.; Maher, L.; Drummer, H.E.; et al. B cell immunodominance in primary hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosa, A.I.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; AbouHaidar, M.G.; Tavis, J.E.; Ball, J.K.; Feld, J.J. A bivalent HCV peptide vaccine elicits pan-genotypic neutralizing antibodies in mice. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6864–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; Giang, E.; Kadam, R.U.; Chen, F.; Nagy, K.; Augestad, E.H.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Hua, Y.; Stanfield, R.L.; et al. An alternate conformation of HCV E2 neutralizing face as an additional vaccine target. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentoe, J.; Verhoye, L.; Moctezuma, R.V.; Buysschaert, C.; Farhoudi, A.; Wang, R.; Alter, H.J.; Meuleman, P.; Bukh, J. HVR1-mediated antibody evasion of highly infectious In Vivo adapted HCV in humanised mice. Gut 2016, 65, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartosch, B.; Verney, G.; Dreux, M.; Donot, P.; Morice, Y.; Penin, F.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.-L. An Interplay between Hypervariable Region 1 of the Hepatitis C Virus E2 Glycoprotein, the Scavenger Receptor BI, and High-Density Lipoprotein Promotes both Enhancement of Infection and Protection against Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8217–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khera, T.; Behrendt, P.; Bankwitz, D.; Brown, R.J.; Todt, D.; Doepke, M.; Khan, A.G.; Schulze, K.; Law, J.; Logan, M.; et al. Functional and immunogenic characterization of diverse HCV glycoprotein E2 variants. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.L.M.; Logan, M.; Wong, J.; Kundu, J.; Hockman, D.; Landi, A.; Chen, C.; Crawford, K.; Wininger, M.; Johnson, J.; et al. Role of the E2 Hypervariable Region (HVR1) in the Immunogenicity of a Recombinant Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCaffrey, K.; Gouklani, H.; Boo, I.; Poumbourios, P.; Drummer, H.E. The variable regions of hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2 have an essential structural role in glycoprotein assembly and virion infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, V.J.; Massaccesi, G.; Flyak, A.I.; Mankowski, M.C.; Colbert, M.D.; Osburn, W.O.; Ray, S.C.; Cox, A.L.; Jr, J.E.C.; Bailey, J.R. Plasma deconvolution identifies broadly neutralizing antibodies associated with hepatitis C virus clearance. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4786–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonno, D.; de Vita, S.; Iacobelli, A.R.; Cornacchiulo, V.; Boiocchi, M.; Dammacco, F. Clonal analysis of intrahepatic B cells from HCV-infected patients with and without mixed cryoglobulinemia. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 3594–3601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dammacco, F.; Gatti, P.; Sansonno, D. Hepatitis C Virus Infection, Mixed Cryoglobulinemia, and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: An Emerging Picture. Leuk. Lymphoma 1998, 31, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallat, L.; Benhamou, Y.; Gutierrez, M.; Ghillani, P.; Hercher, C.; Thibault, V.; Charlotte, F.; Piette, J.C.; Poynard, T.; Merle-Béral, H.; et al. Clonal B cell populations in the blood and liver of patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3668–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Sansonno, D.; Piccoli, C.; D’Amore, F.P.; Tucci, F.A.; Dammacco, F. Molecular Characterization of B Cell Clonal Expansions in the Liver of Chronically Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalini, A.R.; Facchetti, F.; Salvi, L.; Fontana, L.; Puoti, M.; Scarpa, A. Clonality of B-cells in portal lymphoid infiltrates of HCV-infected livers. J. Pathol. 1998, 185, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasca, R.; Vaccari, P.; Luppi, M.; Zucchini, P.; Castelli, I.; Barozzi, P.; Cuoghi, A.; Torelli, G. Immunoglobulin Gene Mutations and Frequent Use of VH1-69 and VH4-34 Segments in Hepatitis C Virus-Positive and Hepatitis C Virus-Negative Nodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanovski, M.; Silvestri, F.; Pozzato, G.; Anand, S.; Mazzaro, C.; Burrone, O.R.; Efremov, D.G. Somatic hypermutation, clonal diversity, and preferential expression of the VH 51p1/VL kv325 immunoglobulin gene combination in hepatitis C virus-associated immunocytomas. Blood 1998, 91, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.H.; Hadlock, K.G.; Foung, S.K.H.; Levy, S. VH1-69 gene is preferentially used by hepatitis C virus-associated B cell lymphomas and by normal B cells responding to the E2 viral antigen. Blood 2001, 97, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.A.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J. Ig VH1 genes expressed in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia exhibit distinctive molecular features. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-C.B.; Kipling, D.; Leong, H.S.; Martin, V.; Ademokun, A.A.; Dunn-Walters, D.K. High-throughput immunoglobulin repertoire analysis distinguishes between human IgM memory and switched memory B-cell populations. Blood 2010, 116, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, E.R.; Chan, C.H.; Hadlock, K.G.; Foung, S.K.H.; Flint, M.; Levy, S. The B-cell receptor of a hepatitis C virus (HCV)–associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma binds the viral E2 envelope protein, implicating HCV in lymphomagenesis. Blood 2001, 98, 3745–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brezinschek, H.P.; Brezinschek, R.I.; Lipsky, P.E. Analysis of the heavy chain repertoire of human peripheral B cells using single-cell polymerase chain reaction. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 190–202. [Google Scholar]
- Elhanati, Y.; Sethna, Z.; Marcou, Q.; Callan, C.G., Jr.; Mora, T.; Walczak, A.M. Inferring processes underlying B-cell repertoire diversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colbert, M.D.; Flyak, A.I.; Ogega, C.O.; Kinchen, V.J.; Massaccesi, G.; Hernandez, M.; Davidson, E.; Doranz, B.J.; Cox, A.L.; Crowe, J.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting New Sites of Vulnerability in Hepatitis C Virus E1E2. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, J.R.; Flyak, A.I.; Cohen, V.J.; Li, H.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; Wang, S.; Learn, G.H.; Kose, N.; Loerinc, L.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies with few somatic mutations and hepatitis C virus clearance. JCI Insight 2017, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Pierce, B.G.; Lau, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Underwood, A.; Bull, R.A.; Prentoe, J.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Walker, M.R.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies from an individual that naturally cleared multiple hepatitis C virus infections uncover molecular determinants for E2 targeting and vaccine design. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Tzarum, N.; A Wilson, I.; Law, M. VH1-69 antiviral broadly neutralizing antibodies: Genetics, structures, and relevance to rational vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliyahu, S.; Sharabi, O.; Elmedvi, S.; Timor, R.; Davidovich, A.; Vigneault, F.; Clouser, C.; Hope, R.; Nimer, A.; Braun, M.; et al. Antibody Repertoire Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections Identifies Immune Signatures Associated with Spontaneous Clearance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olbrich, A.; Wardemann, H.; Bohm, S.; Rother, K.; Colpitts, C.C.; Wrensch, F.; Baumert, T.F.; Berg, T.; Benckert, J. Repertoire and Neutralizing Activity of Antibodies Against Hepatitis C Virus E2 Peptide in Patients with Spontaneous Resolution of Hepatitis C. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tzarum, N.; Lin, X.; Giang, E.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Augestad, E.H.; Nagy, K.; He, L.; Hernandez, M.; Fouch, M.E.; et al. Functional convergence of a germline-encoded neutralizing antibody response in rhesus macaques immunized with HCV envelope glycoproteins. Immunity 2021, 54, 781–796.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.D.; Green, R.M.; Marukian, S.; Talal, A.H.; Lake-Bakaar, G.V.; Jacobson, I.M.; Rice, C.M.; Dustin, L.B. Clonal expansion of immunoglobulin M+CD27+ B cells in HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood 2008, 111, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughan, J.E.; Reardon, K.M.; Cogburn, K.E.; Quendler, H.; Pockros, P.J.; Law, M. Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Breaks Tolerance and Drives Polyclonal Expansion of Autoreactive B Cells. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imkeller, K.; Wardemann, H. Assessing human B cell repertoire diversity and convergence. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 284, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Halemano, K.; Schmitt, K.; Katuwal, M.; Wang, Y.; Harper, M.S.; Heilman, K.J.; Kuwata, T.; Stephens, E.B.; Santiago, M.L. Immunoglobulin VH gene diversity and somatic hypermutation during SIV infection of rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 2015, 67, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patera, A.C.; Graham, C.M.; Thomas, D.B.; Smith, C.A. Immunodominance with progenitor B cell diversity in the neutralizing antibody repertoire to influenza infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kluwe, C.A.; Lungu, O.I.; DeKosky, B.J.; Kerr, S.A.; Johnson, E.L.; Tanno, H.; Lee, C.-H.; Jung, J.; Rezigh, A.B.; et al. Facile Discovery of a Diverse Panel of Anti-Ebola Virus Antibodies by Immune Repertoire Mining. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racanelli, V.; Brunetti, C.; de Re, V.; Caggiari, L.; de Zorzi, M.; Leone, P.; Perosa, F.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F. Antibody V(h) repertoire differences between resolving and chronically evolving hepatitis C virus infections. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; et al. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.C.A.; Yang, F.; Jackson, K.J.L.; Hoh, R.A.; Roltgen, K.; Jean, G.H.; Stevens, B.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Rustagi, A.; Rogers, A.J.; et al. Human B Cell Clonal Expansion and Convergent Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 516–525.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype from Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus Into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salmona, M.; Caporossi, A.; Simmonds, P.; Thélu, M.-A.; Fusillier, K.; Mercier-Delarue, S.; De Castro, N.; LeGoff, J.; Chaix, M.-L.; François, O.; et al. First next-generation sequencing full-genome characterization of a hepatitis C virus genotype 7 divergent subtype. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 947.e1–947.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Chang, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Moreno, C.; Shafran, S.D.; Borgia, S.M.; Asselah, T.; Alric, L.; Abergel, A.; et al. Identification of 19 Novel Hepatitis C Virus Subtypes—Further Expanding HCV Classification. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, W.O.; Snider, A.E.; Wells, B.L.; Latanich, R.; Bailey, J.R.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Clearance of hepatitis C infection is associated with the early appearance of broad neutralizing antibody responses. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R. HIV-1 Vaccines Based on Antibody Identification, B Cell Ontogeny, and Epitope Structure. Immunity 2018, 48, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binley, J.M.; Lybarger, E.A.; Crooks, E.T.; Seaman, M.S.; Gray, E.; Davis, K.L.; Decker, J.M.; Wycuff, D.; Harris, L.; Hawkins, N.; et al. Profiling the Specificity of Neutralizing Antibodies in a Large Panel of Plasmas from Patients Chronically Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11651–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Klein, R.M.; Manion, M.M.; O’Dell, S.; Phogat, A.; Chakrabarti, B.; Hallahan, C.W.; Migueles, S.A.; Wrammert, J.; Ahmed, R.; et al. Frequency and Phenotype of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope-Specific B Cells from Patients with Broadly Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2008, 83, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Verkoczy, L.; Wiehe, K.; Alam, S.M.; Nicely, N.I.; Santra, S.; Bradley, T.; Pemble, C.W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; et al. Initiation of immune tolerance–controlled HIV gp41 neutralizing B cell lineages. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 336ra62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hraber, P.; Seaman, M.S.; Bailer, R.T.; Mascola, J.R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Korber, B.T. Prevalence of broadly neutralizing antibody responses during chronic HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2014, 28, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Moquin, S.; Zhang, B.; Acharya, P.; Georgiev, I.S.; Altae-Tran, H.R.; Chuang, G.-Y.; Joyce, M.G.; et al. Multidonor Analysis Reveals Structural Elements, Genetic Determinants, and Maturation Pathway for HIV-1 Neutralization by VRC01-Class Antibodies. Immunity 2013, 39, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jardine, J.G.; Kulp, D.W.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Sarkar, A.; Briney, B.; Sok, D.; Sesterhenn, F.; Ereño-Orbea, J.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Deresa, I.; et al. HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody precursor B cells revealed by germline-targeting immunogen. Science 2016, 351, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kallewaard, N.L.; Corti, D.; Collins, P.J.; Neu, U.; McAuliffe, J.M.; Benjamin, E.; Wachter-Rosati, L.; Palmer-Hill, F.J.; Yuan, A.Q.; Walker, P.A.; et al. Structure and Function Analysis of an Antibody Recognizing All Influenza A Subtypes. Cell 2016, 166, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingwood, D.; McTamney, P.M.; Yassine, H.M.; Whittle, J.R.R.; Guo, X.; Boyington, J.C.; Wei, C.-J.; Nabel, G.J. Structural and genetic basis for development of broadly neutralizing influenza antibodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 489, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sack, B.K.; Oyen, D.; Zenklusen, I.; Piccoli, L.; Barbieri, S.; Foglierini, M.; Fregni, C.S.; Marcandalli, J.; Jongo, S.; et al. A public antibody lineage that potently inhibits malaria infection through dual binding to the circumsporozoite protein. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; Giang, E.; Kong, L.; He, L.; Prentoe, J.; Augestad, E.; Hua, Y.; Castillo, S.; Lauer, G.M.; Bukh, J.; et al. Genetic and structural insights into broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus by human V(H)1-69 antibodies. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, J.R.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; El-Diwany, R.; Osburn, W.O.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.K.; Ray, S.C. Naturally selected hepatitis C virus polymorphisms confer broad neutralizing antibody resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freedman, H.; Logan, M.R.; Law, J.L.M.; Houghton, M. Structure and Function of the Hepatitis C Virus Envelope Glycoproteins E1 and E2: Antiviral and Vaccine Targets. ACS Infect. Dis. 2016, 2, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
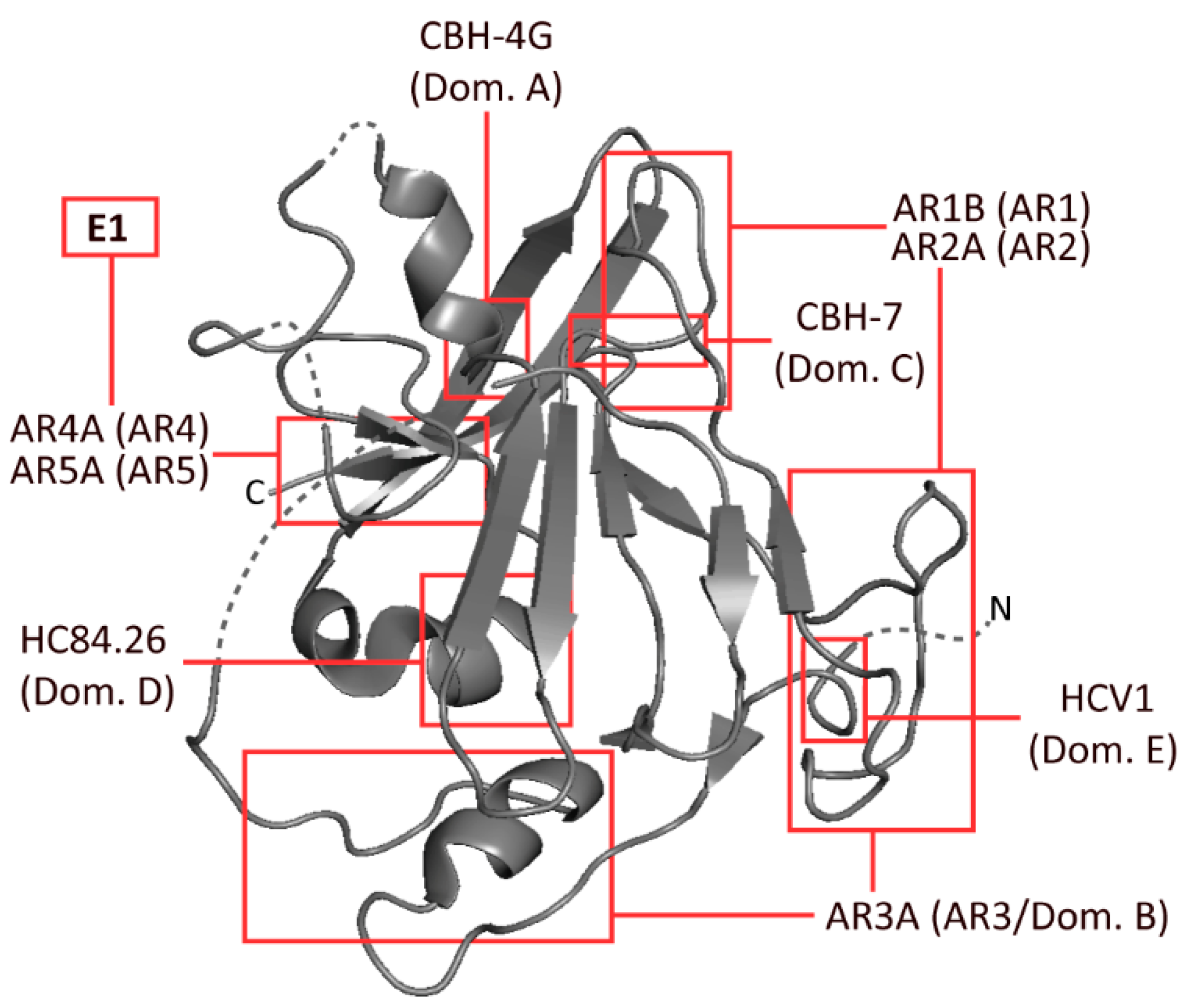
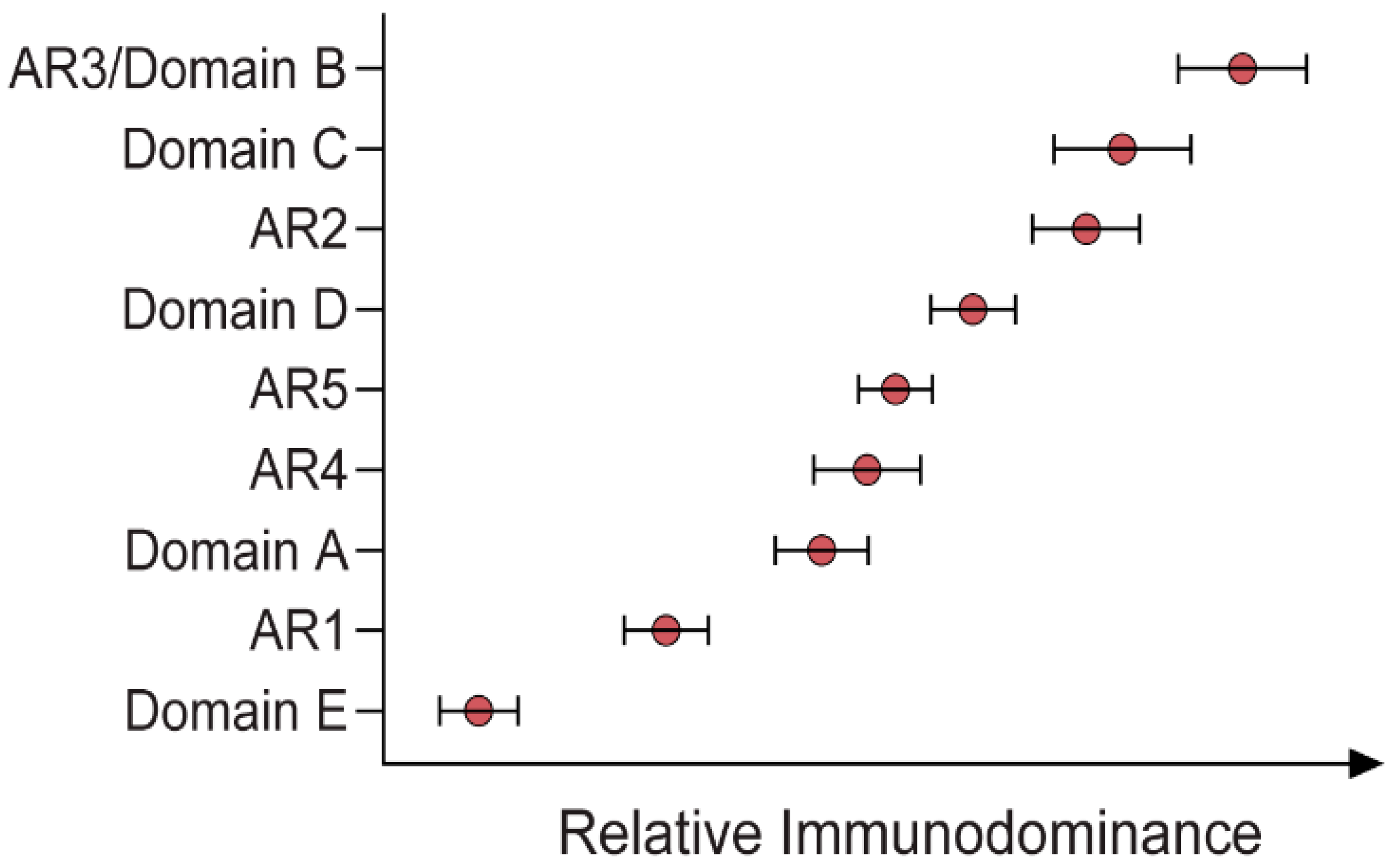
| Ab Name | Antigenic Region | Binding Type | Binding Residues (Determined by ASM) | Neutralisation (IC50 μg/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR1A | 1 | C | 495, 519, 544, 545, 547, 548, 549, 632 | 5.7 | [12,19] |
| AR1B | 1 | C | 412, 417, 420–423, 483–489, 523–526, 530–532, 534, 538–540, 544–549 | 0.06 | [12] |
| AR2A | 2 | C | 625, 628 | 0.47 | [12,19] |
| AR3A | 3/B | C | 425, 427–429, 436–438, 440–442, 485, 503, 518, 520, 529, 530, 535, 616 | 0.5 | [12,19] |
| A8 | 3/B | C | 523, 529, 530, 535 | 0.56 | [20] |
| CBH-5 | 3/B | C | 523, 525, 530, 535, 540 | 0.04–13 | [21,22] |
| HC-1 | 3/B | C | 426, 428, 429, 430, 503, 529, 530, 535 | 0.16 | [19,23] |
| AR4A | 4 | C | 201, 205, 459, 486, 487, 543, 545, 569, 585, 594, 597, 652, 677, 679, 698 | 0.03–38.5 | [9,19] |
| AR5A | 5 | C | 201, 205, 459, 486, 513, 543, 569, 585, 594, 597, 639, 652, 657, 677, 679 | 15 | [9,19] |
| CBH-4G | A | C | 201, 204–206 | >100 | [13] |
| CBH-7 | C | C | 544, 545, 547, 549, 597, 626 | 10 | [15,19] |
| HC84.26 | D | C | 441, 442, 446, 616 | 0.005–12.91 | [16,19] |
| HC84.27 | D | C | 425, 426, 428, 429, 441–443, 446, 530, 536, 612, 613, 615 | 0.22–0.26 | [16] |
| HCV1 | E | L | 412–423 | 0.15–15 | [14,24] |
| AP33 | E (mouse) | L | 412–423 | 0.6–32 | [25] |
| MAb24 | E (mouse) | L | 411–428 | 17.5 | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brasher, N.A.; Adhikari, A.; Lloyd, A.R.; Tedla, N.; Bull, R.A. Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity. Viruses 2021, 13, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060983
Brasher NA, Adhikari A, Lloyd AR, Tedla N, Bull RA. Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060983
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrasher, Nicholas A., Anurag Adhikari, Andrew R. Lloyd, Nicodemus Tedla, and Rowena A. Bull. 2021. "Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity" Viruses 13, no. 6: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060983
APA StyleBrasher, N. A., Adhikari, A., Lloyd, A. R., Tedla, N., & Bull, R. A. (2021). Hepatitis C Virus Epitope Immunodominance and B Cell Repertoire Diversity. Viruses, 13(6), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060983






